Stream 사용 / 엑셀 / mariadb 설치
데이터 - 프로그램 +> 처리(방법)
임시 데이터
변수 / 상수
영구데이터
CRUD
- CRUD는 대부분의 컴퓨터 소프트웨어가 가지는 기본적인 데이터 처리 기능인 Create(생성), Read(읽기(가공)), Update(갱신), Delete(삭제)를 묶어서 일컫는 말이다.
로컬데이터
일반파일 - 메모장에서 내용을 볼 수 있는 파일
- txt
oracle에서 제공
일반파일에 접근
1. 파일/디렉토리 정보를 알아야 한다. - java.io.File - NIO
=> 탐색기 / dir 만들 수 있다.
- 파일(txt) 내용에 접근
2-1. 1차 스트림 - 메서드명
- 데이터 분류
InputStream / OutputStream
Reader / Writer
I/O
InputStream / Reader
OutputStream / Writer
=> 구현 - FileInputStream / FileOutputStream
FileReader / FileWriter
2-2. 2차 스트림
조금 더 확장된 메서드 사용
BufferedInputStream / BufferedOutputStream
BufferedReader / BufferedWriter
바이너리파일 - 특별한 프로그램이 존재
- image/sound
- docx, xls, ppt, hwp
third party
원격데이터
데이터베이스
OpenAPI
주소 뽑기 (읍면동 이름 넣으면 해당 주소록 출력)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CheckJuminEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 입력값 검사
// System.out.println(args.length);
if (args.length != 1) {
System.out.println("'java 클래스명 동이름' 형식으로 입력하셔야 합니다.");
System.exit(0);
}
if (args[0].length() <= 1) {
System.out.println("동이름을 두 자 이상 입력하셔야 합니다.");
System.exit(0);
}
String strDong = args[0];
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("./zipcode_seoul_utf8_type2.csv"));
String address = null;
while ((address = br.readLine()) != null) {
// System.out.println(address);
String[] addresses = address.split(",");
// System.out.println(addresses[3]);
// 검색할수있는 방법들 / 밑에 것들로도 사용해보쟝 ~
// startsWith : ~로 시작하면
// contains
// indexOf
if (addresses[3].startsWith(strDong)) {
System.out.printf("[%s] %s %s %s %s %s%n", addresses[0], addresses[1], addresses[2], addresses[3],
addresses[4], addresses[5]);
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if (br != null)
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
}
쭈루룩 ~

기본형으로 데이터 넣기 - DataOutputStream
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
// 기본형으로 데이터 넣기
public class DataOutputStreamEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
DataOutputStream dos = null;
try {
dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./value,dat"));
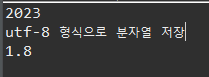
dos.writeInt(2023);
dos.writeUTF("utf-8 형식으로 분자열 저장");
dos.writeFloat(1.8f);
System.out.println("출력완료");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(dos != null) try {dos.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
바이너리 코드로 인해 앞뒤 텍스트 출력은 깨져서 나옴

데이터 읽기 - DataInputStream
저장된 데이터 형식, 순서대로 읽어야한다
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DataInputStreamEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
DataInputStream dis = null;
try {
dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("./value.dat"));
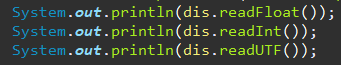
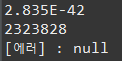
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
System.out.println(dis.readFloat());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(dis != null) try {dis.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
정상 출력
순서가 바뀌면?
에러
객체방식을 저장 - ObjectOutputStream
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
// 객체방식을 저장
public class ObjectOutputStreamEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./object.dat"));
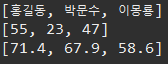
String[] names = {"홍길동", "박문수", "이몽룡"};
int[] ages = {55, 23, 47};
double[] weights = {71.4, 67.9, 58.6};
oos.writeObject(names);
oos.writeObject(ages);
oos.writeObject(weights);
System.out.println("출력 완료");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(oos != null) try {oos.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}

객체방식 읽기 - ObjectInputStream
형변환 해줘야한다
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ObjectInputStreamEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("./object.dat"));
String[] names = (String[])ois.readObject();
int[] ages = (int[])ois.readObject();
double[] weights = (double[])ois.readObject();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(names));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ages));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(weights));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(ois != null) try {ois.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
사용자정의 객체넣기 - ObjectOutputStream
Person 사용자 정의 클래스 생성
Person implements Serializable 직렬화 시켜준다.
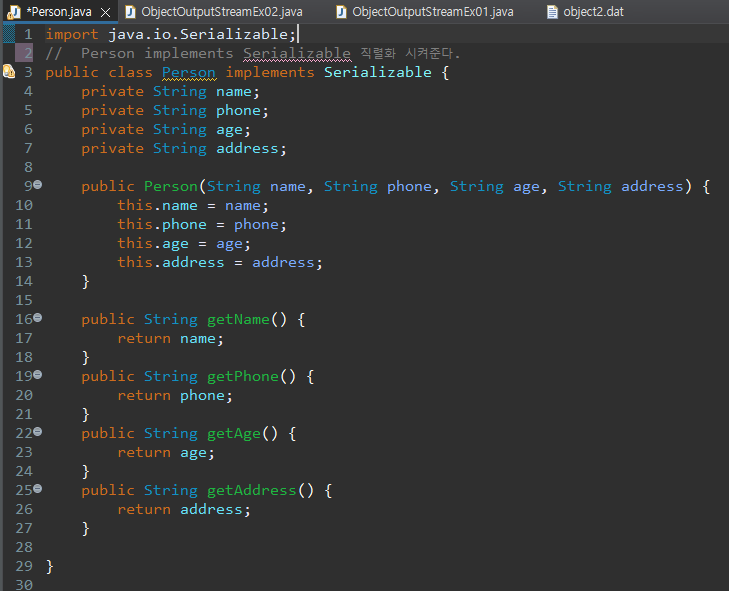
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class ObjectOutputStreamEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("./object2.dat"));
Person p = new Person("홍길동", "010-111-1111", "20", "서울시");
oos.writeObject(p);
System.out.println("출력 완료");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(oos != null) try {oos.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
사용자 정의 객체 읽기 - ObjectInputStream
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class ObjectInputStreamEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("./object2.dat"));
Person p = (Person)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(p.getName());
System.out.println(p.getPhone());
System.out.println(p.getAge());
System.out.println(p.getAddress());
System.out.println("입력 완료");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(ois != null) try {ois.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}

직렬화에서 빼기
transient 직렬화에서 빠진다.
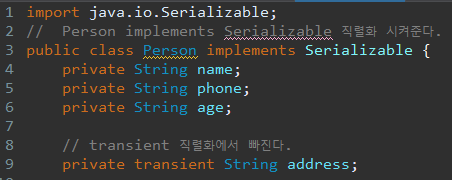
출력 값

여러번 선언해서 직렬화로 순서대로 뽑기
Person 클래스 (위의 코드들과 같은 코드임)
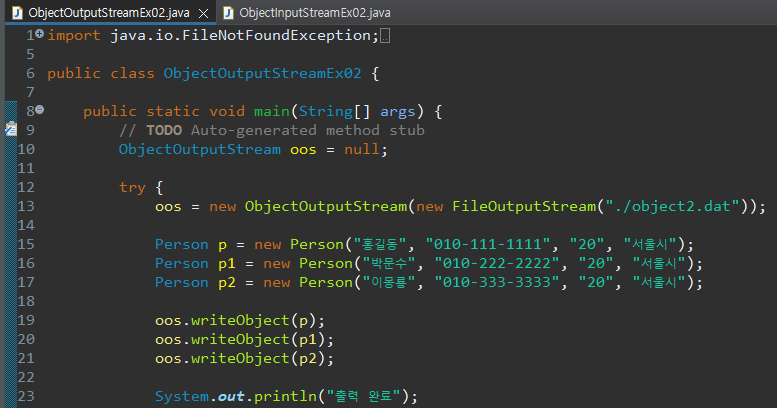
위의 코드에서 추가 작성한 것
출력
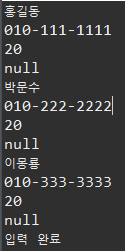
키보드로 입력받기 - System.in
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class SystemEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 키보드 입력
InputStream is = null;
// in이 inputStream
try {
is = System.in;
System.out.print("데이터 입력 : ");
System.out.println(is.read()); // 아스키코드로 나옴 문자로 보고싶으면 char형변환 필요
System.out.println((char)is.read());
System.out.println((char)is.read());
System.out.println("입력 완료");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(is != null) try {is.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
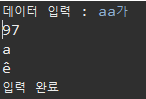
InputStreamReader로 축약 / 한글 출력
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class SystemEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 키보드 입력
// InputStream is = null;
InputStreamReader isr = null;
// in이 inputStream
try {
// is = System.in;
isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in); // 축약시킴
System.out.print("데이터 입력 : ");
System.out.println(isr.read()); // 아스키코드로 나옴 문자로 보고싶으면 char형변환 필요
System.out.println((char)isr.read());
System.out.println((char)isr.read());
System.out.println("입력 완료");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(isr != null) try {isr.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}

Buffered로 성능업 시키기
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class SystemEx03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("데이터 입력 : ");
System.out.println(br.read()); // 아스키코드로 나옴 문자로 보고싶으면 char형변환 필요
System.out.println((char)br.read());
System.out.println((char)br.read());
System.out.println("입력 완료");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(br != null) try {br.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}

한줄을 다 한번에 읽으려면
System.out.println(br.readLine()); 사용
구구단 만들어보기
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Gugudan {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("시작 단수 : ");
int start = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.print("끝 단수 : ");
int end = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
for (int j =1; j <= 9; j++) {
System.out.println(i + "x" + j + "=" + (i*j));
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if (br != null)
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
}
쭉쭉나옴

엑셀
2003버전
- 이전
xls
https://jexcelapi.sourceforge.net
Apache POI
https://poi.apache.org - 이후 - xlsx
=> ObjectStram방식으로 저장
=> 공개 후 Open Source Library
JXL 접근해서 확인
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import jxl.Cell;
import jxl.Sheet;
import jxl.Workbook;
import jxl.read.biff.BiffException;
public class JXLEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Workbook workBook = null;
try {
workBook = Workbook.getWorkbook(new FileInputStream("./jxlrwtest.xls"));
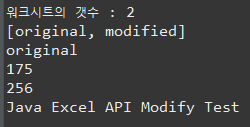
// 2.6.12출력 : jxl버전
System.out.println(workBook.getVersion());
// worksheet의 갯수
System.out.println("워크시트의 갯수 : " + workBook.getNumberOfSheets());
// 워크시트 이름
String[] sheetNames = workBook.getSheetNames();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sheetNames));
// 한 개의 시트에 접근
Sheet sheet = workBook.getSheet(0);
System.out.println(sheet.getName());
// 행과 컬럼 (행과 열)
System.out.println(sheet.getRows()); // 행
System.out.println(sheet.getColumns()); // 열
// 엑셀 데이터에 접근 / 내용 읽어오기 - 컬럼에서 셀을 읽는다.
Cell cell = sheet.getCell(0,0);
System.out.println(cell.getContents());
} catch (BiffException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(workBook != null) workBook.close();
}
}
}
로또 통계표 텍스트로 뽑기 (집가서 해보기)
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import jxl.Cell;
import jxl.Sheet;
import jxl.Workbook;
import jxl.read.biff.BiffException;
public class JXLEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Workbook workBook = null;
try {
workBook = Workbook.getWorkbook(new FileInputStream("./lotto(1~1060).xls"));
Sheet sheet = workBook.getSheet(0);
// Cell cell1 = sheet.getCell(2-1,4-1); // 열, 행
// Cell cell2 = sheet.getCell(3-1,4-1);
// Cell cell3 = sheet.getCell(14-1,4-1);
// Cell cell4 = sheet.getCell(15-1,4-1);
// Cell cell5 = sheet.getCell(16-1,4-1);
// Cell cell6 = sheet.getCell(17-1,4-1);
// Cell cell7 = sheet.getCell(18-1,4-1);
// Cell cell8 = sheet.getCell(19-1,4-1);
// Cell cell9 = sheet.getCell(20-1,4-1);
for(int i=0; i<sheet.getColumns(); i++) {
for(int j=4-1; j<sheet.getRows(); j++) {
Cell cell1 = sheet.getCell(i,j);
System.out.println(cell1.getContents());
}
}
// System.out.println(cell1.getContents());
// System.out.println(cell2.getContents());
// System.out.println(cell3.getContents());
// System.out.println(cell4.getContents());
// System.out.println(cell5.getContents());
// System.out.println(cell6.getContents());
// System.out.println(cell7.getContents());
// System.out.println(cell8.getContents());
// System.out.println(cell9.getContents());
} catch (BiffException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(workBook != null) workBook.close();
}
}
}
메모리 기반의 입/출력 처리
import java.io.CharArrayReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CharArrayReaderEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 메모리에서 스트림 기능이 가능.
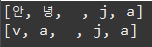
char[] memory = { '안', '녕', ' ', 'j', 'a', 'v', 'a' };
try (CharArrayReader charArry = new CharArrayReader(memory)) {
char[] buffer = new char[5];
int read = 0;
while ((read = charArry.read(buffer)) > 0) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buffer));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
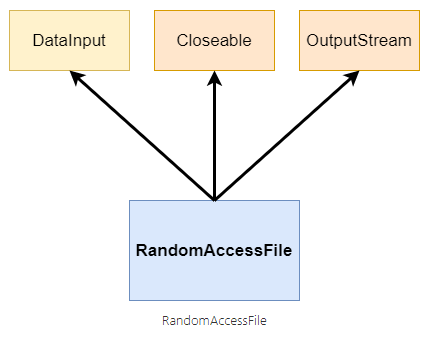
위치 지정하여 읽기 - RandomAccessFile
RandomAccessFile이라는 객체 하나로 쓰기와 읽기 둘 다 할 수 있다.
DataInput, DataOutput을 둘다 implements 했기 때문
import java.io.EOFException;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class RandomAccessFileEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
RandomAccessFile raf = null;
// read / write 둘 다 사용 가능
try {
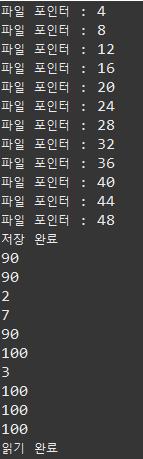
raf = new RandomAccessFile("./score.dat", "rw");
int[] scores = {
1, 100, 90, 90,
2, 7, 90, 100,
3, 100, 100, 100
};
for(int i=0; i<scores.length; i++) {
// 기본 자료형 저장
raf.writeInt(scores[i]);
System.out.println("파일 포인터 : " + raf.getFilePointer());
}
System.out.println("저장 완료");
// 4의 배수만큼만 입력
raf.seek(32);
while(true) {
System.out.println(raf.readInt());
}
} catch (EOFException e) {
System.out.println("읽기 완료");
}catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(raf != null) try {raf.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
BasicFileAttributes - 집가서 보쟈
많은 파일 시스템에 공통적인 기본 파일 속성 세트 보기를 제공하는 파일 속성 보기입니다
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.attribute.BasicFileAttributes;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class FileEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
File file = new File("./value.dat");
Path filePath = file.toPath();
BasicFileAttributes attributes = null;
try {
attributes = Files.readAttributes(filePath, BasicFileAttributes.class);
long creationTime = attributes.creationTime().to(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
System.out.println(creationTime);
Date date = new Date(creationTime);
System.out.println(date.toLocaleString());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
퀴즈
자바기초
캡처 - 로또 번호별 통계
3306번 통해서 들어감
로또 통계
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class LottoEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("./lotto(1~1059).csv"));
String str = "";
int[] count = new int[45];
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
String[] arrLotto = str.split(",");
for (int i=0; i<45; i++) {
for(int j=2; j<arrLotto.length; j++) {
if(Integer.parseInt(arrLotto[j])==(i+1)) {
count[i]++;
}
}
}
}
for(int k=0; k<45; k++) {
System.out.println((k+1)+ "번의 개수 : " + count[k]);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(br != null) try {br.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}