How Web Browsers Can Store Local Data?
web browsers can store local data using several methods to retain information on the client side.
Let's get information How web browers store local data.
1. Cookies
A cookies is small pieces of data sent from website and stored in user's web browser while the user is browsing.
-
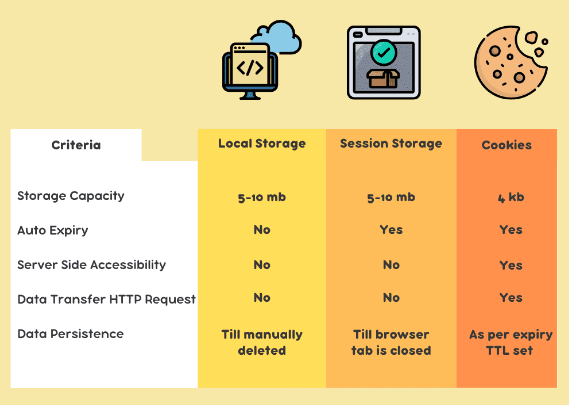
Storage Size: Limited size is usually around 4KB per cookie.
-
Accessibility: Accessible from both client-side and server-side. it sent with every HTTP request to the origination server. So they can affect performace and privacy.
they are sent to server, it is best way for server side session. -
Expiration: They have an expiration date. or when the browser is close, they are also removed.
-
Security: As I mentioned no.3 already, They have less secure as they are sent with every HTTP request, which can expose them to network sniffing. However, they can be made more secure with the HttpOnly and Secure flags.
-
Use Case: they are often used for session management, storing authentication token, user preferences that need to be sent to the server.
2. Local Storage
A more morden way of storing data that allows for large amounts of data to be stored locally with no expiration time.
-
Storage Size: Typically the max size of storing data is 5KB per domain.
-
Accessibility: The data is not sent to the server with each request. Data is stored only in client side.
-
Expiration: the Data is persistent until explicitly deleted by JS or user.
-
Security: it is more secure than cookies but still vulnerable to XSS attacks.
-
Use Case: it used for storing large amounts of data that do not need to be sent to the server with every request, such as user preferences, state of the application.
3. Session Storage
it has smaller capacity than Local Storage, but the data is only available for the duration of the page session. it means that the data is deleted when the page session ends, like closing the tab or browser.
Which one is more fit to store login information?
the cookies are generally bertter suited for storing login information (like session token).
the reason is below.
1. Server-Side Accessibility: Cookies allow the server to verify the user's authentication status on every request without additional effort.
2. Security Features: Cookies can use the 'HttpOnly' flag to prevent access from JS and the 'Secure' flag to ensure access from HTTPS only
3. Session Management: Cookies are inherently designed for session management. they are designed to be a mechanism for maintaining state between the client and server.
Local Storage can be used for login informaion, but it has issues below.
- Client Side only: Local storage is not accessible from the server side, so you would need to manually include authenticaton tokens in HTTP header.
- Persistent Storage: Tockens stored in local storage is persistent until removed. it can be a security risk.
- Security Risks: Local storage data is vulnerable to XSS attacks.
why cookies send with every HTTP request?
- session management
- Maintaining State: each HTTP request is independent and does not retain information about previous requests. Cookies help maintain state by storing session identifiers, which the server can use to recognize subsequent requests from the same client.
- Authentication: For authenticated sessions, cookies often store session tokens or identifiers. When a user logs in, the server sends a session token in a cookie. This cookie is sent back to the server with each subsequent request, allowing the server to identify the user and grant access to protected resources without requiring the user to log in again.
- Server-Side Management:
- Session Handling: Using cookies for session management simplifies the server-side handling of user sessions. The server can set and read cookies directly through HTTP headers without additional client-side scripting or handling. This uniform approach ensures consistent session management across various client requests.
