목차
리액트 생명주기
리액트 컴포넌트의 생명주기(Lift Cycle)은 페이지가 렌더링 되기 전인 준비과정에서 시작하여 페이지에서 사라질 때 끝납니다.
리액트의 생명주기는 크게 3가지로 나눠집니다.
1. Mount : DOM이 생성되고 브라우저에 나타나는 것. 즉 페이지에 컴포넌트가 나타남
2. Update : 컴포넌트가 업데이터 되는것
3. UnMount : 컴포넌트를 DOM에서 제거하는 것. 즉 페이지에 컴포너트가 사라짐
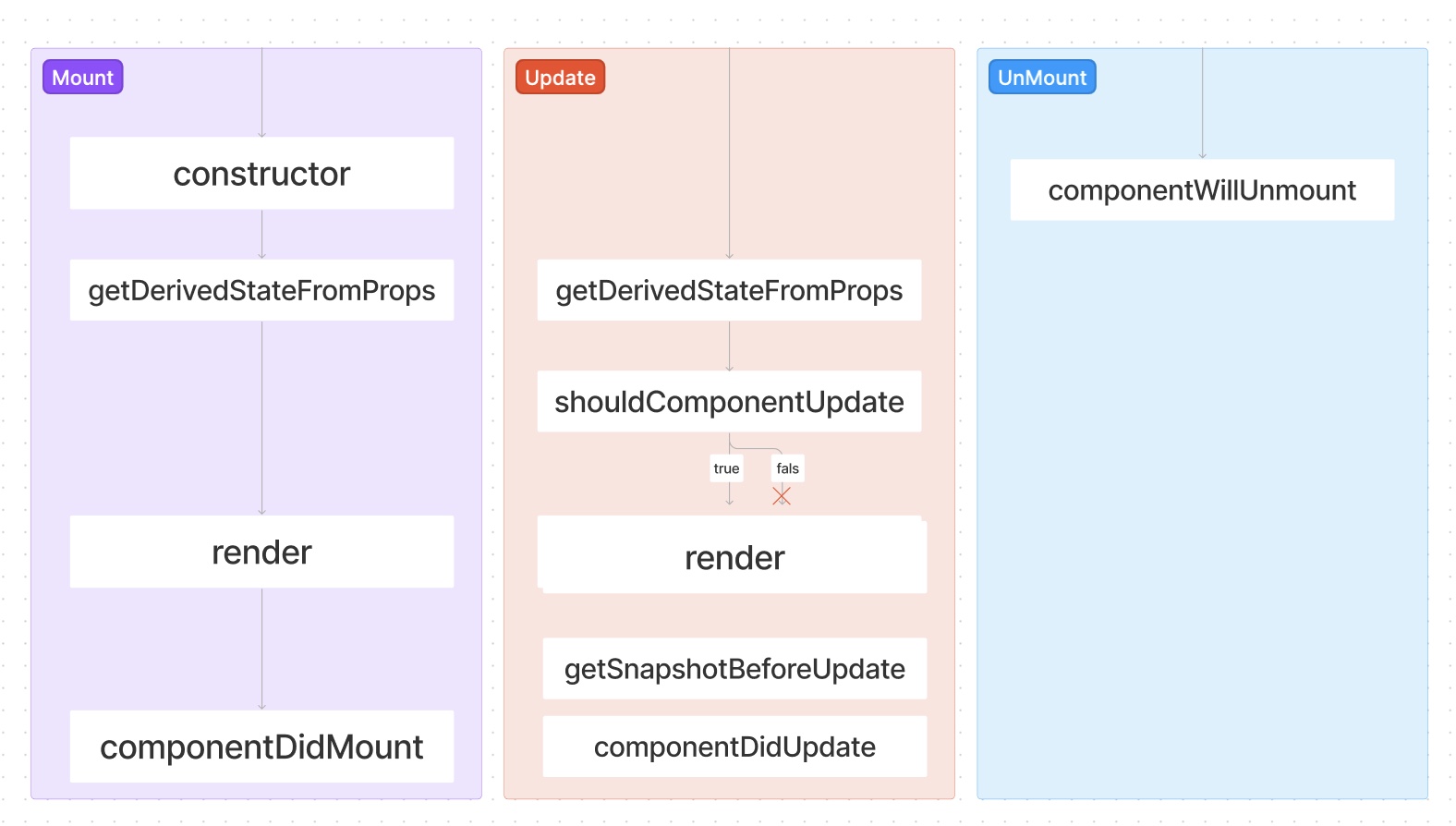
클래스형 컴포넌트 라이프 사이클
Mount
-
Constructor: 컴포넌트를 새로 만들 때마다 호출되는 클래스 생성자 메서드로서 초기 state값을 정할 수 있습니다. -
getDerivedStateFromProps: props로 받아온 값을 state에 동기화 시키는 용도로 사용하는 메서드이며, 컴포넌트가 마운트될 때, 업데이트될 때 호출됩니다. -
render: UI를 렌더링 하는 메서드이며, 이 메서드 안에서 this.props, this.state에 접근할 수 있습니다. -
componentDidMount: 컴포넌트가 브라우저상에 나타난 후 호출하는 메서드로서 DOM 정보를 가져오거나 state에 변화를 줄 때, 이벤트 등록, 프레임워크의 함수 호출, 비동기 작업 등을 처리하는데 사용합니다.
Update
컴포넌트가 업데이트 되는 경우는 총 4가지가 있습니다.
props가 바뀔 때state가 바뀔 때부모 컴포넌트가 리렌더링 될 때this.forceUpdate로 강제 렌더링 될 때
업데이트 시 사용하는 메서드는 아래와 같습니다.
-
getDerivedStateFromProps: props의 변화에 따라 state 값에도 변화를 주고싶을 때 사용합니다. -
shouldComponentUpdate: 컴포넌트가 리렌더링 할지 말지 결정하는 메서드로서 true,false를 반환하며 true를 반환하면 다음 라이프사이클 메서드를 계속 실행하고, false를 반환하면 작업을 중지합니다. -
render: 컴포넌트를 리렌더링 합니다. -
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate: 컴포넌트 변화를 DOM에 반영하기 바로 직전에 호출되는 메서드입니다. -
componentDidUpdate: 컴포넌트의 업데이트 작업이 끝난 후 호출하는 메서드입니다.
UnMount
componentWillUnMount: 컴포넌트가 브라우저상에서 사라지기 전에 호출하는 메서드이며, componentWillUnMount에서 등록한 이벤트, 타이머, 직접 생성한 DOM이 있을경우 여기서 제거 작업을 해야 합니다.
왜 제거작업을 할까요?
만약 제거 작업을 하지 않는다면 메모리 누수가 발생할 수 있습니다.
메모리 누수는 애플리케이션의 성능 저하나 예기치 않은 동작을 초래할 수 있으며, 장기적으로는 애플리케이션의 안정성과 사용자 경험에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
예를들어 타이머가 남아있는데, 제거하지 않았다면 불필요한 동작을 초래할 수 있기 때문에 제거 작업을 해주는것입니다.
이론 끝 실제로 사용하기
어떻게 작동하는지 console.log 찍어보겠습니다.
마운트 됐을때
- 생성자 -> props값을 상태값으로 동기화 -> render -> 컴포넌트가 브라우저에 나타난후 메서드 호출

업데이트 될때 1 (자식 컴포넌트 state값 변경시)
- props값을 상태값으로 동기화 -> 리렌더링 할지 말지 결정 -> render -> 컴포넌트 변화를 Dom에 반영하기 전 메서드 호출 -> 업데이트 후 메서드 호출

업데이트 될때 2 (부모 컴포넌트 리랜더링시)
- 부모 컴포넌트 리랜더링 -> props와 state 동기화 -> 리렌더링 할지 말지 결정 -> render -> 컴포넌트 변화를 Dom에 반영하기 전 메서드 호출 -> 업데이트 후 메서드 호출(snapshot, 이전 상태값, 현재상태값 등 확인)

코드는 아래와 같습니다.
import { Component } from 'react';
class LifeCycleTest extends Component {
state = {
number: 0,
color: null,
};
myRef = null;
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log('constructor');
}
// 이전 상태값,props와 현재 상태값,props를 동기화 하는 함수
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) {
console.log('getDerivedStateFromProps');
if (nextProps.color !== prevState.color) return { color: nextProps.color };
return null;
}
// 컴포넌트가 웹 브라우저상에서 나타난 뒤 호출되는 함수
componentDidMount() {
console.log('componentDidMount');
}
// 렌덜이 할지 말지 결정 하는 함수
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate');
return nextState.number % 10 !== 4;
}
// 컴포넌트가 웹 브라우저상에서 사라지기 전에 호출되는 메서드
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('componentWillUnmount');
}
// render를 통해 만들어진 결과물이 브라우저에 실제로 반영되기 직전에 호출되는 메서드
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log('getSnapshotBeforeUpdate');
if (prevProps.color !== this.props.color) return this.myRef.style.color;
return null;
}
// 업데이트가 끝난 직후 실행되는 메서드
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
console.log(`componentDidUpdate`);
if (snapshot) {
console.log(
`snapshot : ${snapshot},
this.state.color : ${this.hexToRgb(this.state.color)},
prevState.color : ${this.hexToRgb(prevState.color)}`
);
}
}
componentToHex(c) {
const hex = c.toString(16);
return hex.length === 1 ? '0' + hex : hex;
}
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({
number: this.state.number + 1,
});
};
handleReset = () => {
this.setState({
number: 0,
});
};
hexToRgb(hex) {
// HEX 색상 코드에서 불필요한 문자 제거
const sanitizedHex = hex.replace('#', '');
// HEX 색상 코드를 각각의 구성 요소로 분할
const r = parseInt(sanitizedHex.substr(0, 2), 16);
const g = parseInt(sanitizedHex.substr(2, 2), 16);
const b = parseInt(sanitizedHex.substr(4, 2), 16);
// RGB 구성 요소 반환
return `rgb(${r}, ${g}, ${b})`;
}
render() {
console.log('render');
const style = {
color: this.props.color,
};
return (
<div>
<h1 style={style} ref={(ref) => (this.myRef = ref)}>
{this.state.number}
</h1>
<p>color : {this.hexToRgb(this.state.color)}</p>
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>Click</button>
<button onClick={this.handleReset}>Reset</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default LifeCycleTest;
정리
아래의 사진은 컴포넌트의 라이프사이클 메서드 흐름을 파악하기 쉽게 표로 만들었습니다.