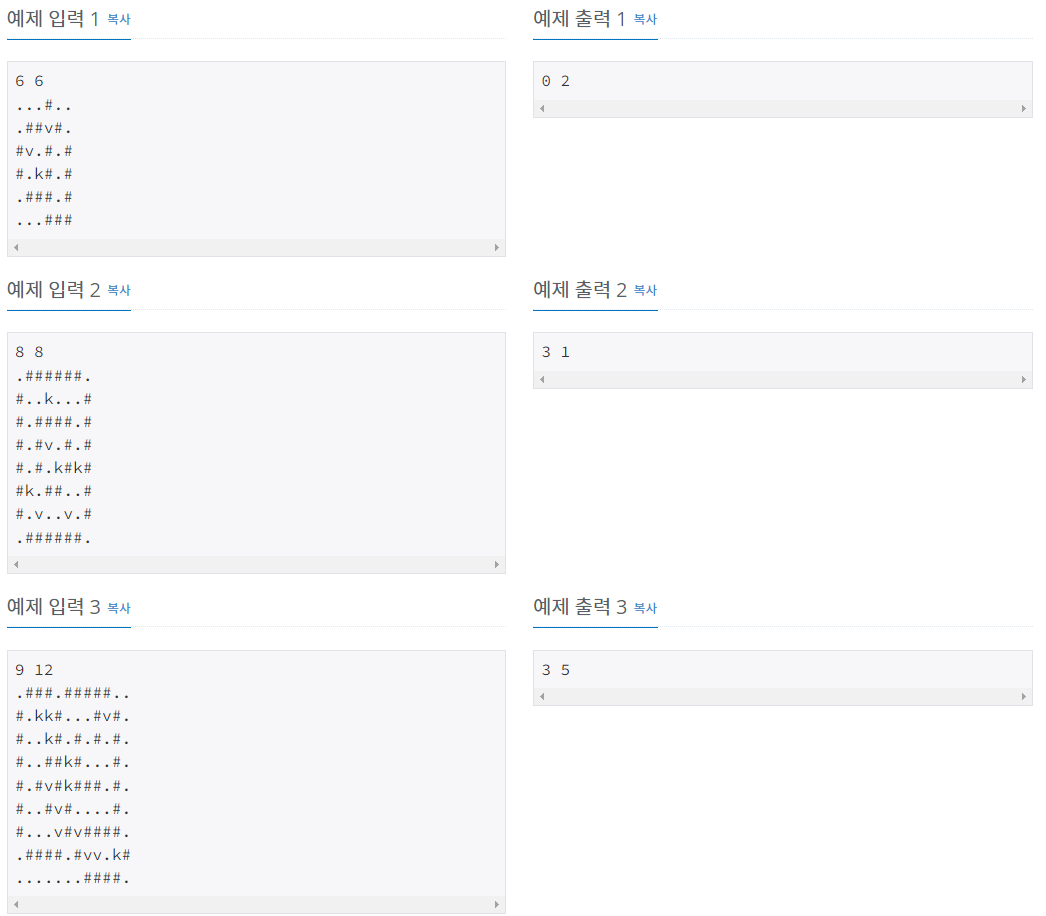
문제 설명
접근법
정답
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int N, M;
static int totalSheep = 0;
static int totalWolf = 0;
static int[] dx = { 0, 1, 0, -1 };
static int[] dy = { 1, 0, -1, 0 };
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
char[][] board = new char[N][M];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
board[i] = br.readLine().toCharArray();
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (board[i][j] != '#') {
BFS(i, j, board);
}
}
}
System.out.println(totalSheep +" "+ totalWolf);
}
public static void BFS(int x, int y, char[][] board) {
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<int[]>();
q.add(new int[] { x, y });
int wolf = 0;
int sheep = 0;
if (board[x][y] == 'v') {
wolf++;
} else if (board[x][y] == 'k') {
sheep++;
}
board[x][y] = '#';
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] now = q.poll();
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int nx = now[0] + dx[d];
int ny = now[1] + dy[d];
if (0 <= nx && nx < N && 0 <= ny && ny < M && board[nx][ny] != '#') {
if (board[nx][ny] == 'v') {
wolf++;
} else if (board[nx][ny] == 'k') {
sheep++;
}
board[nx][ny] = '#';
q.add(new int[] { nx, ny });
}
}
}
if (sheep > wolf) {
totalSheep += sheep;
}else {
totalWolf += wolf;
}
}
}



