📌 프로세스 주소공간
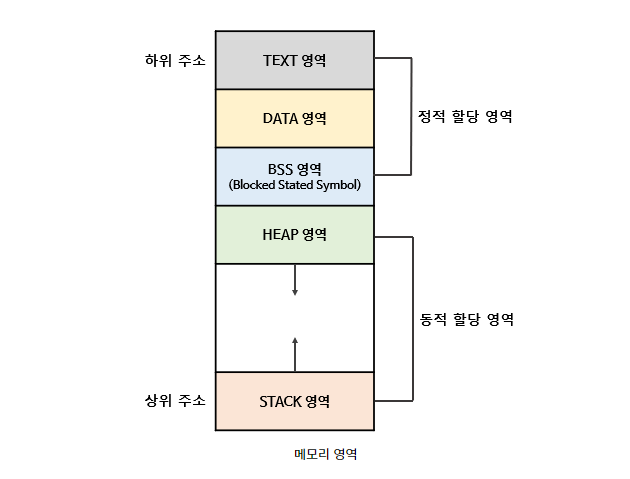
.text
코드영역.data
초기화된 전역변수.heap
malloc으로 만든 변수들.stack
지역변수✨Thread는 Process내에서 text, data, heap은 공유하며, stack은 따로 할당
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int t;
int g = 32;
int main()
{
int q = 31;
int *p = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int));
while(1)
{
printf("%DATA(%D) = %llX\n",g, &g);
printf("%BSS = %llX\n", &t);
printf("%HEAP = %llX\n", p);
printf("STACK = %llX\n", &q);
printf("====================\n");
sleep(1);
g++;
}
return (0);
}📌 Process
- Linux를 부팅하면 최초의 Process가 존재
=> 각 Process는 ID가 존재 : PID - 최초 Process가를 제외한 모든 Process가들은 부모 Process가에서 복제되어 생성
(Fork System Call) - 부모 Process는 자식의 ID를 모르고, 자식 Process는 부모 Process의 ID값을 알고있다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
pid_t child_pid = fork();
if(child_pid > 0) {
// parent
while(1);
}
else if(child_pid == 0) {
// son
// Die
}
}- Linux에서 Process를 확인하는 법
// -e : kernel process를 제외한 모든 process 출력
// -f : Full Format(PID 등 모든 정보) 출력
$ps -efVirtual Address Space
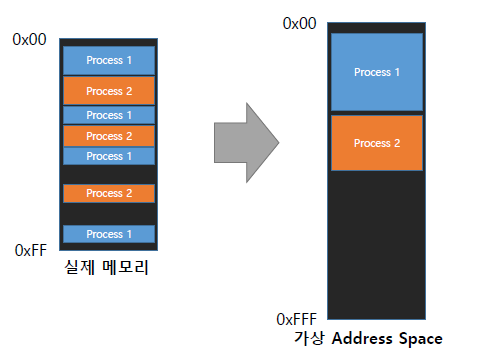
process가 연속적인 메모리를 사용하고 있다고 착각하도록 함.
-> 메모리 파편화에 대한 구현이 쉬워짐
// 메모리주소 | 권한 | offest | dev | inode | path
$cat /proc/[PID]/mapsPCB(Process Control Block)
- Kernel이 Process를 제어하기 위한 정보를 저장하는 블럭 - Process Descriptor 라고도 함. - Process State, PID...문맥교환(Context Switching)
각각의 프로세스는 독립적인 메모공간을 가지고 있음
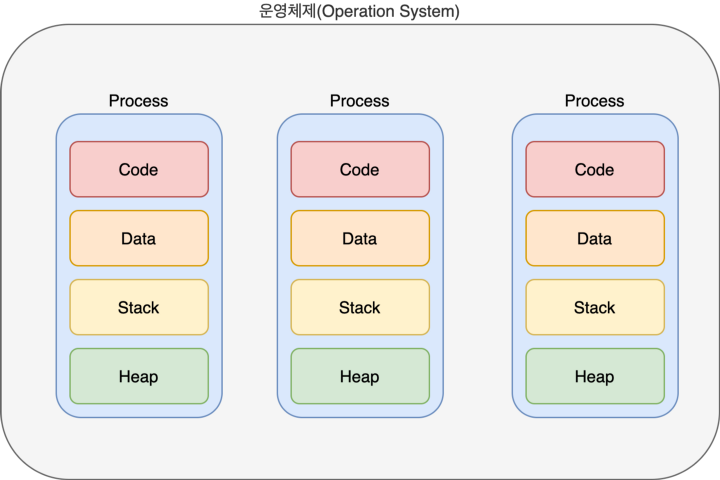
> 출처 : https://charlezz.medium.com/process%EC%99%80-thread-%EC%9D%B4%EC%95%BC%EA%B8%B0-5b96d0d43e37프로세스는 동시에 실행되고 관리되는것 처럼 보이지만, 실제로는 한번에 한가지 명렁만 처리
=> Firmware 개발 Level로는 어렵기때문에 RTOS 또는 Linux OS를 통해 개발
=> 재빠르게 번갈아가며 실행, 관리 (Context Switching)
Context Switching
하나의 Process가 CPU를 사용 중인 상태에서 다른 Process가 CPU를 사용하도록 하기 위해 이전의 Process의 상태를 보관하고 새로운 Process의 상태를 적재하는 작업
다음 process를 수행할 때 현재 Register를 PCB에 저장 후 다음 process 로 전환
-> process 전환 시 "Context Switching 비용(cost)이 발생했다"고 표현
-> 이러한 비용 관리를 위한 적절한 스케줄링 정책이 필요함
Linux Process State
R : Running / Runnable
S : Interruptible Sleep
- Sleep System Call 사용
- I/O 처리 후 응답이 오기까지 대기
- Timer 사용
D : Uninterruptible Sleep - mkdir 사용 시 응답이 올 때 까지 멈출 수 없는 잠을 잔다
T : Stopped
Z : Zombie
📌 Thread
>출처 : https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/09/14/process-vs-thread.html한 프로세스 내에서 하나의 캐릭터가 뛰어놀 수 있도록 개발하는 것은 쉽다.
-> but, 한 프로세스 내에서 여러 캐릭터가 독립적으로 뛰어놀도록 개발하는 것은 어렵다.!!
-> 이럴 때 사용하는 것이 Thread!!
쓰레드 생성 예제
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// void *는 모든 타입의 주소를 저장할 수 있지만, 사용할 수는 없다!!
// void *p1 = &x;
// printf("%d", *p1); ==> 불가능!!
// printf("%d", *(int *)p1); ==> 형변환으로 가능!!
void *abc()
{
while(1) {
printf("ABC\n");
sleep(1);
}
return (0);
}
void *bts() {
while(1) {
printf("BTS\n");
sleep(1);
}
return (0);
}
int main()
{
pthread_t t1, t2;
// pthread_create(thread id, 쓰레드 속성, 함수, 파라미터)
pthread_create(&t1, NULL, abc, NULL);
pthread_create(&t2, NULL, abc, NULL);
// pthread_join(thread id, thread 리턴값) ==> thread 종료 후 메모리해제 (like close())
pthread_join(t1, NULL);
pthread_join(t2, NULL);
return (0);
} 구조체 쓰레드 예제
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
struct Node
{
int y;
int x;
}
void *abc(void *p)
{
struct Node *val = (struct Node *)p;
while(1) {
printf("%d %d \n", val->x, val->y);
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
struct Node val = {2, 4};
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, abc, &val);
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
return (0);
}