스프링 시큐리티 : 막강한 인증(Authentication)과 인가(Authorization) 기능을 가진 프레임워크
스프링 시큐리티와 스플이 시큐리티 OAuth2 클라이언트
OAuth 로그인 구현시 다음의 사항을 구글, 페이스북, 네이버 등에 맡길 수 있어 서비스 개발에 집중할 수 있다.
- 로그인 시 보안
- 회원가입 시 이메일 혹은 전화번호 인증
- 비밀번호 찾기
- 비밀번호 변경
- 회원정보 변경
Google OAuth2
CommonOAuth2Provider
public enum CommonOAuth2Provider {
GOOGLE {
@Override
public Builder getBuilder(String registrationId) {
ClientRegistration.Builder builder = getBUilder(registrationId, ClientAuthenticationMethod.BASIC, DEFAULT_REDIRECT_URL);
builder.scope("openid", "profile", "email");
builder.authorizationUri("https://acounts.google.com/o/oauth2/v2/auth");
builder.tokenUri("https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token");
builder.jwkSetUri("https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v3/certs");
builder.userInfoUri("https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v3/userinfo");
builder.userNameAttributeName(IdTokenClaimNames.SUB);
builder.clientName("Google");
return builder;
}
}
}구글 서비스 등록

프로젝트 선택 - 새 프로젝트
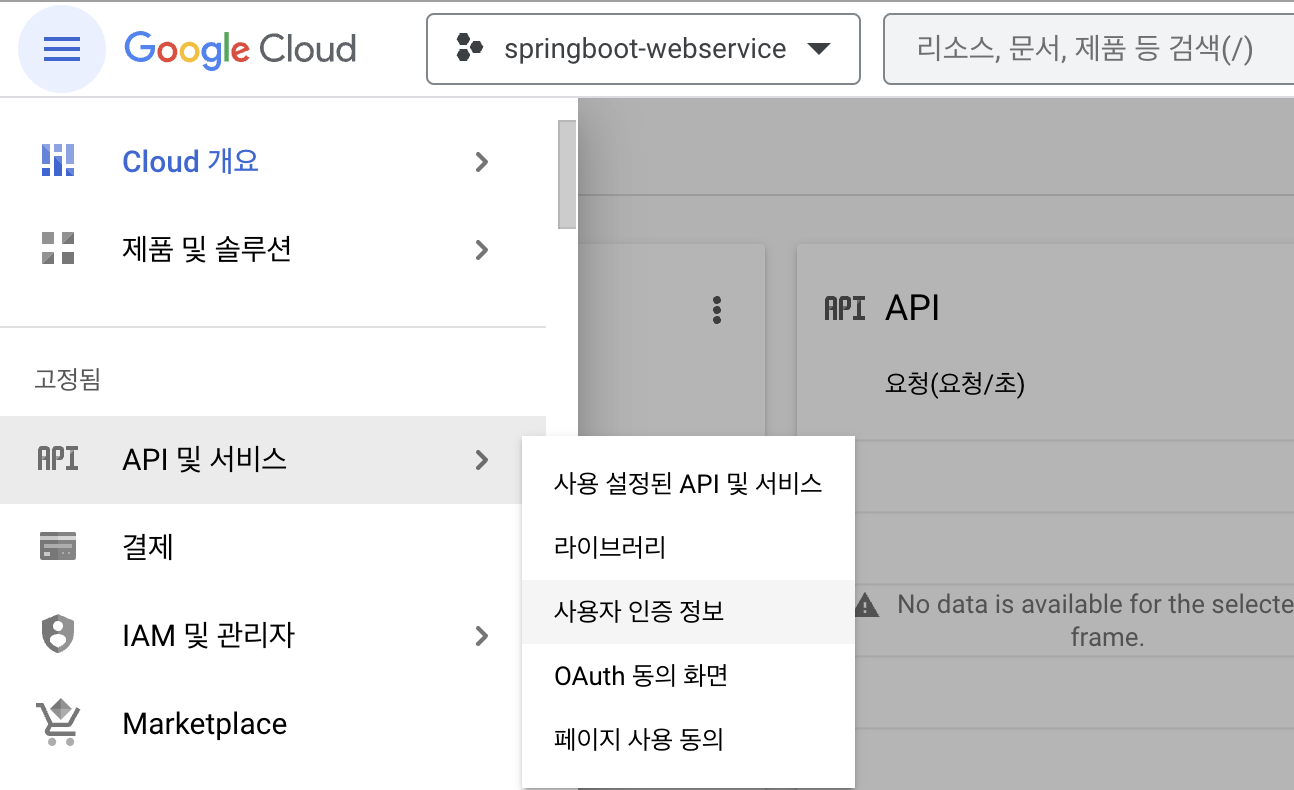
왼쪽 메뉴바 - API 및 서비스 - 사용자 인증 정보
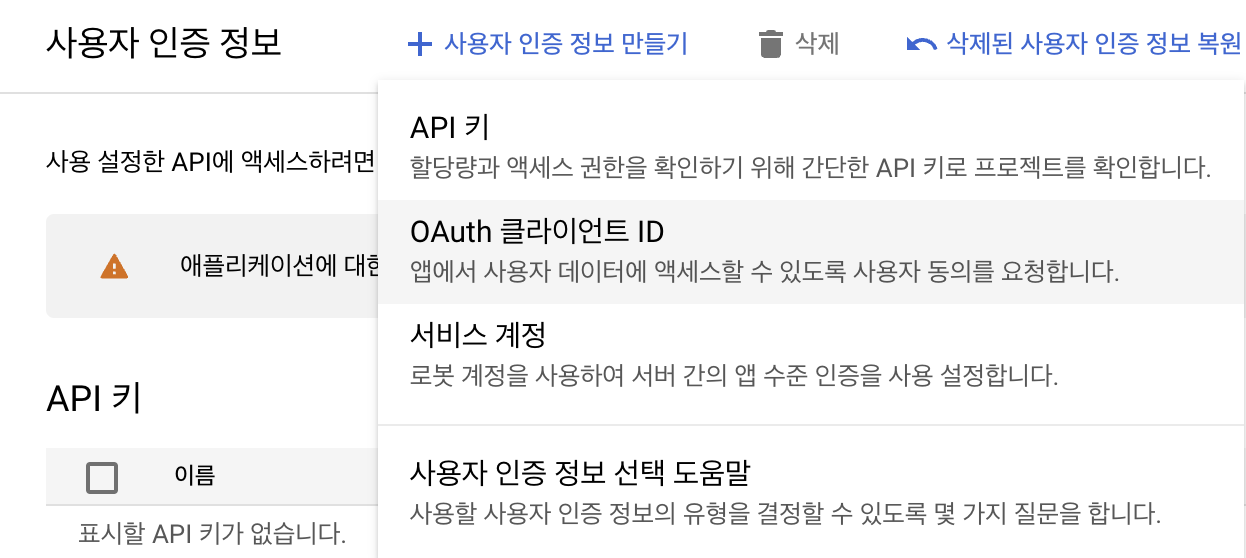
사용자 인증 정보 만들기 - OAuth 클라이언트 ID
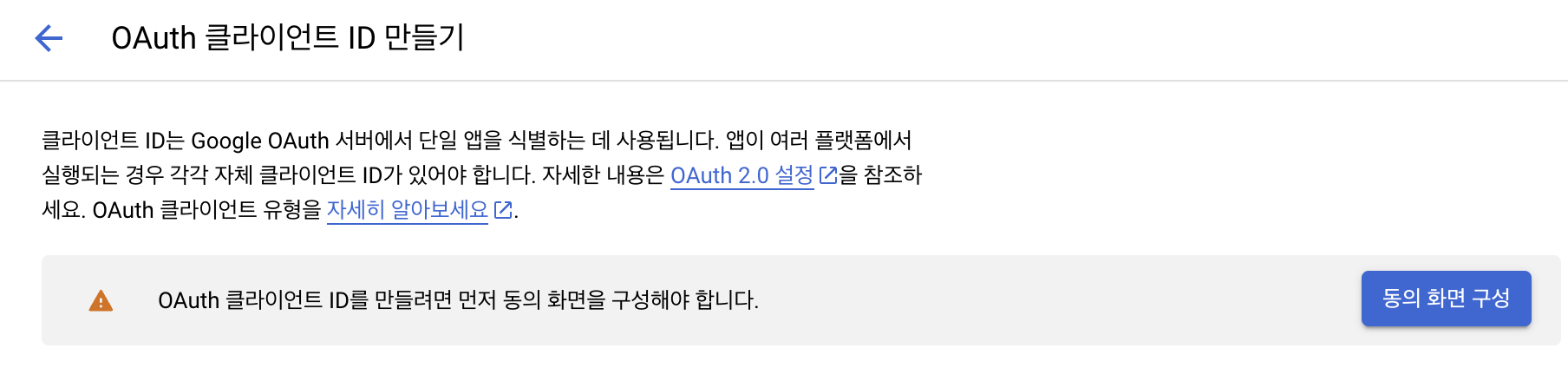
동의 화면 구성
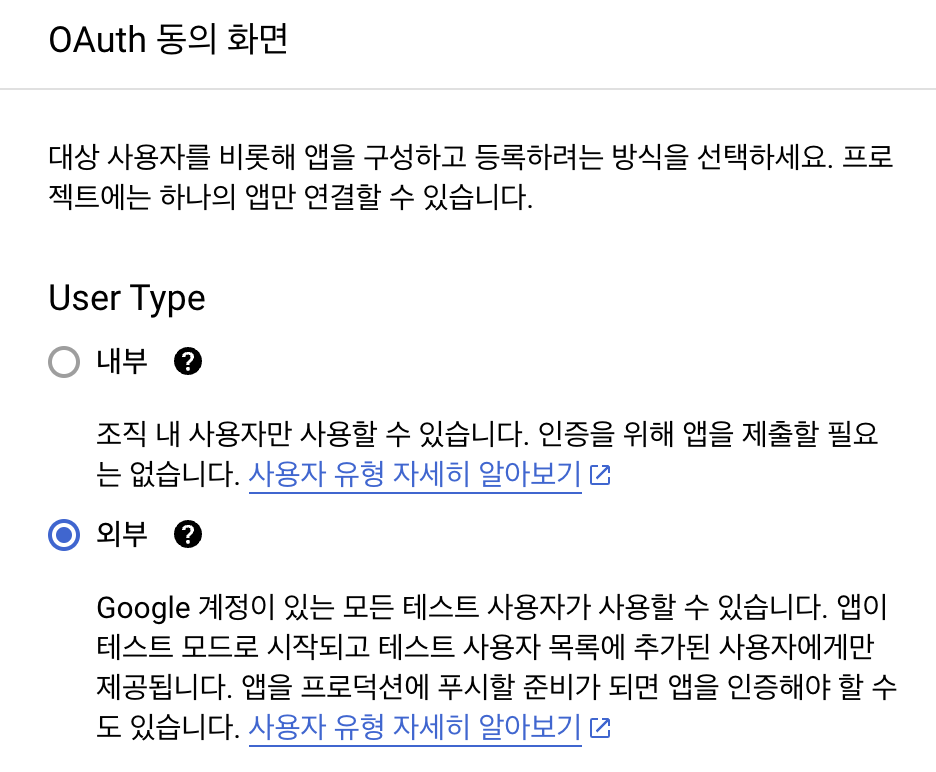
Google Workspace 사용자가 아니기에 내부는 선택할 수 없어서 외부로 선택했다.
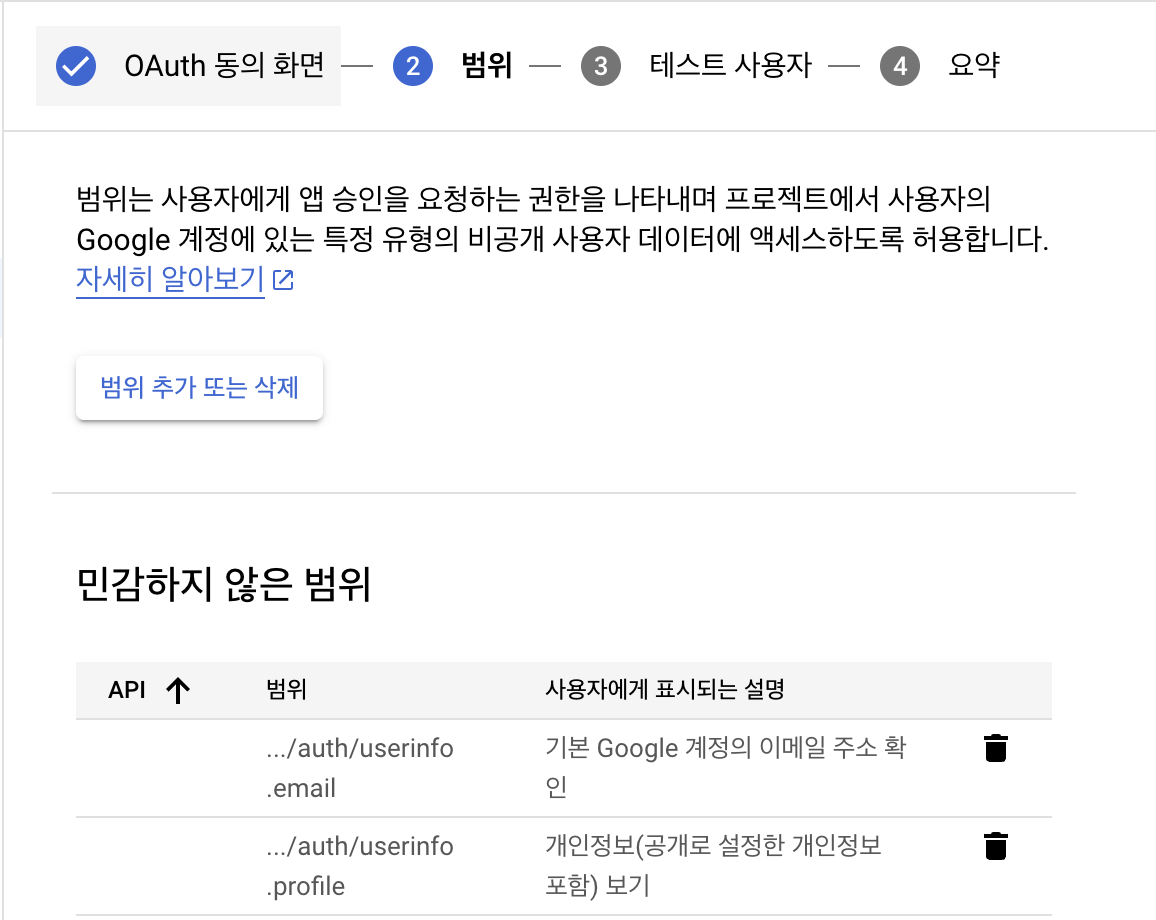
범위엔 이메일, 프로필, openid를 추가

사용자 인증정보 - 애플리케이션 유형 : 웹 애플리케이션 - 승인된 리디렉션 URI : http://localhost:8080/login/oauth2/code/google
승인된 리디렉션 URI
- 서비스에서 파라미터로 인증 정보를 주었을 때 인증이 성공하면 구글에서 리다이렉트할 URL
- 스프링 부트 2 버전의 시큐리티에서는 기본적으로 (도메인)/login/oauth2/code/(소셜서비스코드)로 리다이렉트 URL을 지원하고 있다.
- 사용자가 별도로 리다이렉트 URL을 지원하는 Controller를 만들 필요가 없다. 시큐리티에서 이미 구현해 놓은 상태이다.
- AWS 서버에 배포시 localhost외에 추가로 주소를 추가해야 한다.
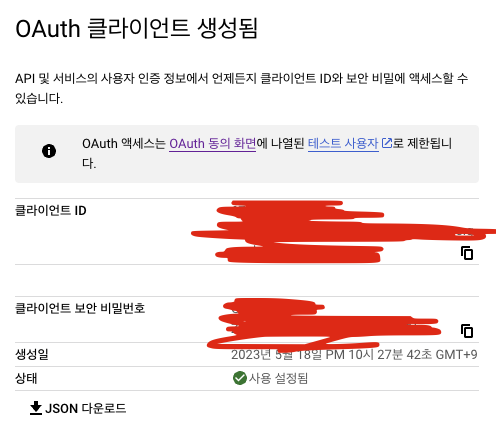
clientId, clientSecret 획득
application-oauth
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.google.client-id=구글클라이언트ID
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.google.client-secret=구글클라이언트시크릿
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.google.scope=profile,email
스프링 부트에서 properties 이름을 application-xxx.properties로 만들면 xxx 라는 이름의 profile 이 생성되어 이를 통해 관리할 수 있다. 즉, profile=xxx 라는 식으로 호출하여 해당 properties의 설정들을 가져올 수 있다.
User
package com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.domain.user;
import com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.domain.BaseTimeEntity;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.EnumType;
import javax.persistence.Enumerated;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@Entity
public class User extends BaseTimeEntity {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String email;
@Column
private String picture;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
@Column(nullable = false)
private Role role;
@Builder
public User(String name, String email, String picture, Role role) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.picture = picture;
this.role = role;
}
public User update(String name, String picture) {
this.name = name;
this.picture = picture;
return this;
}
public String getRoleKey() {
return this.role.getKey();
}
}@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
- JPA로 데이터베이스로 저장할 때 Enum 값을 어떤 형태로 저장할지를 결정한다.
- 기본적으로는 int로 된 숫자가 저장된다.
- 숫자로 저장되면 데이터베이스로 확인할 때 그 값이 무슨 코드를 의미하는지 알 수가 없다.
- 그래서 문자열(EnumType.STRING)로 저장될 수 있도록 선언한다.
Role
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public enum Role {
GUEST("ROLE_GUEST", "손님"),
USER("ROLE_USER", "일반 사용자");
private final String key;
private final String title;
}스프링 시큐리티에서는 권한 코드에 항상 ROLE_이 앞에 있어야 한다. 그래서 코드별 키 값을 ROLE_GUEST, ROLE_USER 등으로 지정한다.
UserRepository
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import java.util.Optional;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
Optional<User> findByEmail(String email);
}findByEmail
- 소셜 로그인으로 반환되는 값 중 email 을 통해 이미 생성된 사용자인지 처음 가입하는 사용자인지 판단하기 위한 메소드이다.
스프링 시큐리티 설정
build.gradle 에 스프링 시큐리티 관련 의존성 하나 추가
implementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client') // 권한 관련implementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client') // 권한 관련
- 소셜 로그인 등 클라이언트 입장에서 소셜 기능 구현 시 필요한 의존성이다.
- spring-security-oauth2-client와 spring-security-oauth2-jose를 기본으로 관리해준다.
SecurityConfig
package com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.config.auth;
import com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.domain.user.Role;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private final CustomOAuth2UserService customOAuth2UserService;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().disable()
.headers().frameOptions().disable()
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/", "/css/**", "/images/**", "/js/**", "/h2-console/**", "/profile").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/v1/**").hasRole(Role.USER.name())
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.logout()
.logoutSuccessUrl("/")
.and()
.oauth2Login()
.userInfoEndpoint()
.userService(customOAuth2UserService);
}
}@EnableWebSecurity
- Spring Security 설정들을 활성화시킨다.
.csrf().disable() .headers().frameOptions().disable()
- h2-console 화면을 사용하기 위해 해당 옵션들을 disable한다.
.authorizeRequests()
- URL별 권한 관리를 설정하는 옵션의 시작점이다.
- authorizeRequests 가 선언되어야만 antMatchers 옵션을 사용할 수 있다.
antMatchers
- 권한 관리 대상을 지정하는 옵션이다.
- URL, HTTP 메소드별로 관리가 가능하다.
- "/"등 지정된 URL들은 permitAll()옵션을 통해 전체 열람 권한을 주었다.
- "/api/v1/**" 주소를 가진 API는 USER 권한을 가진 사람만 가능하도록 했다.
anyRequest
- 설정된 값들 이외 나머지 URL들을 나타낸다.
- 여기서는 authenticated() 를 추가하여 나머지 URL들은 모두 인증된 사용자들에게만 허용하게 한다.
- 인증된 사용자 즉, 로그인한 사용자들을 이야기한다.
.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/")
- 로그아웃 기능에 대한 여러 설정의 진입점이다.
- 로그아웃 성공 시 / 주소로 이동한다.
.oauth2Login()
- OAuth 2 로그인 기능에 대한 여러 설정의 진입점이다.
.userInfoEndpoint()
- OAuth 2 로그인 성공 이후 사용자 정보를 가져올 때의 설정들을 담당한다.
userService
- 소설 로그인 성공 시 후속 조치를 진행할 UserService 인터페이스의 구현체를 등록한다.
- 리소스 서버(소셜 서비스들)에서 사용자 정보를 가져온 상태에서 추가로 진행하고자 하는 기능을 명시할 수 있다.
CustomeOAuth2UserService
package com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.config.auth;
import com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.domain.user.User;
import com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.domain.user.UserRepository;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.userinfo.DefaultOAuth2UserService;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.userinfo.OAuth2UserRequest;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.userinfo.OAuth2UserService;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.OAuth2AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.user.DefaultOAuth2User;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.user.OAuth2User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.util.Collections;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class CustomOAuth2UserService implements OAuth2UserService<OAuth2UserRequest, OAuth2User> {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
private final HttpSession httpSession;
@Override
public OAuth2User loadUser(OAuth2UserRequest userRequest) throws OAuth2AuthenticationException {
OAuth2UserService delegate = new DefaultOAuth2UserService();
OAuth2User oAuth2User = delegate.loadUser(userRequest);
String registrationId = userRequest.getClientRegistration().getRegistrationId();
String userNameAttributeName = userRequest.getClientRegistration().getProviderDetails()
.getUserInfoEndpoint().getUserNameAttributeName();
OAuthAttributes attributes = OAuthAttributes.of(registrationId, userNameAttributeName, oAuth2User.getAttributes());
User user = saveOrUpdate(attributes);
httpSession.setAttribute("user", new SessionUser(user));
return new DefaultOAuth2User(
Collections.singleton(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(user.getRoleKey())),
attributes.getAttributes(),
attributes.getNameAttributeKey());
}
private User saveOrUpdate(OAuthAttributes attributes) {
User user = userRepository.findByEmail(attributes.getEmail())
.map(entity -> entity.update(attributes.getName(), attributes.getPicture()))
.orElse(attributes.toEntity());
return userRepository.save(user);
}
}
registrationId
- 현재 로그인 진행 중인 서비스를 구현하는 코드
- 지금은 구글만 사용하는 불필요한 값이나 이후 네이버 로긍니 연동 시 네이버 로기인인지 구글 로그인인지 구분하기 ㅜ이해 사용한다.
userNameAttributeName
- OAuth2 로그인 진행 시 키가 되는 필드값을 이야기한다. Primary Key와 같은 의미이다.
- 구글의 경우 기본적으로 코드를 지원하나 네이버 카카오 등은 기본 지원하지 않는다. 구글의 기본 코드는 "sub" 이다.
- 이후 네이버 로그인과 구글 로그인을 동시 지원할 때 사용된다.
OAuthAttributes
- OAuth2UserService를 통해 가져온 OAuth2User의 attribue를 담을 클래스이다.
- 이후 네이버 등 다른 소셜 로그인도 이 클래스를 사용한다.
SessionUser
- 세션에 사용자 정보를 저장하기 위한 Dto 클래스이다.
- 왜 User 클래스를 쓰지 않고 새로 만들어서 쓰는지 뒤에서 설명
OAuthAttributes
import com.jojoldu.book.springboot.domain.user.Role;
import com.jojoldu.book.springboot.domain.user.User;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import java.util.Map;
@Getter
public class OAuthAttributes {
private Map<String, Object> attributes;
private String nameAttributeKey;
private String name;
private String email;
private String picture;
@Builder
public OAuthAttributes(Map<String, Object> attributes, String nameAttributeKey, String name, String email, String picture) {
this.attributes = attributes;
this.nameAttributeKey = nameAttributeKey;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.picture = picture;
}
public static OAuthAttributes of(String registrationId, String userNameAttributeName, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
if("naver".equals(registrationId)) {
return ofNaver("id", attributes);
}
return ofGoogle(userNameAttributeName, attributes);
}
private static OAuthAttributes ofGoogle(String userNameAttributeName, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
return OAuthAttributes.builder()
.name((String) attributes.get("name"))
.email((String) attributes.get("email"))
.picture((String) attributes.get("picture"))
.attributes(attributes)
.nameAttributeKey(userNameAttributeName)
.build();
}
private static OAuthAttributes ofNaver(String userNameAttributeName, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
Map<String, Object> response = (Map<String, Object>) attributes.get("response");
return OAuthAttributes.builder()
.name((String) response.get("name"))
.email((String) response.get("email"))
.picture((String) response.get("profile_image"))
.attributes(response)
.nameAttributeKey(userNameAttributeName)
.build();
}
public User toEntity() {
return User.builder()
.name(name)
.email(email)
.picture(picture)
.role(Role.GUEST)
.build();
}
}of()
- OAuth2User 에서 반환하는 사용자 정보는 Map이기 때문에 값 하나하나를 변환해야 한다.
toEntity()
- User 엔티티를 생성한다.
- OAuthAttributes에서 엔티티를 생성하는 시점은 처음 가입할 때이다.
- 가입할 때의 기본 권한을 GUEST로 주기 위해서 role 빌더 값에는 Role.GUEST를 사용한다.
- OAuthAttributes 클래스 생성이 끝났으면 같은 패키지에 SessionUser 클래스를 생성한다.
SessionUser
import com.jojoldu.book.springboot.domain.user.User;
import lombok.Getter;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Getter
public class SessionUser implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String email;
private String picture;
public SessionUser(User user) {
this.name = user.getName();
this.email = user.getEmail();
this.picture = user.getPicture();
}
}SessionUser 에는 인증된 사용자 정보만 필요하다. 그외 필요한 정보가 없으니 name, email, picture 만 필드로 선언한다.
엔티티 클래스에는 언제 다른 엔티티와 관계가 형성될지 모른다. 자식 엔티티를 갖고 있다면 직렬화 대상에 자식들까지 포함되니 성능 이슈, 부수 효과가 발생할 확률이 높다. 그래서 직렬화 기능을 가진 세션 Dto를 하나 추가로 만드는 것이 이후 운영 및 유지보수 때 많은 도움이 된다.
index.mustache
{{#userName}}
Logged in as: <span id="user">{{userName}}</span>
<a href="/logout" class="btn btn-info active" role="button">Logout</a>
{{/userName}}
{{^userName}}
<a href="/oauth2/authorization/google" class="btn btn-success active" role="button">Google Login</a>{{#userName}}
- 머스테치는 다른 언어와 같은 if 문을 제공하지 않는다.
- true/false 여부만 판단한다.
- 그래서 머스테치에는 항상 최종값을 넘겨줘야 한다.
- 여기서도 역시 userName이 있다면 userName을 노출시키도록 구성한다.
a href="/logout"
- 스프링 시큐리티에서 기본적으로 제공되는 로그아웃 URL이다.
- 개발자가 별도로 저 URL에 해당하는 컨트롤러를 만들 필요가 없다.
- SecurityConfig 클래스에서 URL을 변경할 순 있지만 기본 URL을 사용해도 충분하니 여기서 그대로 사용한다.
{{^userName}}
- 머스테치에서 해당 값이 존재하지 않는 경우에는 ^를 사용한다.
- 여기서는 userName이 없다면 로그인 버튼을 노출시키도록 구성했다.
a href="/oauth2/authorization/google"
- 스프링 시큐리티에서 기본적으로 제공하는 로그인 URL이다
- 로그아웃 URL과 마찬가지로 개발자가 별도의 컨트롤러를 생성할 필요가 없다.
IndexController
@GetMapping("/")
public String index(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("posts", postsService.findAllDesc());
SessionUser user = (SessionUser) model.getAttribute("user");
if (user != null) {
model.addAttribute("userName", user.getName());
}
return "index";
}(SessionUser) model.getAttribute("user");
- 앞서 작성된 CustomeOAuth2UserService에서 로그인 성공 시 세션에 SessionUser를 저장하도록 구성했다.
- 로그인 성공 시 httpSession.getAttribute("user")에서 값을 가졍로 수 있다.
if (user != null)
- 세션에 저장된 값이 있을 때만 model에 userName으로 등록한다.
- 세션에 저장된 값이 없으면 model엔 아무런 값이 없는 상태이니 로그인 버튼이 보이게 된다.
실행화면
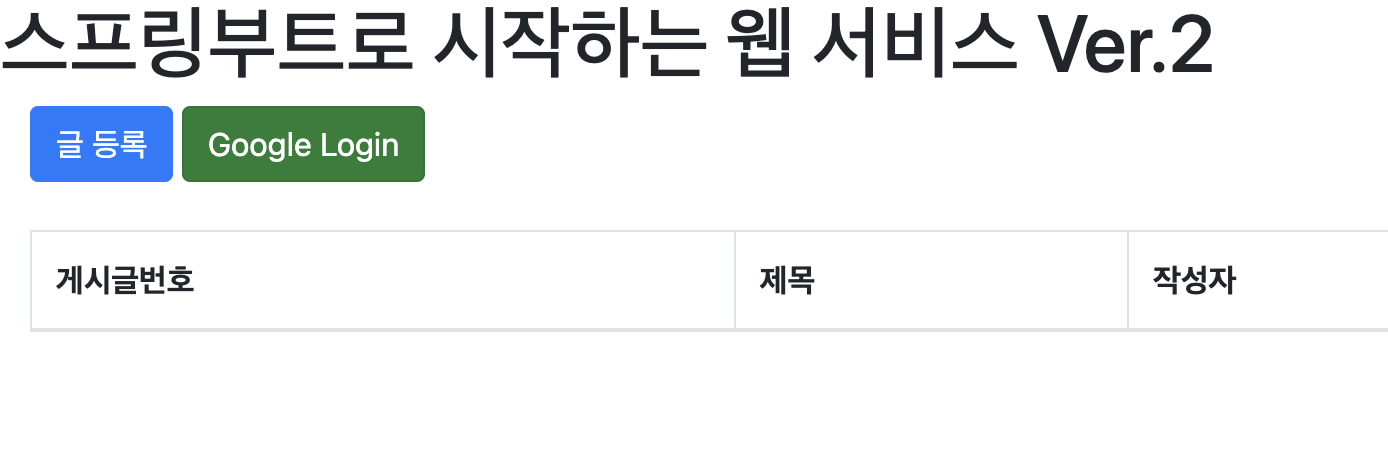
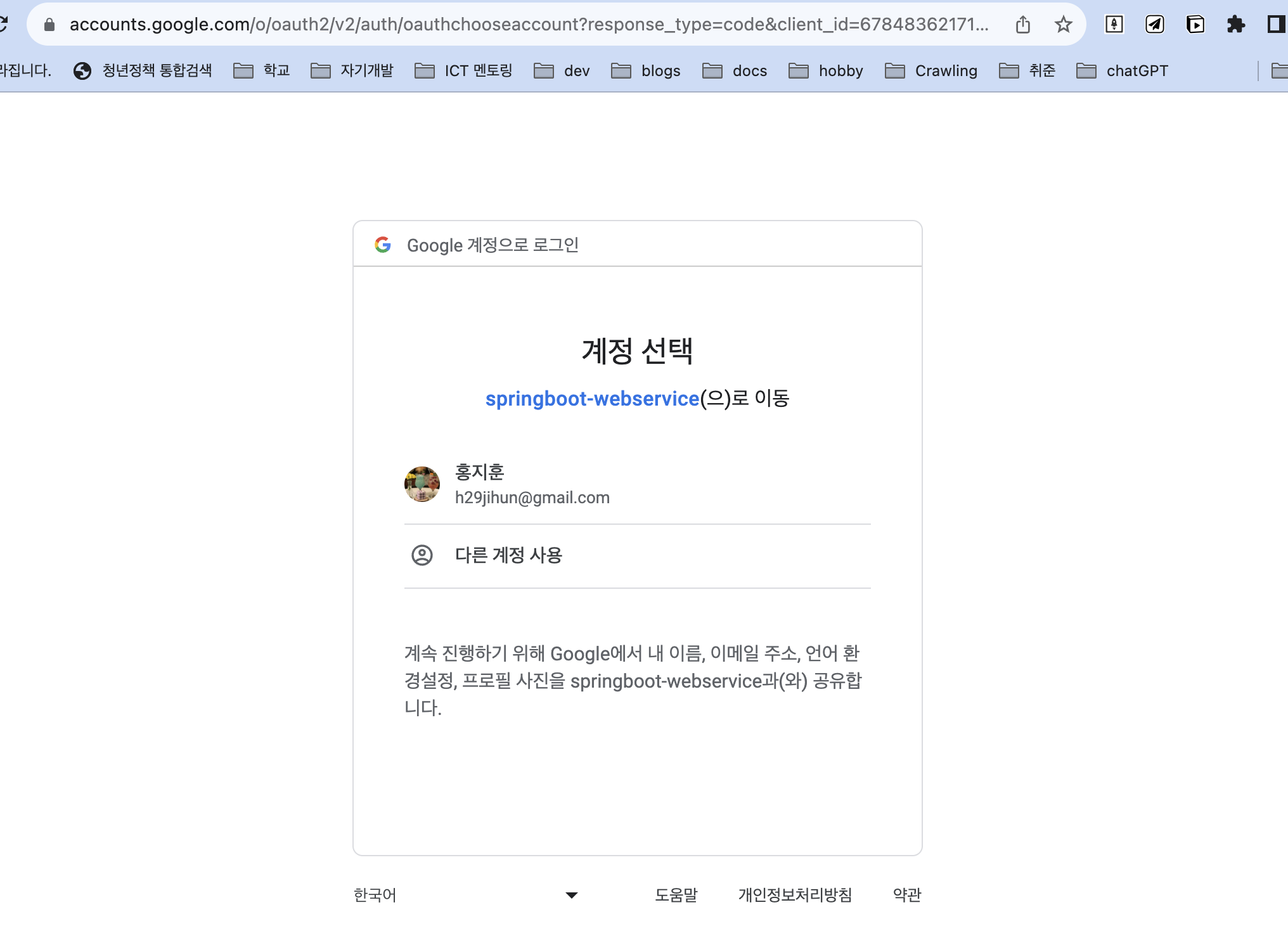
어노테이션 기반 개선
package com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.config.auth;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface LoginUser {
}@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
- 이 어노테이션이 생성될 수 있는 위치를 지정한다.
- PARAMETER로 지정했으니 메소드의 파라미터로 선언된 객체에서만 사용할 수 있다.
- 이 외에도 클래스 선언문에 쓸 수 있는 TYPE등이 있다.
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
- @Retention 어노테이션은 어노테이션의 라이프 사이클, 즉 어노테이션이 언제까지 살아 남아 있을지를 정하는 것이다.
- RetentionPolicy.SOURCE : 소스 코드 까지 남아 있는다. (컴파일 과정에서 어노테이션 정보가 사라짐)
- RetentionPolicy.CLASS : 클래스 파일까지 남아 있는다. (런타임시 유지되지 않는다.)
Maven/Gradle로 다운받은 라이브러리와 같이 jar 파일에는 소스가 포함되어 있지 않고 ㅊlass 파일만 포함되어 있다.- class 파일만 존재하는 라이브러리 같은 경우에도 타입체커, IDE 부가 기능등을 사용할 수 있으려면 CLASS 정책이 필요하다.
- RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME : 런타임까지 남아 있는다. (Reflection API로 어노테이션 정보 조회 가능)
@Controller, @Service, @Autowired 등- 스프링이 올라오는 실행중인 시점에 컴포넌트 스캔이 가능해야 하기에 RUNTIME 정책이 필요하다.
@interface
- 이 파일을 어노테이션 클래스로 지정한다.
- LoginUser라는 이름을 가진 어노테이션이 생성되었다고 보면 된다.
LoginUserArgumetnResolver
package com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.config.auth;
import com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.config.auth.dto.SessionUser;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.support.WebDataBinderFactory;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.NativeWebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodArgumentResolver;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.ModelAndViewContainer;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Component
public class LoginUserArgumentResolver implements HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
private final HttpSession httpSession;
@Override
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
boolean isLoginUserAnnotation = parameter.getParameterAnnotation(LoginUser.class) != null;
boolean isUserClass = SessionUser.class.equals(parameter.getParameterType());
return isLoginUserAnnotation && isUserClass;
}
@Override
public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception {
return httpSession.getAttribute("user");
}
}supportsParameter()
- 컨트롤러 메서드의 특정 파라미터를 지원하는지 판단한다.
- 파라미터에 @LoginUser 어노테이션이 붙어 있고 파라미터 클래스 타입이 SessionUser.class 인 경우 true를 반환한다.
resolveArgument()
- 파라미터에 전달할 객체를 생성한다.
- 세션에서 객체를 가져온다.
LoginUserArgumentResolver 가 스프링에서 인식될 수 있도록 WebMvcConfigurer에 추가
WebConfig
package com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.config;
import com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.config.auth.LoginUserArgumentResolver;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodArgumentResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
import java.util.List;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private final LoginUserArgumentResolver loginUserArgumentResolver;
@Override
public void addArgumentResolvers(List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> argumentResolvers) {
argumentResolvers.add(loginUserArgumentResolver);
}
}HandlerMethodArgumentResolver 는 항상 WebMvcConfigurer의 addArgumentResolvers()를 통해 추가해야 한다.
변경사항
@GetMapping("/")
public String index(Model model, @LoginUser SessionUser user) {
model.addAttribute("posts", postsService.findAllDesc());
// SessionUser user = (SessionUser) httpSession.getAttribute("user");
if (user != null) {
model.addAttribute("userName", user.getName());
}
return "index";
}@LoginUser SessionUser user
- 기존에 (User) httpSession.getAttribute("user")로 가져오던 세션 정보 값이 개선되었다.
- 이제 어느 컨트롤러든지 @LoginUser만 사용하면 세션 정보를 가져올 수 있게 되었다.
세션 저장소로 데이터베이스 사용하기
현재 서비스는 애플리케이션을 재실행시 로그인이 풀린다. 이는 세션이 톰캣의 메모리에 저장되기 때문이다.
세션 저장소
1. 톰캣 세션 사용
- 기본
- 톰캣(WAS, Web Application Session)에 세션이 저장되므로 2대 이상의 WAS가 구동되는 환경에서는 톰캣들 간의 세션 공유를 위한 추가 설정 필요
- MySQL과 같은 데이터베이스를 세션 저장소로 사용
- 가장 쉬운 방법
- 로그인 요청마다 DB IO가 발생하여 성능상 이슈 발생 가능
- 로그인 요청이 많이 없는 백오피스, 사내 시스템 용도로 사용
- Redis, Memcached와 같은 메모리 DB를 세션 저장소로 사용
- B2C 서비스에서 가장 많이 사용하는 방식
- 실제 서비스로 사용하기 위해서 Embedded Redis와 같은 방식이 아닌 외부 메모리 서버가 필요
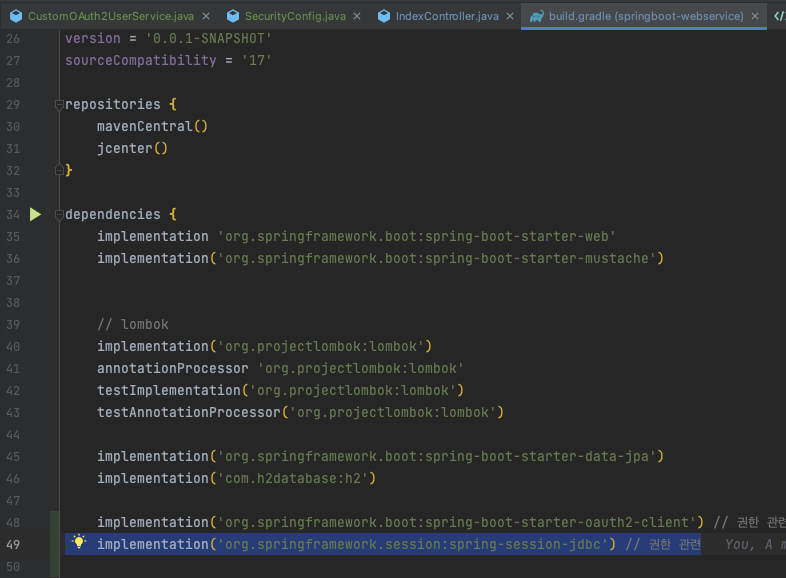
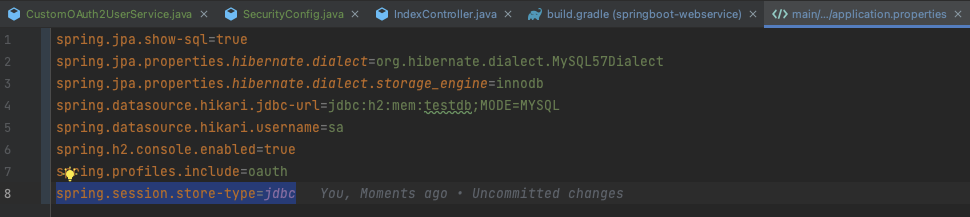
spring-session-jdbc 등록
h2-console을 보면 세션을 위한 테이블 2개 SPRING_SESSION, SPRING_SESSION_ATTRIBUTES가 생성되었다.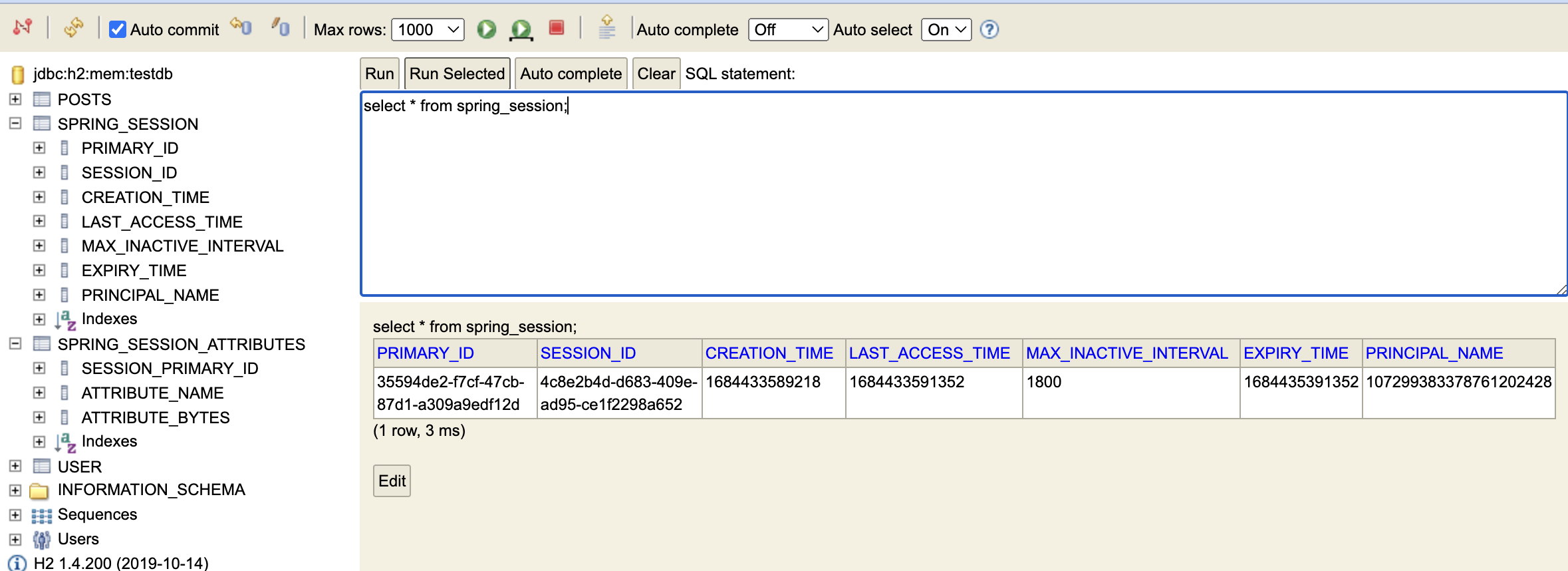
로그인을 하니 세션 정보가 저장되었다.
이 상태에선 여전히 스프링을 재시작하면 세션이 풀리는데 그 이유는 h2기반으로 스프링이 재실행될 때 h2도 재시작되기 때문이다. 이후 AWS 의 RDS를 사용하면 세션이 풀리지 않게 된다.
네이버 로그인
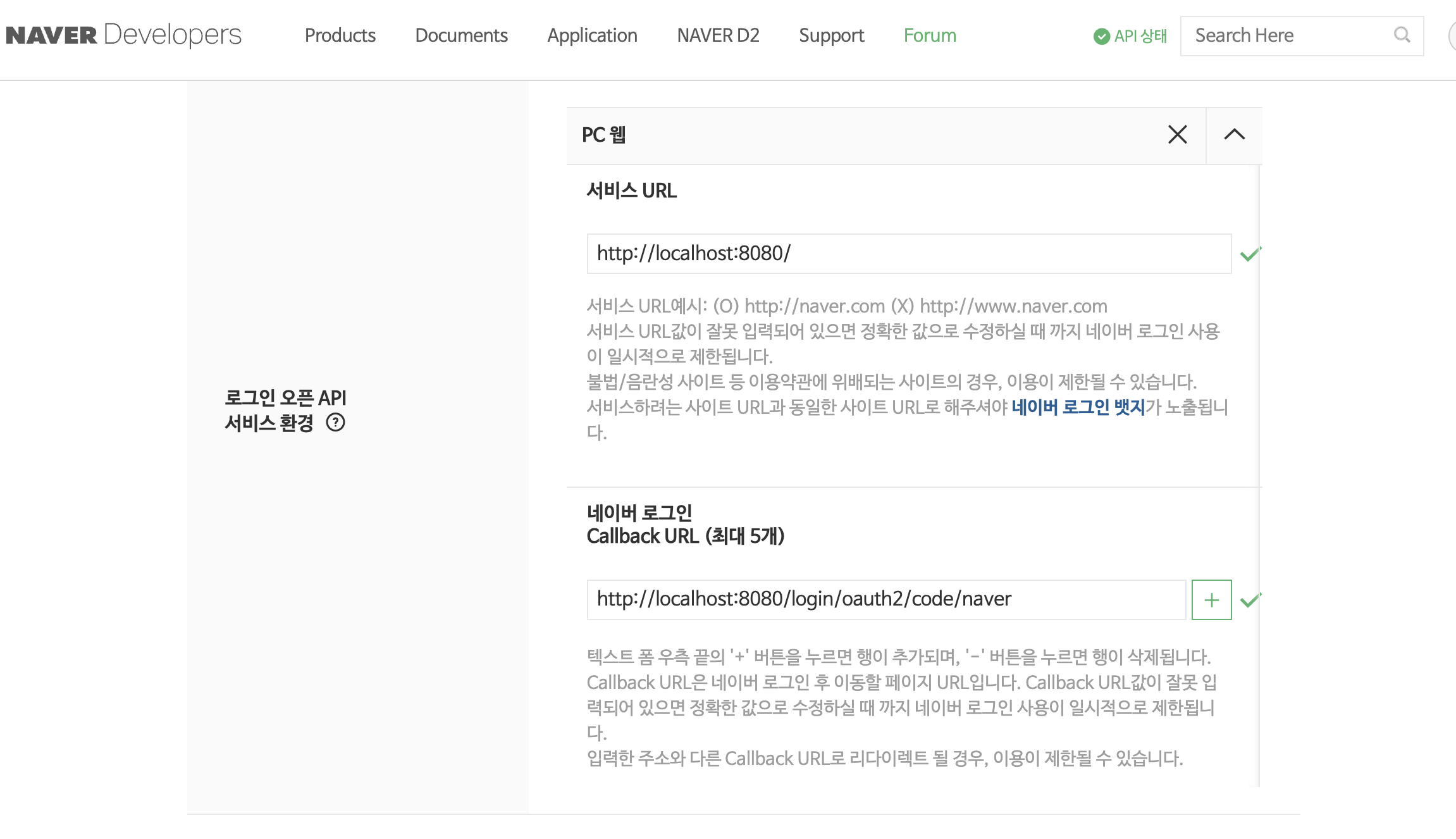
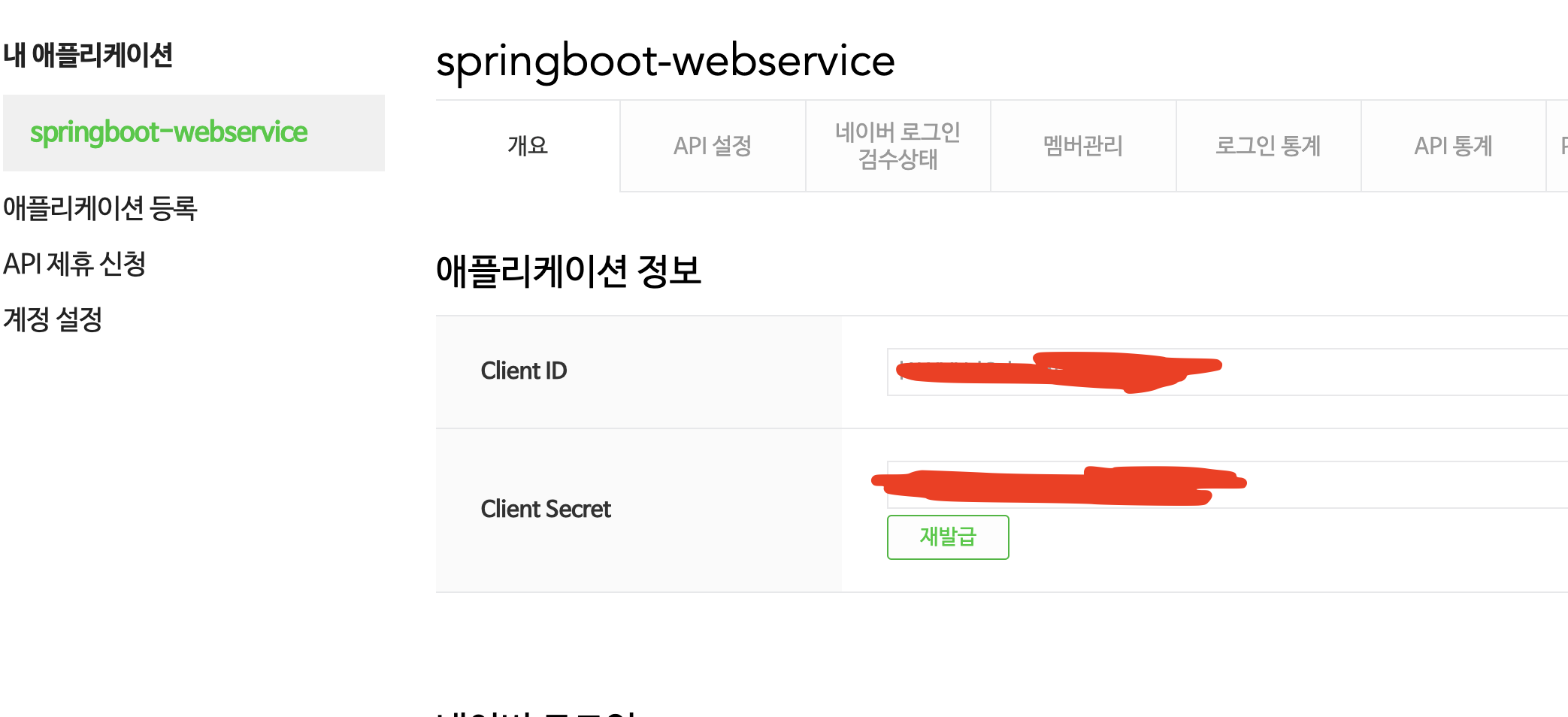
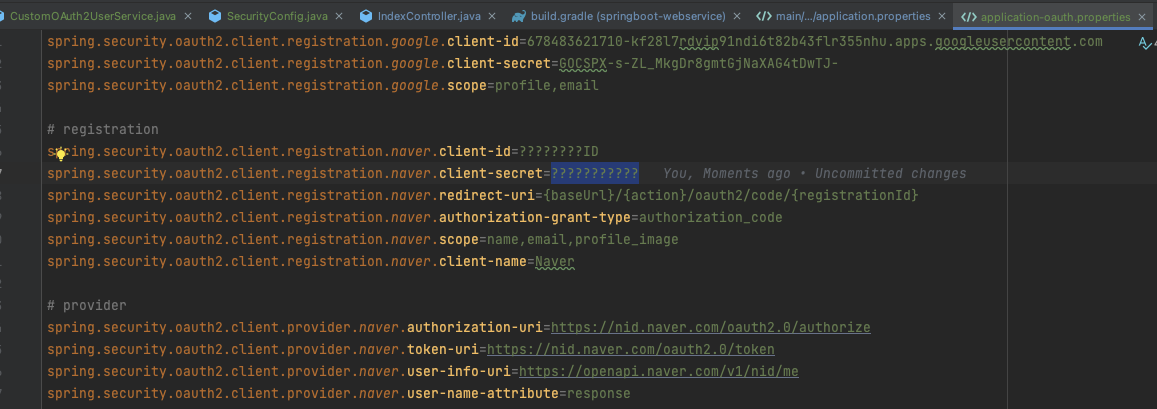
user-name-attribute=response
- 기준이 되는 user_name의 이름을 네이버에서는 response로 해야 한다.
- 그 이유는 네이버의 회원 조회 시 반환되는 JSON 형태 때문이다.
naver open api 로그인 회원 결과
- 네이버 응답값 최상위 필드는 resultCode, message, response 이며 스프링 시큐리티에선 하위 필드를 명시할 수 없고 최상위 필드들만 user_name으로 지정 가능하다.
스프링 시큐리티 설정 등록 - OAuthAttributes
package com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.config.auth.dto;
import com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.domain.user.Role;
import com.springboot.book.springbootwebservice.domain.user.User;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import java.util.Map;
@Getter
public class OAuthAttributes {
private Map<String, Object> attributes;
private String nameAttributeKey;
private String name;
private String email;
private String picture;
@Builder
public OAuthAttributes(Map<String, Object> attributes, String nameAttributeKey, String name, String email, String picture) {
this.attributes = attributes;
this.nameAttributeKey = nameAttributeKey;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.picture = picture;
}
public static OAuthAttributes of(String registrationId, String userNameAttributeName, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
if("naver".equals(registrationId)) {
return ofNaver("id", attributes);
}
return ofGoogle(userNameAttributeName, attributes);
}
private static OAuthAttributes ofNaver(String userNameAttributeName, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
Map<String, Object> response = (Map<String, Object>) attributes.get("response");
return OAuthAttributes.builder()
.name((String) response.get("name"))
.email((String) response.get("email"))
.picture((String) response.get("profile_image"))
.attributes(response)
.nameAttributeKey(userNameAttributeName)
.build();
}
}index.mustache
<a href="/oauth2/authorization/naver" class="btn btn-secondary active" role="button">Naver Login</a>- 네이버 로그인 URL은 application-oauth.properties에 등록한 redirect-uri 값에 맞춰 자동으로 등록된다.
- /oauth2/authorization/ 까지 고정이고 마지막 Path만 각 소셜 로그인 코드를 사용한다.

기존 테스트에 시큐리티 적용하기
전체 테스트
gradle - Tasks - verification - test
302 에러
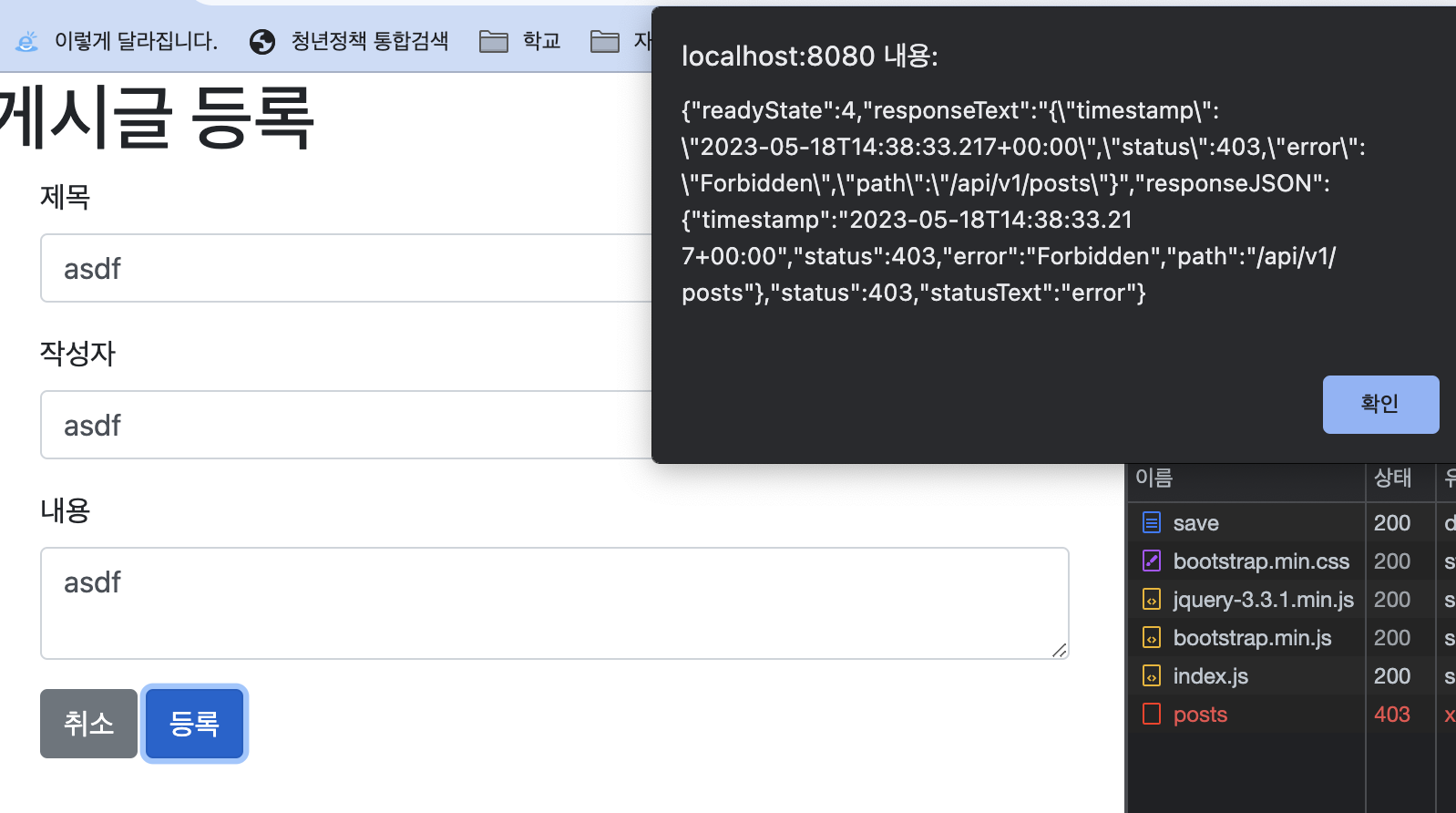
- 스프링 시큐리티 설정 때문에 인증되지 않은 사용자의 요청을 이동시키기 때문에 발생한다. 이런 API요청은 임의로 인증된 사용자를 추가하여 API만 테스트해 볼 수 있도록 코드를 수정
testImplementation("org.springframework.security:spring-security-test") // 권한 관련
@WithMockUser(roles="USER")
- 인증된 모의 사용자를 만들어서 사용한다.
- role 에 권한을 추가할 수 있다.
- 이 어노테이션으로 인해 ROLE_USER 권한을 가진 사용자가 API를 요청하는 것과 동일한 효과를 가지게 된다.
HelloControllerTest 에서 오류가 발생하던 원인
@WebMvcTest는 일반적인 @Configuration을 스캔하지 않는다. 따라서 Application 에서 @EnableJpaAuditing을 제거하고 config 에 JpaConfig를 추가하니 해결되었다.