Scailing
cv2.resize(src, dsize, [,dst [, fx[, fy [,interpolation]]]])- src : 입력 이미지
- dsize : 출력 이미지 크기
- fx : 가로 방향 배율
- fy : 세로 방향 배율
- interpolation : 이미지 크기 조정 시 누락되거나 축소되는 픽셀 값 결정 방법
- cv2.INTER_NEAREST
- cv2.INTER_LINEAR
- cv2.INTER_CUBIC
- cv2.INTER_AREA
- cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4
- cv2.INTER_LINEAR_EXACT
- cv2.INTER_MAX
- cv2.WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS
- cv2.WARP_INVERSE_MAP
축소는 INTER_AREA, 확대는 INTER_CUBIC,INTER_LINEAR 사용
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('emoji1.png')
h,w = img.shape[:2]
shrink = cv2.resize(img,None,fx=0.5,fy=0.5,interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
zoom1 = cv2.resize(img,(w*2,h*2),interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
zoom2 = cv2.resize(img,None,fx=2,fy=2,interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
cv2.imshow('Original',img)
cv2.imshow('Shrink',shrink)
cv2.imshow('Zoom1',zoom1)
cv2.imshow('Zoom2',zoom2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()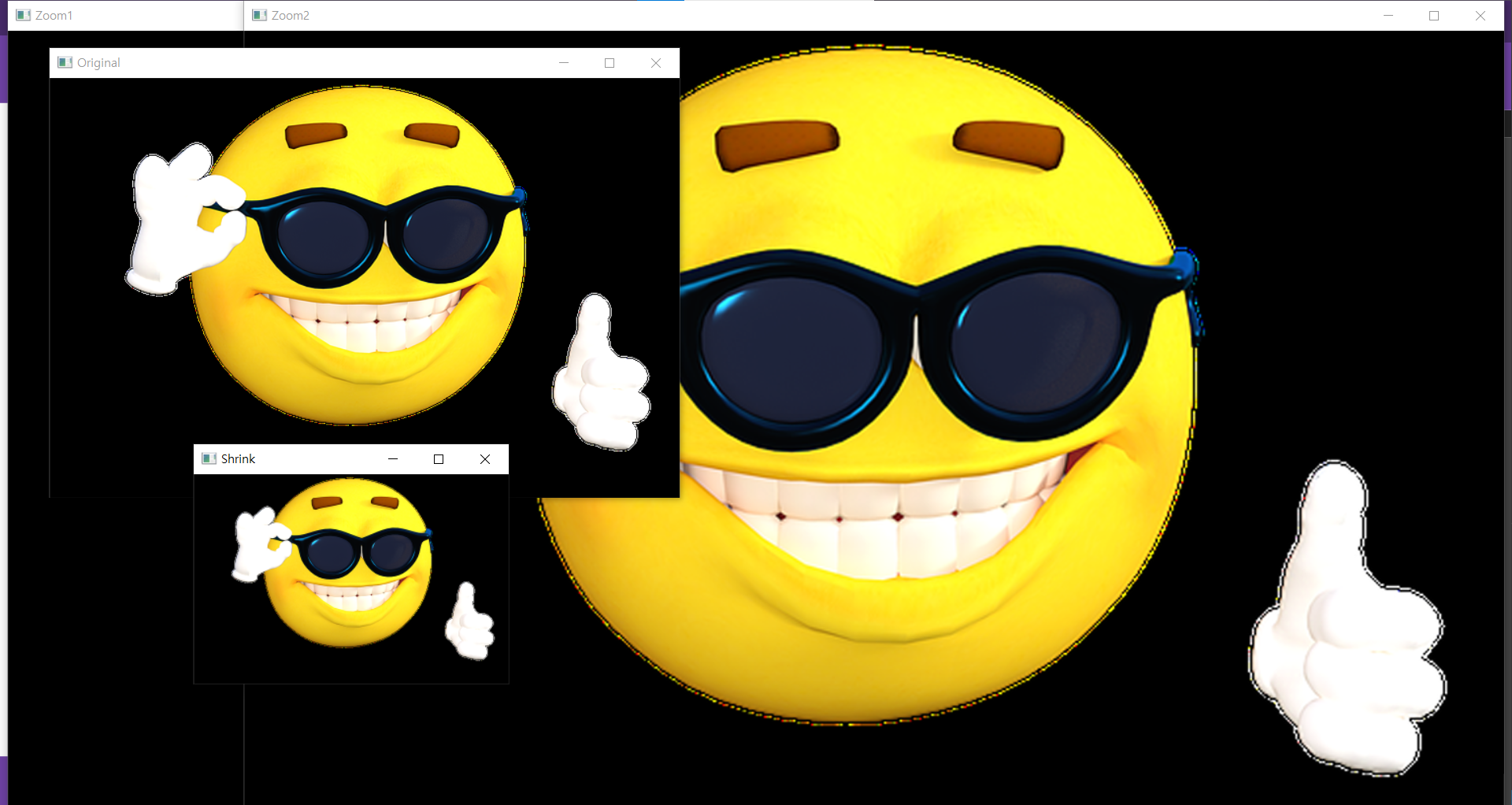
Translation
cv2.warpAffine(src,M,dsize)
# M - 변환 행렬import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('emoji1.png')
rows,columns = img.shape[:2]
M = np.float32([[1,0,100],[0,1,200]])
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(columns,rows))
cv2.imshow('Original',img)
cv2.imshow('Translation',dst)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()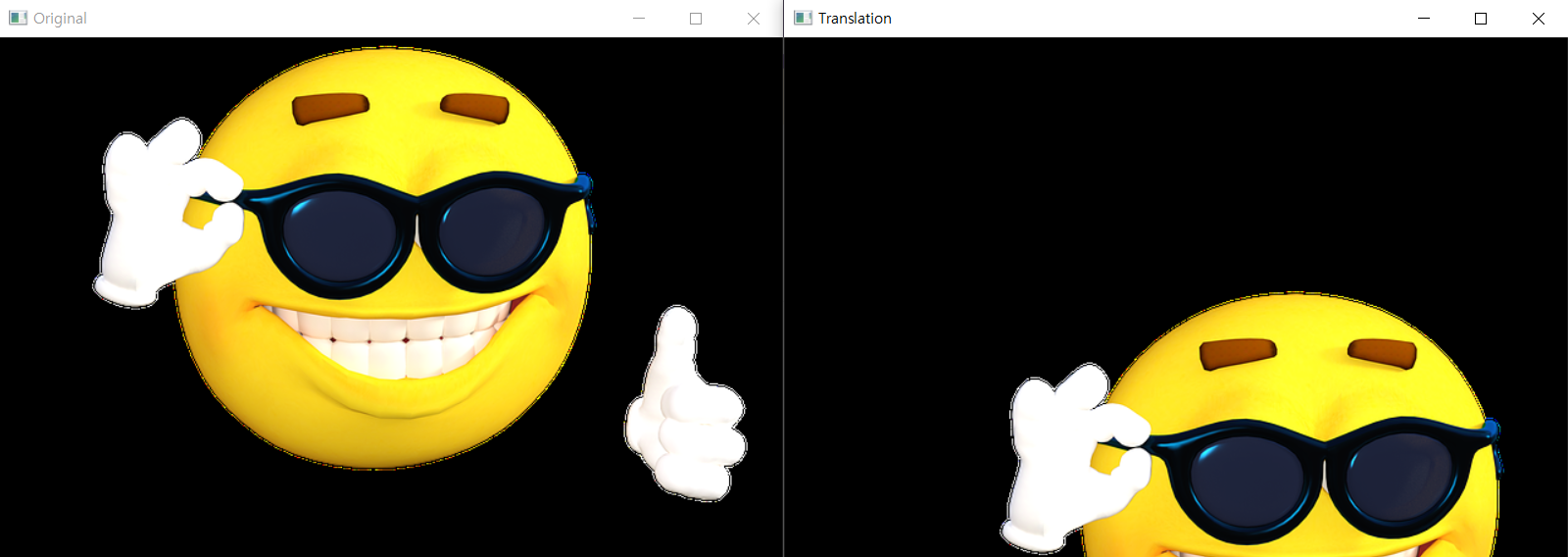
Rotation
cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center,angle,scale) -> M- center : 이미지의 중심 좌표
- angle : 회전 좌표(반시계 방향)
- scale : 스케일
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('emoji1.png')
rows,columns = img.shape[:2]
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((columns/2,rows/2),90,0.5)
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(columns,rows))
cv2.imshow('Original',img)
cv2.imshow('Rotation',dst)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()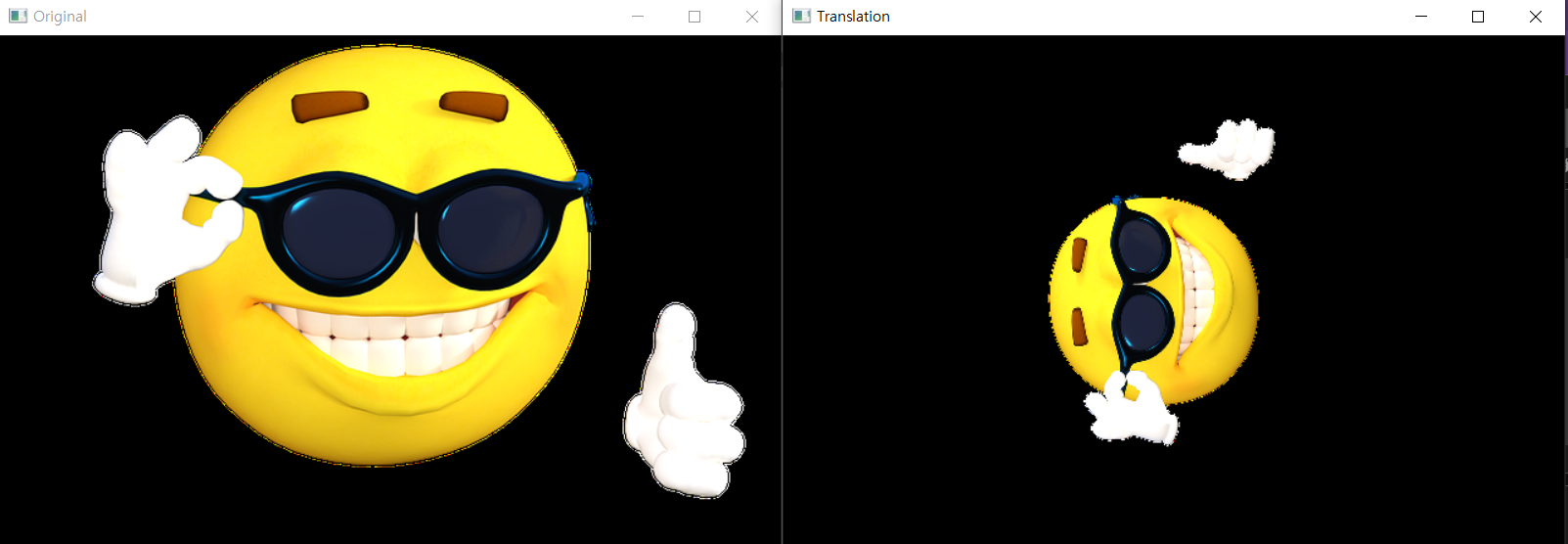
Affine Transformation
선의 평행성은 유지하며 변환. 이동, 확대, Scale, 반전이 포함
3개의 Match가 되는 점이 있으면 변환 행렬을 구할 수 있다.
cv2.getAffineTransform(pts1,pts2) -> Mimport cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('emoji1.png')
rows,columns,channels = img.shape
pts1 = np.float32([[200,100],[400,100],[200,200]])
pts2 = np.float32([[200,200],[400,100],[200,300]])
cv2.circle(img,(200,100),10,(255,0,0),-1)
cv2.circle(img,(400,100),10,(0,255,0),-1)
cv2.circle(img,(200,200),10,(0,0,255),-1)
M = cv2.getAffineTransform(pts1,pts2)
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img,M,(columns,rows))
cv2.imshow('Original',img)
cv2.imshow('Affine Transform',dst)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()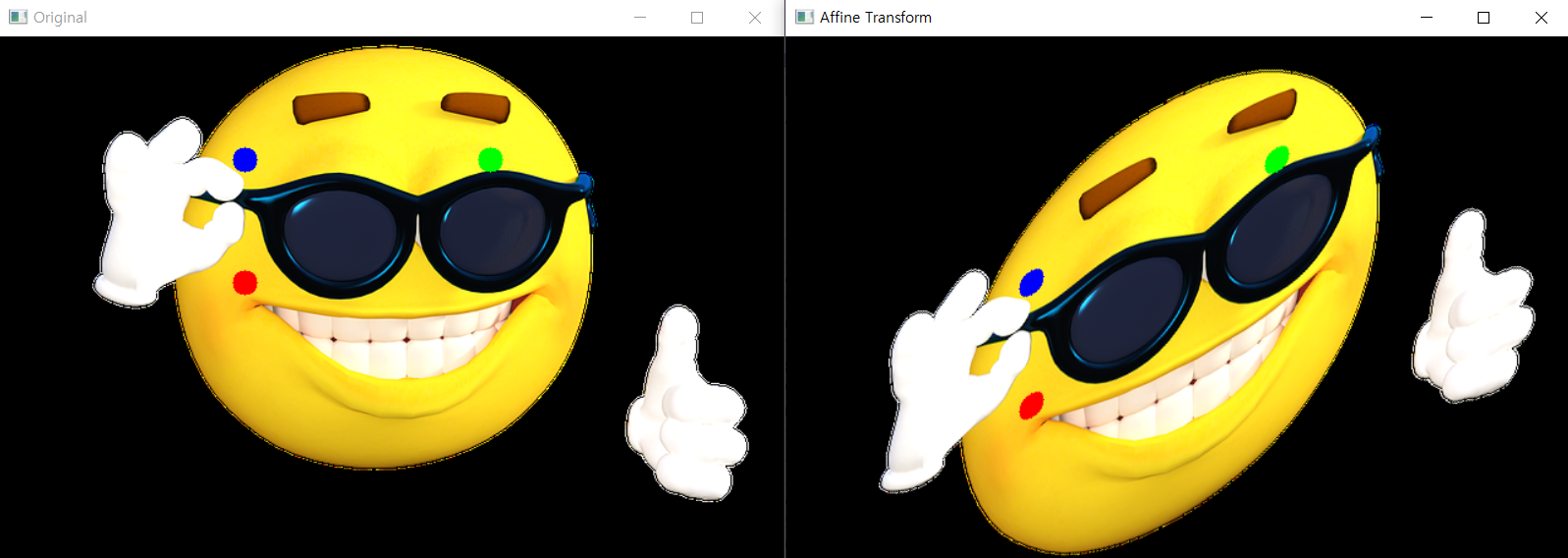
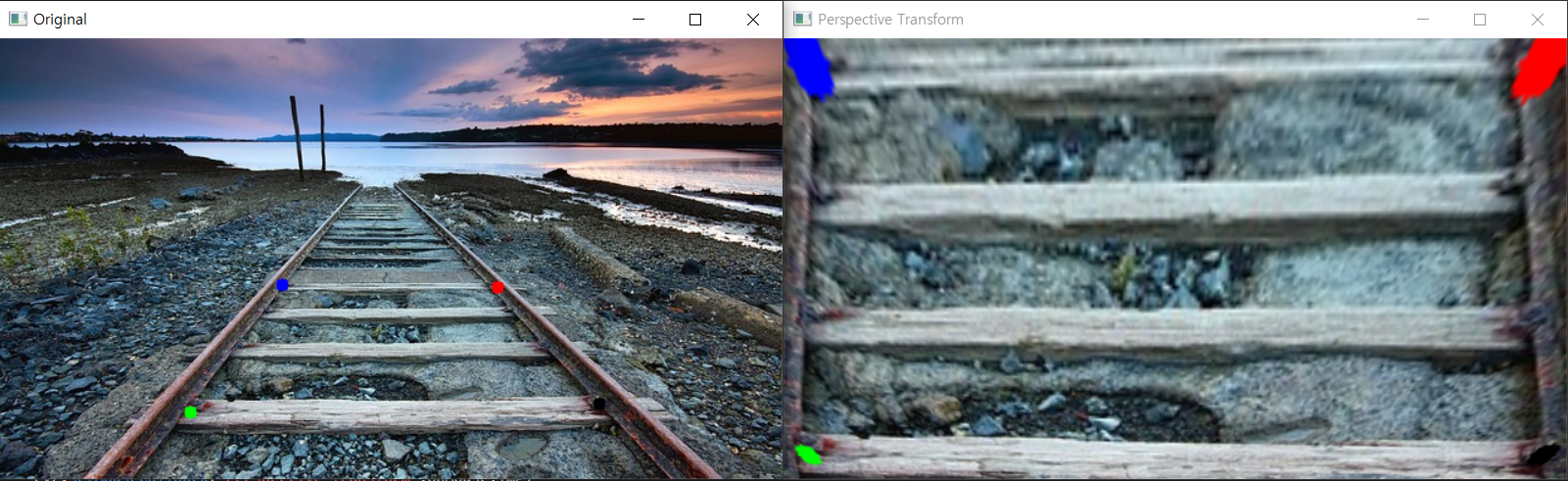
Perspective Transform
직선의 성질만 유지. 기차길이 평항하지만 원근변환을 거치면 만나는 것 처럼 보인다.
cv2.getPerspectiveTransform() -> M
cv2.warpPerspective() -> dstimport cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
pts1 = []
colors = [(255,0,0),(0,255,0),(0,0,255),(0,0,0)]
def onMouse(event,x,y,flags,param):
global pts1
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
cv2.circle(param,(x,y),5,colors[len(pts1)],-1)
pts1.append([x,y])
cv2.imshow('Perspective Transform',param)
def WritePoints():
img = cv2.imread('train_road1.jpg')
# [x,y] 좌표를 4개 작성
# 좌상 -> 좌하 -> 우상 -> 우하
cv2.imshow('Perspective Transform',img)
cv2.setMouseCallback('Perspective Transform',onMouse,img)
while True:
cv2.imshow('Perspective Transform',img)
k = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF
if k == 27:
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
return img
img = WritePoints()
rows,columns = img.shape[:2]
pts1 = np.float32(pts1)
pts2 = np.float32([[20,20],[20,340],[620,20],[620,340]])
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pts1,pts2)
dst = cv2.warpPerspective(img,M,(columns,rows))
cv2.imshow('Original',img)
cv2.imshow('Perspective Transform',dst)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()