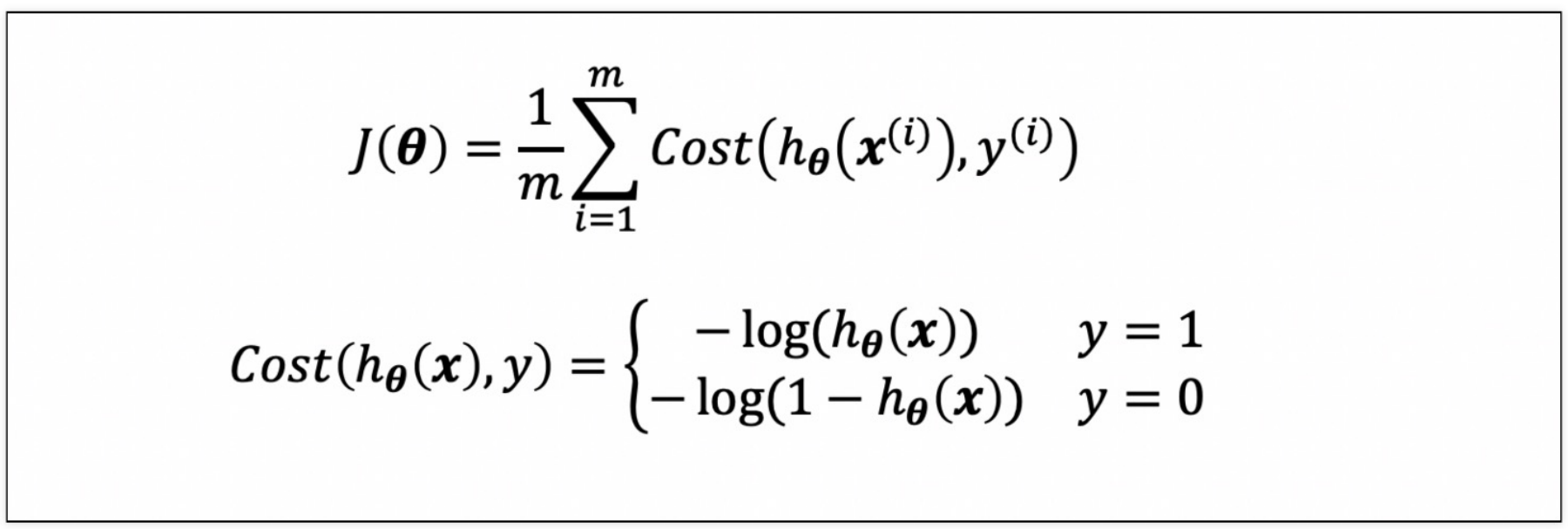1. Logistic Regression
- Linear Resgression을 분류 문제 해결방법을 그대로 적용해도 잘 동작할 수 있을것으로 보인다
-> 그러나 Linear Regression으로 분류문제에 적용하기 힘들듯 하다
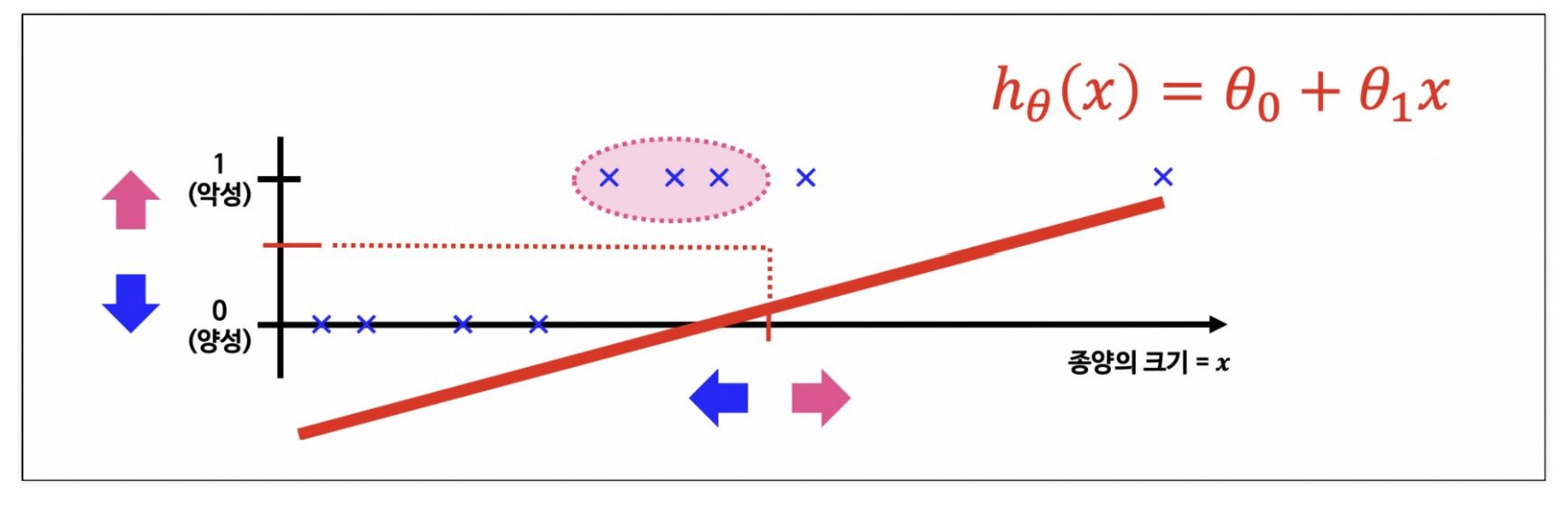
- 분류문제는 0또는 1로 예측해야 하나 Linear Resgression을 그대로 적용하면 예측값 hθ(x) 는 0보다 작거나 1보다 큰 값을 가질 수 있다
- hθ(x)가 항상 0에서 1사이의 값을 가지도록 Hypothesis 함수를 수정 해야한다
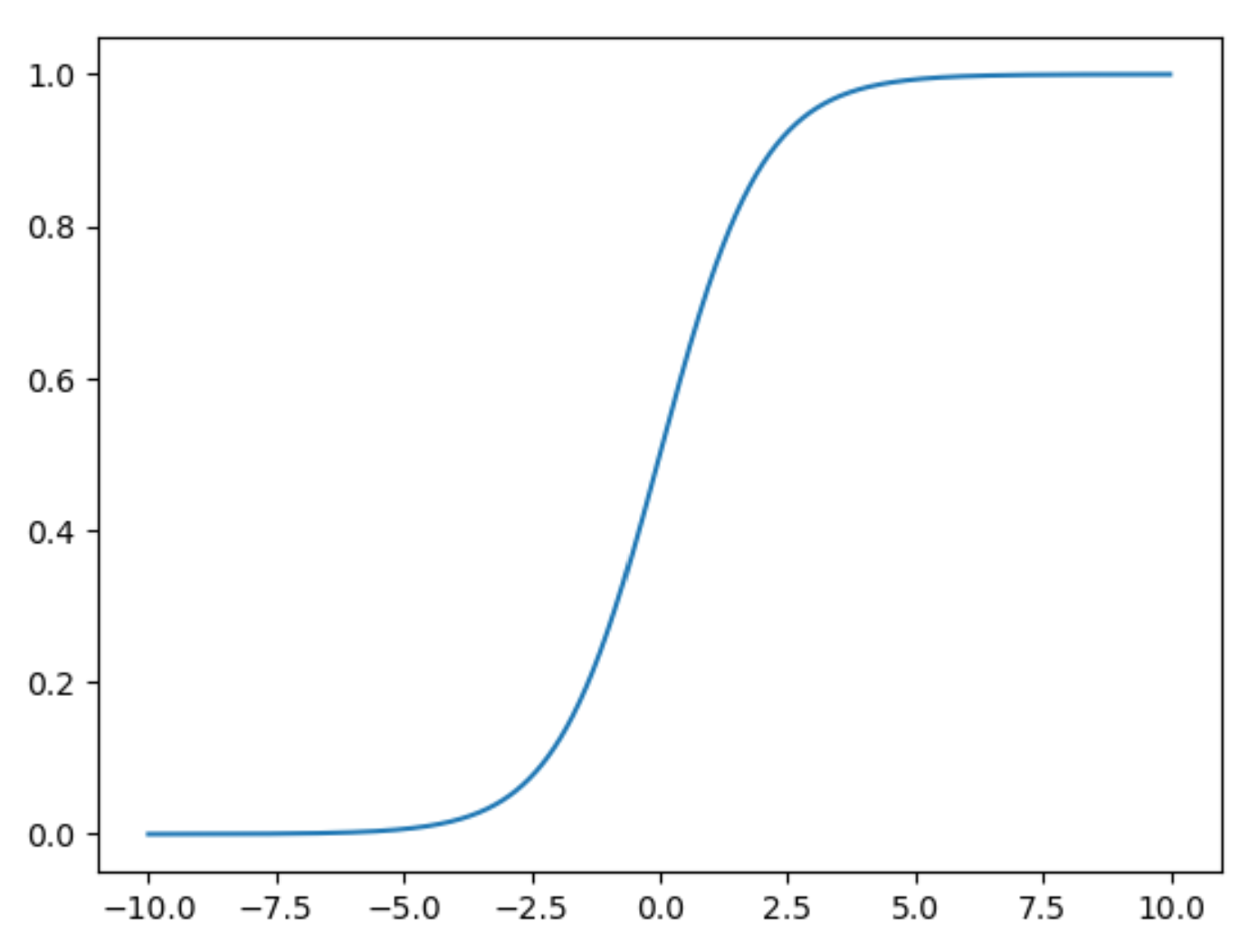
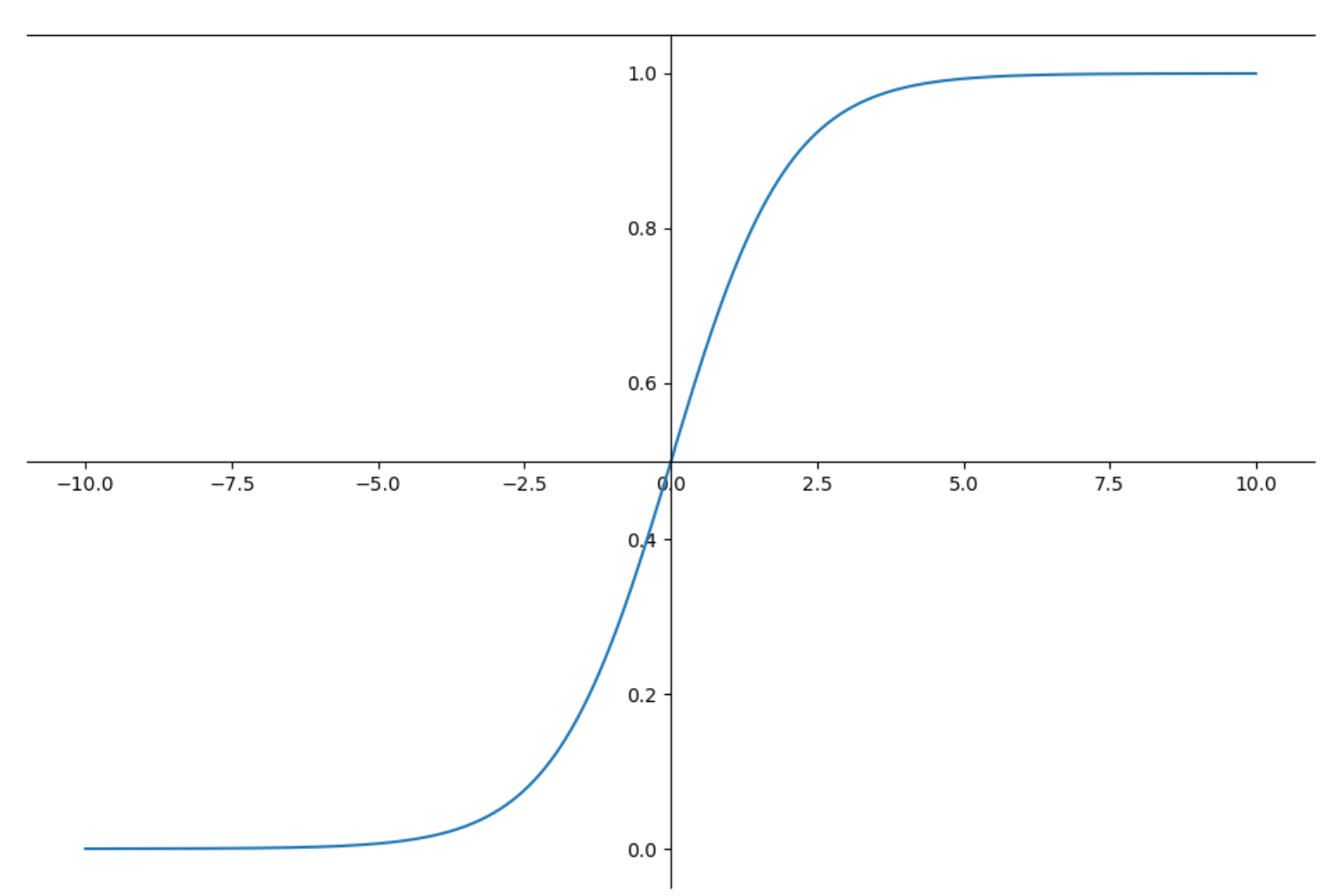
2. Logistic Function 간단히 확인 해보기
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
z = np.arange(-10,10,0.01)
g = 1 / (1+np.exp(-z))
plt.plot(z,g)
# 그래프 자세하게 그려보기
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
ax = plt.gca()
ax.plot(z,g)
ax.spines['left'].set_position('zero')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position('center')
ax.spines['top'].set_position('none')
plt.show()
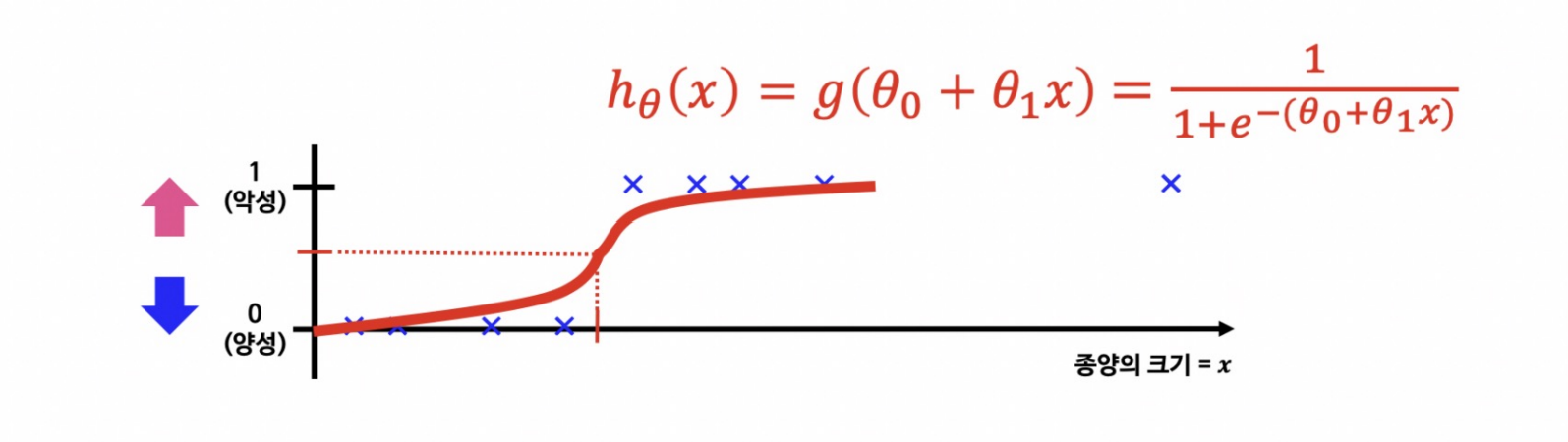
3. Hypothesis 함수의 결과에 따른 분류
- hθ(x)는 주어진 입력 x 에서의 예측 결과가 1이 될 확률을 의미한다.
- hθ(x)가 0.7이라면 1일 확률이 70%이다.
1) 분류 문제용 hypothesis
- hθ(x)가 0.5보다 크거나 같으면 1로 예측
- hθ(x)가 0.5보다 작으면 0으로 예측
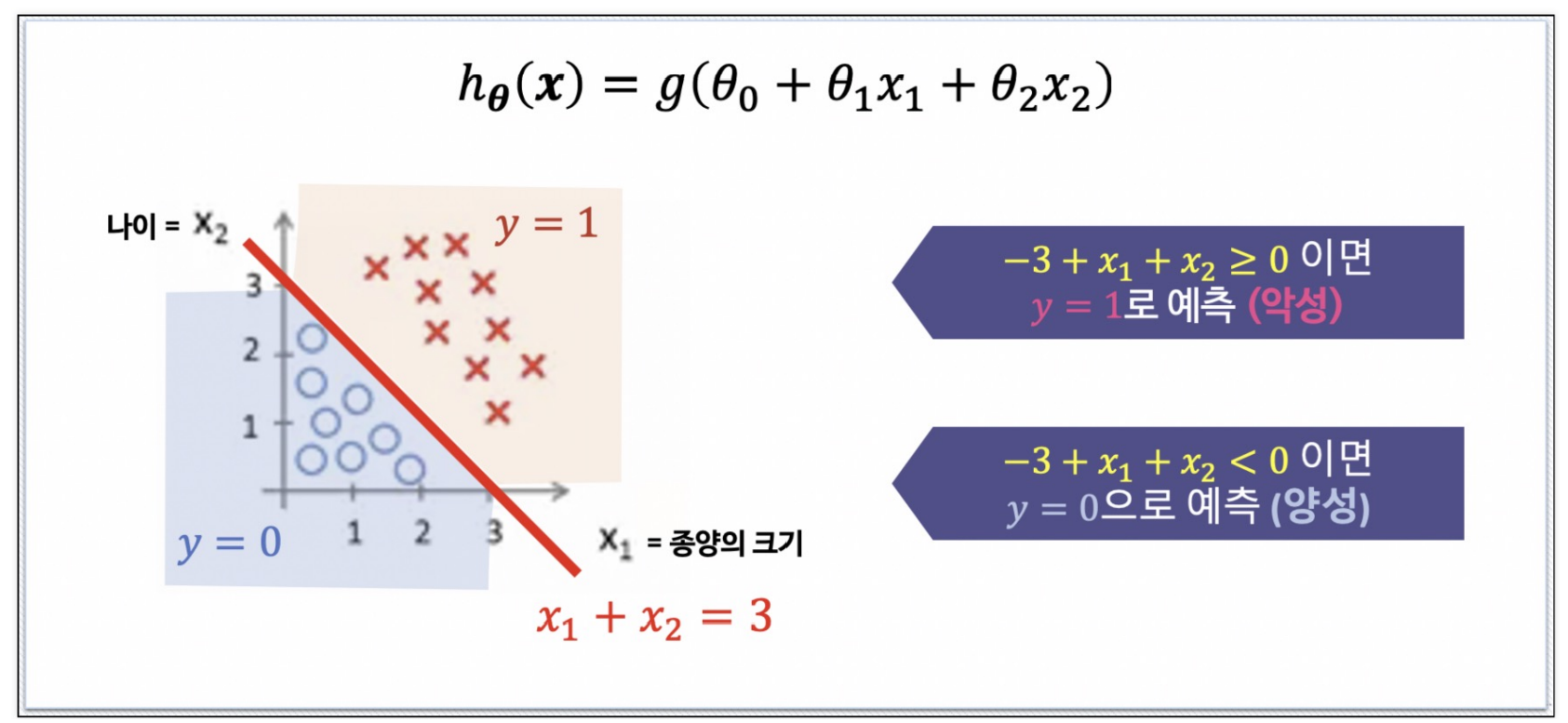
(1) Decision Boundary_1
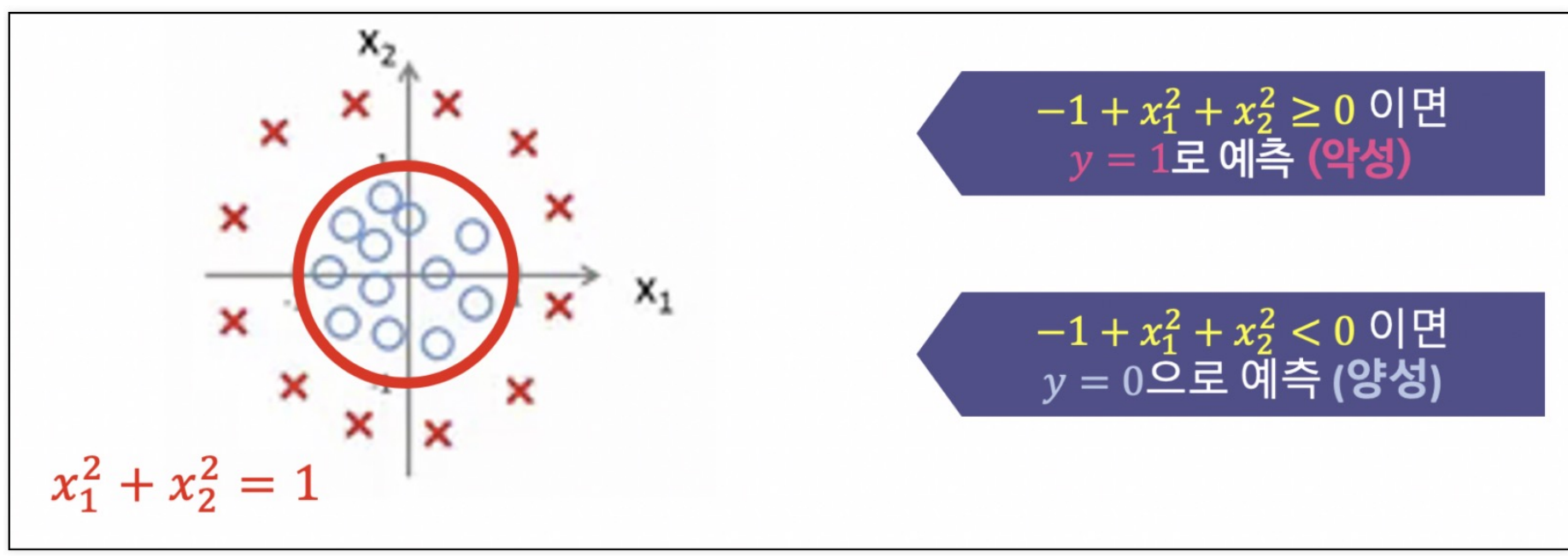
(2) Decision Boundary_2
(3) Cost Function 확인
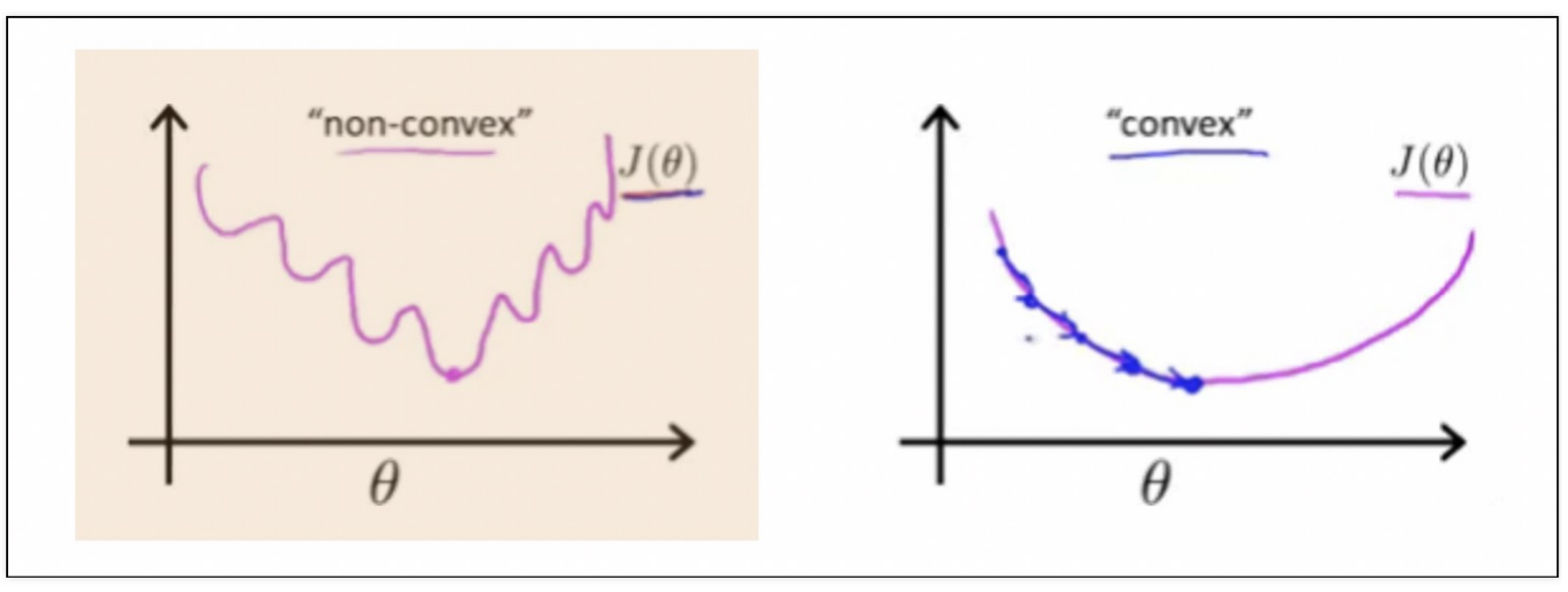
(4) Logistic Regression에서 Cost Function을 재정의
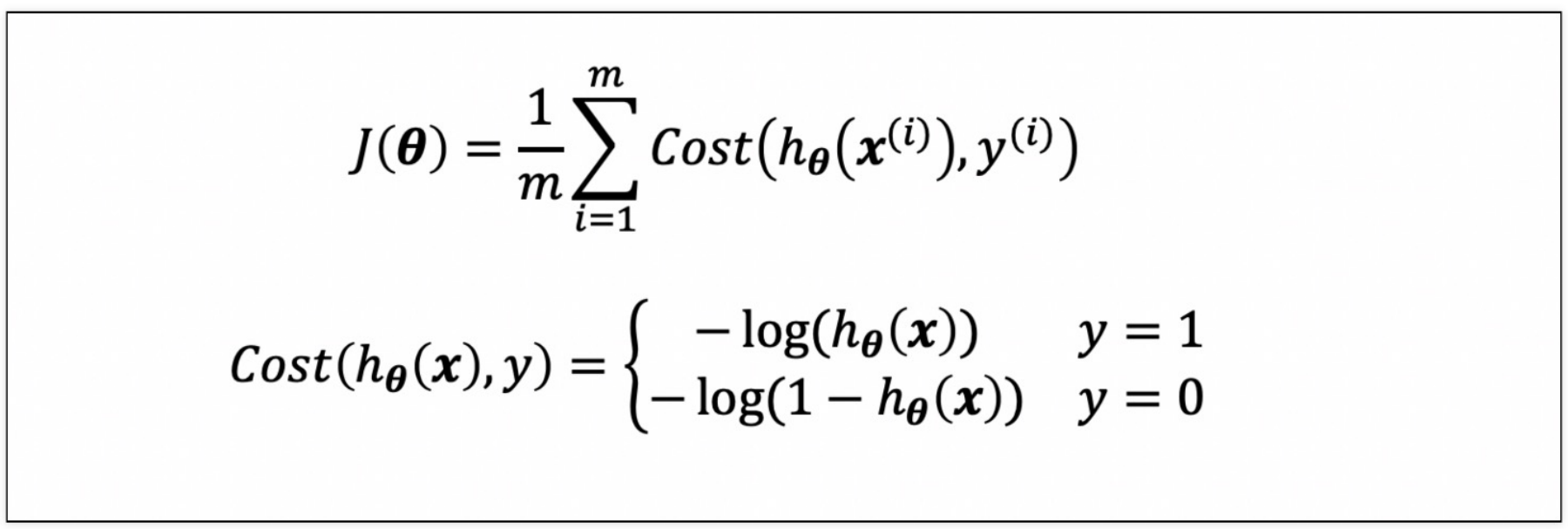
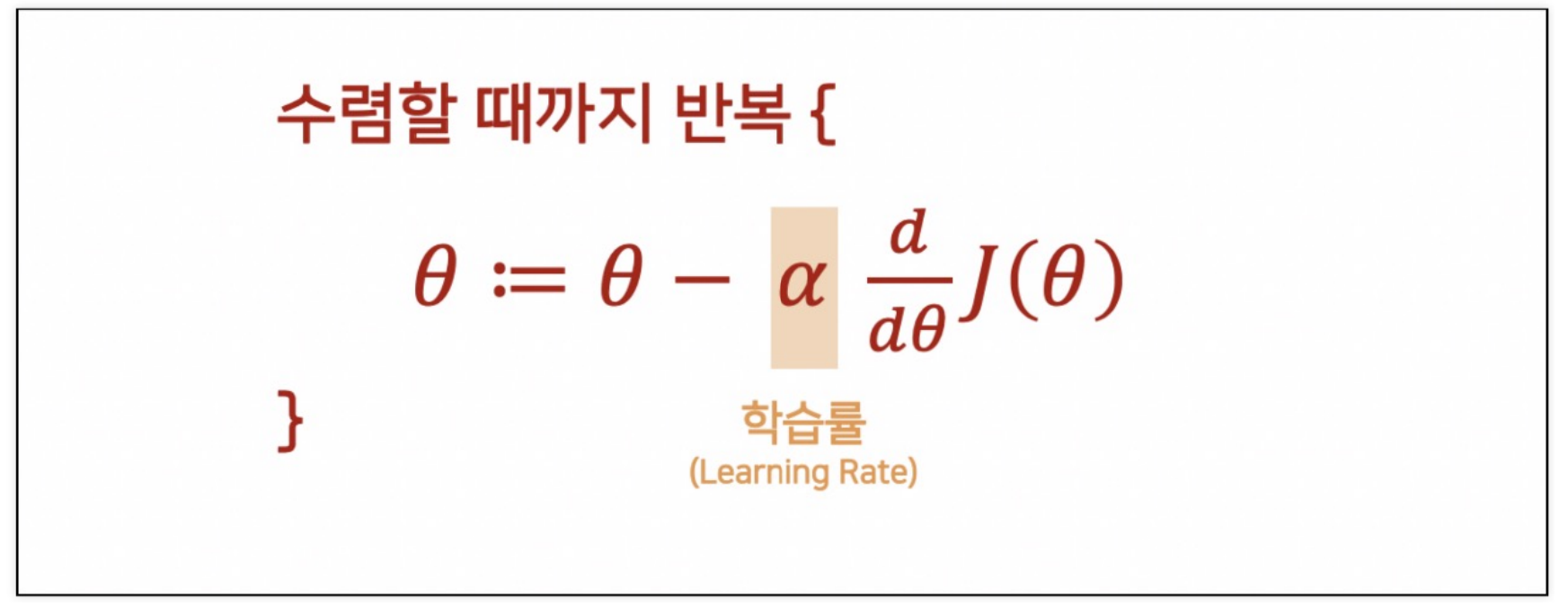
(5) Learning 알고리즘은 동일
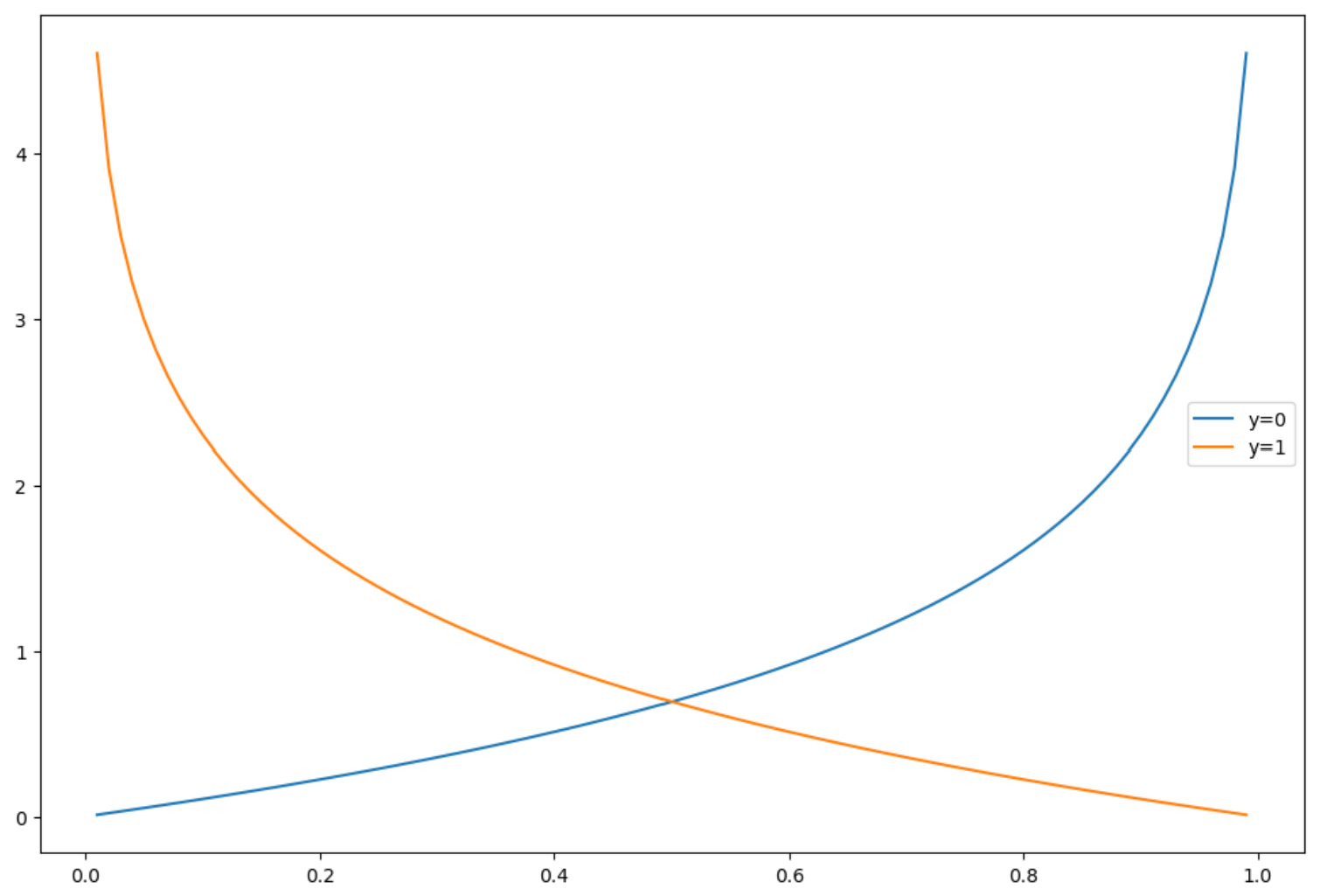
2) Logistic Reg. Cost Function의 그래프
h = np.arange(0.01, 1, 0.01)
C0 = -np.log(1-h)
C1 = -np.log(h)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
plt.plot(h, C0, label='y=0')
plt.plot(h, C1, label='y=1')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
3. 와인데이터로 실습
1) 데이터 정리
(1) 와인 데이터 가져오기
import pandas as pd
wine_url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PinkWink/ML_tutorial/master/dataset/wine.csv'
wine = pd.read_csv(wine_url, index_col=0)
(2) 맛 등급 만들어 넣기
wine['taste'] = [1. if grade>5 else 0. for grade in wine['quality']]
X = wine.drop(['taste','quality'], axis=1)
y = wine['taste']
2) 로지스틱 회귀
(1) 데이터 분리
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=13
)
(2) 간단하게 로지스틱 회귀 테스트 진행
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# solver : 최적합 알고리즘 선택
lr = LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear', random_state=13)
lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_tr = lr.predict(X_train)
y_pred_test = lr.predict(X_test)
print('Train Acc : ', accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_tr))
print('Test Acc : ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_test))
# Train Acc : 0.7429286126611506
# Test Acc : 0.7446153846153846
(3) 스케일러를 적용해서 파이프라인 구축
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
estimators = [
('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('clf', LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear', random_state=13))
]
pipe = Pipeline(estimators)
(4) fit
pipe.fit(X_train, y_train)
Pipeline(steps=[('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('clf',
LogisticRegression(random_state=13, solver='liblinear'))])
(5) 결과 확인
y_pred_tr = pipe.predict(X_train)
y_pred_test = pipe.predict(X_test)
print('Train Acc : ', accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_tr))
print('Test Acc : ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_test))
# Train Acc : 0.7444679622859341
# Test Acc : 0.7469230769230769
2) Decision Tree와의 비교해보기
(1) Decision Tree 작업
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
wine_tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2,random_state= 13)
wine_tree.fit(X_train, y_train)
models = {'logistic': pipe, 'decisin': wine_tree}
for model_name, model in models.items():
print(model_name)
print(model)
logistic
Pipeline(steps=[('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('clf',
LogisticRegression(random_state=13, solver='liblinear'))])
decisin
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2, random_state=13)
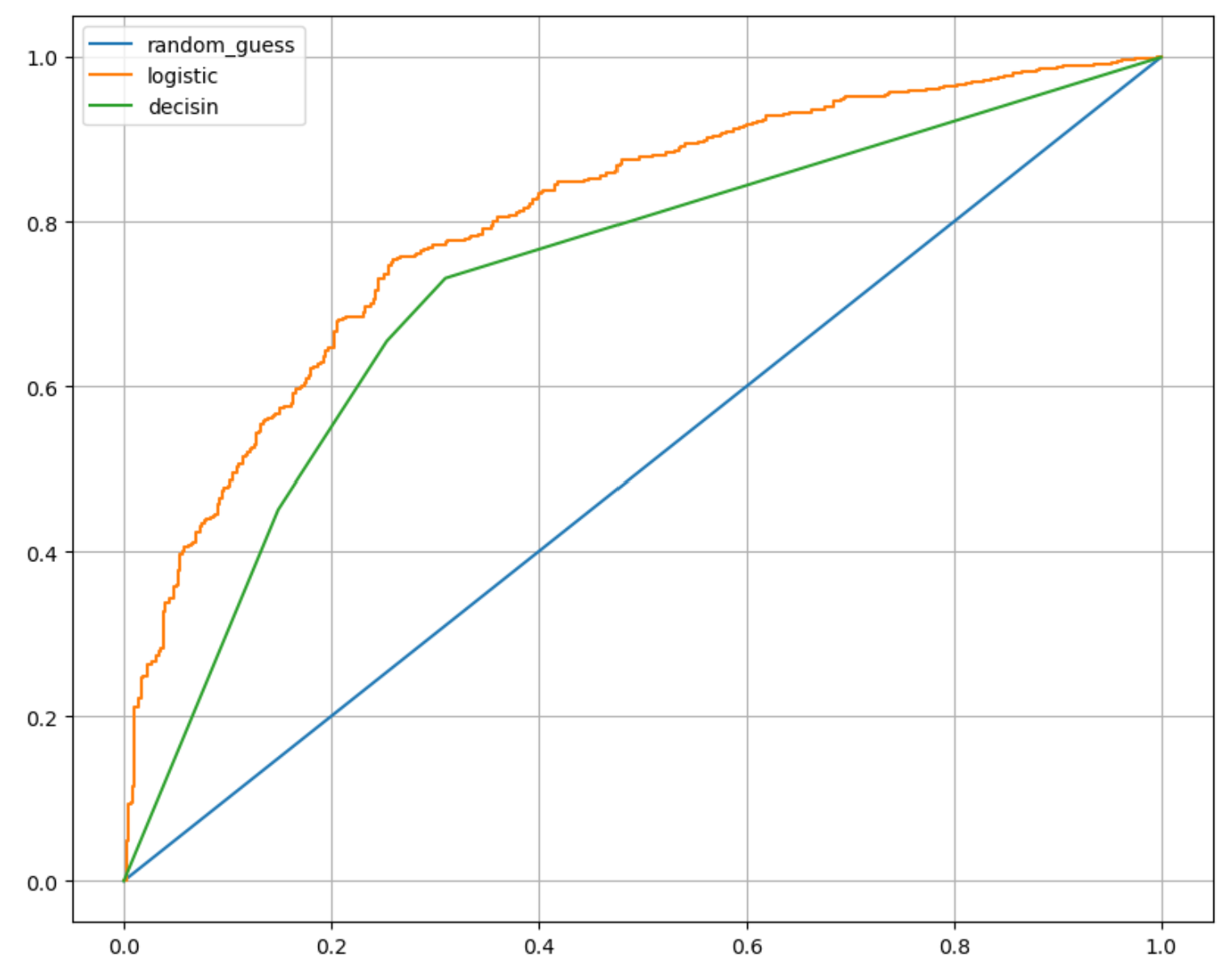
(2) AUC 그래프를 이용한 모델간 비교
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
plt.plot([0,1],[0,1], label = 'random_guess')
for model_name, model in models.items():
pred = model.predict_proba(X_test)[:,1]
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test,pred)
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, label=model_name)
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
plt.show()