개요
iOS 와의 협업을 위해 로그인 기능을 Spring Boot3에서 REST API 로 만들고자 합니다. 이 과정을 기록합니다.
공부 중이므로 틀린 내용, 의견, 질문 있으시면 댓글 남겨주시면 감사하겠습니다.
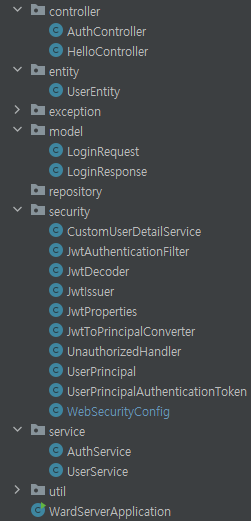
전체 구조
Testing
모든 endpoint 가 정상 작동하는지 mock 어노테이션을 이용하여 Test를 작성해봅니다. 또한 로그인 없이 다른 권한에 대한 endpoint를 테스트 하는 방법을 알아봅니다.
테스트 만드는 단축키
Windows에서는 일반적으로 Alt + Insert 키를 사용합니다. 따라서 IntelliJ IDEA에서 테스트 클래스를 만들려면:
1. 테스트를 작성하려는 클래스나 메서드에 커서를 놓습니다.
2. Alt + Insert 키를 누릅니다.
3. "Generate" 옵션을 선택합니다.
4. 그 다음에 "Test..."를 선택합니다.
5. 새로운 테스트 대화 상자에서 원하는 테스트 유형을 선택하고 확인을 누릅니다.
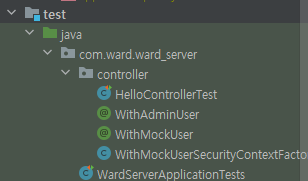
HelloControllerTest.java 작성
이 코드는 Spring Boot 애플리케이션에서 MockMvc를 사용하여 컨트롤러 테스트를 수행하는 JUnit 테스트입니다. 이 테스트는 HelloController의 / 엔드포인트에 대한 테스트 중 하나로, 모든 사용자가 이 엔드포인트에 접근할 수 있는지 확인합니다.
1. oneCanViewPublicEndpoint() Test 작성
이 테스트는 루트 경로에 대한 요청이 "Hello"를 포함하는 응답을 반환하는지 확인하고, 상태 코드가 "200 OK"인지 확인합니다.
1.1. 코드
package com.ward.ward_server.controller;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsStringIgnoringCase;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class HelloControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc api;
@Test
void anyoneCanViewPublicEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsStringIgnoringCase("Hello")));
}
}1.2. 방법
- api.perform(get("/")) 이거 작성하다가 get import 하려는데 적절한 get import 문 못 찾아서 직접 타이핑하여 추가헀습니다. (get 이 너무 많아서)
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*; .andExpect(status().isOk());여기서 status 의 import 문 추가import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
- containsStringIgnoringCase() 추가할 때 import hamcrest~~ 추가
1.3. 설명
- @AutoConfigureMockMvc
- 테스트에서 MockMvc 인스턴스를 자동으로 구성하도록 하는 어노테이션입니다.
- MockMvc를 사용하면 웹 애플리케이션을 테스트할 수 있습니다.
- @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
- 스프링 부트 테스트를 위한 어노테이션으로, 실제 서버를 시작하고 무작위 포트를 사용하여 웹 환경을 설정합니다.
- MockMvc를 사용하면 실제 서버 없이도 웹 컨트롤러를 테스트할 수 있습니다.
- @Autowired private MockMvc api;
- MockMvc 인스턴스를 필드로 주입합니다.
- api는 테스트에서 HTTP 요청을 수행하고 응답을 검증하는 데 사용됩니다.
- api.perform(get("/"))
- HTTP GET 요청을 수행합니다. 여기서는 루트 경로(/)로 요청합니다.
- perform 메서드는 ResultActions 객체를 반환합니다.
- .andExpect(status().isOk())
- 예상한 HTTP 상태 코드가 "200 OK" 인지 확인합니다.
- 즉, 요청이 성공적으로 처리되었음을 의미합니다.
- .andExpect(content().string(containsStringIgnoringCase("Hello")))
- 응답 본문에 "Hello" 문자열이 포함되어 있는지 확인합니다.
- containsStringIgnoringCase 메서드는 대소문자를 무시하고 지정된 문자열이 포함되어 있는지 확인합니다.
1.4. warning
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM warning: Sharing is only supported for boot loader classes because bootstrap classpath has been appended
테스트 가동 시 위와 같은 문구가 빨간색으로 떠서 실패한건가 했는데, 오류가 아니라 경고여서 무시하고 진행하여도 된다고 합니다.
2.notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeSecuredEndpoint() Test 추가
이 테스트는 인증되지 않은 사용자가 /secured 엔드포인트에 액세스하려고 시도할 때 "401 Unauthorized" 상태 코드가 반환되는지 확인합니다. 이는 해당 엔드포인트가 보호되어 있어 인증된 사용자만이 액세스할 수 있음을 의미합니다.
2.1. notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeSecuredEndpoint()코드
@Test
void notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/secured"))
.andExpect(status().isUnauthorized());
}2.1.1 설명
- @Test
JUnit 테스트 메서드를 나타내는 어노테이션입니다. - void notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception
테스트의 메서드 시그니처입니다. 테스트 메서드는 예외(Exception)을 던질 수 있습니다. - api.perform(get("/secured"))
HTTP GET 요청을 수행합니다. 여기서는 보호된 엔드포인트(/secured)로 요청합니다.
perform 메서드는 ResultActions 객체를 반환합니다. - .andExpect(status().isUnauthorized())
예상한 HTTP 상태 코드가 "401 Unauthorized" 인지 확인합니다.
즉, 요청이 인증되지 않아 액세스가 거부되었음을 의미합니다.
2.2. 방법
처음 그냥 이렇게만 코드 작성하면 403에러가 뜹니다. 이를 해결하기 위해 unauthorized Handler 라고 불리는 것을 security 패키지에 추가합니다.
2.3. UnauthorizedHandler.java 추가
2.3.1. UnauthorizedHandler 코드
package com.ward.ward_server.security;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.AuthenticationEntryPoint;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
@Component
public class UnauthorizedHandler implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED, authException.getMessage());
}
}2.3.2. 설명
이 코드는 Spring Security의 AuthenticationEntryPoint를 구현한 UnauthorizedHandler 클래스입니다. 이 클래스는 인증되지 않은 사용자가 보호된 리소스에 액세스하려고 할 때 호출됩니다. 주요 메서드와 역할에 대한 설명은 다음과 같습니다:
-
public class UnauthorizedHandler implements AuthenticationEntryPoint
- AuthenticationEntryPoint를 구현한 클래스입니다. 이 인터페이스는 인증이 필요한 엔드포인트에 접근할 때 호출되는 메서드를 정의합니다.
-
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException
- commence 메서드는 사용자의 인증이 실패하거나 인증되지 않은 상태에서 보호된 리소스에 액세스하려고 할 때 호출됩니다.
- HttpServletRequest와 HttpServletResponse는 현재 요청 및 응답에 대한 정보를 나타냅니다.
- AuthenticationException은 인증 예외에 대한 정보를 제공합니다.
-
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED, authException.getMessage())
- HTTP 응답으로 "401 Unauthorized" 상태 코드를 반환합니다.
- authException.getMessage() 를 통해 예외 메시지를 응답에 포함시킵니다.
이러한 방식으로, 클라이언트가 인증되지 않은 상태에서 보호된 리소스에 액세스하려고 할 때 이 핸들러가 호출되어 적절한 응답을 생성합니다.
2.4. WebSecurityConfig 수정
2.4.1. 코드
package com.ward.ward_server.security;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configurers.AbstractHttpConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class WebSecurityConfig {
private final JwtAuthenticationFilter jwtAuthenticationFilter;
private final CustomUserDetailService customUserDetailService;
private final UnauthorizedHandler unauthorizedHandler;
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain applicationSecurity(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
http
.cors(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.securityMatcher("/**") // map current config to given resource path
.sessionManagement(sessionManagementConfigurer
-> sessionManagementConfigurer.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS))
.formLogin(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.exceptionHandling()
.authenticationEntryPoint(unauthorizedHandler)
.and()
.authorizeHttpRequests(registry -> registry // 요청에 대한 권한 설정 메서드
.requestMatchers("/").permitAll() // / 경로 요청에 대한 권한을 설정. permitAll() 모든 사용자, 인증되지않은 사용자에게 허용
.requestMatchers("/auth/login").permitAll()
.requestMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 다른 나머지 모든 요청에 대한 권한 설정, authenticated()는 인증된 사용자에게만 허용, 로그인해야만 접근 가능
);
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManager(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
return http.getSharedObject(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class)
.userDetailsService(customUserDetailService)
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder())
.and().build();
}
}2.4.2. 설명
- .exceptionHandling()
- 예외 처리를 위한 구성 옵션을 설정합니다.
- .authenticationEntryPoint(unauthorizedHandler)
- unauthorizedHandler를 사용하여 사용자가 인증되지 않은 상태에서 보호된 리소스에 액세스하려고 할 때 호출되는 커스텀 AuthenticationEntryPoint를 설정합니다.
- unauthorizedHandler는 commence 메서드에서 401 Unauthorized 응답을 생성하고, 필요에 따라 추가적인 메시지를 제공합니다.
여기까지 하면 테스트 통과
3. @Test loggedIn_shouldSeeSecuredEndpoint() 추가
3.1. 코드
package com.ward.ward_server.controller;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsStringIgnoringCase;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class HelloControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc api;
@Test
void anyoneCanViewPublicEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsStringIgnoringCase("Hello")));
}
@Test
void notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/secured"))
.andExpect(status().isUnauthorized());
}
@Test
void loggedIn_shouldSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/secured"))
.andExpect(status().isOk());
}
}3.2. 추가된 부분
@Test
void loggedIn_shouldSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/secured"))
.andExpect(status().isOk());
}3.3. 설명
-
@Test 어노테이션:
JUnit에서 테스트 메소드를 나타내는 어노테이션입니다. 해당 메소드는 단위 테스트를 수행하는 메소드임을 나타냅니다. -
loggedIn_shouldSeeSecuredEndpoint 메소드:
로그인한 사용자가 "/secured" 엔드포인트에 접근했을 때의 테스트를 정의한 메소드입니다. -
api.perform(get("/secured")):
MockMvc 객체(api)를 사용하여 "/secured" 엔드포인트에 대한 GET 요청을 수행합니다. -
.andExpect(status().isOk()):
수행한 요청에 대한 응답을 검증합니다.
status().isOk() 는 HTTP 응답의 상태코드가 200 (OK) 인지 확인하는 기대값입니다.
4. WithMockUserSecurityContextFactory 추가
-
loggedIn_shouldSeeSecuredEndpoint() 는 로그인한 사용자 테스트 하는건데 어떻게 로그인 시켜서 테스트해보지? 이를 위해 utilities 가 있다.
-
WithMocUser.java 에서 사용하기 위해서 만듭니다.
-
createSecurityContext 메소드에서는 주어진 WithMockUser 어노테이션을 기반으로 사용자의 SecurityContext를 생성하면 됩니다. 이 부분은 테스트에서 @WithMockUser 어노테이션을 사용하여 특정 사용자 정보를 가지고 테스트를 수행할 때 사용됩니다.
4.1. 코드
package com.ward.ward_server.controller;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext;
import org.springframework.security.test.context.support.WithMockUser;
import org.springframework.security.test.context.support.WithSecurityContextFactory;
public class WithMockUserSecurityContextFactory implements WithSecurityContextFactory<WithMockUser> {
@Override
public SecurityContext createSecurityContext(WithMockUser annotation) {
return null;
}
}
4.2. 주의
WithMockUser import 할 때 내가 갖고 있는 WithMockUser 로 신경쓰기
4.3. 설명
- WithMockUserSecurityContextFactory 클래스:
- WithSecurityContextFactory<WithMockUser.> 를 구현하는 클래스로, @WithMockUser 어노테이션을 사용하는 테스트에서 사용자 인증 정보를 설정합니다.
- createSecurityContext 메소드:
- WithSecurityContextFactory 인터페이스에서 상속받은 메소드로, @WithMockUser 어노테이션의 값을 기반으로 사용자의 보안 컨텍스트(SecurityContext) 를 생성합니다.
- WithMockUser 어노테이션:
- Spring Security 테스트에서 사용되며, 해당 어노테이션을 사용하면 테스트 메소드가 실행될 때 임의의 사용자 인증 정보를 제공할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, @WithMockUser(username = "testuser", roles = {"USER"}) 와 같이 사용하여 특정 사용자의 역할을 지정할 수 있습니다.
- Spring Security 테스트에서 사용되며, 해당 어노테이션을 사용하면 테스트 메소드가 실행될 때 임의의 사용자 인증 정보를 제공할 수 있습니다.
- SecurityContext 클래스:
- Spring Security에서 사용자의 보안 정보를 나타내는 클래스입니다.
사용자의 권한, 인증 여부 등을 저장하고 관리합니다.
- Spring Security에서 사용자의 보안 정보를 나타내는 클래스입니다.
5. WithMocUser 추가
5.1. 코드
package com.ward.ward_server.controller;
import org.springframework.security.test.context.support.WithSecurityContext;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@WithSecurityContext(factory = WithMockUserSecurityContextFactory.class)
public @interface WithMockUser {
long userId() default 1L;
String[] authorities() default "ROLE_USER";
}5.2. 설명
WithMockUser 어노테이션은 Spring Security 테스트에서 사용자의 가짜(Mock) 정보를 지정하기 위한 커스텀 어노테이션으로 보입니다. 여기에 대한 간단한 설명은 다음과 같습니다:
- WithMockUser 어노테이션:
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME): 이 어노테이션의 유지 정책을 실행 시간까지로 설정합니다.
- @WithSecurityContext(factory = WithMockUserSecurityContextFactory.class): 해당 어노테이션을 해석할 때 사용할 SecurityContext를 생성하는 팩토리 클래스를 지정합니다. 여기서는 WithMockUserSecurityContextFactory 클래스가 사용됩니다.
- long userId() default 1L;: 가짜 사용자의 ID를 지정하는 속성으로, 기본값은 1L입니다.
- String[] authorities() default "ROLE_USER";: 가짜 사용자의 권한을 지정하는 속성으로, 기본값은 "ROLE_USER"입니다.
이 어노테이션을 사용하면 테스트 클래스나 메소드에 해당 어노테이션을 추가하여 특정 사용자 정보를 설정할 수 있습니다.
6. 다시 WithMockUserSecurityContextFactory
WithMockUserSecurityContextFactory 클래스는 @WithMockUser 애너테이션을 사용하여 테스트에서 사용자를 모의로 생성하는 데 도움을 주는 역할을 합니다.
6.1. 코드
package com.ward.ward_server.controller;
import com.ward.ward_server.security.UserPrincipal;
import com.ward.ward_server.security.UserPrincipalAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContext;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.test.context.support.WithSecurityContextFactory;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class WithMockUserSecurityContextFactory implements WithSecurityContextFactory<WithMockUser> {
@Override
public SecurityContext createSecurityContext(WithMockUser annotation) {
var authorities = Arrays.stream(annotation.authorities())
.map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new)
.toList();
var principle= UserPrincipal.builder()
.userId(annotation.userId())
.email("fake@email.com")
.authorities(authorities)
.build();
var context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication(new UserPrincipalAuthenticationToken(principle));
return context;
}
}
6.2. 설명
이 클래스는 WithSecurityContextFactory를 구현하고 있어서, @WithMockUser 애너테이션이 테스트 메서드에 사용될 때 해당 애너테이션의 속성들을 기반으로한 SecurityContext를 생성합니다.
createSecurityContext 메서드에서는 주어진 @WithMockUser 애너테이션으로부터 받은 정보들을 사용하여 사용자의 권한과 주요 정보를 갖는 UserPrincipal 객체를 만들고, 이를 SecurityContext에 설정합니다. 그 후, SecurityContextHolder를 사용하여 이 SecurityContext를 현재의 보안 컨텍스트로 설정합니다.
이것은 테스트에서 @WithMockUser 애너테이션을 사용하여 가짜 사용자를 생성하고, 이를 기반으로 보안 컨텍스트를 설정하여 서비스의 보안 기능을 테스트하는 데 유용합니다.
7. HelloControllerTest.java 수정
7.1.코드
package com.ward.ward_server.controller;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsStringIgnoringCase;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class HelloControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc api;
// 어떤 요청에도 HTTP 상태코드 200, HELLO 가 포함되어있는지 테스트
@Test
void anyoneCanViewPublicEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsStringIgnoringCase("Hello")));
}
// 인증되지 않은 사용자 접근에 HTTP 상태코드 401인지 테스트
@Test
void notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/secured"))
.andExpect(status().isUnauthorized());
}
// 로그인한 사용자가 접근했을 때 HTTP응답의 상태코드가 200 OK 인지 확인하는 테스트
@Test
@WithMockUser
void loggedIn_shouldSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/secured"))
.andExpect(status().isOk());
}
}7.2. 추가된 부분
@ WithMockUser어노테이션 한 줄 추가 됐습니다.
@Test
@WithMockUser
void loggedIn_shouldSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/secured"))
.andExpect(status().isOk());
}7.3. 설명
여기까지 하고 Test 돌리면 Test Pass 해야됩니다.
8. HelloControllerTest 추가 작성
8.1. 코드
package com.ward.ward_server.controller;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsStringIgnoringCase;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class HelloControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc api;
// 어떤 요청에도 HTTP 상태코드 200, HELLO 가 포함되어있는지 테스트
@Test
void anyoneCanViewPublicEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsStringIgnoringCase("Hello")));
}
// 로그인 안 한 사용자가 접근했을 때 HTTP 상태코드 401인지 테스트
@Test
void notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/secured"))
.andExpect(status().isUnauthorized());
}
// 로그인한 사용자가 접근했을 때 HTTP응답의 상태코드가 200 OK 인지, 작성한 test 포함하는지 확인하는 테스트
@Test
@WithMockUser
void loggedIn_shouldSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/secured"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsStringIgnoringCase("User ID: 1")));
}
// 로그인 안하고 /admin 접근할 때 401
@Test
void notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeAdminEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/admin"))
.andExpect(status().isUnauthorized());
}
//로그인 하고 ROLE_USER 일 때, /admin 접근 제한
@Test
@WithMockUser
void simpleUser_shouldNotSeeAdminEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/admin"))
.andExpect(status().isForbidden());
}
// 로그인하고 ROLE_ADMIN 일 때, /admin 접근 성공+ 작성한 문구 포함 확인
@Test
@WithMockUser(authorities = "ROLE_ADMIN")
void admin_shouldSeeAdminEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/admin"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsStringIgnoringCase("User ID: 1")));
}
}8.2. 설명
-
anyoneCanViewPublicEndpoint: 누구나 접근 가능한 엔드포인트("/")에 대한 테스트로, HTTP 응답 상태 코드가 200이며 응답 본문에 "Hello"가 포함되어 있는지 확인합니다.
-
notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeSecuredEndpoint: 로그인하지 않은 사용자가 /secured 엔드포인트에 접근할 때 401 Unauthorized 코드를 기대하는 테스트입니다.
-
loggedIn_shouldSeeSecuredEndpoint: @WithMockUser 애너테이션을 사용하여 모의 사용자를 생성하고, 이 사용자가 /secured 엔드포인트에 접근할 때 200 OK 코드를 기대하며 응답 본문에 "User ID: 1"이 포함되어 있는지 확인하는 테스트입니다.
-
notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeAdminEndpoint: 로그인하지 않은 사용자가 /admin 엔드포인트에 접근할 때 401 Unauthorized 코드를 기대하는 테스트입니다.
-
simpleUser_shouldNotSeeAdminEndpoint: @WithMockUser 애너테이션을 사용하여 모의 사용자를 생성하고, 이 사용자가 /admin 엔드포인트에 접근할 때 403 Forbidden 코드를 기대하는 테스트입니다.
-
admin_shouldSeeAdminEndpoint: @WithMockUser 애너테이션을 사용하여 권한이 "ROLE_ADMIN"인 모의 사용자를 생성하고, 이 사용자가 /admin 엔드포인트에 접근할 때 200 OK 코드를 기대하며 응답 본문에 "User ID: 1"이 포함되어 있는지 확인하는 테스트입니다.
9. HelloController 개선
@WithMockUser(authorities = "ROLE_ADMIN") -> @WithAdminUser** 변경. 많이 써서 반복된다면 짧게 사용가능하도록 변경합니다.
9.1. 코드
package com.ward.ward_server.controller;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsStringIgnoringCase;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
class HelloControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc api;
// 어떤 요청에도 HTTP 상태코드 200, HELLO 가 포함되어있는지 테스트
@Test
void anyoneCanViewPublicEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsStringIgnoringCase("Hello")));
}
// 로그인 안 한 사용자가 접근했을 때 HTTP 상태코드 401인지 테스트
@Test
void notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/secured"))
.andExpect(status().isUnauthorized());
}
// 로그인한 사용자가 접근했을 때 HTTP응답의 상태코드가 200 OK 인지, 작성한 test 포함하는지 확인하는 테스트
@Test
@WithMockUser
void loggedIn_shouldSeeSecuredEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/secured"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsStringIgnoringCase("User ID: 1")));
}
// 로그인 안하고 /admin 접근할 때 401
@Test
void notLoggedIn_shouldNotSeeAdminEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/admin"))
.andExpect(status().isUnauthorized());
}
//로그인 하고 ROLE_USER 일 때, /admin 접근 제한
@Test
@WithMockUser
void simpleUser_shouldNotSeeAdminEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/admin"))
.andExpect(status().isForbidden());
}
// 로그인하고 ROLE_ADMIN 일 때, /admin 접근 성공+ 작성한 문구 포함 확인
@Test
@WithAdminUser
void admin_shouldSeeAdminEndpoint() throws Exception {
api.perform(get("/admin"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsStringIgnoringCase("User ID: 1")));
}
}9.2.1 수정한 부분
- @WithMockUser(authorities = "ROLE_ADMIN") 을 @WithAdminUser: 로 변경했습니다. Admin 권한의 MockUser 어노테이션을 많이 써야된다면 긴거 반복해야되니까 수정합니다.
이를 위해 WithAdminUser 를 생성해줍니다.
9.2.2. WithAdminUser 어노테이션 생성
package com.ward.ward_server.controller;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@WithMockUser(authorities = "ROLE_ADMIN")
public @interface WithAdminUser {
}
마무리
SB3 환경에서의 Spring Security 기초가 끝났습니다. 여기서 확장해서 쓰면 됩니다.
