
1330
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
if (num1 < num2) {
System.out.println("<");
} else if (num1 > num2) {
System.out.println(">");
} else {
System.out.println("==");
}
}
}9498
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int score = sc.nextInt();
if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("A");
} else if (score >= 80) {
System.out.println("B");
} else if (score >= 70) {
System.out.println("C");
} else if (score >= 60) {
System.out.println("D");
} else {
System.out.println("F");
}
}
}2753
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
if (num >= 1 && num <= 4000) {
if (num % 4 == 0 && num % 100 != 0 || num % 400 == 0) {
System.out.println(1);
}else {
System.out.println(0);
}
}
sc.close();
}
}14681
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
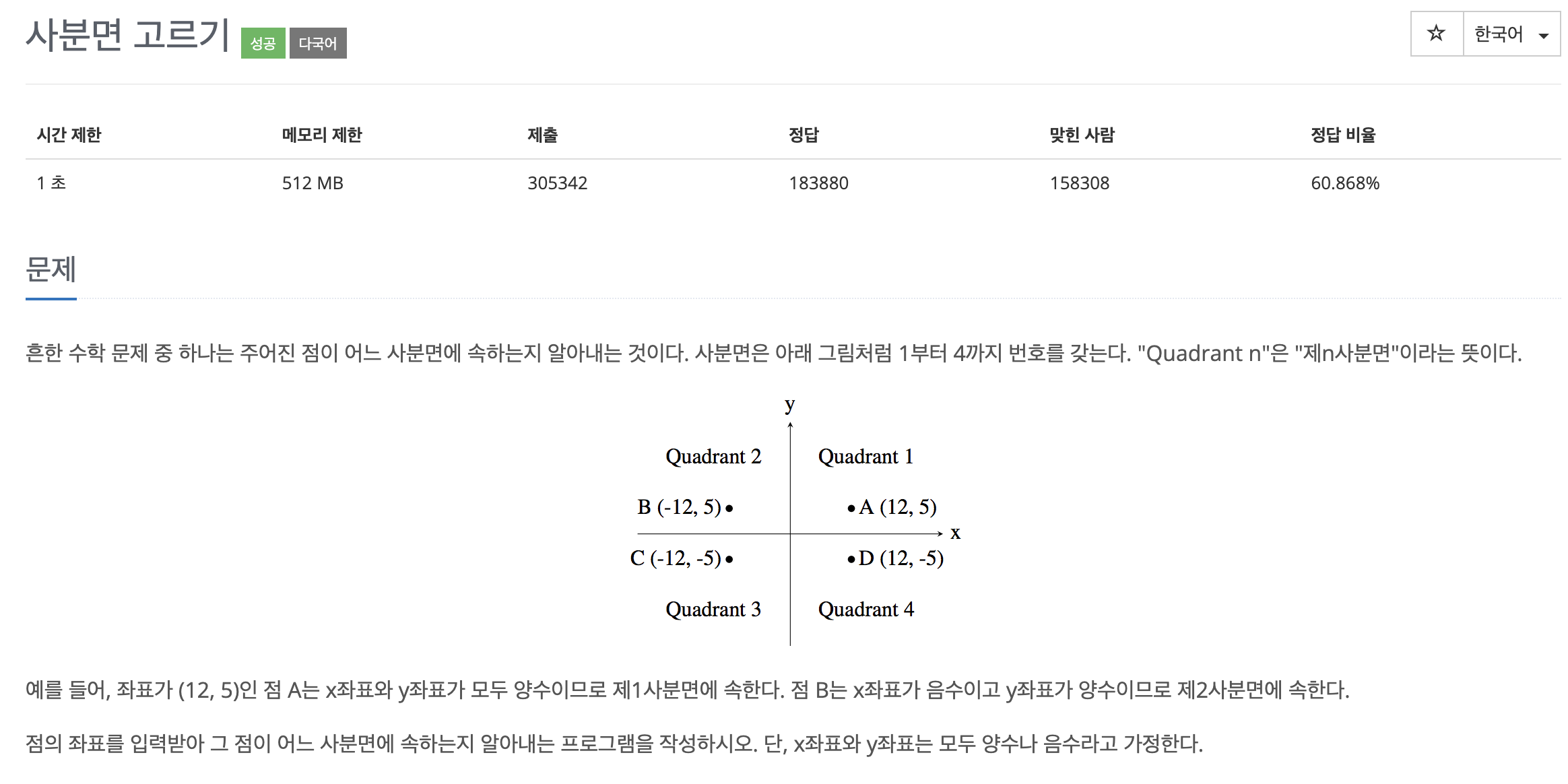
if (x > 0 && y > 0) {
System.out.println(1);
} else if (x > 0 && y < 0) {
System.out.println(4);
} else if (x < 0 && y > 0) {
System.out.println(2);
} else {
System.out.println(3);
}
sc.close();
}
}코드 개선 - 삼항 연산자
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
int quadrant = (x > 0) ? ((y > 0) ? 1 : 4) : ((y > 0) ? 2 : 3);
System.out.println(quadrant);
sc.close();
}
}
-
중복 조건 제거
- 삼항 연산자 (
?:) 를 사용하여 조건문을 간결하게 표현. - x와 y의 부호를 기준으로 분기하는 동일안 패턴 축약.
- 삼항 연산자 (
-
가독성 향상
quadrant라는 변수에 결과값을 저장함으로써 코드의 의미를 명확히 함.
2884
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int H = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
int a = M + 15;
int b = M - 45;
if (0 <= H && H <= 23 && 0 <= M && M <= 59) {
if (M < 45 && H !=0) {
System.out.println(H - 1 + " " + a);
} else if (M < 45 && H == 0) {
System.out.println(23 + " " + a);
} else if (M >= 45) {
System.out.println(H + " " + b);
}
}
sc.close();
}
}코드 개선
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int H = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
// 새로운 시간 계산
M -= 45;
if (M < 0) {
M += 60;
H -= 1;
if (H < 0) {
H = 23;
}
}
System.out.println(H + " " + M);
sc.close();
}
}
- 불필요한 조건 제거
0 <= H && H <= 23 && 0 <= M && M <= 59조건은 입력값이 유효하다 가정하여 생략.M < 45와M >= 45에 따른 분리 로직을 단일if로 간략화.
- 불필요한 변수 제거
- a와 b 변수 없이 직접 M값을 조정.
- 로직 단순화
M -= 45를 기반으로 음수 여부만 체크 처리.
2525
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int H = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int totalMinutes = H * 60 + M + m;
int newH = (totalMinutes / 60) % 24;
int newM = totalMinutes % 60;
System.out.println(newH + " " + newM);
sc.close();
}
}
// //실패 코드
// int sumTime = M + m;
//
// if (sumTime >= 60 && H < 23) {
// System.out.println(H + (sumTime / 60) + " " + sumTime % 60);
// } else if (sumTime < 60) {
// System.out.println(H + " " + sumTime);
// } else if (sumTime >= 60 && H == 23) {
// System.out.println(0 + " " + sumTime % 60);
// }- 처음 접근했던 방법은 24시간을 처리하는 로직에서 0시가 넘어갔을 경우를 제대로 치리하지 못했다.
새롭게 접근한 방법 풀이
- 총 분 계산
- 현재 시간과 추가 시간을 모두 분 단위로 변경한 뒤 합산
H * 60 + M + m
- 24시간 처리
- 총 분을 시간 단위로 변환(
totalMinutes/60) 하고, 24로 나눈 나머지를 계산하여 하루를 넘길 경우를 처리
- 총 분을 시간 단위로 변환(
- 분 처리
- 전체 분에서 시간 단위만 제외하고 남은 분을 계산
-newM = totalMinutes % 60
- 전체 분에서 시간 단위만 제외하고 남은 분을 계산