PyTorch
PyTorch 란?
- 파이썬에서 제공되는 딥러닝 프레임워크
- 유연하고 코드가 간결하다는 특징이 있음
PyTorch 시작하기
- 다음의 공식문서를 참고해 PyTorch의 API들을 익혀보려고 합니다.
- https://tutorials.pytorch.kr/beginner/basics/intro.html
1) Dataset 준비
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.transform import ToTensor
# Fashion-MNIST라는 기사 이미지 데이터셋을 불러오려고 함
# 본 데이터셋은 60,000개의 학습 예제와 10,000개의 테스트 예제로 구성
# 각 예제는 흑백의 28 * 28 이미지와 10개의 분류 class 및 정답으로 구성
# 공개 데이터셋에서 학습 데이터 다운로드
training_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root = "data", # 데이터가 저장될 위치 지정
train = True, # 데이터의 용도 (train/test) 지정
download = True, # 데이터가 path에 없을 시 온라인에서 다운로드
transform = ToTensor(), # 데이터를 tensor로 바꿔줌
)
# 공개 데이터셋에서 테스트 데이터 다운로드
test_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root = "data",
train = False,
download = True,
transform = ToTensor(),
)실행결과
다음과 같이 ./data 디렉토리가 생성되며 해당 디렉토리 안에 데이터가 다운로드 된 것을 확인할 수 있음
2) DataLoader 생성
Dataset은 샘플과 정답(label)로 구성됨DataLoader란 dataset을 순회 가능한 객체로 감싸 샘플에 쉽게 접근할 수 있도록 하는 장치
train_dataloader = DataLoader(training_data, batch_size=64)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=64)
# DataLoader 확인
for X,y in test_dataloader:
print(f"Shape of X [N,C,H,W]: {X.shape}") # [batch size, channels, height, width]
print(f"Shape of y: {y.shape} {y.dtype}")실행결과

3) 모델 만들기
3-1) 모델 학습에 필요한 기본 설정
- 하이퍼파리미터 설정
- 학습에 사용할 디바이스 설정
epochs = 5
batch_size = 64
learning_rate = 1e-3
device = (
"cuda"
if torch.cuda.is_available()
else "mps"
if torch.backends.mps.is_available()
else "cpu"
)
print(f"Using {device} device")실행결과

다음과 같이 학습에 사용할 디바이스를 얻을 수 있게 됩니다.
3-2) 모델 정의
- 모델을 정의할 때, nn.Module을 상속받는 class를 만들어 정의함
__init__함수에서는 모델에서 사용될 module, activation function 등을 정의forward함수에서는 모델에서 실행되어야 하는 계산을 정의
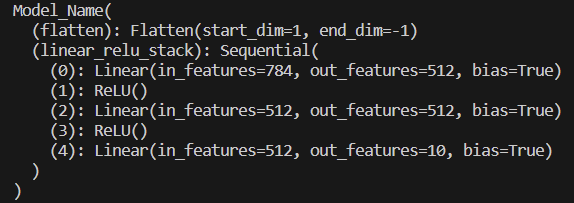
class Model_Name(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.linear_relu_stack = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(28*28, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512,512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512,10)
)
def forwared(self, x):
x = self.flatten(x)
logits = self.linear_relu_stack(x)
return logits
model = Model_Name().to(device) # device에 최적화된 모델로 변환
print(model)실행결과
3-3) 모델 매개변수 최적화하기
- 모델 학습을 위한 손실함수와 옵티마이저 설정
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) # SDG 알고리즘을 이용하여 모델 매개변수 최적화3-4) Training 및 Testing
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
for batch, (X,y) in enumerate(dataloader):
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# 예측 오류 계산
pred = model(X) # 모델에 input X를 넣어 출력값을 구함
loss = loss_fn(pred,y)
# 역전파
optimizer.zero_grad() # gradient 초기화
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch % 100 == 0:
loss, current = loss.item(), (batch+1) * len(X)
print(f"loss: {loss:>7f} [{current:>5d}/{size:>5d}]")
def test(dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
num_batches = len(dataloader)
model.eval()
test_loss, correct = 0, 0
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in dataloader:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
pred = model(X)
test_loss += loss_fn(pred, y).item()
correct += (pred.argmax(1)==y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_loss /= num_batches
correct /= size
print(f"Test Error: \n Accuracy: {(100*correct):>0.1f}%, Avg loss: {test_loss:>8f}\n")
for t in range(epochs):
print(f"Epoch {t+1}\n----------------------------")
train(train_dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
test(test_dataloader, model, loss_fn)
print("Done!!!")실행결과
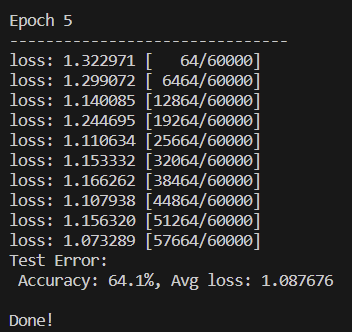
이런 식으로 epoch별 loss와 accuracy를 출력할 수 있음
3-5) 모델 저장 및 불러오기
- 모델을 저장할 때,
{모델명}.pth파일로 저장하며torch.save메소드를 사용하여 저장 - 모델을 불러올 때,
torch.load메소드를 사용하여 불러옴
# 모델 저장하기
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "model.pth")
print("Saved PyTorch Model State to model.pth")
# 모델 불러오기
model = Model_Name().to(device)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("model.pth"))실행결과


다음과 같이 모델을 저장한 파일이 생성되는 것을 확인할 수 있음
3-6) 모델을 사용하여 task 수행
model.eval()메소드로 모델을 평가모드로 전환
classes = [
"T-shirt/top",
"Trouser",
"Pullover",
"Dress",
"Coat",
"Sandal",
"Shirt",
"Sneaker",
"Bag",
"Ankle boot",
]
model.eval()
x, y = test_data[0][0], test_data[0][1]
with torch.no_grad():
x = x.to(device)
pred = model(x)
predicted, actual = classes[pred[0].argmax(0)], classes[y]
print(f'Predicted: "{predicted}", Actual: "{actual}"')실행결과

다음과 같이 test_data[0]에 대한 평가를 수행한 것을 확인
정리
이번 포스팅을 통해서 PyTorch로 데이터를 불러오고 모델을 만들어 이용하는 방법에 대해 알아봤습니다.

정보 감사합니다.