Apply Sentry!
Why we need Client-Side Error log Tracking?
If an Error occurs, There are two ways to check client side errors.
1. Check the browser using a remote control machine.
2. Ask user to check the browser ;)
So, It is easier to check client errors without those situations as I mentioned!
What is the Sentry?
the Sentry is an error tracking service for Applications.
There are so many libraries available that can be used with Sentry.


And It also provides us with enough information.
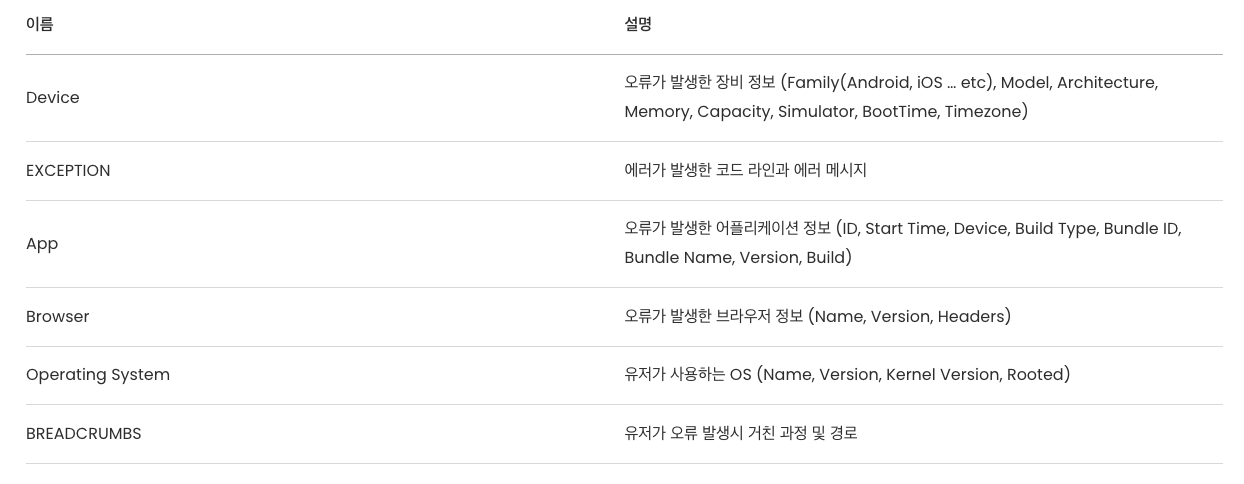
How can Apply Sentry?
Setting it up in our project is already written in our wiki!
Sentry options
import * as Sentry from "@sentry/react";
const causeCustomError = () => {
try {
throw new Error("Error");
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
Sentry.captureException(error); // Send this error to Sntry
Sentry.captureMessage("에러가 발생했습니다.");
}
};
{...}
return (
<div>
<button onClick={causeCustomError}> Custom Error</button>
</div>
);-
dsn : this is a key to send the event. this information is passed to SDK and should be stored in '.env' file.
-
release: the application's version
-
tracesSampleRate
-
replaysSessionSampleRate: Control the Session Replay rate
-
replaysOnErrorSampleRate: Control the Session Replay data rate
-
maxBreadcrumbs: Control the count of breadcrumbs
-
tracePropagationTargets: Setting the url target
Scope Error
the Scope allows us to add more information or modify it before an event capture occurs.
- configureScope
: to apply settings to all events on a global scope
Sentry.configureScope(function (scope) {
scope.setTag(userType, "admin");
scope.setUser({ email: "admin@example.com" });
});
Sentry.captureException(new Error("This is another error"));
- withScope
: to apply settings to a specific event on a specific scope
Sentry.withScope(function (scope) {
scope.setTag("page_locale", "en-US");
scope.setLevel(Sentry.Severity.Warning);
Sentry.captureException(new Error("This is an error"));
});these methodes below can also be used in Scope.
- setTag, setUser, setLevel, setExtras(extra data), addEventProcessor(modify an event)
Level
the Level setting indicates How serious the error is.
it can be used individual events or in Scope.
Sentry.captureMessage("디버그 레벨의 에러 발생", "debug");
Sentry.withScope(function (scope) {
scope.setLevel("fatal");
Sentry.captureException(new Error("매우 심각한 에러 발생"));
});Context
the context provides us with more information an event.
const causeNetworkError = async () => {
try {
const response = await fetch(
"https://api.causeNetworkError.com/causeNetworkError"
);
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error("Network error: " + response.statusText);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
Sentry.withScope((scope) => {
scope.setContext("apiInfo", {
url: "https://api.causeNetworkError.com/causeNetworkError",
method: "GET",
status: 401,
// (헤더, 파라미터 등의 추가정보 등록)
});
scope.setTag("errorType", "NetworkError"); // 태그 설정
scope.setLevel("fatal"); // 레벨 설정
Sentry.captureException(error); // 에러를 Sentry에 전송
});
}
};Fingerprint
the Fingerprint can group errors together.
Sentry.withScope((scope) => {
scope.setFingerprint([
originalRequest.method,
error.response?.status,
originalRequest.url,
]);
error.name = errorType;
Sentry.captureException(error);
});
Source Map
we can indentify the location of an error using the Sourch Map.
const { sentryWebpackPlugin } = require("@sentry/webpack-plugin");
module.exports = {
// ... other config above ...
devtool: "source-map",
plugins: [
sentryWebpackPlugin({
org: "example-org",
project: "example-project",
authToken: process.env.SENTRY_AUTH_TOKEN,
}),
],
};
references
https://teawon.github.io/react/Sentry/
