쿼터니언(Quaternion)
게임 오브젝트를 회전시키기 위해서는 transform.rotation 프로퍼티를 사용하면 됩니다.
다만, 인스펙터 뷰에서 공개된 Rotation 프로퍼티가 Vector3 형식인 것과 달리 스크립트에서는 쿼터니언(Quaternion) 구조체를 사용합니다.

Quaternion rotation = new Quaternion();
rotation.w
rotation.x
rotation.y
rotation.z유니티는 짐벌락 현상을 해결하기 위해 쿼터니언을 사용합니다.
짐벌락이란 X,Y,Z축이 회전하다가 2개의 축이 겹쳐 저서 한 축의 회전이 상실되는것을 말합니다.
쿼터니언 구조체는 벡터와는 다른 사원수(w,x,y,z)라는 체계를 사용해서 오브젝트의 회전을 표현합니다.
이 사원수라는 체계는 상당히 난해한 체계이기 때문에 유니티의 공식 문서에서는 사원수에 대한 지식을 충분히 가지고 있지 않다면 쿼터니언을 직접 수정하지 않도록 권장하고 있습니다.
따라서 유니티는 유저의 편의성을 위해 인스펙터뷰에서의 Rotation 프로퍼티처럼 3차원 벡터(오일러 각)을 통해 회전을 다룹니다. 그리고 이렇게 외부에서 작업한 오일러 각을 내부적으로는 쿼터니언(사원수)로 변환한 후에 사용하게 됩니다.
유니티 엔진의 쿼터니언
쿼터니언에 대하여 공부하려면 복소수까지 배워야하므로 쿨하게 스킵하고 유니티에서 제공하는 쿼터니언 관련 프로퍼티로 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
Quaternion.Euler
오일러 각도를 쿼터니언으로 변환시킵니다. ex) Quaternion.Euler(0, 60, 0) => y방향 60도
public class Example : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
// A rotation 30 degrees around the y-axis
Quaternion rotation = Quaternion.Euler(0, 30, 0);
}
}Quaternion.LookRotation
해당 벡터를 바라보게합니다.
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform target; //바라 볼 오브젝트
void Update()
{
// 두 번째 인수는 타깃 오브젝트의 어느 부분을 바라볼것인지를 정합니다.
//(예: 타깃 오브젝트의 앞면을 바라볼지 윗면을 바라볼지) 기본값은 Vector3.up입니다.
Quaternion rotation = Quaternion.LookRotation(target.position,Vector3.up);
transform.rotation = rotation;
}
}Quaternion.Angle
두 회전 a와 b 사이의 각도를 반환합니다.
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform target;
void Update()
{
float angle = Quaternion.Angle(transform.rotation, target.rotation);
}
}Quaternion.Slerp
일정 시간을 두어 목표 방향(a->b방향)으로 회전합니다.
a와 b 각도 사이를 비율 t로 구형으로 보간합니다. 매개 변수 t는 시간을 뜻하며 [0, 1] 범위로 고정됩니다.
(보간 : 점들을 단순하게 직선으로 연결하는 것이 아니라, 여러 개의 점들을 지나는 곡선으로 연결하는 방법)
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform from;
public Transform to;
private float timeCount = 0.0f;
void Update()
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(from.rotation, to.rotation, timeCount);
timeCount = timeCount + Time.deltaTime;
}
}Quaternion.FromToRotation
fromDirection에서 toDirection으로 회전하는 회전을 만듭니다.
public class Example : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.FromToRotation(Vector3.up, transform.forward);
}
}Quaternion.identity
이 쿼터니언은 "회전 없음"에 해당합니다 - 객체가 월드 또는 부모 축과 완벽하게 정렬됩니다.
void Start()
{
transform.rotation = Quaternion.identity;
}Rotation
Transform.Rotation
Transform.Rotation은 게임오브젝트의 절대적인 회전 각도를 나타냅니다. 회전은 쿼터니언으로 되어있기 때문에 우리가 일반적으로 알고 있는 Vector3의 오일러각도를 쿼터니언으로 변환해서 대입해야 합니다.
Quaternion.Euler(x, y, z)를 사용하면 Vector3의 오일러각도를 쿼터니언으로 변환해 줍니다.
다음은 Transform.Rotation의 예제 코드입니다.
//오일러 => 쿼터니언
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Euler(x,y,z);transform.eulerAngles
transform.eulerAngles은 월드 공간에서의 회전을 나타냅니다.
우리가 익숙한 오일러 각도를 이용해서 회전하는 방법입니다. eulerAngles 축 중 하나를 별도로 설정하지 않고 (예 : eulerAngles.x = 10; ) 새 값으로 설정할 때는 아래와 같이 한 번에 모두 설정합니다.
float timer = 0.0f;
void Update()
{
timer += Time.deltaTime * 50.0f;
transform.eulerAngles = new Vector3(0.0f, timer, 0.0f);
}Transform.localRotation
Transform.Rotation은 게임오브젝트의 상대적인 회전 각도를 나타냅니다. 게임오브젝트의 부모가 있을 경우 부모를 기준으로 상대적인 회전 각도를 나타냅니다. 부모가 없을 경우에는 Transform.Rotation과 동일합니다. Transform.Rotation에 Vector3의 오일러각도를 대입하면 해당 각도로 회전합니다.
//부모 오브젝트를 기준으로 회전?
transform.localRotation = Quaternion.Euler(x, y, z);Transform.Rotate
Transform.Rotate는 게임오브젝트를 회전시키기 위한 함수입니다. 회전하고자 하는 Vector3의 오일러 각도를 인자로 넘겨주면 됩니다.
현재 게임오브젝트의 절대적인 회전 각도로 회전할 경우에는 Space.World 옵션을 사용하면 됩니다.
public class RotateExample : MonoBehaviour
{
void Update()
{
// 게임 오브젝트 기준으로 회전
transform.Rotate(new Vector3(10f, 20f, 30f) * Time.deltaTime);
// 절대 좌표 기준으로 회전
transform.Rotate(new Vector3(10f, 20f, 30f) * Time.deltaTime, Space.World);
}
}Transform.RotateAround
Transform.RotateAround는 특정 좌표를 기준으로 게임오브젝트를 회전시키기 위한 함수입니다. 회전할 기준 좌표, 회전할 기준 축, 회전할 각도를 인자로 넘겨주면 됩니다. 지구가 태양 주위를 공전하는 것 처럼 특정 좌표를 기준으로 공전할 경우 Transform.RotateAround 함수를 사용합니다.
public class RotateAroundExample : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform Target;
void Update()
{
transform.RotateAround(Target.position, Vector3.up, 20 * Time.deltaTime);
}
}transform.forward로 바라보는 방향 정하기
게임 오브젝트를 회전시키는 다른 방법으로는 transform.forward 프로퍼티를 이용하면 게임 오브젝트의 forward, 즉 정면을 설정해서 특정한 방향을 바라보게 할 수 있습니다. 프로퍼티로 가져올 수 있는 방향으로는 forward, up, right가 있습니다.
float timer = 0f;
void Update()
{
timer += Time.deltaTime;
ForwardControl(new Vector3(Mathf.Cos(timer), 0f, Mathf.Sin(timer)));
}
public void ForwardControl(Vector3 newForward)
{
transform.forward = newForward;
}transform.LookAt() 함수로 원하는 위치를 바라보게 하기
transform 컴포넌트에 있는 LookAt() 함수를 사용하면 원하는 지점을 바라보게 할 수 있습니다. LookAt() 함수의 매개변수로 Vector3 뿐만 아니라 다른 게임 오브젝트의 트랜스폼 컴포넌트를 넣어서 다른 게임 오브젝트를 따라가며 바라보게 할 수도 있습니다. 바라보는 방향은 월드 좌표계를 기준으로 합니다.
float timer = 0f;
void Update()
{
timer += Time.deltaTime;
ForwardControl(new Vector3(Mathf.Cos(timer), 0f, Mathf.Sin(timer)));
}
public void LookObject(Vector3 pos)
{
transform.LookAt(pos);
}플레이어 회전 시키기
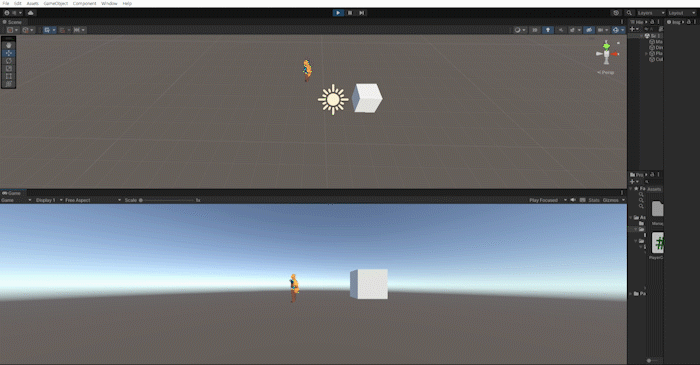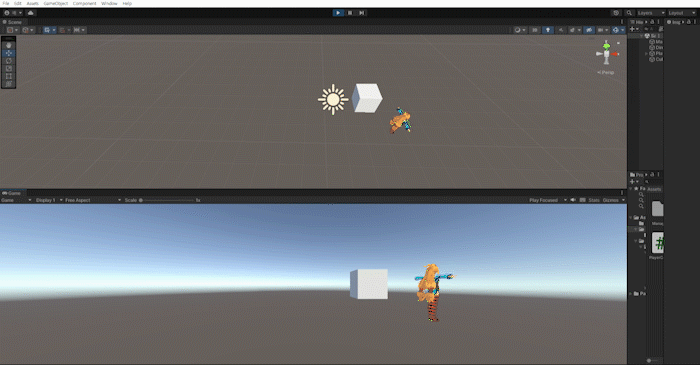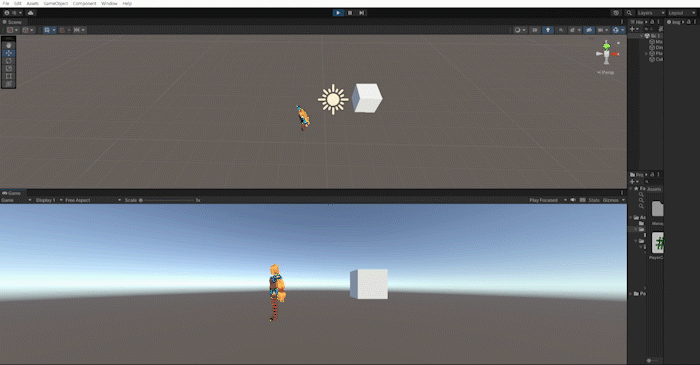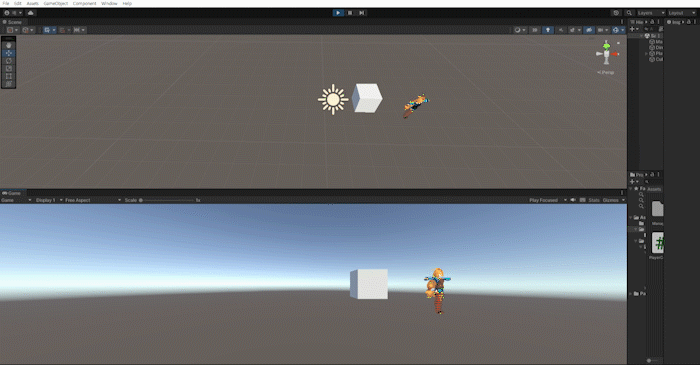
위 방법들을 사용하여 방향키를 눌렀을때 해당 방향으로 플레이어를 바라보게하고, 포지션을 변경하는 작업을 해보겠습니다.
이 방법은 3d 캐릭터가 움직이는 방식보다는 2d 캐릭터가 움직이는 방법과 유사하지만 마우스를 이용하여 회전하는 방식은 나중에 알아보도록 하고, 지금은 회전을 연습하는 차원에서 진행하겠습니다.
Slerp를 통해 캐릭터의 회전에 살짝 시간차를 두고 LookRotation을 통해 해당 방향을 바라보는 방식으로 만듭니다.
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
public class PlayerController : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField]
float _speed = 1.0f;
void Start()
{
}
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.W))
{
transform.position += Vector3.forward * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation,
Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.forward),
Time.deltaTime * _speed);
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.S))
{
transform.position += Vector3.back * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation,
Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.back),
Time.deltaTime * _speed);
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.A))
{
transform.position += Vector3.left * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation,
Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.left),
Time.deltaTime * _speed);
}
if (Input.GetKey(KeyCode.D))
{
transform.position += Vector3.right * Time.deltaTime * _speed;
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Slerp(transform.rotation,
Quaternion.LookRotation(Vector3.right),
Time.deltaTime * _speed);
}
}
}