class의 상속을 prototype으로 구현해보기
시작하기에 앞서 용어가 헷갈릴 수 있기 때문에 poiemaweb-prototype에 나온 용어를 빌려 통일해서 사용하겠다.
- 프로토타입 또는 프로토타입객체 :
__proto__가 가르키는 객체 (아래에서 편하게__proto__라고도 사용 할 것이다.) - 프로토타입 프로퍼티 : 함수가 갖고 있는 prototype프로퍼티가 가르키는 객체
class로 구현한 상속 코드
class Car {
constructor(brand) {
this.carname = brand;
}
present() {
return 'I have a ' + this.carname;
}
}
class Model extends Car {
constructor(brand, mod) {
super(brand);
this.model = mod;
}
show() {
return this.present() + ', it is a ' + this.model;
}
}
const mycar = new Model('Ford', 'Mustang');1. 일단 상속 신경안쓰고 prototype형태로 변경
function Car(brand){
this.carname = brand
}
Car.prototype.present = function(){
return 'I have a ' + this.carname
}
function Model(brand,mod){
this.model = mod
}
Model.prototype.show = function(){
return this.present() + ', it is a ' + this.model;
}
const mycar = new Model('Ford', 'Mustang');음... present는 어떻게 넣을까 생각해보다가 mycar class형태의 구조를 봤다.
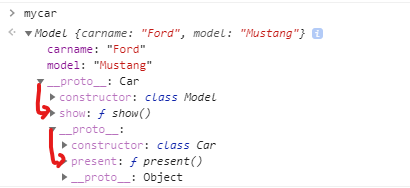
프로토타입(__proto__)의 프로토타입(__proto__)에 present가 있다.
Model의 프로토타입 프로퍼티의 프로토타입에 Car의 프로토타입 프로퍼티를 넣어줘야한다. (말이 참..)
=> 즉, Model.prototype.proto에 Car.prototype를 넣어주면 된다. 이걸 해주는 것이 있는데 Object.create이다.
Object.create
Object.create는 인자로 들어오는 객체를 빈객체의 프로토타입에 넣어서 반환해준다.
mdn Object.create의 예제를 보고 확인하자. 아래 예제를 보면 me의 프로토타입(__proto__)에 person객체가 들어가 있는 빈객체가 저장돼있다.
const person = {
isHuman: false,
printIntroduction: function() {
console.log(`My name is ${this.name}. Am I human? ${this.isHuman}`);
}
};
const me = Object.create(person);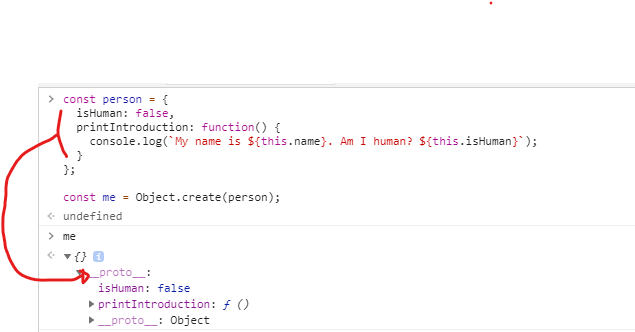
2. 다시 돌아와서 Model.prototype.__proto__에 Car.prototype를 Object.create를 이용해서 넣어주자.
function Car(brand){
this.carname = brand
}
Car.prototype.present = function(){
return 'I have a ' + this.carname
}
function Model(brand,mod){
this.model = mod
}
Model.prototype = Object.create(Car.prototype)
Model.prototype.show = function(){
return this.present() + ', it is a ' + this.model;
}
const mycar = new Model('Ford', 'Mustang');Model.prototype.__proto__에 Car.prototype을 넣어준 객체를 Model.prototype에 먼저 설정해주고 확인해 봤더니 클래스 예제하고 똑같이 present메소드를 갖게 됐다.

이제 다시 문제. 부모 클래스 Car의 this.carname을 어떻게 Model에도 선언을 해줄까???
3. call 또는 apply를 사용해 Car함수를 Model에서 호출해줘야한다. 이때 this는 Model을 가르키게 해야된다.
function Car(brand){
this.carname = brand;
}
Car.prototype.present = function(){
return 'I have a ' + this.carname
}
function Model(brand,mod){
Car.call(this,brand); // 또는 Car.call(this,[brand]);
this.model = mod;
}
Model.prototype = Object.create(Car.prototype)
Model.prototype.show = function(){
return this.present() + ', it is a ' + this.model;
}
const mycar = new Model('Ford', 'Mustang');
이제 원하는 대로 mycar가 생성됐다!
class의 extends와 완벽하게 일치한다고는 볼 수 없을 것 같지만 그래도 기본적 상속 기능은 잘 작동된다!
학습 과정에서 작성된 글입니다. 용어 또는 잘못된 정보가 있으면 댓글로 알려주시면 감사하겠습니다!
