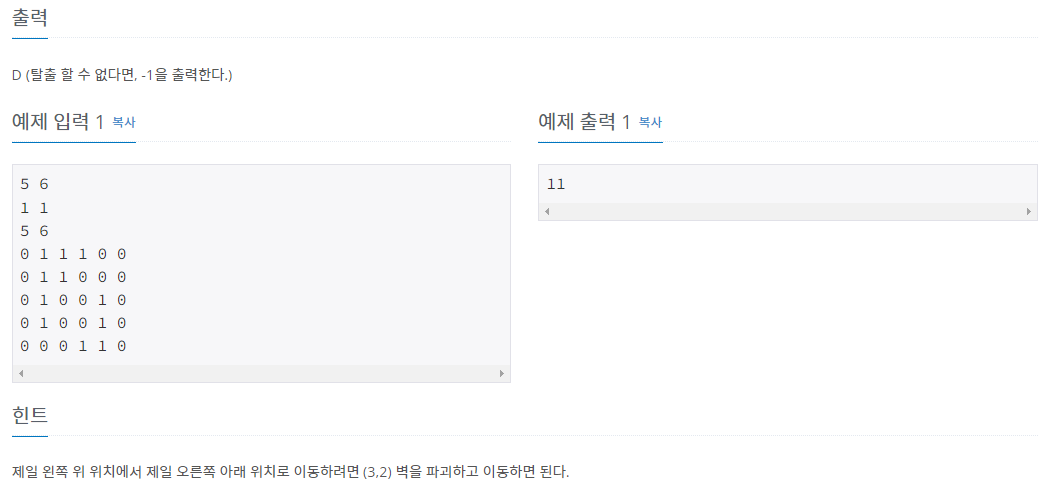
문제 설명
접근법
- 벽을 부쉈는지에 대한 정보를 포함한 3차원의 방문배열을 만듭니다.
정답
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int R, C, sx, sy, ex, ey;
static int[] dx = {0,1,0,-1};
static int[] dy = {1,0,-1,0};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
R = sc.nextInt();
C = sc.nextInt();
sx = sc.nextInt()-1;
sy = sc.nextInt()-1;
ex = sc.nextInt()-1;
ey = sc.nextInt()-1;
int[][] board = new int[R][C];
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < C; j++) {
board[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println(BFS(board));
}
public static int BFS(int[][] board) {
boolean[][][] v = new boolean[R][C][2];
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<int[]>();
q.add(new int[] { sx, sy, 1 });
v[sx][sy][1] = true;
int cnt = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
while(--size>=0) {
int[] now = q.poll();
if(now[0] == ex && now[1] == ey) {
return cnt;
}
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int nx = now[0]+dx[d];
int ny = now[1]+dy[d];
if(0 <= nx && nx < R && 0 <= ny && ny < C && !v[nx][ny][now[2]]) {
if(board[nx][ny] == 0) {
v[nx][ny][now[2]] = true;
q.add(new int[] {nx,ny,now[2]});
} else if(board[nx][ny] == 1 && now[2] == 1) {
v[nx][ny][0] = true;
q.add(new int[] {nx,ny,0});
}
}
}
}
cnt++;
}
return -1;
}
}



