퍼셉트론: 가장 간단한 신경망
입력(x), 출력(y), 가중치(w), 절편(b)
⇒ y=f(wx+b) (➕ wx+b를 아핀 변환이라고도 부른다고…)
- 파이토치로 구현한 퍼셉트론
#퍼셉트론 기본 구조
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class Perceptron(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim):
'''
매개변수: input_dim(int) 입력 특성의 크기
'''
super(Perceptron, self).__init__()
self.fc1=nn.Linear(input_dim, 1)
def forward(self, x_in):
'''퍼셉트론의 정방향 계산 feed forward~~
매개변수: x_in (torch.Tensor) 입력 데이터 텐서
반환값: 결과 텐서.
'''
return torch.sigmoid(self.fc1(x_in)).squeeze()
#squeeze() -> 차원이 1인 부분 제거.(차원 축소..) vs unsqueeze() -> size 1인 차원 생성.활성화 함수
-
시그모이드
import torch import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x=torch.range(-5.,5.,0.1) y=torch.sigmoid(x) plt.plot(x.numpy(), y.numpy()) plt.show()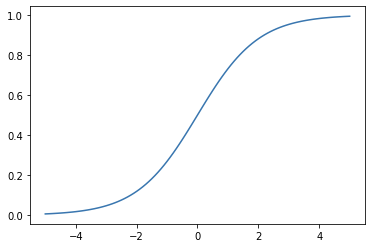
- 출력 : (0, 1)
- 출력 극단적 → 그레디언트 소실 문제(0이 됨) or 그레디언트 폭주 문제(발산) ⇒ 은닉층에서는 사용❌ 출력층에서만 사용. (특히 확률로 압축할 때.)
- 그레디언트 소실 문제: 시그모이드 함수에서 입력값이 조금만 작아지거나 커지면 기울기가 거의 0이어서 back propagation 할 때 기울기가 점점 0에 수렴하게 됨…
- 그레디언트 폭주 문제: 소실 문제와 반대로 입력이 0에 가까울때 기울기가 커서 발산하게 되는 것이 아닐지…
-
하이퍼볼릭 탄젠트
import torch import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x=torch.range(-5.,5.,0.1) y=torch.tanh(x) plt.plot(x.numpy(),y.numpy()) plt.show()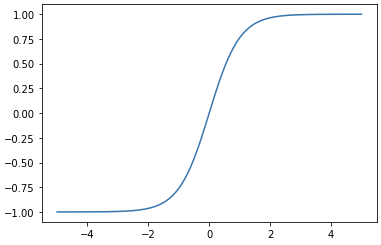
- 출력: [-1, +1]
- 시그모이드와 마찬가지로 그레디언트 소실 문제 발생.
-
렐루 (ReLU)
import torch import matplotlib.pyplot as plot relu=torch.nn.ReLU() x=torch.range(-5,5,0.1) y=relu(x) plt.plot(x.numpy(),y.numpy()) plt.show()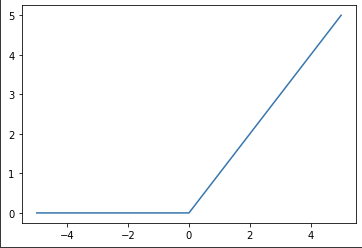
- 출력: [0, +inf)
- 입력값이 양수일 경우, 입력값에 상관없이 항상 미분값은 동일하게 1이다. ⇒ 역전파 과정에서의 그레디언트 소실 문제 해결 가능‼
- 다른 함수들에 비해 연산이 매우 단순… ⇒ 연산 속도 빠름‼
- 입력값이 음수일 경우 미분값이 0 → 역전파 과정에서 해당 뉴런 ☠ ‘죽어가는 ReLU’ ⇒ 대안 : LeakyReLU, PReLU
-
소프트맥스 (softmax)
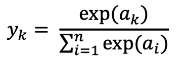
import torch.nn as nn import torch softmax=nn.Softmax(dim=1) x_input=torch.randn(1,3) y_output=softmax(x_input) print(x_input) print(y_output) print(torch.sum(y_output, dim=1)) #확률 분포라서 합이 1>>>
tensor([[-0.2528, -0.3826, -1.0988]]) tensor([[0.4334, 0.3806, 0.1860]]) tensor([1.])- 출력: [0, 1] → k개 클래스에 대한 이산 확률 분포 → 합이 1, 분류 작업 때 유용.. ➕ 보통 cross entropy와 함께 쓰임.
손실 함수
올바른 파라미터를 선택하도록 훈련 알고리즘을 도움.
-
평균 제곱 오차 (MSE)
- 회귀에서 주로 쓰임.
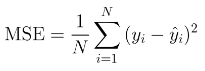
- 예측(^y)과 타깃값(y)의 차이 제곱 평균
- 유사 제품으로는 ~ 평균 절댓갑 오차(MAE)와 평균 제곱근 오차(RMSE)가 있습니다~
import torch import torch.nn as nn mse_loss=nn.MSELoss() outputs=torch.randn(3,5, requires_grad=True) targets=torch.randn(3,5) loss=mse_loss(outputs, targets) print(loss)>>>
tensor(2.3196, grad_fn=<MseLossBackward0>) -
범주형 크로스 엔트로피 (Cross Entropy)
- 클래스 소속 확률에 대한 예측 → 다중 분류 문제에 사용 (고양이? 개? 호랑이?)
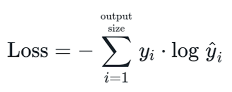
- in PyTorch.. 소프트맥스 + 크로스 엔트로피 ⇒ 크로스 엔트로피
log_softmax() + NLLLoss() = CrossEntropyLoss()import torch import torch.nn as nn ce_loss=nn.CrossEntropyLoss() outputs=torch.randn(3,5, requires_grad=True) #샘플 3개마다 5가지 클래스에 대한 확률값 targets=torch.tensor([1,0,3], dtype=torch.int64) #각 샘플의 정답 클래스 loss=ce_loss(outputs, targets) print(loss) -
이진 크로스 엔트로피 (Binary Cross Entropy, BCE)
- 이진 분류에 사용.
- 얘는 시그모이드랑 친한듯💕 시그모이드는 출력을 확률값(0~1사이)으로 만들고, 이를 정답과 비교할 때 BCE를 사용.
bce_loss=nn.BCELoss() sigmoid=nn.Sigmoid() probabilities=sigmoid(torch.randn(4,1,requires_grad=True)) #출력 targets=torch.tensor([1,0,1,0], dtype=torch.float32).view(4,1) #view=reshape (1,4)->(4,1) loss=bce_loss(probabilities, targets) print(probabilities) print(loss)>>>
tensor([[0.5639], [0.4057], [0.8600], [0.6237]], grad_fn=<SigmoidBackward0>) tensor(0.5554, grad_fn=<BinaryCrossEntropyBackward0>)
지도 학습 훈련 알아보기
나의 쁘띠한 그림실력..
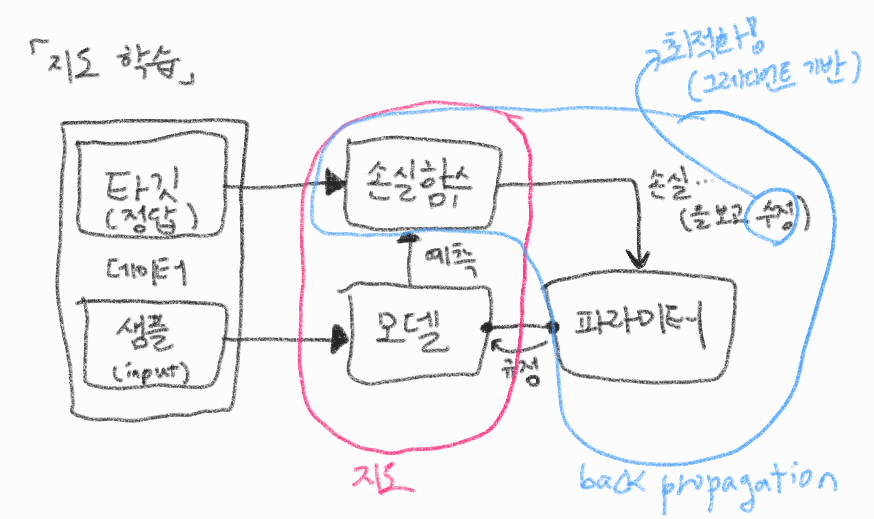
역전파(backpropagation) 알고리즘
- 지도 학습에서 훈련 데이터의 입력과 출력 쌍을 이용하여 모델 내부의 파라미터 값을 조정하는 과정
- 역전파 알고리즘을 이용하여 파라미터 값을 조정할 때는 손실 함수의 그레디언트를 최소화하는 방향으로 파라미터를 조정합니다.
미니배치(mini-batch) 학습
- 대부분의 경우, 모든 훈련 데이터를 한꺼번에 처리하지 않고, 작은 묶음으로 나누어 처리합니다.
- 이를 미니배치(mini-batch) 학습이라고 합니다.
- 미니배치를 사용하면, 모델의 파라미터를 더욱 효과적으로 업데이트할 수 있습니다.
참고
- 책 <파이토치로 배우는 자연어 처리>
