
1000
처음 풀 때 코드
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] str = br.readLine().split(" ");
int A = Integer.parseInt(str[0]);
int B = Integer.parseInt(str[1]);
System.out.println(A + B);새롭게 풀어본 코드
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] split = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
int A = Integer.parseInt(split[0]);
int B = Integer.parseInt(split[1]);
System.out.println(A + B);처음 풀 때는 접근 자체를 어떻게 하는지 모르겠어서 이것 저것 찾아보다가 BufferdeReader를 사용해 봤다.
오랜만에 다시 풀어보려고 들어와보니 다른 방법으로 풀 수 있을 것 같아 적용해보았다.
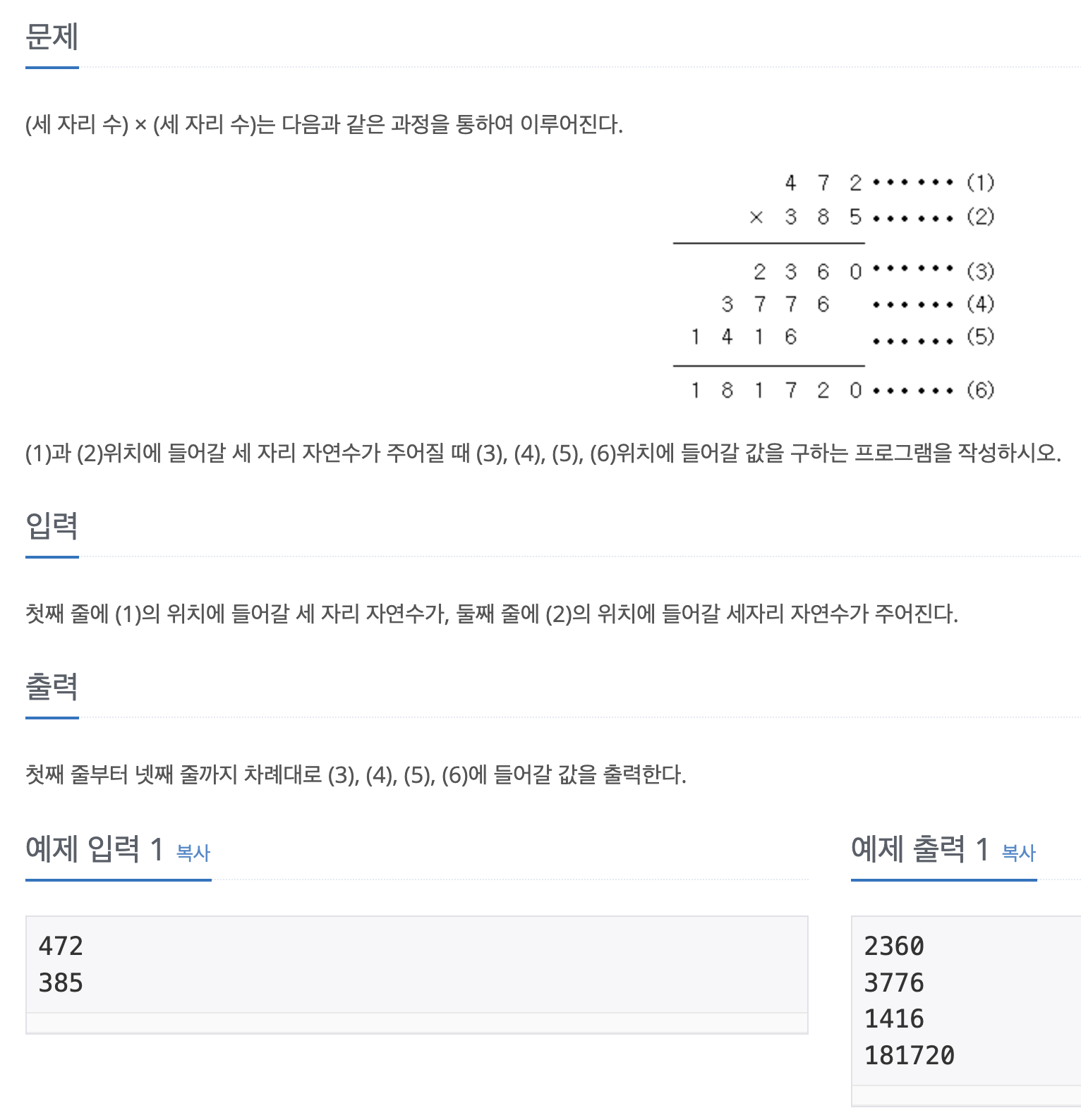
2588
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String firstInput = scanner.nextLine();
int numA = Integer.parseInt(firstInput);
String secondInput = scanner.nextLine();
int numB = Integer.parseInt(secondInput);
String[] split = secondInput.split("");
int B = Integer.parseInt(split[0]);
int C = Integer.parseInt(split[1]);
int D = Integer.parseInt(split[2]);
System.out.println(numA * D);
System.out.println(numA * C);
System.out.println(numA * B);
System.out.println(numA * numB);나는 이렇게 풀었지만 아스키코드를 이용하여 푸는 방법도 있다.
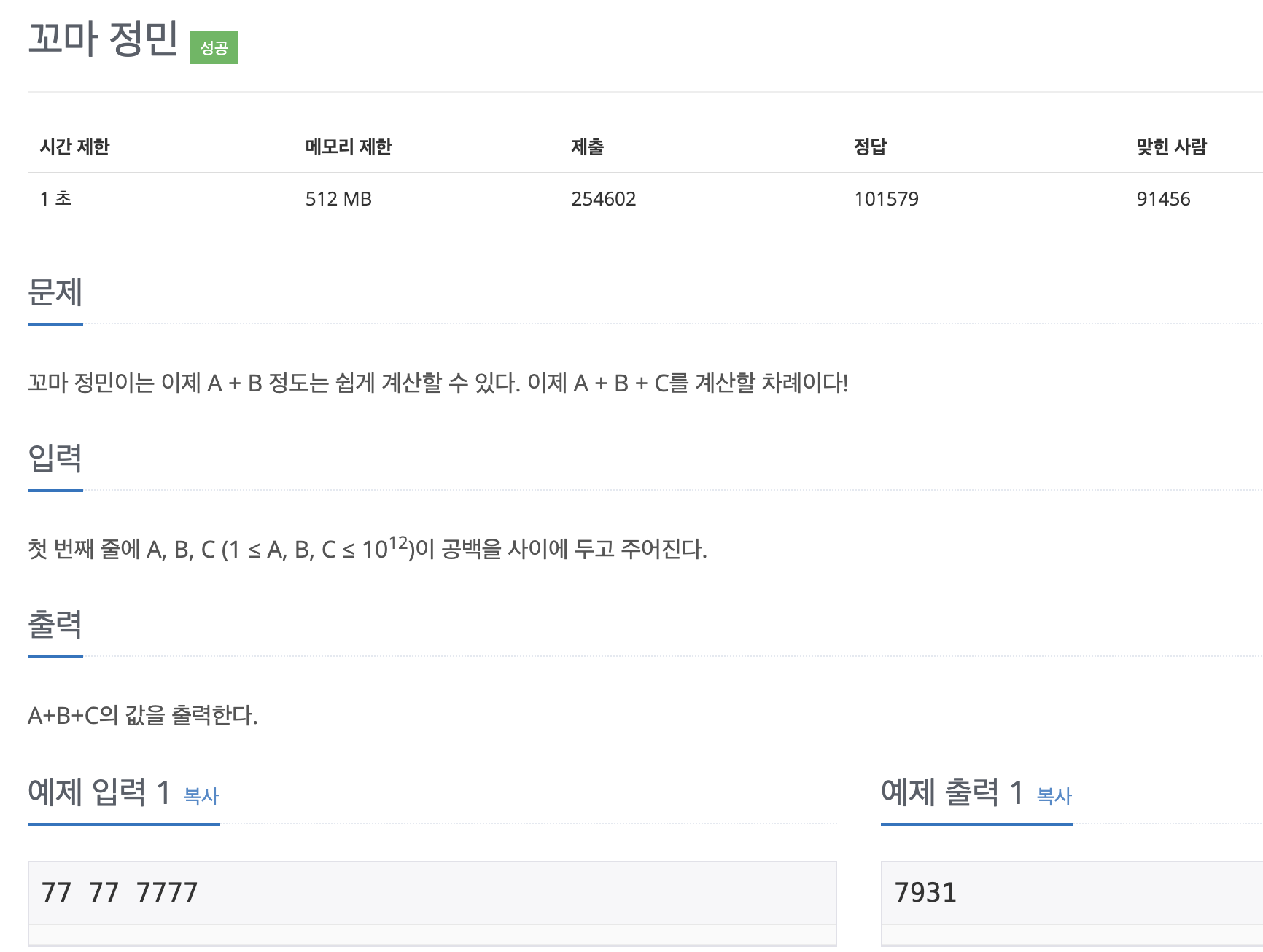
11382
처음 문제를 풀 때는 런타임 에러나 나왔다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] split = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
int A = Integer.parseInt(split[0]);
int B = Integer.parseInt(split[1]);
int C = Integer.parseInt(split[2]);
System.out.println(A + B +C);
}
}계산에는 문제가 없어보여 찾아보던 중
받는 숫자가 int형 보다 큰 값을 출력하기 때문에 long을 사용해야함을 알았다.
추가로 입력 받는 값을 따로 저장하지 않고 바로 받을 수 있는것을 알게되어 이를 반영해 코드를 수정해 보았다.
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
long a = sc.nextLong();
long b = sc.nextLong();
long c = sc.nextLong();
System.out.println(a + b + c);