InputStream의 메모리 효율에 대해

InputStream으로 파일을 읽어드리면 모든 데이터를 한꺼번에 메모리에 적재하지 않고 필요한 만큼만 메모리에 적재하고 처리할 수 있어 메모리 효율적입니다. 이에 대한 얘기를 해보겠습니다.
MultipartFile
InputStream의 메모리 효율을 얘기하기 전에, MultipartFile를 살펴보면 좋습니다. 왜냐하면 MultipartFile은 InputStream과 반대로 파일 전체를 한번에 메모리 또는 디스크에 적재하기 때문입니다.
메모리에 적재할지 또는 디스크에 적재할지는 spring.servlet.multipart.file-size-threshold 속성값에 의해 정해집니다. 해당 값을 초과하는 파일은 디스크에 적재되고, 해당 값보다 작은 파일은 메모리에 적재됩니다. SpringBoot를 사용할 때 file-size-threshold의 기본값은 0으로 기본적으로 모든 파일을 디스크에 적재합니다.
이 디스크란 Spring과 톰캣이 자동으로 관리하는 저장 경로로, System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir")를 통해 그 경로를 얻을 수 있습니다.
실습
간단한 실습을 통해 MultipartFile의 동작을 살펴봅시다.
MultipartFileController.java
@RestController
public class MultipartFileController {
@PostMapping
public void getFile(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {
System.out.printf("파일 크기 : %.2f KB \n", file.getSize() / 1024.0);
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir"));
try{
Thread.sleep(100000);
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Err");
}
}
}- 임시 파일은 요청이 종료되면 자동으로 삭제됩니다. 저는 파일을 눈으로 확인하기 위해 sleep을 걸었습니다. 임시파일은 request의 lifecycle동안만 존재하기 때문에 요청이 완료되면 임시파일은 삭제됩니다.
postman
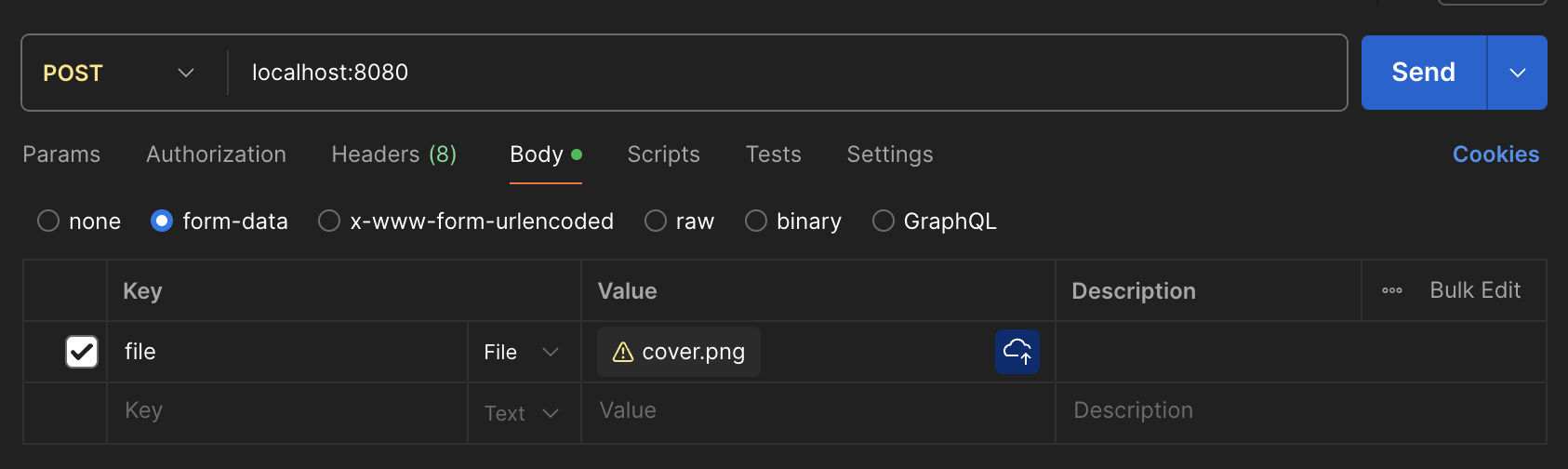
- 파일을 업로드하는 요청을 보냅니다.
출력 결과
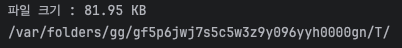
- 제 경우 임시 저장 경로는
/var/folders/gg/gf5p6jwj7s5c5w3z9y096yyh0000gn/T/입니다.
임시 파일 확인

/var/folders/gg/gf5p6jwj7s5c5w3z9y096yyh0000gn/T/경로에 여러 폴더가 생성되어 있습니다. 그 중tomcat.8080.xxx폴더 안으로 쭉 들어가면
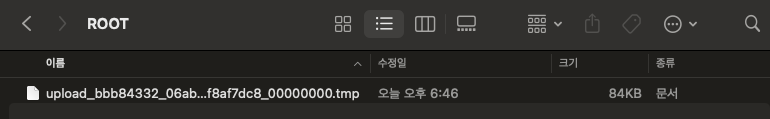
- 다음과 같은 tmp파일을 확인할 수 있습니다. 이 파일이 제가 Postman으로 전송한 파일입니다. tmp파일을 원래 파일의 확장자인
.png로 바꿔보면 Postman으로 전송했던 파일과 일치하는걸 확인할 수 있습니다.
다음으로 spring.servlet.multipart.file-size-threshold속성값을 사용해 파일을 디스크에 곧바로 적재해 봅시다.
application.yml
spring:
servlet:
multipart:
file-size-threshold: 100KB임시 파일 확인
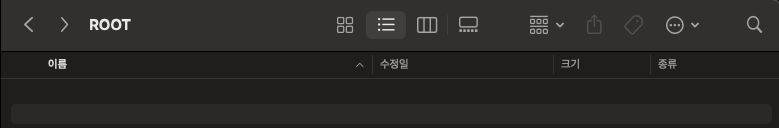
- 81.95KB짜리 파일은 메모리에 곧바로 적재됐기 때문에 디스크에 임시 파일이 생성되지 않았습니다.
MultipartFile을 메모리에 적재했을 때의 문제점
MultipartFile을 메모리에 적재할 때는 파일의 일부분이 아닌 파일 전체를 한번에 적재합니다. 만약 업로드하는 파일의 용량이 크다면 많은 메모리 공간을 차지하게 될 것이고, 이는 OOM등의 문제가 발생할 위험이 있습니다. 이러한 문제를 InputStream을 통해 해결할 수 있습니다.
InputStream
InputStream은 파일 전체를 한번에 메모리에 적재하지 않고 한번에 버퍼의 크기만큼만 메모리에 적재합니다.
@RestController
public class InputStreamController {
@GetMapping
public void getFile() throws Exception {
File file = new File("file.txt");
long fileSize = file.length();
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file)) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead;
int count = 0;
long totalRead = 0;
while ((bytesRead = in.read(buffer)) != -1) {
totalRead += bytesRead;
count++;
System.out.printf("%03d번째 읽기: %d bytes (누적: %.2f%%) \n",
count, bytesRead, (totalRead * 100.0 / fileSize));
}
System.out.println("전체 읽기 완료");
}
}
}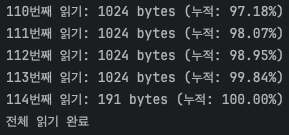
- 버퍼 배열에 값이 계속 덮어씌이기 때문에 이전 값을 남아있지 않아 메모리가 누적되지 않습니다.
하지만, InputStream으로 읽어드리는 데이터를 어딘가에 저장한다면 이때는 MultipartFile과 마찬가지로 전체 파일이 메모리에 적재됩니다.
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
while ((bytesRead = in.read(buffer)) != -1) {
out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
byte[] result = out.toByteArray();결론
- MultipartFile은 파일 전체를 한번에 메모리 또는 디스크에 적재한다.
- InputStream으로 파일을 읽어드리면 모든 데이터를 한꺼번에 메모리에 적재하지 않고, 필요한 만큼만 메모리에 적재하고 처리해 효과적이다.
- InputStream을 이용하더라도 버퍼 단위로 끊어온 데이터를 곧바로 처리하는게 아니라, 모든 데이터를 읽은 뒤 처리하는 형태라면 결국 파일 전체가 메모리에 적재된다.
