SSD모델 구축 및 WIDER FACE데이터셋 활용
Dataset
WIDER FACE 데이터셋 활용
-
Face detection위한 데이터셋
-
넓은 공간에 다수가 등장하는 데이터셋

-
내부 구성
- WIDER Face Training Images
- WIDER Face Validation Images
- WIDER Face Testing Images
- Face annotations
#작업환경 설정
! mkdir -p ~/aiffel/face_detector/assets
! mkdir -p ~/aiffel/face_detector/dataset
! mkdir -p ~/aiffel/face_detector/checkpoints
#준비된 데이터 연결
! ln -s ~/data/* ~/aiffel/face_detector데이터셋 전처리 - 분석 -
WIDER FACE Bounding Box
Ground Truth는 Bounding box정보
분석 포인트
wider_face_split 디렉토리 내에 wider_face_train_bbx_gt.txt과 wider_face_val_bbx_gt.txt, 이 2개 파일 안에 포함되어 있는 Bounding box 정보입니다.
!cd ~/aiffel/face_detector/widerface && ls wider_face_split WIDER_test WIDER_train WIDER_val
#결과: bbox좌표의 상세정보
#왼쪽 4개(죄상 꼭짓점의 X,Y좌표, 너비, 높이)
!cd ~/aiffel/face_detector/widerface/wider_face_split && head -20 wider_face_train_bbx_gt.txt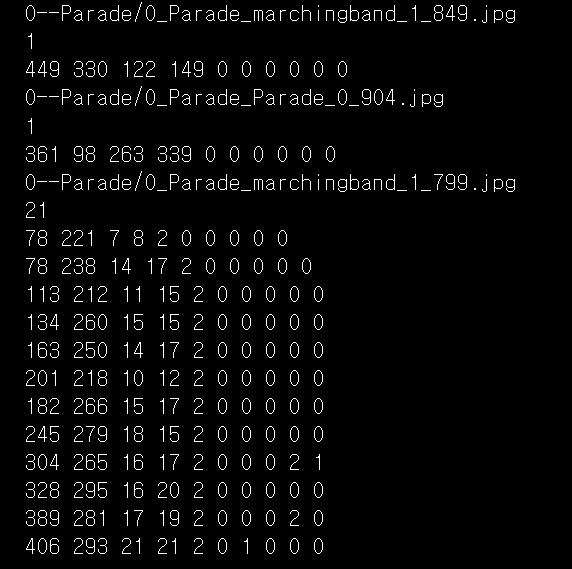
데이터셋 전처리 -tf_example-
TFRecodr
-
데이터셋의 처리속도 향상(전처리 작업)
-
TensorFlow만의 학습 데이터 저장 포맷
-
이진 레코드의 시퀀스 저장
-
여러 개의 tf.train.Example로 이뤄짐
-
한 개의 tf.train.Example는 여러 개의 tf.train.Feature로 이뤄짐
-
tf.train.Example:데이터 단위를 이루는 인스턴스 생성
def make_example(image_string, image_infos):
for info in image_infos:
filename = info['filename']
width = info['width']
height = info['height']
depth = info['depth']
classes = info['class']
xmin = info['xmin']
ymin = info['ymin']
xmax = info['xmax']
ymax = info['ymax']
if isinstance(image_string, type(tf.constant(0))):
encoded_image = [image_string.numpy()]
else:
encoded_image = [image_string]
base_name = [tf.compat.as_bytes(os.path.basename(filename))]
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'filename':tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=base_name)),
'height':tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[height])),
'width':tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[width])),
'classes':tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=classes)),
'x_mins':tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=xmin)),
'y_mins':tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=ymin)),
'x_maxes':tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=xmax)),
'y_maxes':tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=ymax)),
'image_raw':tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=encoded_image))
}))
return example
print('슝=3')SSD모델 구현 - priors box
*priors box
object가 존재할만한 다양한 크기의 box좌표 및 클래스 정보를 일정 개수만큼 고정 후 사용합니다.
*정확도 추출
bbox와 IoU를 계산하고 일정 크기 이상 겹치는 prior box를 선택하는 방식으로 빠르고 높은 정확도를 얻습니다.
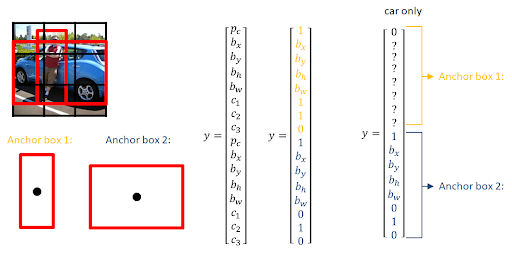
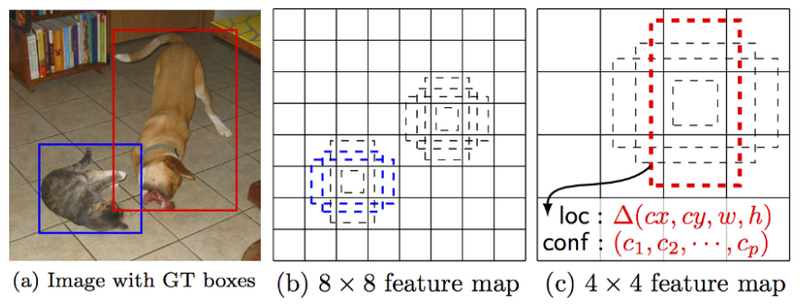
위의 그림을 구현하기 위해 아래 코드를 진행합니다.
def prior_box():
image_sizes = (IMAGE_HEIGHT, IMAGE_WIDTH)
min_sizes = PRIOR_MIN_SIZES
steps= PRIOR_STEPS
feature_maps = [
[math.ceil(image_sizes[0] / step), math.ceil(image_sizes[1] / step)]
for step in steps
]
anchors = []
for k, f in enumerate(feature_maps):
for i, j in product(range(f[0]), range(f[1])):
for min_size in min_sizes[k]:
s_kx = min_size / image_sizes[1]
s_ky = min_size / image_sizes[0]
cx = (j + 0.5) * steps[k] / image_sizes[1]
cy = (i + 0.5) * steps[k] / image_sizes[0]
anchors += [cx, cy, s_kx, s_ky]
boxes = np.asarray(anchors).reshape([-1, 4])
return boxes
print('슝=3')모델 구현 -SSD-
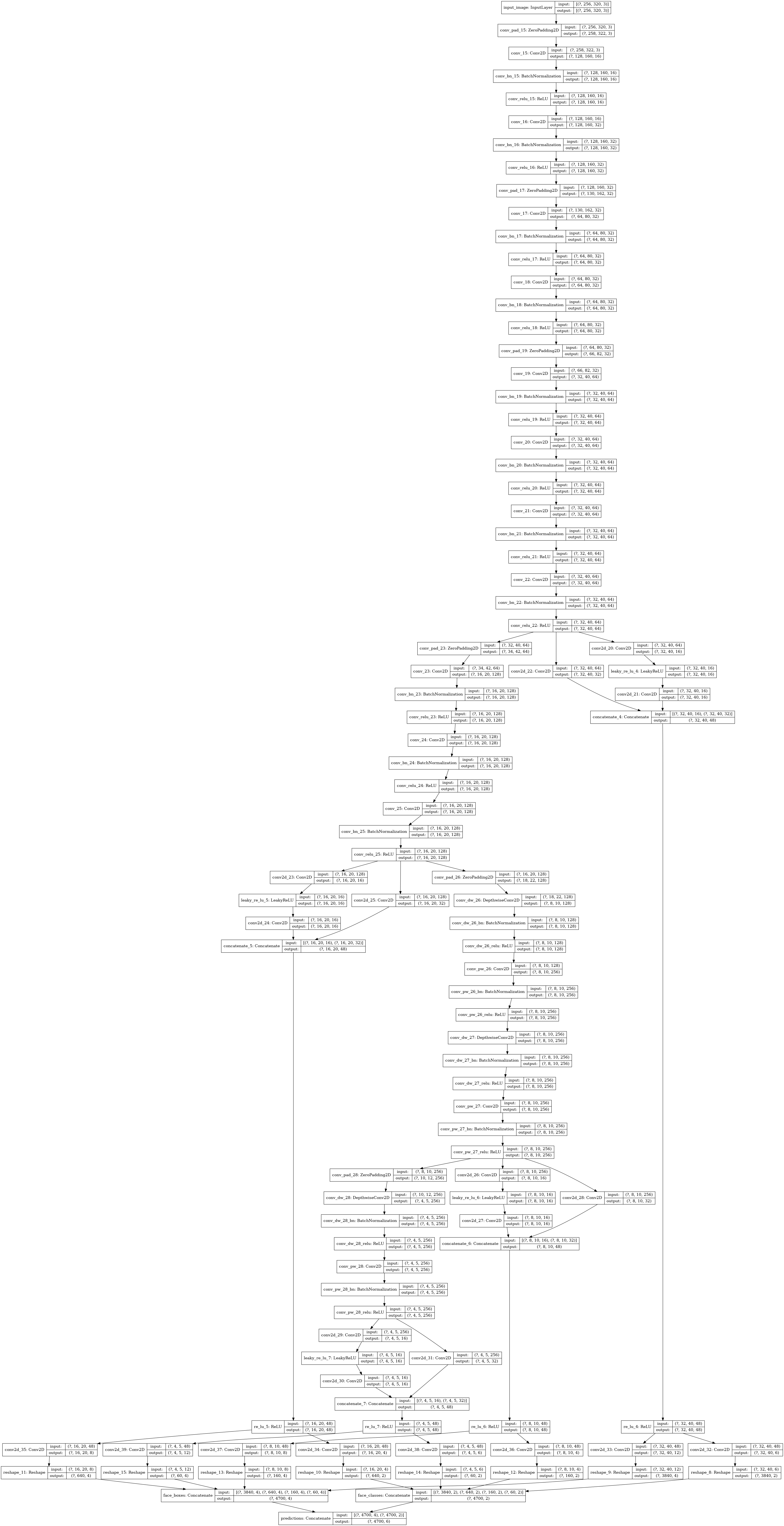
SSD model 빌드업
*내부 레이어 쌓기
-
Convolution block
-
Depthwise convolution block
-
Branch block(Skip connection쓰임)
*모델 쌓기
-
여러 블록 쌓기
-
중간 branch부분에 헤드(convolution layer)붙이기
-
하나의 헤드에 convolution layer 2개 필요
- confidence 예측, location 예측
- 결과
Branch마다 헤드가 연결 되어있기에 모델 중간 레이어에서 예측을 위한 정보를 가질 수 있게 됩니다.
def SsdModel():
base_channel = 16
num_cells = [3, 2, 2, 3]
num_class = len(IMAGE_LABELS)
x = inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[IMAGE_HEIGHT, IMAGE_WIDTH, 3], name='input_image')
x = _conv_block(x, base_channel, strides=(2, 2))
x = _conv_block(x, base_channel * 2, strides=(1, 1))
x = _conv_block(x, base_channel * 2, strides=(2, 2))
x = _conv_block(x, base_channel * 2, strides=(1, 1))
x = _conv_block(x, base_channel * 4, strides=(2, 2))
x = _conv_block(x, base_channel * 4, strides=(1, 1))
x = _conv_block(x, base_channel * 4, strides=(1, 1))
x = _conv_block(x, base_channel * 4, strides=(1, 1))
x1 = _branch_block(x, base_channel)
x = _conv_block(x, base_channel * 8, strides=(2, 2))
x = _conv_block(x, base_channel * 8, strides=(1, 1))
x = _conv_block(x, base_channel * 8, strides=(1, 1))
x2 = _branch_block(x, base_channel)
x = _depthwise_conv_block(x, base_channel * 16, strides=(2, 2))
x = _depthwise_conv_block(x, base_channel * 16, strides=(1, 1))
x3 = _branch_block(x, base_channel)
x = _depthwise_conv_block(x, base_channel * 16, strides=(2, 2))
x4 = _branch_block(x, base_channel)
extra_layers = [x1, x2, x3, x4]
confs = []
locs = []
for layer, num_cell in zip(extra_layers, num_cells):
conf, loc = _compute_heads(layer, num_class, num_cell)
confs.append(conf)
locs.append(loc)
confs = tf.keras.layers.Concatenate(axis=1, name="face_classes")(confs)
locs = tf.keras.layers.Concatenate(axis=1, name="face_boxes")(locs)
predictions = tf.keras.layers.Concatenate(axis=2, name='predictions')([locs, confs])
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=predictions, name='ssd_model')
return model
print('슝=3')