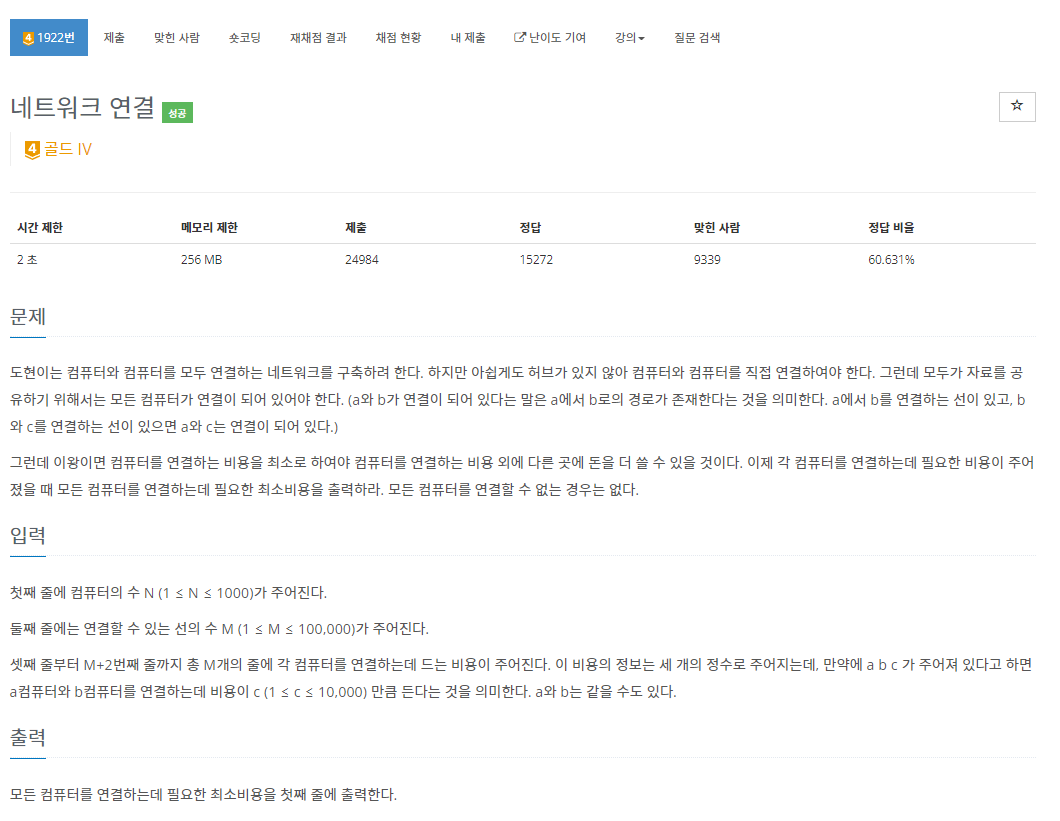
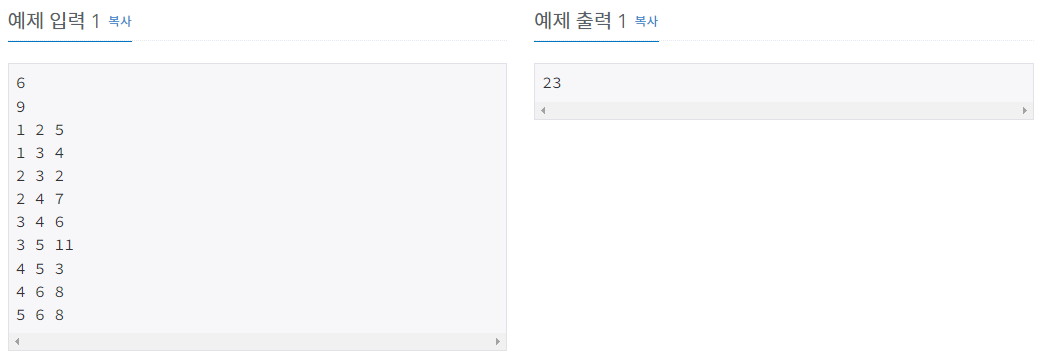
문제 설명
- https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1922
- MST문제입니다.
- Minimum Spanning Tree(최소신장트리)란 N개의 노드를 연결하는 N-1의 비용이 최소가 되는 간선을 연결한 트리를 얘기합니다.
접근법
-
알고리즘을 모르는 상태에서 저에게 최소비용으로 길을 연결하라고 하면 다음과 같이 생각할 거 같습니다.
- 비용이 최소가 되어야 하니깐 선분의 개수가 작아야 될 거 같아.
- 그럼 N개의 선을 연결할려면 N-1개의 선분이 필요하겠지?
- 그러면 선분의 값이 작은 순서대로 N-1개를 선택하면 되지않을까?
- 그런데 필요하지 않은 선분이 선택되네?
- 점 a,b,c가 있을 때 a-b로 이동하는 선분1의 값이 2, a-b로 이동하는 선분2의 값이 3, a-c로 이동하는 선분3의 값이 5라고 한다면 선분1,3을 선택해야되는데 선분 1,2를 선택해 버리구나
- 그럼 이미 선택된 두 점을 잇는 선분은 선택하지 말아봐야지
- a와b를 잇는 선분을 선택하고, c와d를 잇는 선분을 선택한 뒤에 b와c를 잇는 선분을 선택해야 하는데 b와c는 이미 선택된 두 점이라 이을수가 없구나
- 비용이 최소가 되어야 하니깐 선분의 개수가 작아야 될 거 같아.
-
MST의 이론은 위 의식의 흐름과 비슷합니다.
- N개의 노드를 연결하는 MST는 N-1개의
사이클이 발생하지 않는간선을 비용이 낮은 순서대로 선택합니다. - 사이클이란 다시 자신에게로 돌아오는 경로를 얘기합니다.
- A -> B -> C -> A
- 두 점의 부모가 같으면 사이클이 발생합니다.
- 여기서 부모는 자신과 연결된 노드 중 가장 큰(혹은 작은)노드를 얘기합니다.
- N개의 노드를 연결하는 MST는 N-1개의
- MST를 계산하기 위해서는 PriorityQueue, Union-find가 필요합니다.
- PriorityQueue는 비용이 적은 순서대로 간선을 확인하기 위해 필요합니다.
- Union-find는 사이클을 확인하기 위해 필요합니다.
pseudocode
각 노드에 대한 parent배열 생성
PriorityQueue에 데이터 삽입
for(pq에 있는 값을 하나씩 꺼내면서){
if(해당 값이 사이클을 발생시키지 않으면){
MST비용에 추가
}
}
find_parent(x){
if(x의 부모가 x면) return x
if(x의 부모가 x가 아니면) return x의 최고부모 // 재귀적으로 부모의부모, 부모의부모의부모,...를 찾아감
}
union(a,b){
int pa = a의 최고부모
int pb = b의 최고부모
if(pa == pb){ // a의 최고부모와 b의 최고부모가 같으면
return false // 사이클이 발생함
}else{ // 사이클이 발생하지 않음
pa와pb를 연결 // 연결했다는 건 pa의 부모가 pb가 되거나 pb의 부모가 pa가 된다는 의미입니다.
}
}정답
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static int[] parent;
static int Score = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
parent = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
Queue<pos> pq = new PriorityQueue<pos>();
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
pq.add(new pos(a - 1, b - 1, c));
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
pos link = pq.poll();
if (union(link.a, link.b)) {
Score += link.c;
}
}
System.out.println(Score);
}
public static int find_parent(int x) {
if (x != parent[x]) {
parent[x] = find_parent(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
public static boolean union(int a, int b) {
int pa = find_parent(a);
int pb = find_parent(b);
if (pa == pb) {
return false;
} else if (pa > pb) {
parent[pa] = pb;
} else {
parent[pb] = pa;
}
return true;
}
static class pos implements Comparable<pos> {
int a;
int b;
int c;
public pos(int a, int b, int c) {
super();
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "pos [a=" + a + ", b=" + b + ", c=" + c + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(pos o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.c - o.c;
}
}
}
