이 문제는 수학적으로 접근해서 한 번에 통과했지만, 구현 사고력을 기르기 위해 수학적으로 접근하지 않은 풀이를 했다가 많은 시행착오를 겪고 해결한 문제로서 기록으로 남기려 한다
우선 첫 번째로 한 큐에 통과한 코드는 아래와 같다.
def solution(n, a, b):
answer = 0
while a != b:
a, b = ((a - 1) // 2) + 1, ((b - 1) // 2) + 1
answer += 1
return answer토너먼트 형식이고 2명씩 묶었을 때 a와 b가 같은 위치(a == b)일 때 answer값을 구하도록 구현했다. 사실상 이렇게 접근한 것이 가장 빠른 실행시간을 보이는 것으로 판단된다.
첫 번째 풀이
- a와 b 중 누가 더 크다는 것이 없으므로
min과 max를 통해서 항상a < b의 관계를 보증한다. - 토너먼트 형식이므로 전체적인 시합 횟수는 log2n만큼이 되며, 아래 코드에서는
stage_number이다. (지금 생각해보니 round로 표기하는게 맞는 듯) - 하나의 stage(round)에서 2명씩 대결을 시킨다.
- a와 b가 만나면([a, b] == [first_player, second_player] 일 때) answer에 stage(round)값을 넣어주고 is_player_met flag를
true로 바꿔줌으로써 이중 loop 구문을 모두 탈출한다. - a와 b는 항상 이기므로(first_player in [a, b] or second_player in [a, b]) 다음 스테이지(temp_arr)로 진출시킨다.
- a와 b가 시합하지 않는 경우는 누가 이기던 상관없으므로 random한 사람이 이기도록 하여 다음 스테이지에 진출시킨다.
- a와 b가 만나면([a, b] == [first_player, second_player] 일 때) answer에 stage(round)값을 넣어주고 is_player_met flag를
- a와 b가 만날 때 까지 시합을 계속한다.
import math
import random
def solution(n, a, b):
answer = -1
is_player_met = False
players = [idx for idx in range(n)]
a, b = min(a, b) - 1, max(a, b) - 1
for stage_number in range(1, int(math.log(n, 2)) + 1):
temp_arr = []
while(len(players) > 1):
first_player, second_player = players.pop(0), players.pop(0)
# 첫 번째부터 붙을 때는 서로 붙어 있고 a < b로 상황을 만들었으므로
if [a, b] == [first_player, second_player]:
answer = stage_number
is_player_met = True
break
elif first_player in [a, b]:
temp_arr += [first_player]
elif second_player in [a, b]:
temp_arr += [second_player]
else:
temp_arr.append(random.choice([first_player, second_player]))
if is_player_met:
break
players = temp_arr
return answer두 번째 풀이
import math
import random
def solution(n, a, b):
answer = -1
is_player_met = False
players = [idx for idx in range(n)]
a, b = min(a, b) - 1, max(a, b) - 1
for stage_number in range(1, int(math.log(n, 2)) + 1):
temp_arr = []
for idx in range(0, len(players), 2):
first_player, second_player = players[idx], players[idx + 1]
if [a, b] == [first_player, second_player]:
answer = stage_number
is_player_met = True
break
elif first_player in [a, b]:
temp_arr += [first_player]
elif second_player in [a, b]:
temp_arr += [second_player]
else:
temp_arr += [random.choice([first_player, second_player])]
if is_player_met:
break
players = temp_arr
return answer
두 번째 풀이는 통과했다!!!
차이점은 이번 풀이에서는 배열에 random access를 하여 시간을 단축했다는 점이다. 지금까지 공부하면서 앞에서 pop하는 것에는 상당한 시간을 필요하다는 것 정도만 알았기 때문에 배열에 index로 바로 접근하게 하여 풀이에 성공하였다.하지만, 단순히 아는 정도에서 끝났기 때문에 이러한 점들을 고려하지 못하고 문제풀이에 들어가 한 큐에 성공하지 못한 원인이 되었다. 따라서 앞에서 pop하는 것은 왜 random access보다 시간이 오래 걸릴까에 대한 것은 여기에 정리해놓았다.
간단하게 정리만 하자면 normal array에서 앞에서 요소를 제거하는 것은 O(n)의 시간을 요구하지만 queue는 O(1)의 시간을 요구하기 때문이다.
세 번째 풀이
두 번째 풀이에서 random access로 문제를 풀었지만 원래 풀이대로해서 통과하고 싶었다.
찾아보니 이러한 경우에 from collections import deque를 통해서 구현할 수 있다.
python은 deque를 이용하면 되지만 javascript는 직접구현해야 하는 것으로 알고 있다.
from collections import deque
import math
import random
def solution(n, a, b):
answer = -1
is_player_met = False
players = deque([idx for idx in range(n)]) # ⭕️ deque로 바꿈
a, b = min(a, b) - 1, max(a, b) - 1
for stage_number in range(1, int(math.log(n, 2)) + 1):
temp_arr = deque([])
while(len(players) > 1):
# ⭕️ deque를 이용하여 앞에서 요소를 빼낼시 O(1)의 시간 복잡도를 가지게 구현
first_player, second_player = players.popleft(), players.popleft()
if [a, b] == [first_player, second_player]:
answer = stage_number
is_player_met = True
break
elif first_player in [a, b]:
temp_arr += [first_player]
elif second_player in [a, b]:
temp_arr += [second_player]
else:
temp_arr.append(random.choice([first_player, second_player]))
if is_player_met:
break
players = temp_arr
return answer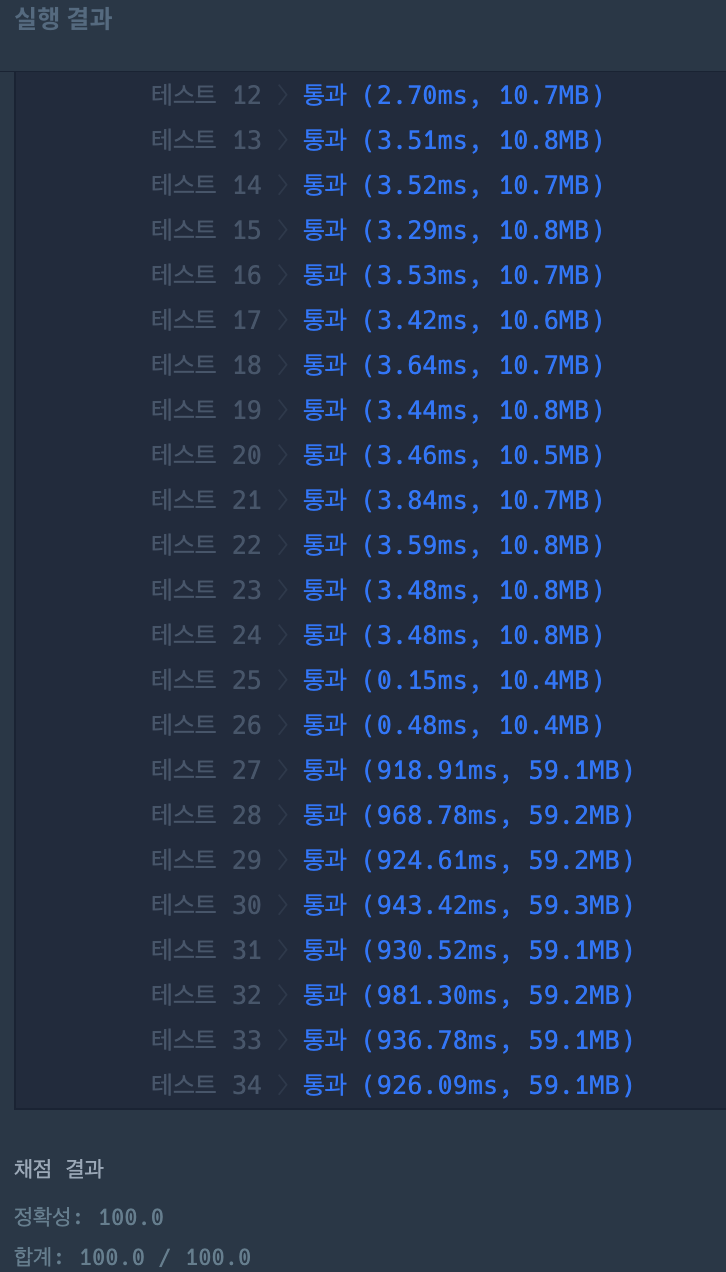
통과했다!!!🎉🥳
javascript 코드
compare array in javascript -> // TODO: javascript에서 배열을 비교하는 방법
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.first = null;
this.last = null;
this.size = 0;
}
enqueue(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (!this.first) {
this.first = this.last = newNode;
} else {
this.last.next = newNode;
this.last = newNode;
}
this.size++;
}
dequeue() {
const tempNode = this.first;
if (!this.first) return null;
if (this.first === this.last) this.last = null;
this.first = this.first.next;
this.size--;
return tempNode.value;
}
}
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
function solution(n, a, b)
{
let answer = 0;
let isMet = false;
const [A, B] = [Math.min(a, b) - 1, Math.max(a, b) - 1];
let players = new Queue();
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) players.enqueue(i);
for (let round = 1; round < Math.log2(n) + 1; round++){
const tempArr = new Queue();
while(players.size > 1){
const [firstPlayer, secondPlayer] = [players.dequeue(), players.dequeue()];
// compare array in javascript is different with in python language -> TODO -> over the linke i attached!!
if ([A, B].toString() === [firstPlayer, secondPlayer].toString()){
isMet = true;
answer = round;
break;
}else if ([A, B].includes(firstPlayer)){
tempArr.enqueue(firstPlayer)
}else if ([A, B].includes(secondPlayer)){
tempArr.enqueue(secondPlayer)
}else{
tempArr.enqueue(firstPlayer)
}
}
if (isMet) break;
players = tempArr;
}
return answer;
}마치며
개발 공부를 하면서 당장 에러나 막히는 부분에 봉착하게 되면 스트레스 받을 때도 있고 한 번 해보자는 거지라는 마음이 들거나 둘 중 하나다. 하지만, 해결했을 때 오는 성취감은 맛있다😋
아래는 javascirpt로 queue를 구현한 것과 왜 일반 배열에서는 앞에서 요소를 제거하고 넣는데 O(n)의 시간 복잡도를 가지는지 정리해놨다.
