개선 전에는 유저가 로그인을 하면 백엔드는 헤더에 jwt 정보를 담아 응답하였다. 프론트에서는 헤더의 값을 읽어와 쿠키를 생성, 해당 정보를 보관했다.
이렇게 하면 문제가 발생하는데
- 프론트와 백엔드의 jwt 유효 시간에 차이가 발생
- 클라이언트가 토큰에 접근 가능 -> 보안 취약
크게 두 가지 단점이 있다.
위 단점을 개선하고자 백엔드에서 httpOnly 설정된 쿠키에 jwt를 담아 응답하기로 결정했다.
이를 위해서는 기존 프론트 로직에 많은 변경이 필요하다... ☹️ 아래는 어떻게 변했는지를 설명한다.
JWT 저장 방식 변경 (백엔드)
변경 전
@Override
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException {
UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails) authResult.getPrincipal();
String role = userDetails.getAuthorities().stream().map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority).findFirst().orElseThrow(NoUserFoundException::new);
String token = jwtUtil.createJwt(userDetails.getUsername(), role, new Date());
response.addHeader(jwtUtil.getJwtHeader(), jwtUtil.getJwtBearer() + token);
}jwtUtil 에서 생성한 jwt를 header에 담아 반환
변경 후
@Override
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException {
UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails) authResult.getPrincipal();
String role = userDetails.getAuthorities().stream().map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority).findFirst().orElseThrow(NoUserFoundException::new);
String token = jwtUtil.createJwt(userDetails.getUsername(), role, new Date());
ResponseCookie jwtCookie = ResponseCookie.from("access-token", token)
.httpOnly(true)
.sameSite("Lax")
.path("/")
.maxAge(Duration.ofHours(3))
.build();
// 쿠키에 담아 반환한다
response.setHeader(HttpHeaders.SET_COOKIE, jwtCookie.toString());
}jwtUtil에서 생성한 jwt를 쿠키에 담아 반환
요청에서 JWT 추출 방식 변경
변경 전
// JwtUtil.class
public String resolveToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
String authHeader = request.getHeader(jwtProperties.HEADER());
return authHeader != null && authHeader.startsWith(jwtProperties.BEARER()) ?
authHeader.substring(jwtProperties.BEARER().length())
: null;
}요청 헤더에서 필요한 부분을 추출한다.
변경 후
// JwtUtil.java
public String resolveToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
if(request.getCookies() == null) {
log.info("No cookies found in request");
return null;
}
for (Cookie cookie : request.getCookies()) {
if("access-token".equals(cookie.getName())) {
return cookie.getValue();
}
}
return null;
}쿠키를 순회하며 jwt 부분을 추출한다.
CORS 설정 변경(백엔드)
변경 전
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedOriginPatterns("http://localhost:5173")
.allowedMethods("*")
.exposedHeaders("Authorization", "Content-Type")
// 노출시킬 헤더명을 명시 했었다
.allowCredentials(true);
}
}exposedHeaders 옵션은 브라우저가 JavaScript에서 접근 가능한 응답 헤더를 명시적으로 지정할 때 필요하다. Authorization 헤더는 CORS 정책에서 클라이언트에서 접근할 수 없는 헤더이므로, vue 프론트에서 response.headers.get("Authorization") 처럼 읽고자 한다면 exposeHeaders() 설정이 필요하다.
하지만 이제 JWT를 HttpOnly 쿠키로 전달하기로 했으므로 Authorization 헤더를 프론트에 노출해줄 필요가 없다. 따라서 해당 설정을 제거한다.
변경 후
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedOrigins("http://localhost:5173")
.allowedMethods("*")
.allowCredentials(true);
}
}allowedOriginPatterns() 와 allowedOrigins()의 차이는 뭔가요?
allowedOriginPatterns()는 와일드 카드를 포함한 도메인을 허용할 때 사용하는 메서드이다. 지금은 고정된 origin만 허용(localhost:5173)하므로 allowedOrigins()를 사용하도록 했다.
allowCredentials(true)는 인증 정보를 포함한 요청을 허용하는 설정으로, 쿠키 기반 인증에 필수다.
이 경우 allowedOrigins()는 반드시 와일드카드(*)를 사용할 수 없다. allowCredentials(true)가 설정되어 있으면 CORS 명세에 따라 정확한 origin을 명시해야 한다.
따라서 allowedOriginPatterns() 대신 allowedOrigins("http://localhost:5173")를 사용한다. 와일드카드가 필요 없는 고정 origin만 허용할 경우 더 명확하고 안전한 방법이다.
상태유지
헤더로 JWT를 통신할 때와 마찬가지로 쿠키로 JWT를 통신할 때도 상태유지가 중요한 포인트이다. 로그인을 성공한 이후 새로고침을 하면 로그인이 해제되는 현상을 똑같이 경험했다.
변경 전
서버에서 발급받은 jwt를 쿠키에 저장한 후 요청할 때마다 쿠키에 저장된 토큰을 헤더에
넣기로 결정
// useAuthStore.ts
import {defineStore} from "pinia";
import {
setCookie,
getCookie,
deleteCookie
} from "@/utils/cookieUtil.ts";
export const useAuthStore = defineStore("auth", {
state: () => ({
token: getCookie("authToken"), // 쿠키에서 토큰을 초기화
}),
actions: {
setToken(token: string) {
this.token = token;
setCookie("authToken", token, new Date());
// 쿠키에 3시간 저장
},
clearToken() {
this.token = null;
deleteCookie("authToken"); // 쿠키 삭제
},
},
});
헤더로 받은 JWT를 쿠키로 저장하는 로직이 있다. 이 부분 때문에 백엔드와 프론트의 JWT 유효 시간이 다른 문제가 발생했다. 그래서 아래와 같이 변경했다. 변경 후에는 CookieUtil을 사용할 필요가 없기 때문에 제거했다.
변경 후
index.ts (라우터 설정 파일)
router.beforeEach(async (to, from, next) => {
const userStore = useUserStore()
if (!userStore.isLoggedIn) {
await userStore.init()
}
next()
})페이지 새로고침 시에도 로그인 상태가 유지되려면 프론트 앱이 시작될 때 서버로부터 유저 정보를 재조회해야한다. 페이지 이동이 일어나기 전에 매번 라우터 설정 파일에서 유저 정보를 확인한다. 만약 유저 정보가 없다면 서버에 유저 정보를 요청한 후 라우터 로직이 실행된다.
useUserStore.ts
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import type User from '@/entities/user.ts'
import axios from 'axios'
import { BASE_URL } from '@/constants/server.ts'
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {
state: () => ({
user: null as User | null,
}),
actions: {
setUser(user: User) {
this.user = user
},
clearUser() {
this.user = null
},
async init() {
try {
const res = await axios.get(`${BASE_URL}/v1/users/me`, {
withCredentials: true,
})
this.setUser(res.data)
} catch {
console.info('userStore error!')
this.clearUser()
}
},
},
getters: {
isLoggedIn: (state): boolean => state.user !== null,
username: (state): string => state.user?.username ?? '',
nickname: (state): string => state.user?.nickname ?? '',
desc: (state): string => state.user?.desc ?? '',
profileImageUrl: (state): string => state.user?.profileImageUrl ?? '',
backgroundImageUrl: (state): string => state.user?.backgroundImageUrl ?? '',
},
})백엔드에 요청한 유저 정보를 저장하는 pinia 파일이다. 백엔드에서 유저 정보를 넘기면 해당 정보들을 모두 여기에 저장하여 사용하게 된다.
로그인이 필요한 요청을 할 때 jwt를 포함하는 방법
변경 전
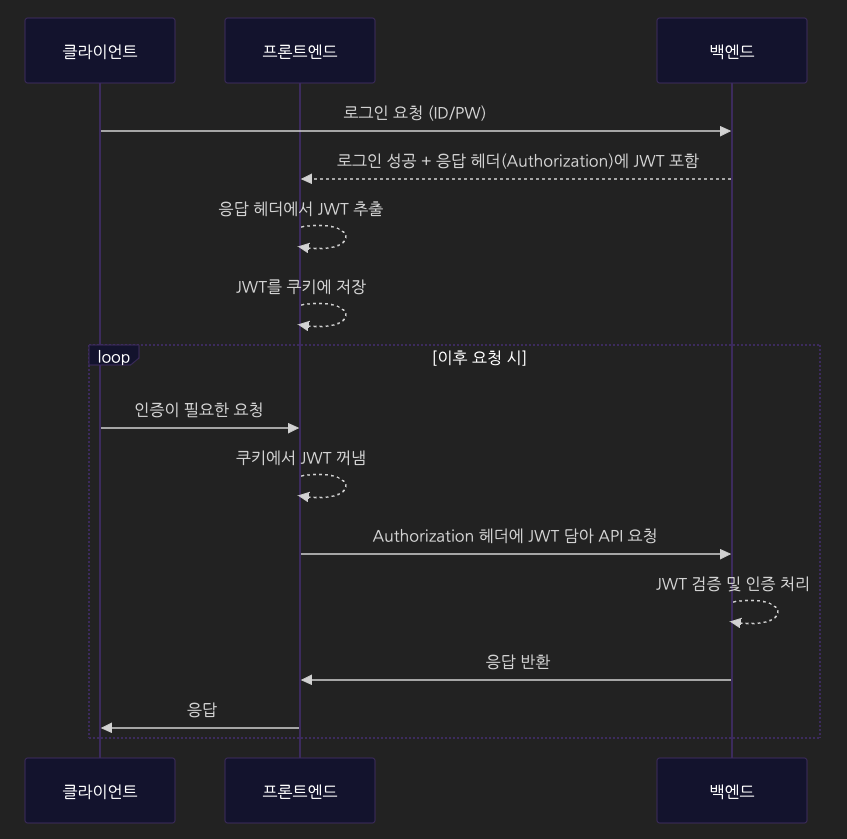
- 클라이언트가 로그인을 요청한다.
- 프론트는 로그인 정보를 백엔드에 전달한다.
- 백엔드는 인증 후 헤더에 jwt를 포함하여 응답한다.
- 프론트는 헤더에서 jwt를 추출, 쿠키에 해당 정보를 저장한다.
- 클라이언트가 인증이 필요한 요청을 진행한다.
- 프론트는 쿠키에 저장한 jwt를 추출, 요청 헤더에 포함하여 백엔드에 요청한다.
- 백엔드는 jwt를 검증 후 응답한다.
axios 요청 설정에서도 아래와 같은 부분을 추가해야한다.
try {
const token = document.cookie.split("=")[1];
const response = await axios.get(`${BASE_URL}/v1/users/getInfo`, {
headers: {
Authorization: token, // header에 jwt 정보를 포함해야한다, 누락시 에러!
}
});
welcome.value = response.data;
} catch (error) {
welcome.value = "error has occured";
} 딱 봐도 엄청난 비효율이 매번 진행되고 있다. 왜 매번 jwt 정보를 헤더에서 꺼내 쿠키에 저장해야하는것이고, 왜 매번 쿠키에서 jwt 정보를 꺼내 헤더에 넣어줘야 하는걸까?
따라서 아래와 같이 개선 되었다.
개선 후
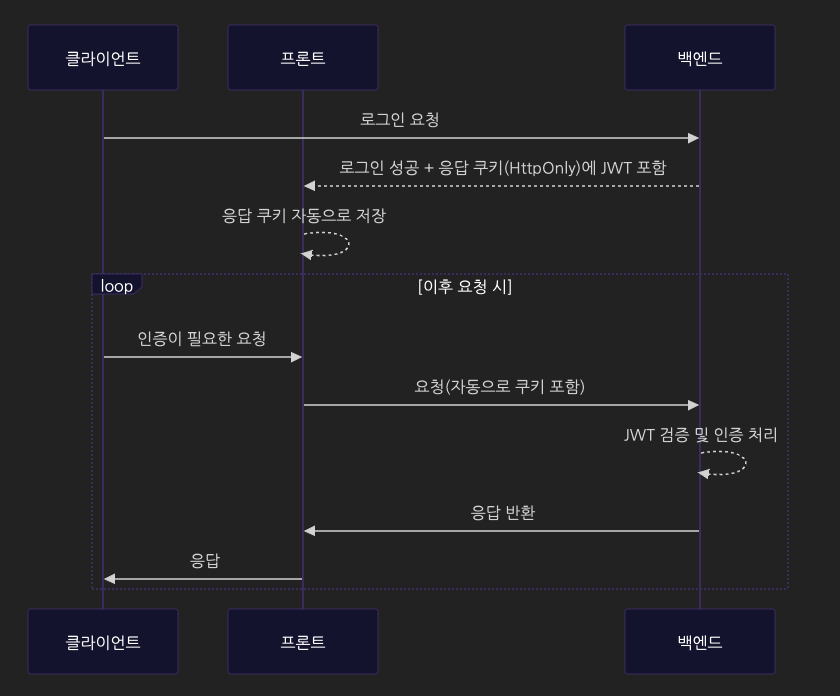
const res = await axios.get(`${BASE_URL}/v1/users/me`, {
withCredentials: true,
})withCredentials: true 설정이 추가되면 자동으로 쿠키의 정보를 포함하여 요청이 만들어진다.
시퀀스 다이어그램을 그려본다면 아래와 같다.
마치며
이번 구조 변경을 통해 아래와 같은 개선이 이루어졌다.
- 보안 강화
- 프론트 로직 단순화
보안 강화
JWT를 HttpOnly 쿠키에 저장하면서 JS에서 접근할 수 없게 되었다. 토큰 탈취 위험이 제거되었다.
더이상 프론트에서 JWT를 관리하지 않으므로, 프론트-백엔드 간 JWT 유효시간 불일치 문제가 해소되었다.
프론트 로직 단순화
JWT를 수동으로 쿠키에 저장하거나 헤더에 삽입하는 로직이 제거되었다.
axios 요청이 안정적으로 변경되었다.
