13.1 텐서플로와 훈련 성능
13.1.1 성능 문제
GPU 사용 이유 : 모델 훈련 시에 파라미터 개수가 급격히 늘어나기 때문에 단일 프로세스로는 힘듦. 따라서, 컴퓨터 안에 포함된 작은 컴퓨터 클러스터로 생각할 수 있는 GPU를 이용해야 함
but, GPU에 머신 러닝 작업에 맞는 코드를 작성하는 일은 CUDA나 OpenCL에서 해야 하는데 편리한 환경이 아님. -> 텐서플로가 개발되어 해결!
13.1.2 텐서플로란?
텐서플로 : 머신 러닝과 딥러닝 알고리즘을 구현하고 실행하기 위한 프로그래밍 인터페이스로, 확장이 용이하고 다양한 플랫폼을 지원
- CUDA 기반의 GPU를 지원
- 텐서플로의 파이썬 API는 완전히 성숙되어 있음
- 텐서플로 기반의 TensorFlow.js와 텐서플로 라이트 : 머신 러닝 모델을 웹 브라우저와 모바일, IoT 장치에서 실행하고 배포하는 데 초점이 맞추어진 라이브러리
- 일련의 노드(0개 이상의 입력이나 출력을 가질 수 있는 연산)로 구성된 계산 그래프를 만듦 -> 이런 연산의 입력과 출력을 참조하기 위한 심벌릭 핸들로 텐서가 만들어짐
- 스칼라 - 랭크 0 텐서, 벡터 - 랭크 1 텐서, 행렬 - 랭크 2 텐서, 3차원 행렬 - 랭크 3 텐서 but, 텐서플로에서 실제 값은 넘파이 배열로 저장되고 텐서는 이 배열에 대한 참조를 제공
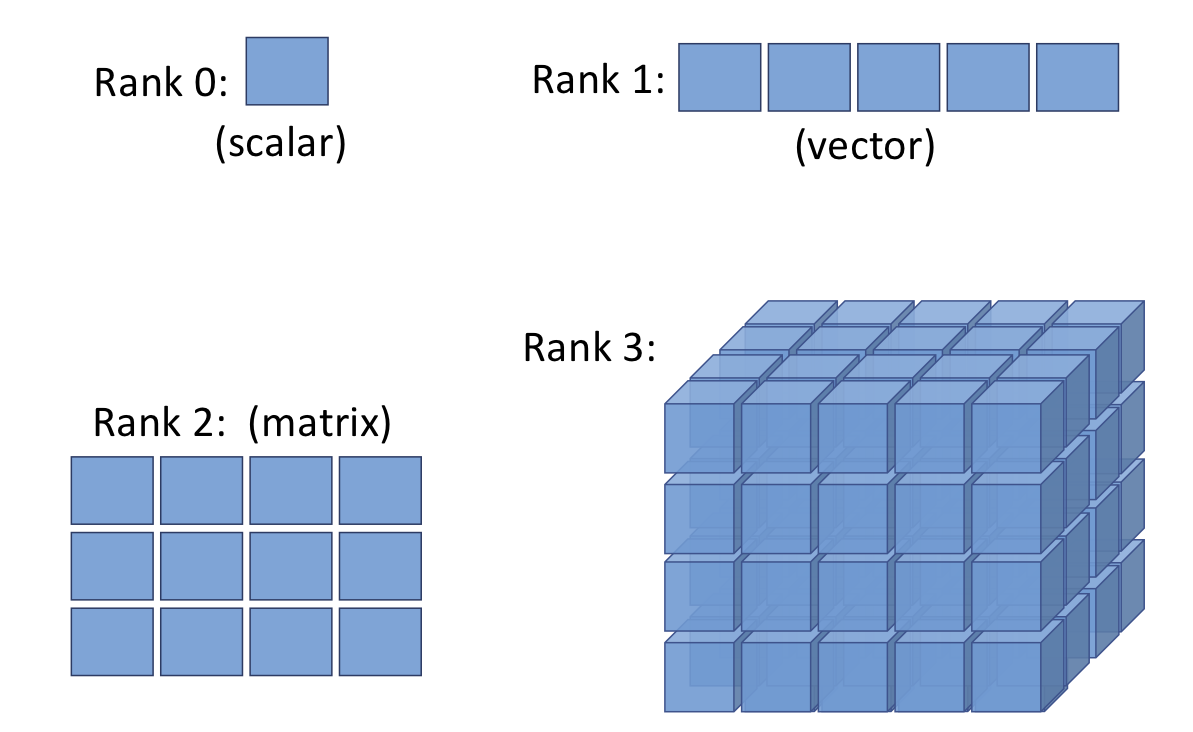
- 텐서플로 2.0 버전 : 유연성을 가진 동적인 계산 그래프를 기본으로 사용
13.1.3 텐서플로 학습 순서
1) 텐서플로의 프로그래밍 방식 : 텐서를 만들고 조작하는 방법
2) 데이터를 로드하는 방법
3) 데이터셋을 효율적으로 순환할 수 있는 텐서플로의 Dataset 객체 사용방법
4) tesorflow_datasets 모듈에 내장되어 제공하는 데이터셋에 대해 소개하고 사용법
5) tf.keras API를 소개하고 머신 러닝 모델 만들기
13.2 텐서플로 처음 시작하기
13.2.1 텐서플로 설치
☑️파이썬의 pip 인스톨러로 텐서플로 설치☑️
pip install tensorflow☑️버전을 명시하여 설치☑️
pip install tensorflow==[desired-version]☑️텐서플로 GPU 버전 설치☑️
pip install tensorflow-gpu☑️텐서플로 버전 확인☑️
python -c 'import tensorflow as tf; print(tf.__version__)'13.2.2 텐서플로에서 텐서 만들기
☑️함수를 사용하여 리스트나 넘파이 배열에서 텐서 만들기☑️
- tf.convert_to_tensor 함수 : 리스트나 넘파이 배열에서 텐서 만드는 함수
a = np.array([1, 2, 3], dtype=np.int32)
b = [4, 5, 6]
t_a = tf.convert_to_tensor(a)
t_b = tf.convert_to_tensor(b)
print(t_a)
print(t_b)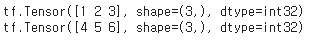
☑️속성 확인하기☑️
t_ones = tf.ones((2, 3))
t_ones.shape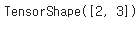
☑️텐서가 참조하는 값 얻기☑️
- numpy() 메서드 : 텐서가 참조하는 값 반환
t_ones.numpy()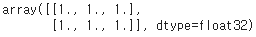
☑️상수 값을 가진 텐서 만들기☑️
const_tensor = tf.constant([1.2, 5, np.pi], dtype=tf.float32)
print(const_tensor)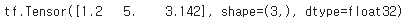
13.2.3 텐서의 데이터 타입과 크기 조작
☑️텐서의 데이터 타입 바꾸기☑️
- tf.cast 함수 : 텐서의 데이터 타입을 원하는 타입으로 바꿔줌
t_a_new = tf.cast(t_a, tf.int64)
print(t_a_new.dtype)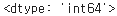
☑️텐서 전치하기☑️
- tf.transpose 함수 : 텐서 전치 해줌
t = tf.random.uniform(shape=(3, 5))
t_tr = tf.transpose(t)
print(t.shape, ' --> ', t_tr.shape)☑️텐서 크기 바꾸기☑️
ex) 1D 벡터에서 2D 배열로
- tf.reshape 함수 : 텐서 크기 바꿔줌
t = tf.zeros((30,))
t_reshape = tf.reshape(t, shape=(5, 6))
print(t_reshape.shape)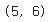
13.2.4 텐서에 수학 연산 적용
☑️두 개의 랜덤한 텐서 만들기 (균등 분포 & 표준 정규 분포 사용)☑️
tf.random.set_seed(1)
t1 = tf.random.uniform(shape=(5, 2),
minval=-1.0,
maxval=1.0)
t2 = tf.random.normal(shape=(5, 2),
mean=0.0,
stddev=1.0)☑️텐서 두 개 원소별 곱셈하기☑️
t3 = tf.multiply(t1, t2).numpy()
print(t3)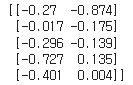
☑️텐서의 각 열 평균 계산☑️
t4 = tf.math.reduce_mean(t1, axis=0)
print(t4)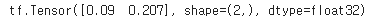
☑️텐서와 텐서의 행렬 곱셈 계산☑️
t5 = tf.linalg.matmul(t1, t2, transpose_b=True)
print(t5.numpy())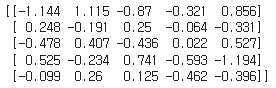
☑️텐서의 Lp 노름 계산☑️
- t1의 노름 L2을 계산
norm_t1 = tf.norm(t1, ord=2, axis=1).numpy()
print(norm_t1)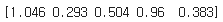
13.2.5 split(), stack(), concat() 함수
tf.split() : 입력된 텐서를 동일한 크기의 텐서 리스트로 나눔
- num_or_size_splits 매개변수 : 분할할 텐서 개수를 지정
- axis 매개변수 : 원하는 차원 지정
- 리스트 : 원하는 크기를 전달
☑️분할 개수 지정하기☑️
tf.random.set_seed(1)
t = tf.random.uniform((6,))
print(t.numpy())
t_splits = tf.split(t, 3)
[item.numpy() for item in t_splits]
➡️크기 6인 텐서가 크기 2인 텐서 세 개로 나누어짐
☑️다른 분할 크기 전달하기☑️
- 크기가 5인 텐서를 크기 3과 2인 텐서 두 개로 나누기
tf.random.set_seed(1)
t = tf.random.uniform((5,))
print(t.numpy())
t_splits = tf.split(t, num_or_size_splits=[3, 2])
[item.numpy() for item in t_splits]tf.stack() : 여러 개의 텐서를 쌓아서 하나의 텐서를 만들어주는 함수
tf.concat() : 여러 개의 텐서를 연결해서 하나의 텐서를 만들어주는 함수
☑️텐서 연결하기☑️
- 크기가 3이고 1로 채워진 1D 텐서 A & 크기가 2이고 0으로 채워진 1D 텐서 B를 연결 -> 크기가 5인 1D 텐서 C 만들기
A = tf.ones((3,))
B = tf.zeros((2,))
C = tf.concat([A, B], axis=0)
print(C.numpy())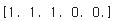
☑️텐서 쌓기☑️
- 텐서 A와 B의 크기가 모두 3일 때 쌓아서 2D 텐서 S 만들기
A = tf.ones((3,))
B = tf.zeros((3,))
S = tf.stack([A, B], axis=1)
print(S.numpy())
