1. PIMA 인디언 당뇨병 문제
- 50년대까지 PIMA 인디언은 당뇨가 없었다
- 20세기 말, 50%의 PIMA 인디언이 당뇨에 걸렸다
2. PIMA 인디언 당뇨병 예측
1)데이터 가져오기
(1) PIMA 인디언 데이터 가져오기
import pandas as pd
pima_url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PinkWink/ML_tutorial/master/dataset/diabetes.csv'
PIMA = pd.read_csv(pima_url)
(2) Data column의 의미
- Pregnancies : 임신횟수
- Glucose : 포도당 부하검사 수치
- BloodPressure : 협압
- SkinThickness : 팔 삼두근 뒤쪽의 피하지방 측정값
- Insulin : 혈청 인슐린
- BMI : 체질량 지수
- DiabetesPedigreeFunction : 당뇨 내력 가중치 값
- Age : 나이
- Outcome : 당뇨유무, 클래스 결정
(3) 데이터 정리
# 머신러닝 학습을 위하여 float으로 데이터로 변환
PIMA.info()
# <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
# RangeIndex: 768 entries, 0 to 767
# Data columns (total 9 columns):
# # Column Non-Null Count Dtype
# --- ------ -------------- -----
# 0 Pregnancies 768 non-null int64
# 1 Glucose 768 non-null int64
# 2 BloodPressure 768 non-null int64
# 3 SkinThickness 768 non-null int64
# 4 Insulin 768 non-null int64
# 5 BMI 768 non-null float64
# 6 DiabetesPedigreeFunction 768 non-null float64
# 7 Age 768 non-null int64
# 8 Outcome 768 non-null int64
# dtypes: float64(2), int64(7)
# memory usage: 54.1 KB
PIMA = PIMA.astype('float')
# 값이 0인 데이터 확인
(PIMA==0).astype(int).sum()
# Pregnancies 111
# Glucose 5
# BloodPressure 35
# SkinThickness 227
# Insulin 374
# BMI 11
# DiabetesPedigreeFunction 0
# Age 0
# Outcome 500
# 상황 상 0(결측값)이면 안되어 보이는 값들 : Glucose, BloodPressure, SkinThickness ,BMI
# 의학적 지식과 PIMA인디언에 대한 정보가 없으므로 일단 평균값으로 대체
zero_features = ['Glucose', 'BloodPressure', 'SkinThickness' ,'BMI']
PIMA[zero_features] = PIMA[zero_features].replace(0, PIMA[zero_features].mean())
2) 데이터 확인
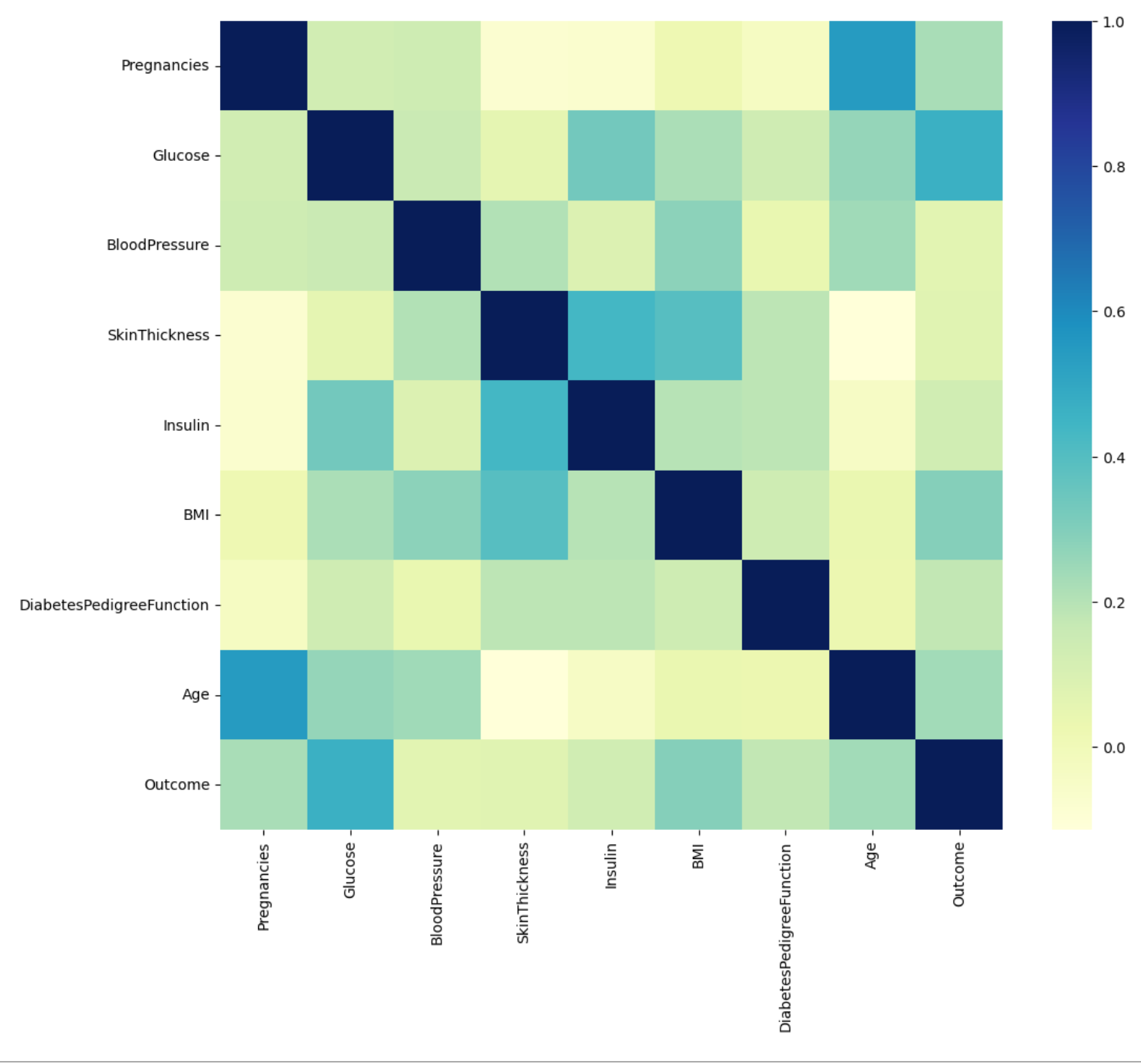
(1) 상관관계 확인
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(12,10))
sns.heatmap(PIMA.corr(), cmap = 'YlGnBu')
plt.show()
(2) 데이터 나누기
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X = PIMA.drop(['Outcome'], axis=1)
y = PIMA['Outcome']
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, stratify=y, random_state=13)
(3) Pipeline 만들기
estimators = [
('scalar' , StandardScaler()),
('clf', LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear', random_state=13))
]
pipe_lr = Pipeline(estimators)
pipe_lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
pred = pipe_lr.predict(X_test)
(4) 수치 확인
from sklearn.metrics import (accuracy_score,
recall_score,
precision_score,
roc_auc_score,
f1_score)
print('accuracy',accuracy_score(y_test, pred))
print('recall', recall_score(y_test, pred))
print('precision', precision_score(y_test, pred))
print('auc_score',roc_auc_score(y_test, pred))
print('f1_score', f1_score(y_test, pred))
# accuracy 0.7727272727272727
# recall 0.6111111111111112
# precision 0.7021276595744681
# auc_score 0.7355555555555556
# f1_score 0.6534653465346535
(5) 다변수 방정식의 각 계수 값을 확인
coeff = list(pipe_lr['clf'].coef_[0])
labels = list(X_train.columns)
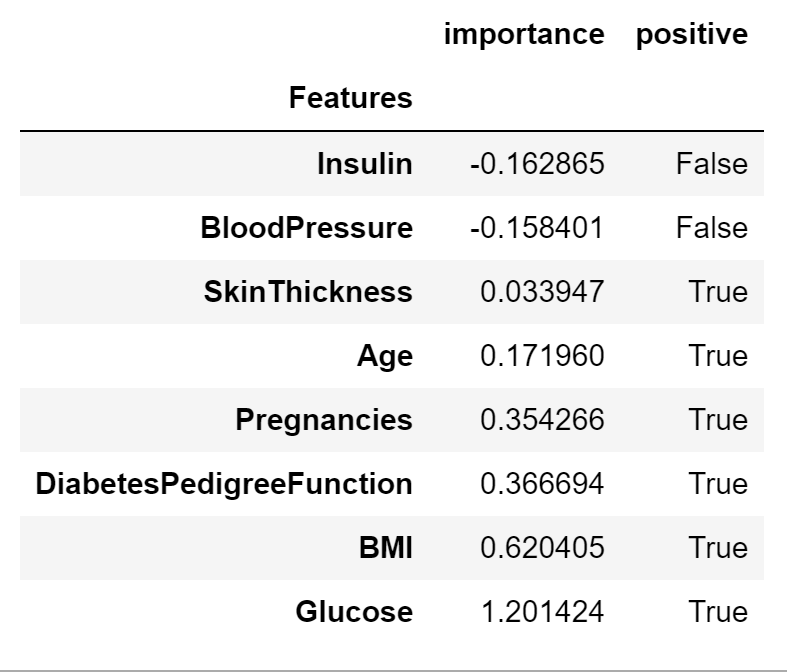
coeff
# [0.354265888441265,
# 1.201424442503758,
# -0.15840135536286706,
# 0.033946577129299486,
# -0.1628647195398812,
# 0.6204045219895111,
# 0.3666935579557874,
# 0.17195965447035097]
(6) 중요한 feature 확인
features = pd.DataFrame({'Features': labels, 'importance': coeff})
features.sort_values(by =['importance'], ascending=True, inplace=True)
features['positive'] = features['importance'] > 0
features.set_index('Features', inplace=True)
features
features['importance'].plot(
kind='barh',
figsize=(11,6),
color=features['positive'].map({True:'blue', False:'red'}))
plt.xlabel('Importance')
plt.show()
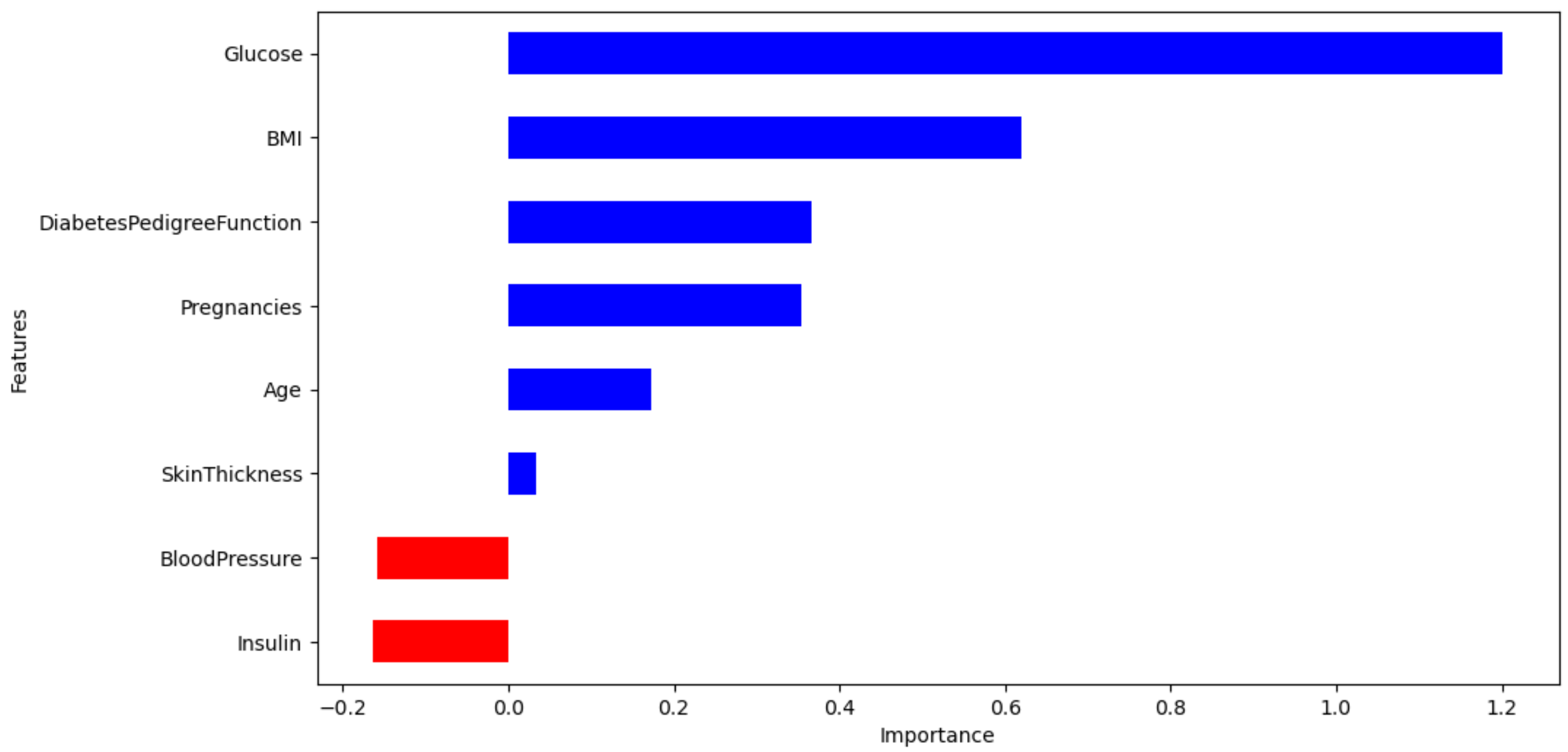
- 포도당, BMI 등은 결과 미치는 정도가 높다
- 혈압은 예측에 부정적인 영향을 준다



