데이터
프로그램을 만들다 = 정보(데이터) 처리
데이터 구분
임시 저장 데이터
프로그램 종료와 동시에 사라지는 데이터
자료 - 임시 저장 데이터
@ 데이터
- 변수 / 상수
- 배열 / 컬렉션 / 객체
이러한 데이터들이 종료와 동시에 사라짐
영구 저장 데이터 - java.io
프로그램 종료와 상관없이 저장된 데이터
@ 로컬 저장
- 프로그램과 같은 컴퓨터에 있는 데이터
- 대명사 = 파일
파일도 분류가 된다
일반파일(메모장에서 읽을 수 있음)
- text파일 / txt로 저장이 된다
바이너리(2진, 사람이 읽을 수 없음, 깨져서나오거나 그런다) 파일
- hwp / docx
- xlsx / pptx
- image / sound
@ 원격저장
- 네트워크상의 컴퓨터에 있는 데이터
- 대명사 = 데이터베이스
File
File은 가장 기본적인 입/출력 장치 중 하나로 파일과 디렉토리를 다루는 클래스
File을 통해서 파일의 크기, 속성, 이름, 경로에 대한 정보를 얻거나 생성, 삭제할 수있다.
java.io 패키지 사용
윈도우는 경로명 대소문자 구분 안함 / 리눅스는 한다.
import java.io.File;
public class FIleEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//File
// 파일 / 디렉토리
// 경로 - 절대 / 상대
// 디렉토리 절대경로
File file1 = new File("c:\\java");
File file2 = new File("c:/java");
// 디렉토리를 상대경로로
File file3 = new File("./java");
File file4 = new File("c:/java/test.txt");
File file5 = new File("./test.txt");
// 경로와 파일명을 분리해서 써주기
File file6 = new File("c:/java/","text.txt");
}
}파일 있는지 확인
exists() : 파일이 존재하는지 여부를 알 수 있다.
import java.io.File;
public class FileEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// c 드라이브에 java 파일 있는지 알려줘
File file1 = new File("c:/java");
System.out.println(file1.exists());
// text1.txt파일을 폴더에 직접 생성해서 실행시키면 true 출력 없으면 false
File file2 = new File("c:/java/test1.txt");
System.out.println(file2.exists());
}
}
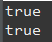
파일이 디렉토리인지 파일인지 확인 / 히든파일인지 확인
디렉토리(directory)는 서로 관련 있는 파일을 하나로 모아놓은 것이다.
import java.io.File;
public class FileEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// c 드라이브에 java 파일 있는지 알려줘
File file1 = new File("c:/java");
System.out.println(file1.exists());
// text1.txt파일을 폴더에 직접 생성해서 실행시키면 true 출력 없으면 false
File file2 = new File("c:/java/test1.txt");
System.out.println(file2.exists());
// 파일이 디렉토리인지, 파일인지 리턴하는 방법
System.out.println(file2.isDirectory());
System.out.println(file2.isFile());
// 파일이 히든파일인지 확인 (숨김파일인지)
System.out.println(file2.isHidden());
}
}
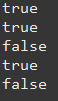
파일에 대한 정보 (이름, 부모, 경로 등) 출력
import java.io.File;
public class FileEx03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("c/java/test1.txt");
// 파일에대한 이름, 부모, 경로 출력
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println(file.getParent());
System.out.println(file.getPath());
}
}
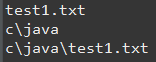
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileEx03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("c/java/test1.txt");
// 파일에대한 이름, 부모, 경로 출력
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println(file.getParent());
System.out.println(file.getPath());
// "."은 현재
File file2 = new File("./");
System.out.println(file2.getPath());
try {
// 언 핸들 발생 / try ~ catch 필요 하여 생성
// getCanonicalPath() : 파일의 정식 경로를 리턴한다. 정식 경로는 절대경로이며
"." 또는 ".."의 상대 경로 기호가 없는 경로
System.out.println(file2.getCanonicalPath());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
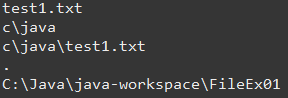
생성(수정)일자, 파일크기 구하기
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Date;
public class FileEx04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
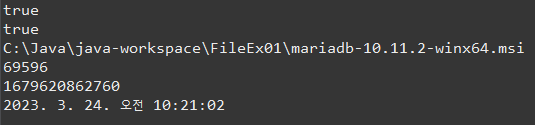
File file1 = new File("c:/java/java-workspace/FileEx01/mariadb-10.11.2-winx64.msi");
File file2 = new File("./mariadb-10.11.2-winx64.msi");
System.out.println(file1.exists());
System.out.println(file2.exists());
try {
System.out.println(file2.getCanonicalPath());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 생성(수정)일자, 파일 크기 구하기
// 파일 크기
// return값은 long / byte 크기로 나와서 KB크기로 구하려면 1024 나눠줘야함
// 1024 나눠주면 KB값으로 나온다
System.out.println(file1.length()/1024);
// 생성일자 / 타임스탬프로 나온다
System.out.println(file1.lastModified());
// 생성일자 날짜로 출력해보기
Date date = new Date(file1.lastModified());
System.out.println(date.toLocaleString());
}
}
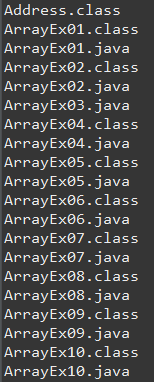
파일이 디렉토리인 경우 자식 파일들 이름을 출력하는 메서드
list() - 이름을 배열로 리턴
listFiles() - File[]형태로 리턴
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class FileEx05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("c:/java");
String[] lists = file.list();
// c:/java 폴더 안에 리스트들을 출력
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(lists));
for(String list : lists) {
// System.out.println(list);
}
File[] fileLists = file.listFiles();
// getName()으로 이름값 가져올 수 있다.
for(File f : fileLists) {
System.out.println(f.getName());
}
}
}
file.list() 출력

file.listFiles(); 출력
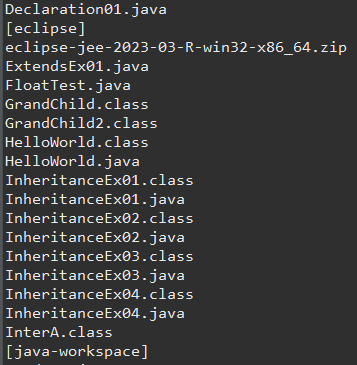
디렉토리 파일은[], 파일은 그대로 출력하기
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class FileEx05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("c:/java");
String[] lists = file.list();
for(String list : lists) {
File subdir = new File("c:/java", list);
if(subdir.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("[" + list + "]");
} else {
System.out.println(list);
}
}
}
}
디렉토리 관련 기능들
import java.io.File;
public class FileEx06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 디렉토리 관련
// mkdir() = make directory
File file = new File("c:/java/dir1"); // 실제로 파일이 없어도 컴파일 에러는 나지않는다.
File file2 = new File("c:/java/dir2");
// mkdir() : 경로상에 없는 디렉토리 만들기
if(file.mkdir()) {
System.out.println("성공");
} else {
System.out.println("실패");
}
// 디렉토리 바꾸기
// file.renameTo(file2);
// 디렉토리 지우기
file2.delete();
}
}
디렉토리 만들기

디렉토리 바꾸기

디렉토리 지우기(dir2 지워짐)

createNewFile() : file 생성 / delete() : 지우기
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileEx06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 디렉토리 관련
// mkdir() = make directory
File file = new File("c:/java/dir1"); // 실제로 파일이 없어도 컴파일 에러는 나지않는다.
File file2 = new File("c:/java/dir2");
// 디렉토리 만들기
// if(file.mkdir()) {
// System.out.println("성공");
// } else {
// System.out.println("실패");
// }
//
// 디렉토리 바꾸기
// file.renameTo(file2);
// 디렉토리 지우기
// file2.delete();
// file 생성
File file3 = new File("c:/java/test3.txt");
try {
file3.createNewFile();
System.out.println("파일 생성");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 파일 지우기
file3.delete();
}
}

I/O와 스트림
I/O란 데이터의 입력(Input)과 출력(Output)을 함께 일컫는 말이다.
Scanner를 통해 받아들이는 것이 입력
System.out.println()으로 값을 표현하는 것이 출력

I/O 참고자료
https://develop-im.tistory.com/54
https://onlyfor-me-blog.tistory.com/193
파일 데이터 접근
스트림으로 접근
- 일정량 ... (buffering) / 버퍼링이 스트림이다. 조금조금씩 읽어오는 것
입력, 출력을 같이 하지못한다.
입력 - 파일을 프로그램에 넣음
- InputStream / Read
출력 - 프로그램에서 파일을 뺌
- OutputStream / Writer
입출력 단위
1byte( 영문자, 특수문자, 숫자 ... )
- InputStram / OutputStream
2byte( 다국어 : char단위 )
- Reader / Writer
직접 / 간접 연결
1차 스트림
- 파일(데이터)에 연결
2차 스트림(보조 스트림)
- 1차 스트림에 연결
파일 읽기
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class InputStreamEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// FileInputStream = input / byte / 1차 스트림
// 파일 열고, 처리하고, 닫고 하는 과정이다
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("./test1.txt"); // 이 안에는 read가 있다. // exception
int data = fis.read(); // read() : 아스키 코드로 1자 읽음
System.out.println((char)data); // 문자로 보기위해 char로 형변환 1 출력
data = fis.read();
System.out.println((char)data); // 2출력
data = fis.read();
System.out.println((char)data); // 3출력
byte[] datas = new byte[5];
fis.read(datas);
System.out.println((char)datas[0]); // 4출력
System.out.println((char)datas[1]); // 5출력
System.out.println((char)datas[4]);// 8출력
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally { // 파일 닫기
try {
fis.close();} catch (IOException e) {}
}
}
}
전체파일 내용 읽기
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class InputStreamEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("./test1.txt");
// 전체파일 내용 읽기
// read() : byte 하나를 읽어서 int로 반환, 더 이상 읽을 값 없으면 -1 리턴
int data = 0;
while( (data = fis.read()) != -1 ) {
System.out.println( (char) data );
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try { fis.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
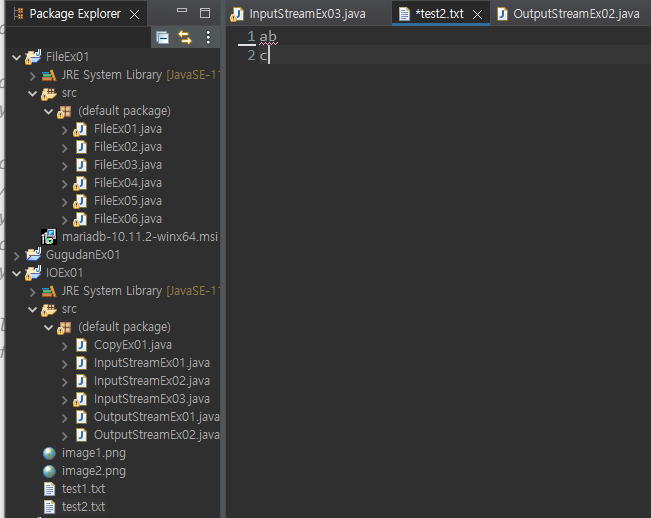
test1.txt
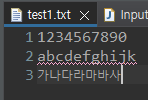
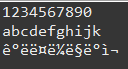
test1.txt의 전체 데이터가 출력 (다국어는 깨진다)
file 생성, 입력
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class OutputStreamEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
// 파일을 생성
// fos = new FileOutputStream("./test2.txt", true); // false면 오버라이드 true면 어펜드
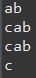
fos = new FileOutputStream("./test2.txt"); // 뒤에 false가 defualt 임 그래서 오버라이드 됨
// 출력 내용 없음
fos.write('a');
fos.write('b');
fos.write('\n');
fos.write('c');
System.out.println("출력 완료");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
}
finally {
try {fos.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
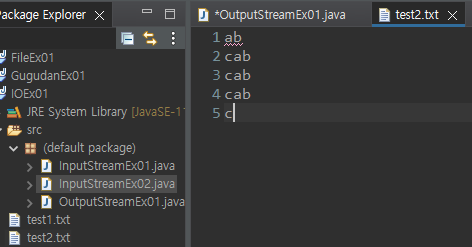
fos = new FileOutputStream("./test2.txt", true); // false면 오버라이드 true면 어펜드
true면 실행할때마다 중복돼서 출력된다.
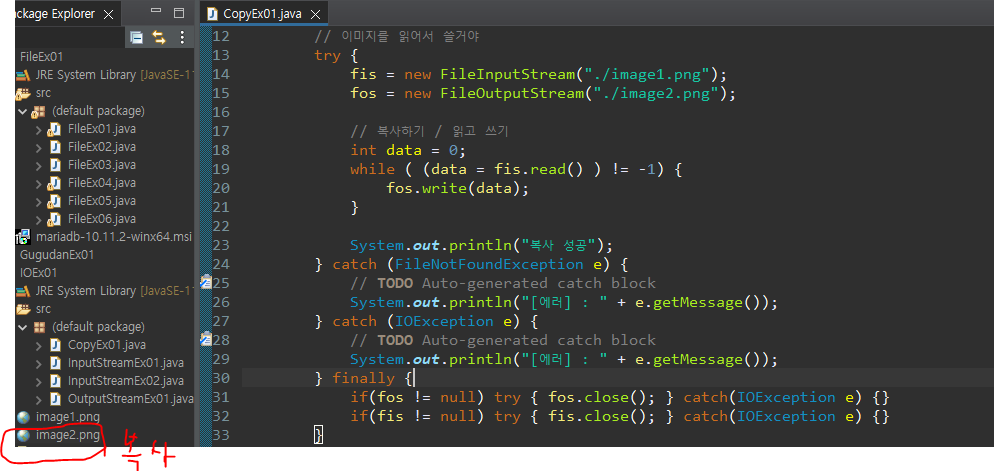
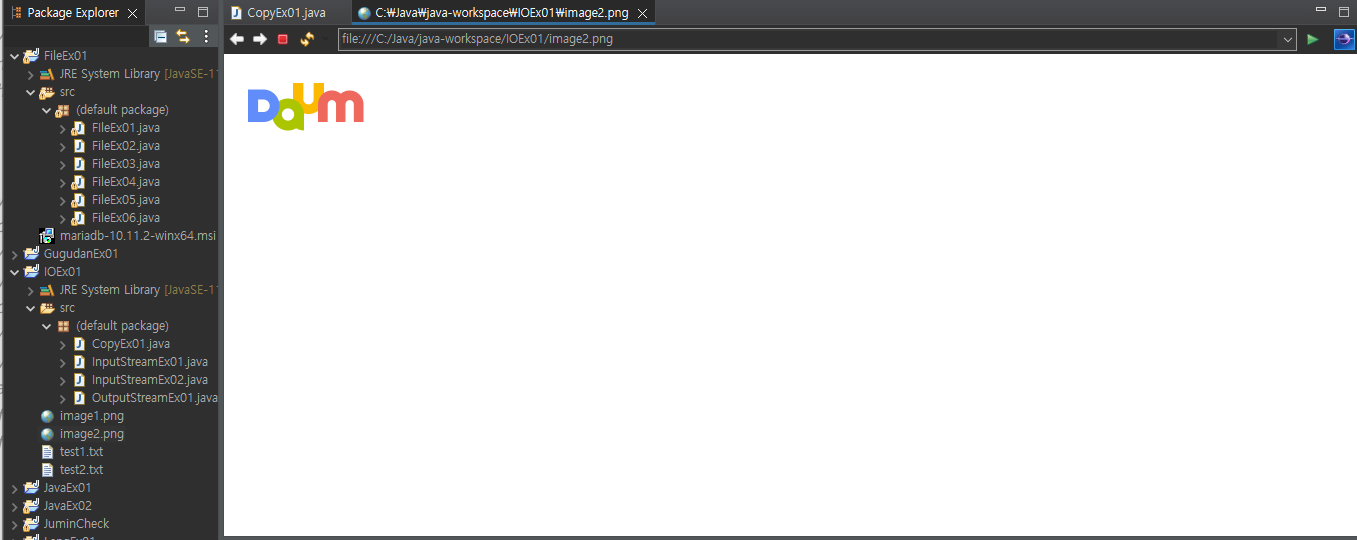
이미지 복사하기
복사할 이미지 다운받아서 프로그램에 넣어줌 image1.png
image1.png 이미지 image2.png로 복사함
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CopyEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
// 이미지를 읽어서 쓸거야
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("./image1.png");
fos = new FileOutputStream("./image2.png");
// 복사하기 / 읽고 쓰기
int data = 0;
while ( (data = fis.read() ) != -1) {
fos.write(data);
}
System.out.println("복사 성공");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(fos != null) try { fos.close(); } catch(IOException e) {}
if(fis != null) try { fis.close(); } catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
클릭하면 사진 나옴
보조스트림
노드 스트림과 달리 노드에 직접 연결되지 않고 다른 스트림과 연결되는 스트림이 있는데 이를 보조스트림이라고 한다.
노드와 직접 연결할 수 없고 노드 트림을 비롯한 다른 스트림과 연결된다.
보조 스트림들이 하는 기능
문자셋(character set)변환, 버퍼링, 기본 데이터형의 전송, 객체 입출력 등
버퍼 사용
대부분 파일을 먼저 애플리케이션의 메모리에 다운 후 메모리의 파일을 비디오 플레이어에서 처리하는데 이떄 애플리케이션의 메모리를 버퍼 라고 한다.
버퍼링은 이 버퍼에 데이터를 쌓는 과정
BufferedInputStream / BufferedOutputStream
속도 향상
byte단위로 파일을 읽어 올때 사용하는 버퍼 스트림
내부적으로 8192byte 크기의 버퍼를 내장
1바이트 단위로 작업이 이루어지는 FileInputStream /FileOutputStream 보다 훨씬 동작이 빠름
BufferedInputStream
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class InputStreamEx03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
try {
// fis가 new BufferedInputStream(fis) 로 들어간다
fis = new FileInputStream("./test2.txt");
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
// 압축하여 쓰기 : bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("./test2.txt"));
// 전체파일 내용 읽기
int data = 0;
while( (data = bis.read()) != -1 ) {
System.out.print( (char) data );
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(bis != null) try { fis.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
if(bis != null) try { fis.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
BufferedOutputStream()
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class OutputStreamEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// FileOutputStream fos = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
bos = new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream("./test2.txt", true));
bos.write('a');
bos.write('b');
bos.write('\n');
bos.write('c');
System.out.println("출력 완료");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
}
finally {
if(bos != null) try {bos.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
FileReader / FileWriter
FileReader와 FileWriter는 문자 단위의 데이터를 파일에서 읽고 쓰는 스트림.
FileReader
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReaderEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader br = null;
try {
br = new FileReader("./test1.txt"); // exception 처리
int data = 0;
while((data = br.read()) != -1) { // // exception 처리
System.out.print((char)data);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if( br != null) try { br.close(); } catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
FileWriter
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WrieterEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter bw = null;
try {
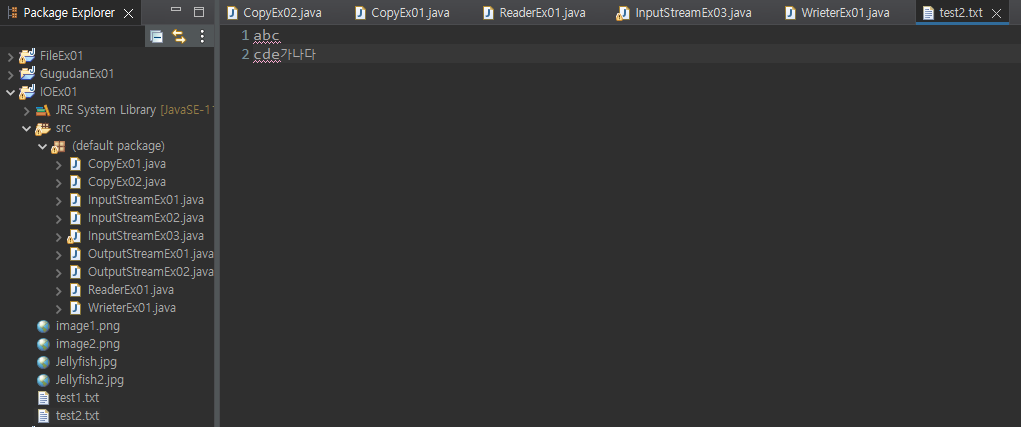
bw = new FileWriter("./test2.txt"); // exception
// 아까와는 다르게 문자열 가능
bw.write("abc");// exception
bw.write("\n");// exception
bw.write("cde");// exception
bw.write("가나다");// exception
System.out.println("출력 완료");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(bw != null) try {bw.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
BufferedReader / BufferedWrite
버퍼를 이용하여 읽고 쓰는 함수
버퍼를 이용하기때문에 입출력 효과가 엄청 좋아진다.
BufferedReader : 문자 입력 스트림에서 텍스트를 읽고 문자를 버퍼링하여 문자, 배열 및 행을 효율적으로 읽을 수 있도록 함
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReaderEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("./test1.txt")); // exception 처리
// 1차
// int data = 0;
// while((data = br.read()) != -1) { // // exception 처리
// System.out.print((char)data);
// }
String str = "";
// br.readLine() - 한줄씩 읽는데 한줄의 개념은 엔터키까지이다. 그래서 줄바꿈 필요하면 println 넣어줘야함
while((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if( br != null) try { br.close(); } catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WrieterEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 가속화된 출력
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("./test2.txt")); // exception
// 아까와는 다르게 문자열 가능
bw.write("abc");// exception
bw.write("\n");// exception
bw.write("cde");// exception
bw.write("가나다");// exception
System.out.println("출력 완료");
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(bw != null) try {bw.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
서울 서초구에 해당하는 데이터 추출하여 따로 저장 => 서초구.txt
- 파일 열고 ( 파잉리더 , 버퍼드 리더
- 그 안에서 서초구만 뽑아낼 수 있어야한다.
- 저장
다 안나옴 집가서 수정
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExamEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("./zipcode_seoul_utf8_type2.csv"));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("./서초구.txt"));
String str = "";
while((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
// System.out.println(str);
String[] arrZipcode = str.split(",");
// System.out.println(arrZipcode[2]); // 서초구
if(arrZipcode[2].equals("서초구")) {
// System.out.println(arrZipcode[0] + ' ' + arrZipcode[1] + ' ' + arrZipcode[2]);
bw.write(str + System.lineSeparator());
}
}
System.out.println("저장 완료");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(br != null) try {br.close();} catch(IOException e) {}
}
}
}
숙제
로또 하기
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class LottoEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
String[] arrLotto2 = new String[45];
for(int i=0; i<45; i++) {
arrLotto2[i] = (i+1)+"";
}
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("./lotto(1~1059).csv"));
String str = "";
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
int sum = 0;
String[] arrLotto = str.split(",");
for (int i = 2; i < arrLotto.length; i++) {
for(int j=1; j<=45; j++) {
if(arrLotto2[j].equals(arrLotto[i])) {
System.out.println(arrLotto2[j]);
}
}
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("[에러] : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}