요청매핑
- @RestController
- 뷰 조회가 아닌 HTTP 메시지 바디에 바로 반환 값을 입력
- 클래스 단위 설정
- @Controller + @ResponseBody(메소드 단위 설정)
- @RequestMapping("/매핑경로")
- 매핑 경로는 배열[]로 다중 설정 가능
({"/mapping1", "/mapping2"})
- 매핑 경로는 배열[]로 다중 설정 가능
HTTP 메서드
- 메서드 속성을 지정하지 않으면 모두 허용
(GET, POST, HEAD, PUT, PATCH, DELETE) - @RequestMapping(value="/매핑경로", method = RequestMethod.GET/POST)
- HTTP 메서드 매핑 축약
- @GetMapping
- @PostMapping
- @PutMapping
- @DeleteMapping
- @PatchMapping
PathVariable(경로 변수)
- 매핑경로: @RequestMapping("/mapping/{data}")
- 파라미터: @PathVariable("data") String data
- 변수명이 같으면 생략 가능
- @PathVariable data
- 다중 사용
- /mapping/id/{id}/order/{order}
- @PathVariable String id, @PathVariable Long order
특정 파라미터 조건 매핑
- @GetMapping(value = "/mapping-param", params = "mode=debug")
- params="mode"
- params="!mode"
- params="mode=debug"
- params="mode!=debug"
특정 헤더 조건 매핑
- @GetMapping(value = "/mapping-header", headers = "mode=debug")
- headers="mode",
- headers="!mode"
- headers="mode=debug"
- headers="mode!=debug"
미디어 타입 조건 매핑 (consume)
- HTTP 요청의 Content-Type 헤더 기반으로 전송할 미디어 타입 매핑
- 맞지 않으면 HTTP 415 상태코드 반환
- @PostMapping(value = "/mapping-consume", consumes = "application/json")
- consumes="application/json", "text/plain" 등
- consumes={"application/*", "text/plain"} -> 다중 설정
- consumes= MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE
미디어 타입 조건 매핑 (produre)
- HTTP 요청의 Accept 헤더 기반으로 수신할 미디어 타입 매핑
- 맞지 않으면 HTTP 406 상태코드 반환
- @PostMapping(value = "/mapping-produce", produces = "text/html")
- produces = "text/plain"
- produces = {"text/plain", "application/*"}
- produces = MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN_VALUE
요청 매핑 - API 예시
- 회원 관리 API
- 회원 전체 조회: GET /users
- 회원 등록: POST /users
- 회원 조회: GET /users/{userId}
- 회원 수정: PATCH /users/{userId}
- 회원 삭제: DELETE /users/{userId}
HTTP 요청 - 기본, 헤더조회
- HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletResponse
- HttpMethod
- Local: Locale 정보 조회(언어 등)
- @RequestHeader MultiValueMap<String, String> headerMap: 모든 HTTP 헤더를 조회
- @RequestHeader("host") String host : 특정 헤더 조회
- @CookieValue(value="value", required=false/true) String cookie : 특정 쿠키 조회
HTTP 요청 파라미터
HTTP 요청 데이터 조회
- GET : 쿼리 파라미터
- POST : HTML Form
- HTTP message body
쿼리 파라미터
- request.getParameter()
- HttpServletRequest가 제공하는 요청 파라미터 조회
HTML Form
- HTML Form - submit
- Form에 입력한 정보를 쿼리 파라미터 형식으로 전송
@RequestParam
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param")
public String requestParam(
@RequestParam("parameterName1") String username,
@RequestParam("parameterName2") int age) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
return "ok";
}-
@ResponseBody : HTTP message body에 내용 입력
-
@RequestParam : 파라미터 이름으로 바인딩
- @RequestParam("파라미터 이름") String 변수 이름
== request.getParameter("파라미터 이름") - HTTP 파라미터 이름이 변수 이름과 같으면 생략 가능
=> @RequestParam String username - String, int 등 단순 타입이면 애노테이션도 생략 가능, 권장X
=> String username, int age
- @RequestParam("파라미터 이름") String 변수 이름
-
@RequestParam.required : 파라미터 필수 여부
- 기본값 true(필수)
- 기본형(primitive type) NULL 주의
- int는 Integer로 받거나 defaultValue 설정
-
@RequestParam.defaultValue : 파라미터 값이 없는 경우 기본값 설정
-
@RequestParam.map
- Map(key=value)
- MultiValueMap(key=[value1, value2 ...])
하나의 파라미터 이름에 여러 개의 값 가능
@ModelAttribute
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/model-attribute")
public String modelAttributeV1(@ModelAttribute HelloData helloData) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", helloData.getUsername(), helloData.getAge());
return "ok";
}- 객체 생성 후 요청 파라미터 이름으로 객체의 프로퍼티(Getter/Setter)를 찾아 setter 호출하여 값을 입력(바인딩)
- 애노테이션 생략 가능
HTTP 요청 메시지 - 단순 텍스트
- HTTP 메시지 바디를 통해 데이터가 직접 넘어오는 경우에는 @RequestParam, @ModelAttribute를 사용할 수 없음
(HTML Form 형식은 요청 파라미터로 받음)
InputStream
ServletInputStream inputStream = request.getInputStream();
String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);- InputStream: HTTP 메시지 바디 데이터를 직접 조회
Input/Ouput Stream
public void requestBodyStringV2(InputStream inputStream, Writer responseWriter) throws IOException {
String messageBody = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
responseWriter.write("ok");
}- InputStream(Reader): HTTP 요청 메시지 바디의 내용을 직접 조회
- OutputStream(Writer): HTTP 응답 메시지의 바디에 직접 결과 출력
HttpEntity
public HttpEntity<String> requestBodyStringV3(HttpEntity<String> httpEntity){
String messageBody = httpEntity.getBody();
log.info("messageBody={}", messageBody);
return new HttpEntity<>("ok");
}- HttpEntity: HTTP header, body 정보를 편리하게 조회
- 메시지 바디를 직접 조회
- HttpMessageConverter -> StringHttpMessageConverter 적용
- 응답도 가능, 메시지 바디 정보를 직접 반환(view 조회X)
- HttpMessageConverter -> StringHttpMessageConverter 적용
- RequestEntity : HTTP 메소드, url 정보 추가, 요청 사용
- ResponseEntity : HTTP 상태코드 설정 가능, 응답 사용
- 메시지 바디를 직접 조회
@RequestBody
@ResponseBody
@PostMapping("/request-body-string-v4")
public String requestBodyStringV4(@RequestBody String messageBody) {
log.info("messageBody={}", messageBody);
return "ok";
}- @RequestBody
- 메시지 바디 정보를 직접 조회(@RequestParam, @ModelAttribute X)
- @ResponseBody
- 메시지 바디 정보를 직접 반환(view 조회 X)
HTTP 요청 메시지 - JSON
- HTTP API 전송 방식에서 주로 사용하는 JSON
- {"name1":"value1", "name2":"value2"} 형식
- content-type: application/json
HelloData data = objectMapper.readValue(messageBody, HelloData.class);- 문자로 된 데이터를 objectMapper 사용하여 자바 객체로 변환
@RequestBody 객체 파라미터
public String requestBodyJson(@RequestBody HelloData data)- @RequestBody를 파라미터에 직접 객체로 지정할 수 있음
- ! HTTP 요청 시 content-type:application/json 확인해야 함
- HttpMessageConverter 사용 -> MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 변환
- @RequestBody는 생략 불가능, 생략 시 @RequesParam 또는 @ModelAttribute로 적용하여 요청파라미터로 처리함
- JSON 형식으로 응답도 가능
HTTP 응답
정적 리소스
- 웹 브라우저에 HTML, css, js로 제공하는 정적 리소스
- 정적 리소스는 해당 파일을 변경 없이 그대로 서비스
- 스프링 부트의 정적 리소스 경로
- /src/main/resources/static
뷰 템플릿
- 웹 브라우저에 동적인 HTML을 제공하는 뷰 템플릿
- JSP, Thymeleaf 등 템플릿 엔진을 통해 서비스
- 스프링 부트의 뷰 템플릿 경로
- /src/main/resources/templates
@RequestMapping("/response-view-v1")
public ModelAndView responseViewV1() {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("response/hello")
.addObject("data", "hello!");
return mav;
}
@RequestMapping("/response-view-v2")
public String responseViewV2(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("data", "hello!!");
return "response/hello";
}- String 반환: 뷰 리졸버를 실행하여 String 이름의 뷰를 찾고 렌더링
- void 사용: 요청 URL을 참고하여 동일한 경로의 뷰 이름 실행, 권장X
HTTP API, 메시지 바디
- HTTP API 제공하는 경우 직접 HTTP 메시지 바디에 JSON 등의 형식으로 전송
- HttpServletResponse
- response.getWriter().write("OK")
- ResponseEntity - String
- return new ResponseEntity<>("OK", HttpStatus.OK)
- @ResponseBody - String
- return "OK"
- ResponseEntity - JSON
- return new ResponseEntity<>(Json, HttpStatus.OK)
- @ResponseBody - JSON
- @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
- return Json
HTTP 메시지 컨버터
- HTTP 요청: @RequestBody, HttpEntity(RequestEntity)
- HTTP 응답: @ResponseBody, HttpEntity(ResponseEntity)
- 대상 클래스 타입과 미디어 타입 지원여부 확인 후 사용 반환
스프링 부트 기본 메시지 컨버터
- 0 = ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter
- 클래스 타입: byte[], 미디어타입: */**
- 요청 (예) @RequestBody byte[] data
- 응답 (예) @ResponseBody return byte[], 미디어 타입 application/octet-stream
- 1 = StringHttpMessageConverter
- 클래스 타입: String, 미디어타입: */**
- 요청 (예) @RequestBody String data
- 응답 (예) @ResponseBody return "String", 미디어 타입 text/plain
- 2 = MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
- 클래스 타입: 객체/HashMap, 미디어타입: application/json 관련
- 요청 (예) @RequestBody Json json
- 응답 (예) @ResponseBody return Json, 미디어 타입 application/json 관련
요청 매핑 핸들러 어댑터 구조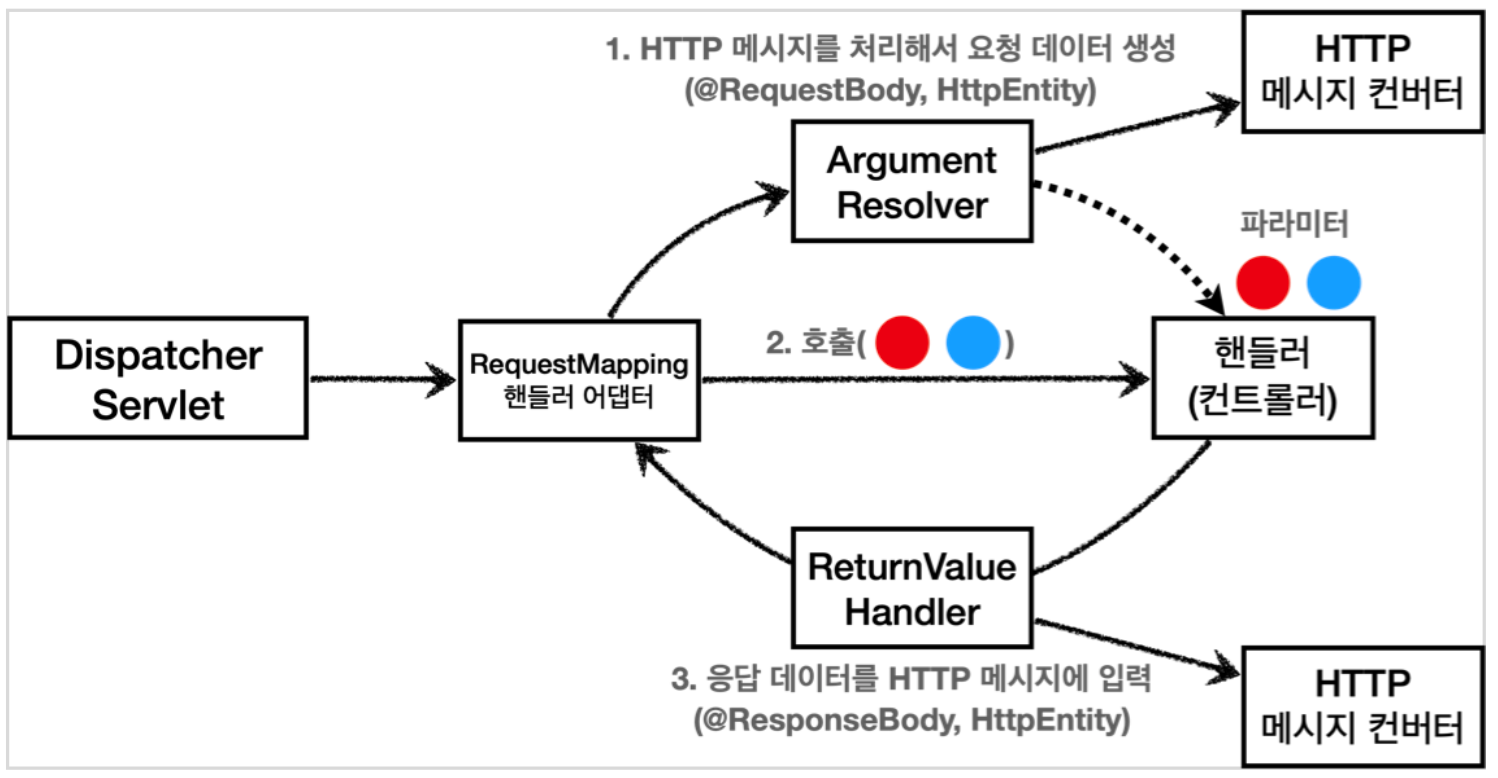
ArgumentResolver
- HttpServletRequest, Model, @RequestBody 등 컨트롤러(핸들러)가 필요로 하는 다양한 파라미터의 값을 생성하여 전달
cf. HttpEntity -> HttpEntityMethodProcessor 사용
ReturnValueHandler
- ArgumentResolver와 유사, @ResponseBody와 같은 응답 값을 변환하고 처리함
[출처] 스프링 MVC 1 - 김영한, 인프런
