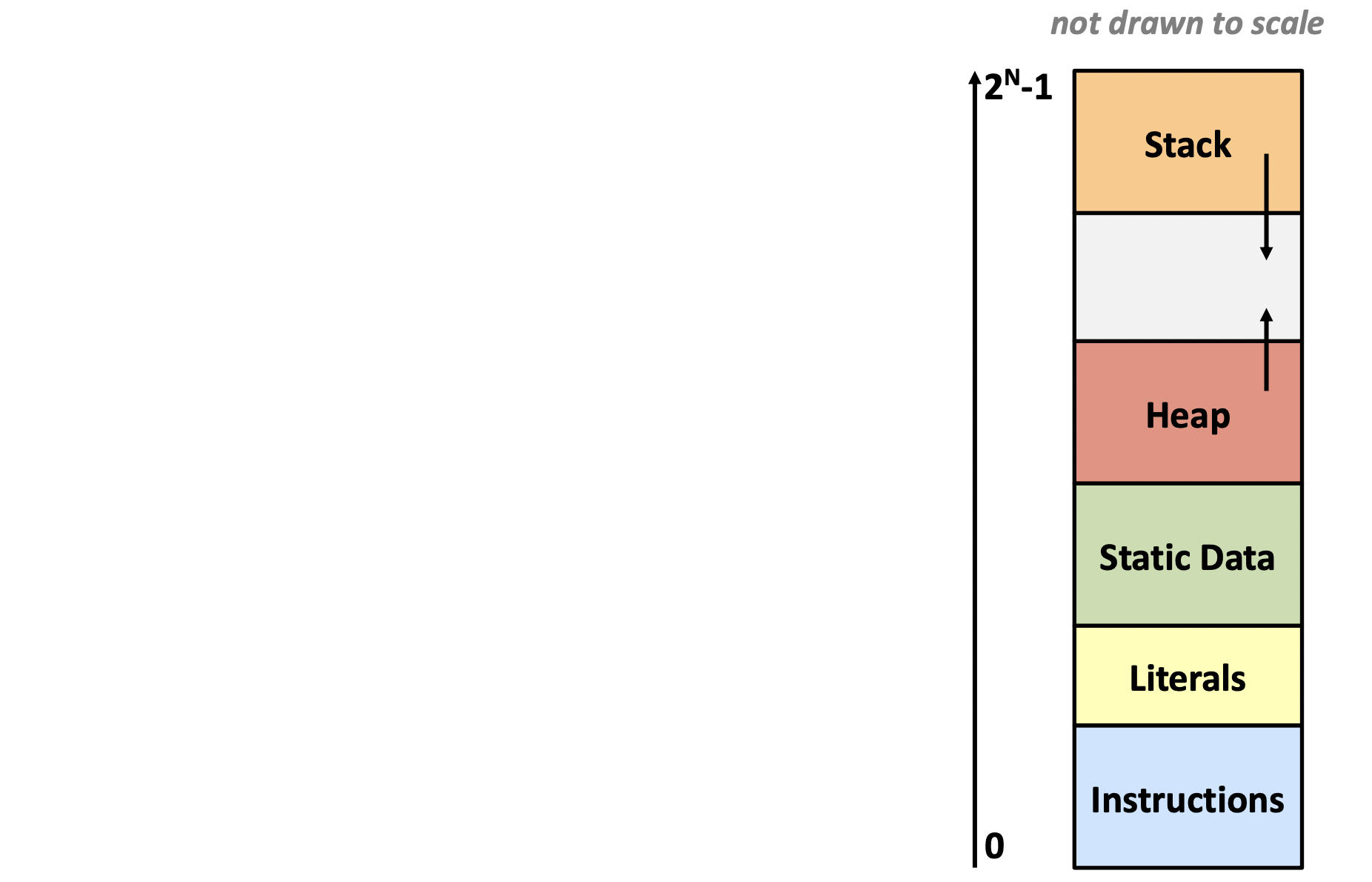
Address space layout
General Memory Layout
- Stack
- local variables
- Heap
- Dynamically allocated as needed
malloc(), calloc(), new, ...
- Statically allocated Data
- Read/Write : global variables (Static Data)
- Read-only : string literals (Literals)
- Code / Instructions
- Executable machine instructions
- Read-only
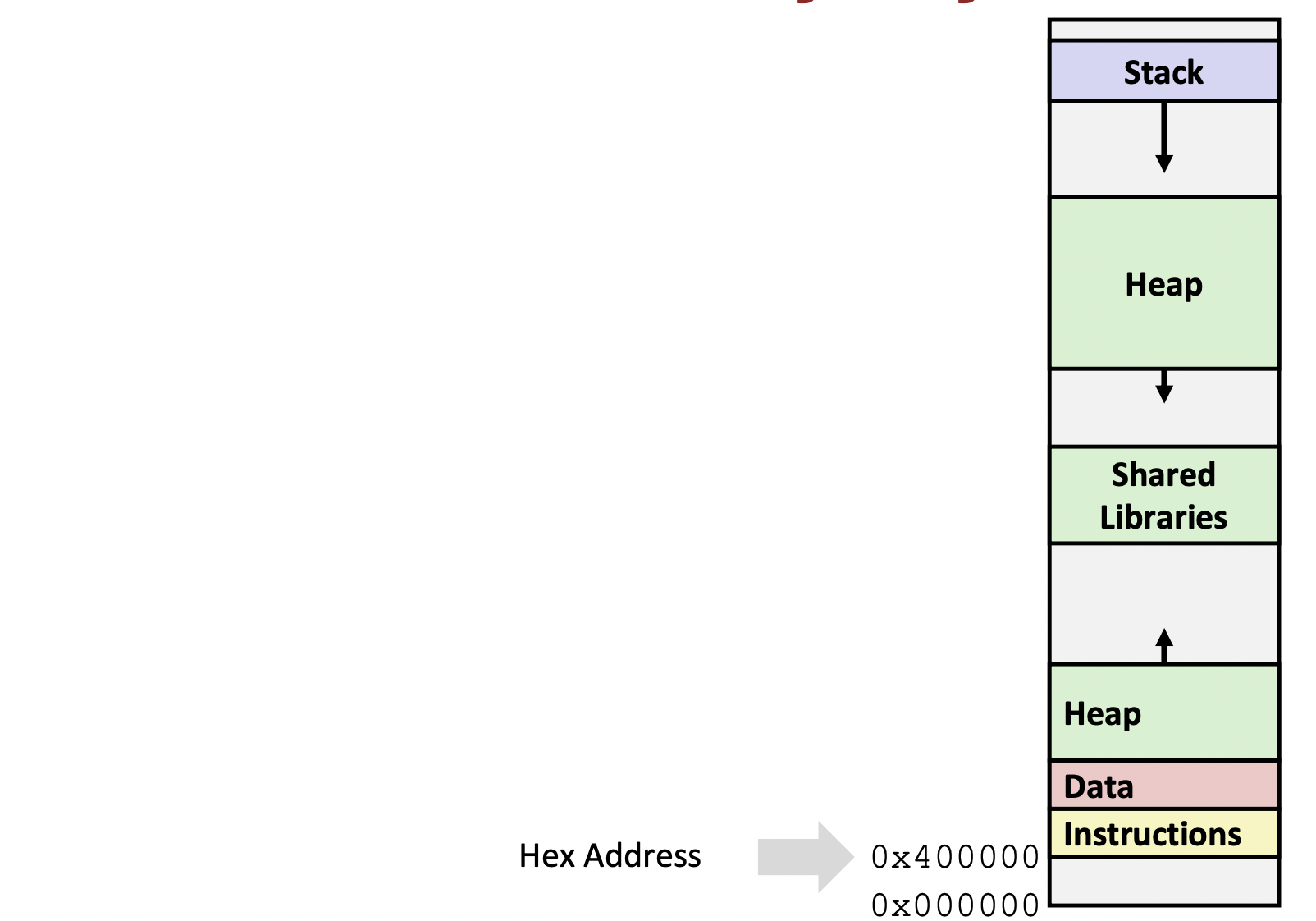
x86-64 Linux Memory Layout
- Stack
- local variables
- Heap
- Dynamically allocated as needed
malloc(), calloc(), new, ...
- Statically allocated Data
- Read/Write : global variables (Static Data)
- Read-only : string literals (Literals)
- Code / Instructions
- Executable machine instructions
- Read-only
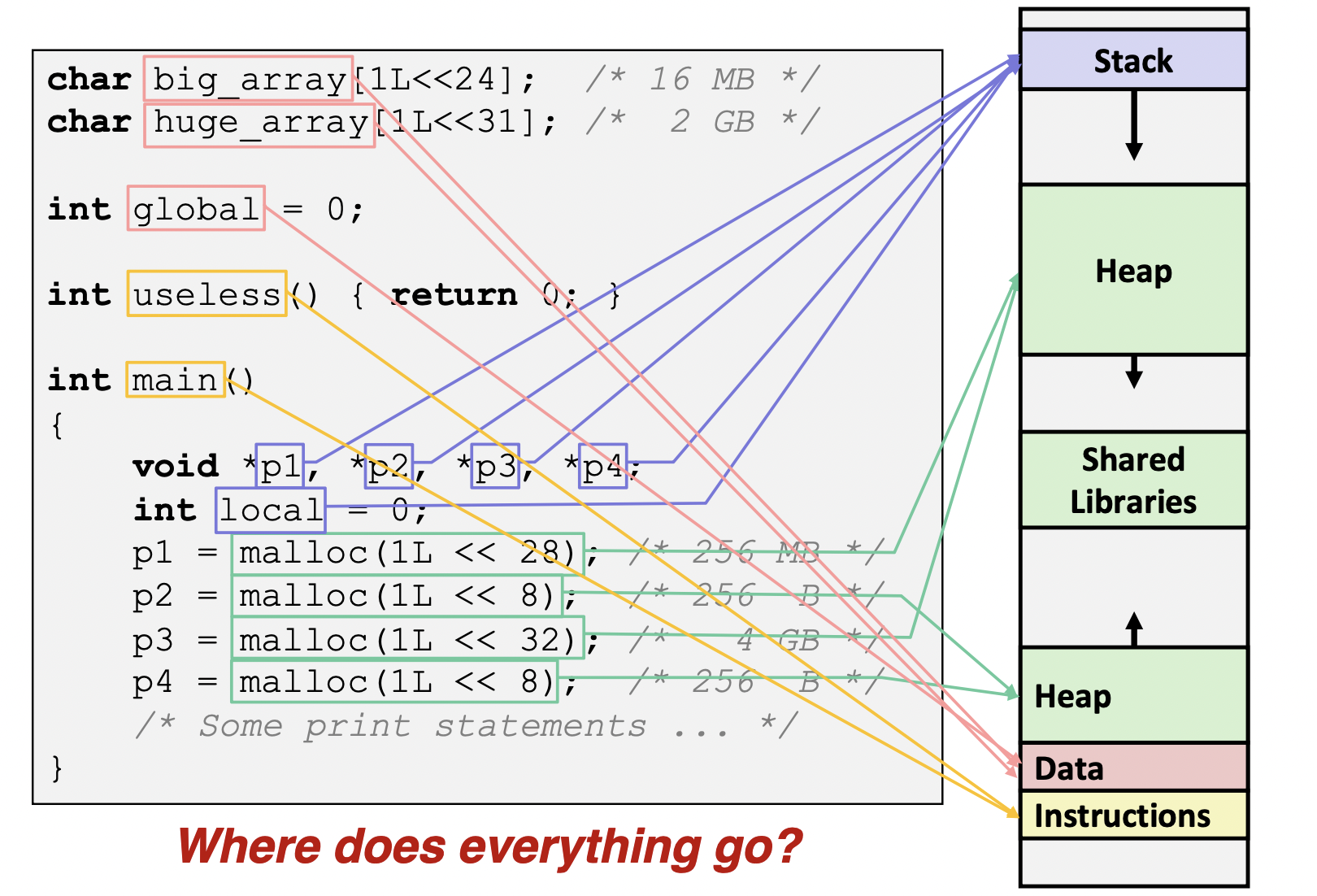
Memory Allocation Example
Input buffers on the stack
What is a Buffer?
- A buffer is an array used to temporarily store data
- Buffers can also store user input
x86-64/Linux Stack Frame
- Caller's Stack Frame
- Arguments (if more than 6 args) for this call
- Current / Callee Stack Frame
- Return address (pushed by
callinstruction) - Old frame pointer (optional)
- Caller-saved pushed before setting up arguments for a function call
- Callee-saved pushed before using long-term registers
- Local variables (if can't be kept in registers)
- "Argument build" area
(need to call a function with >6 arguments? Put them here)
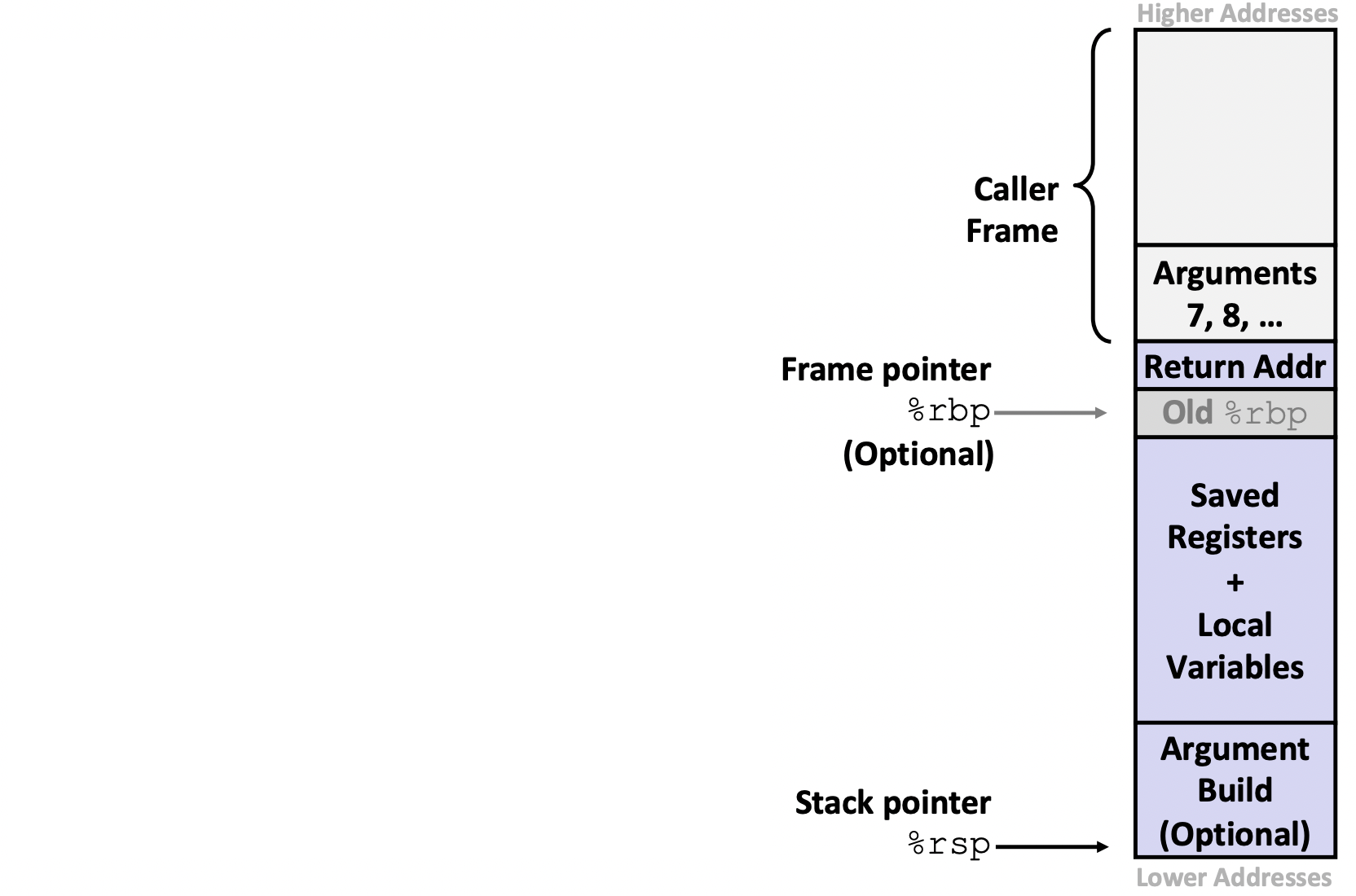
- Return address (pushed by
Overflowing buffers and injecting code
Buffer Overflow in a Nutshell
- C does NOT check array bounds
- Many Unix/Linux/C functions don't check argument sizes
- Allows overflowing (writing past the end) of buffers (arrays)
- "Buffur Overflow" : Writing past the end of an array
example
- Stack grows down towards lower addresses
- Buffer grows up towards higher addresses
- If we write past the end of the array,
we overwrite data on the stack
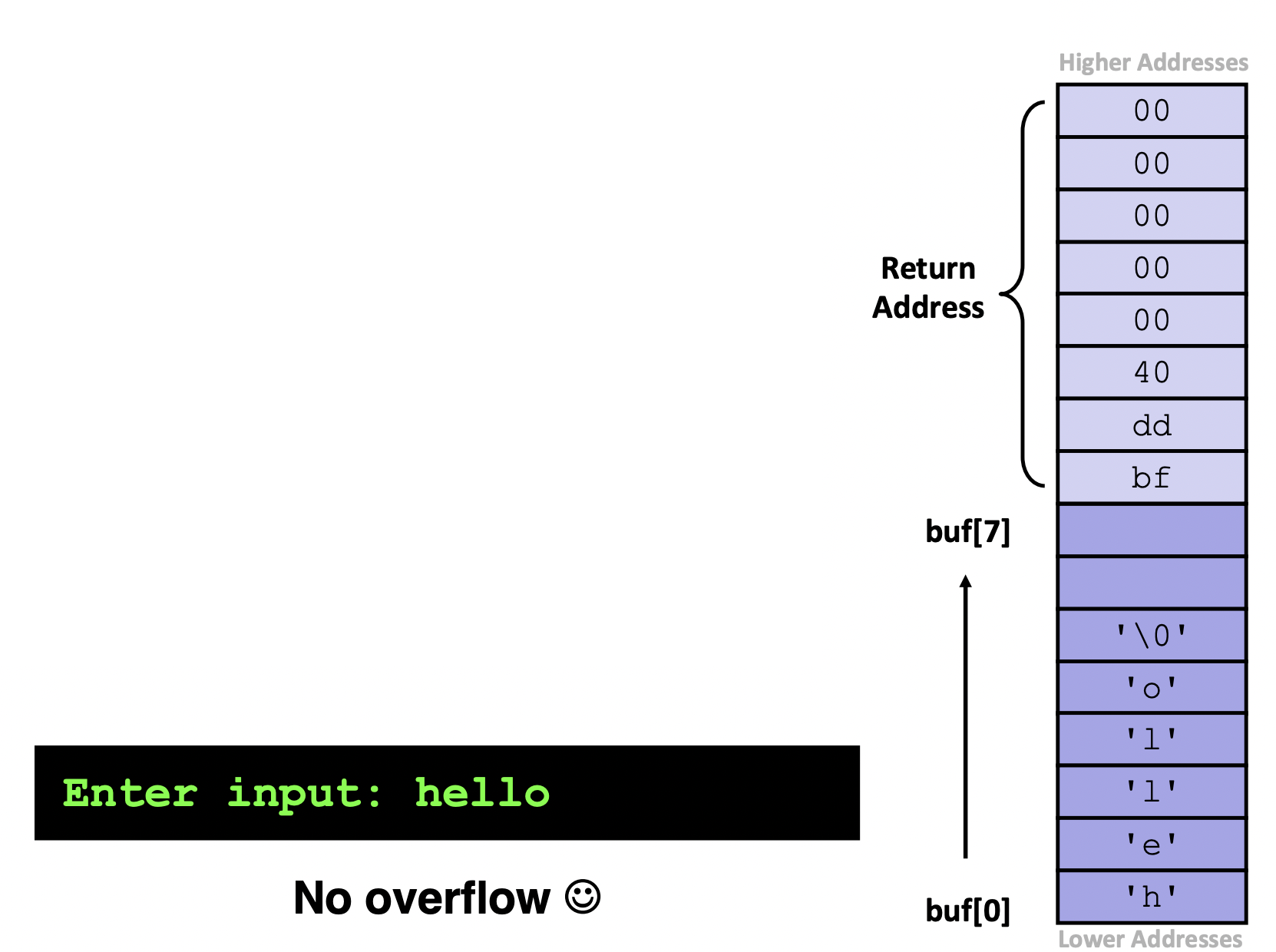
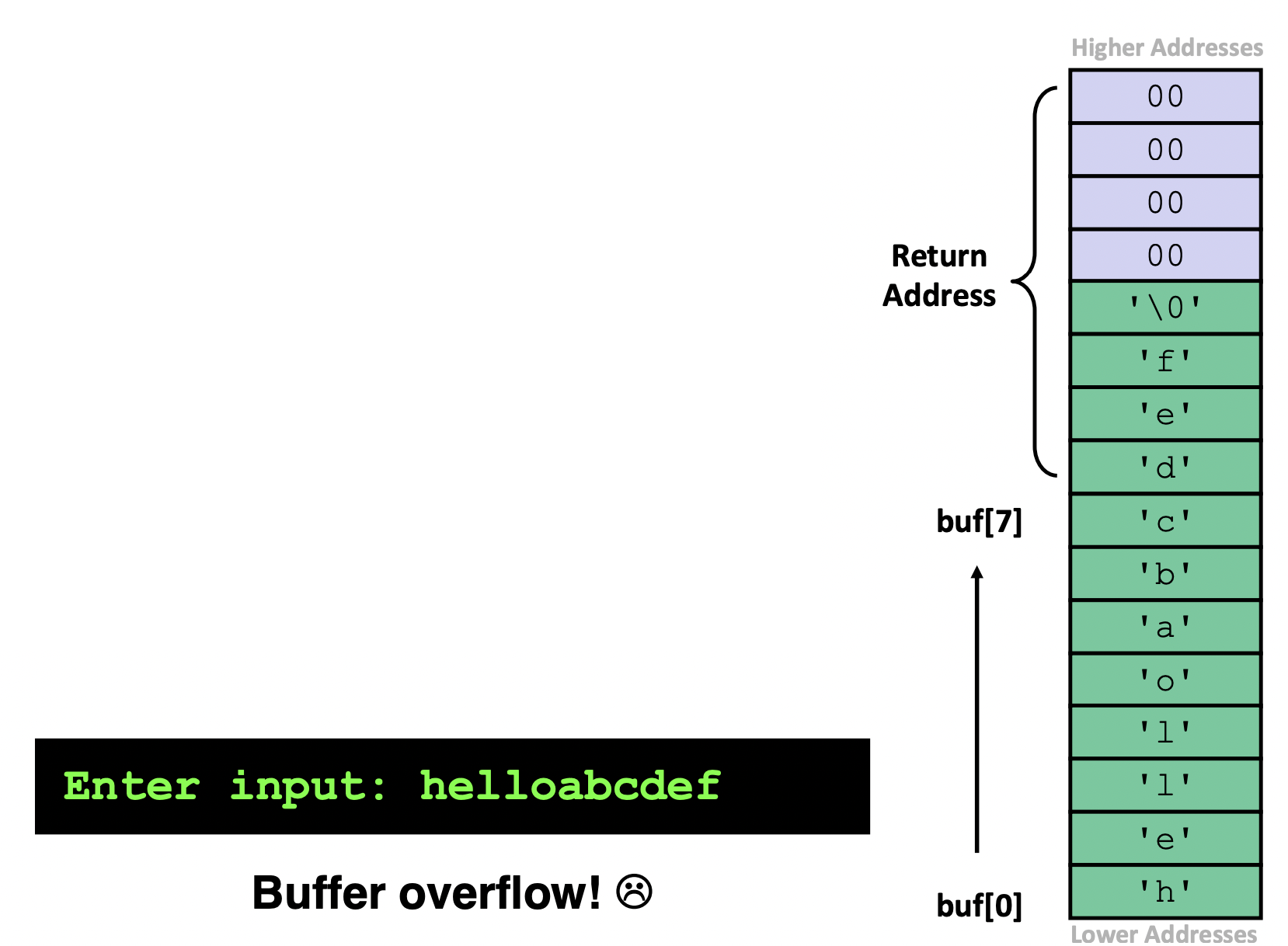
- Buffer overflows on the stack can overwrite "interesting" data
- Attackers just choose the right inputs
- Simplest form ("stack smashing")
- Unchecked length on string input into bounded array causes overwriting of stack data
- Try to change the return address of the current procedure
- Why is this a big deal?
- It was the #1 technical cause of security vulnerablities
String Library Code
- gets()

- No way to specify limit on number of characters to read
- Similar problems with other Unix functions :
- strcpy, scanf, fscanf, sscanf with %s specifier
Vulnerable Buffer Code
-
code & input
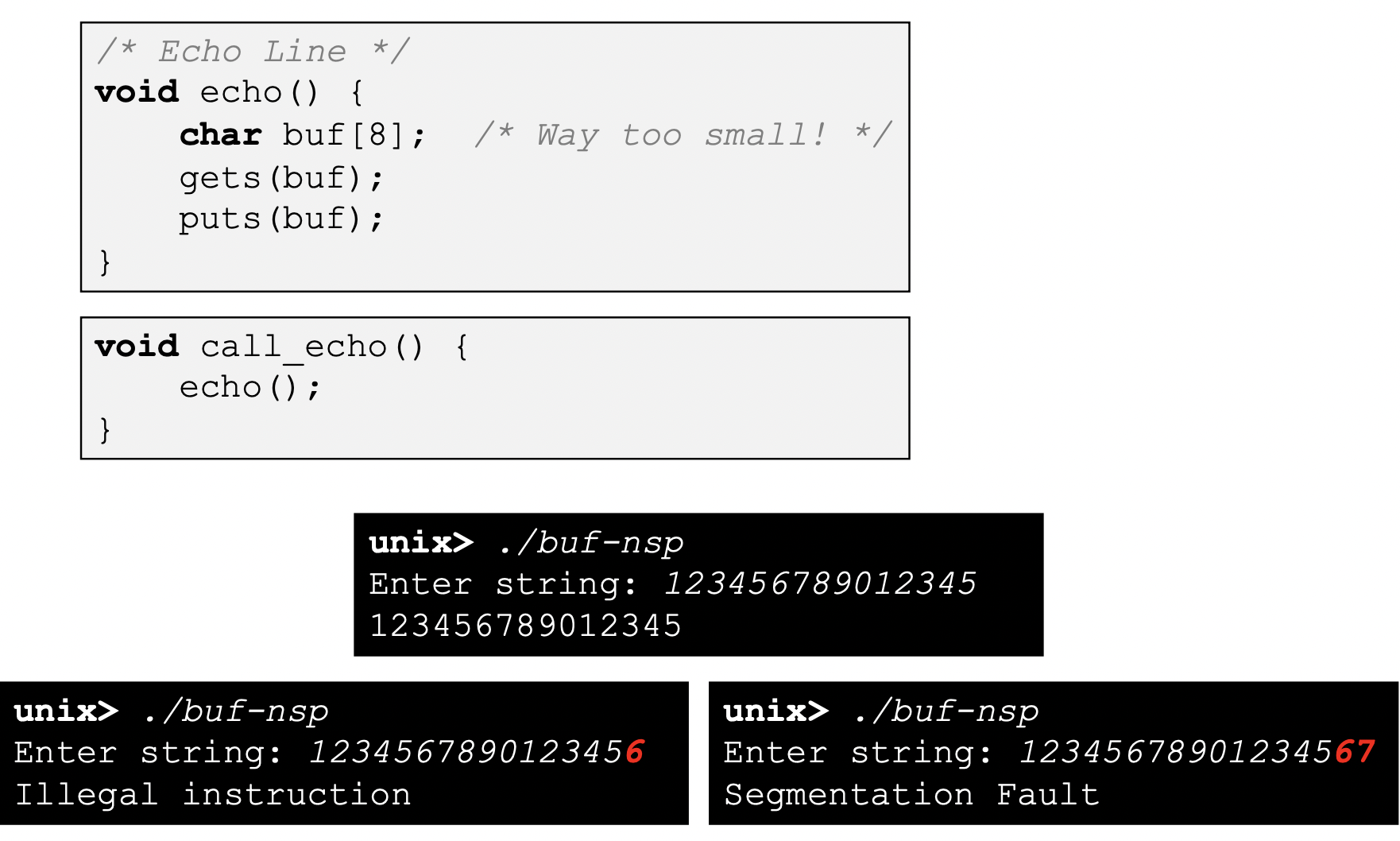
-
dissassmbly
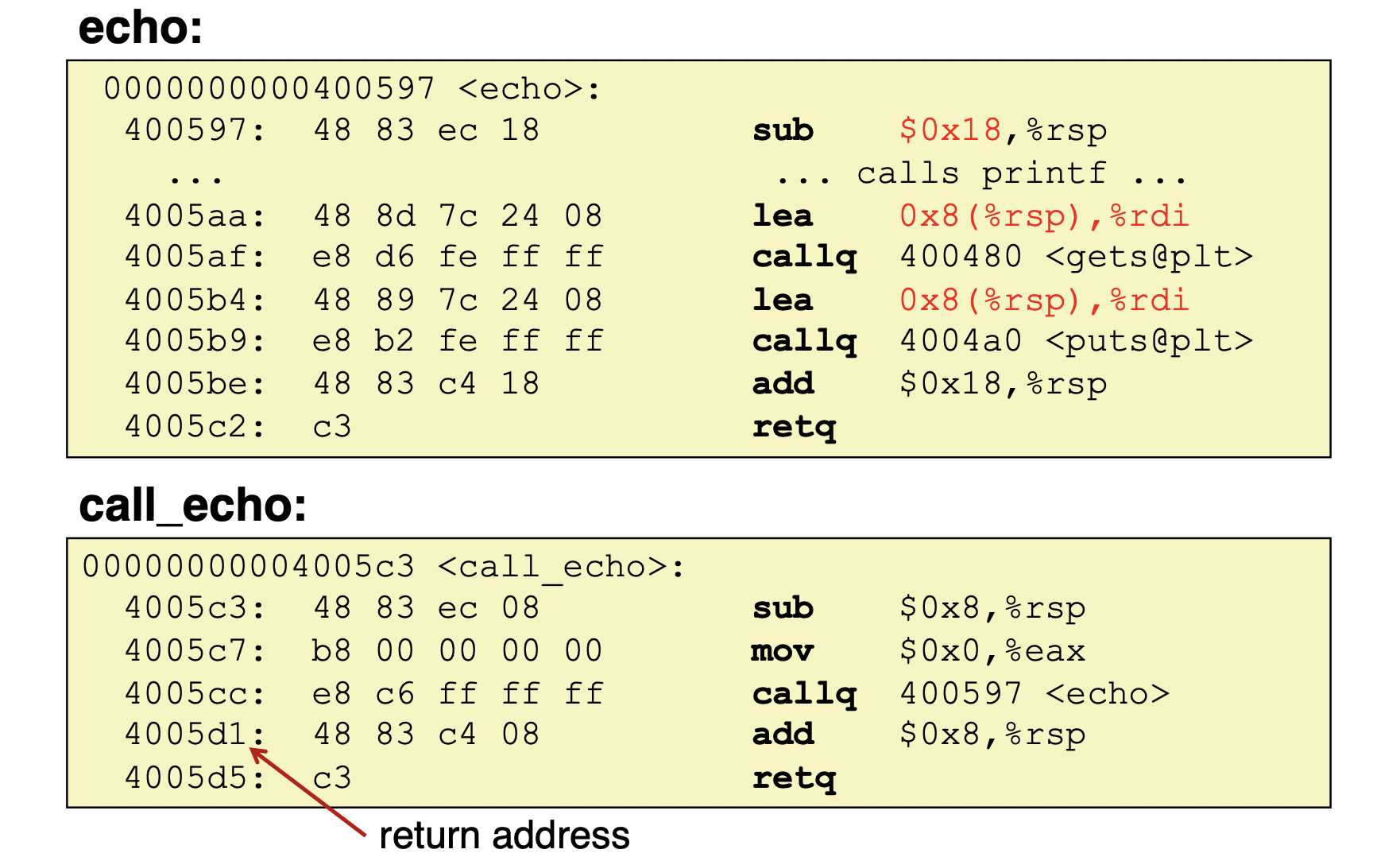
-
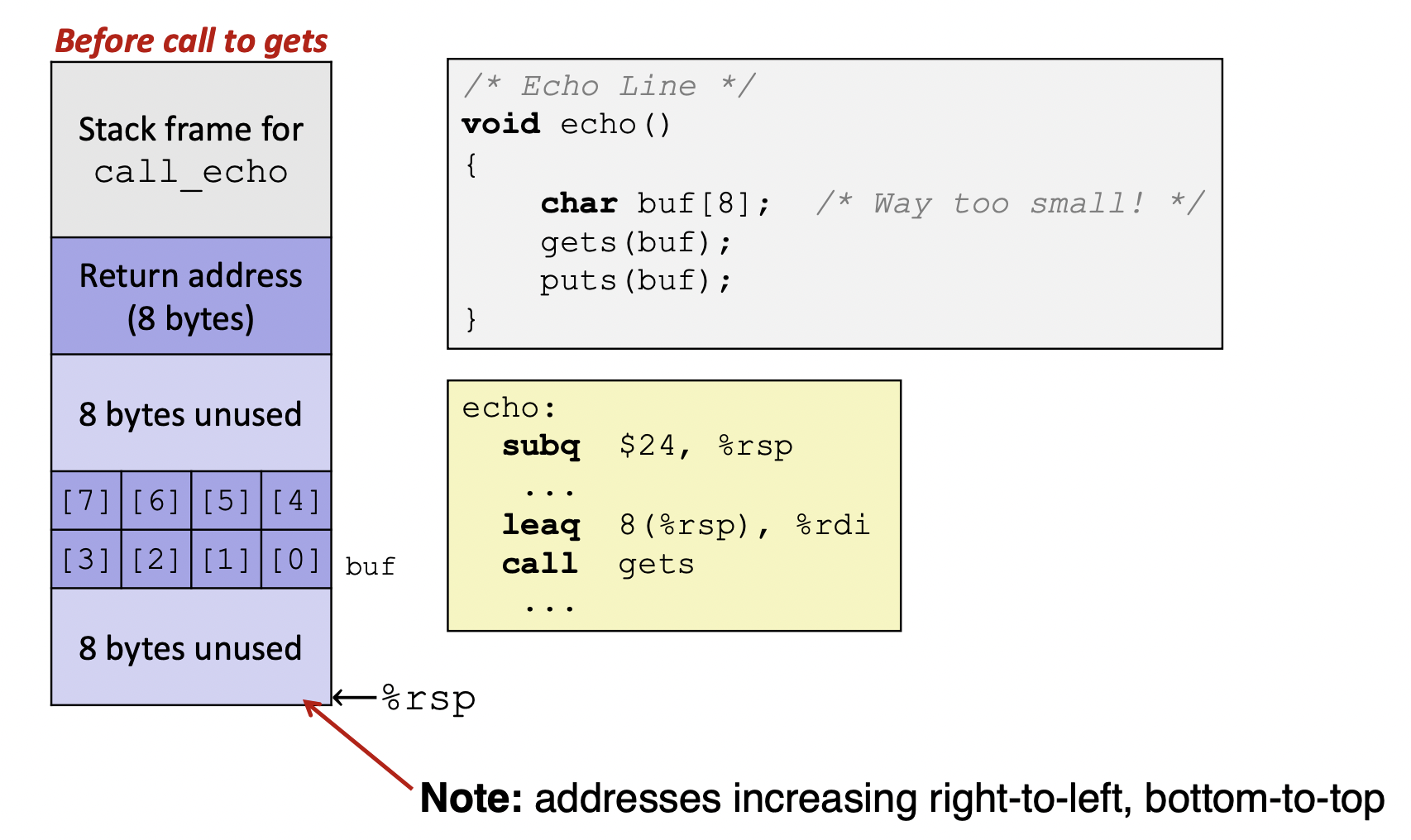
Stack
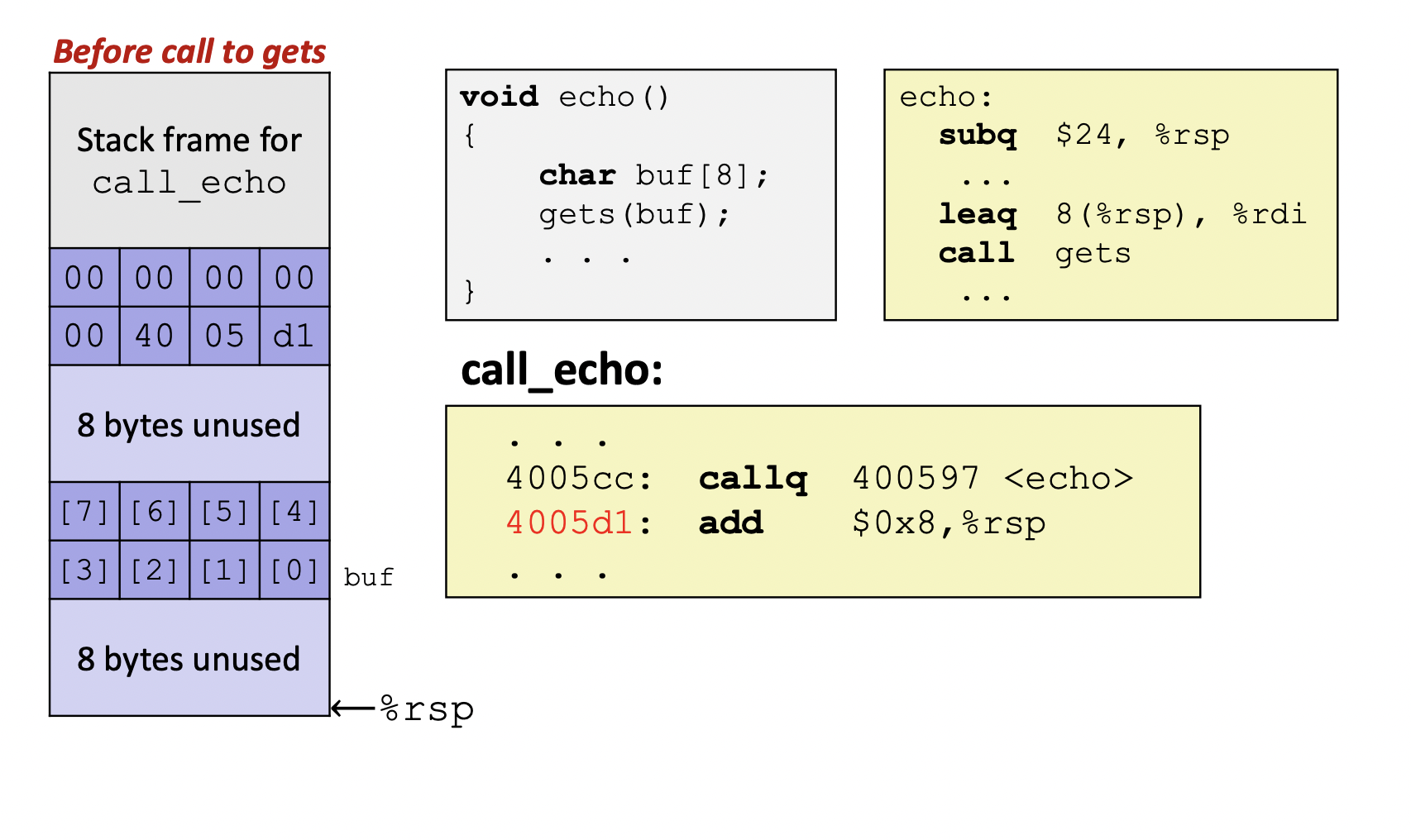
- Before call to gets
- After call to gets
- Example 1
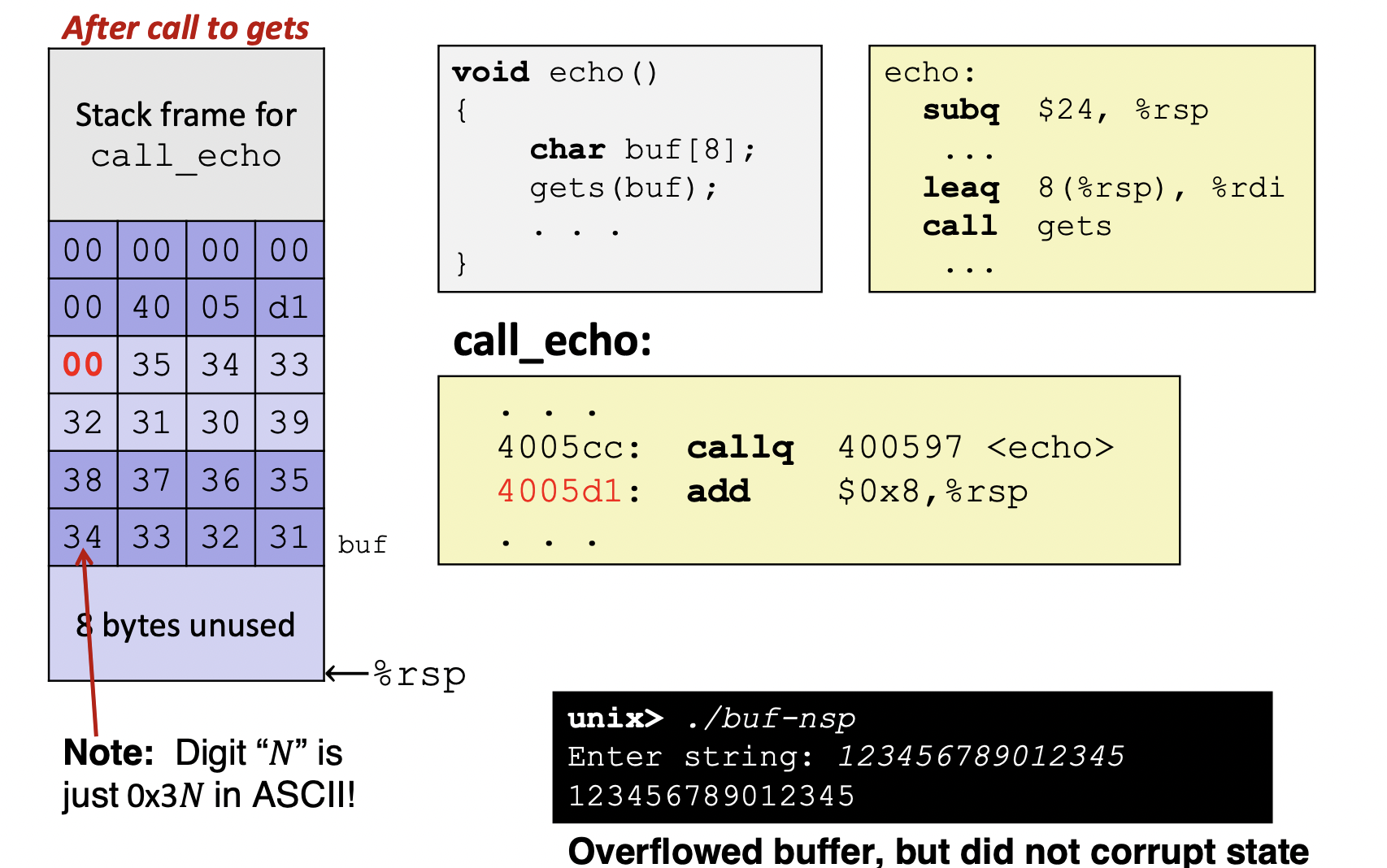
- Example 2
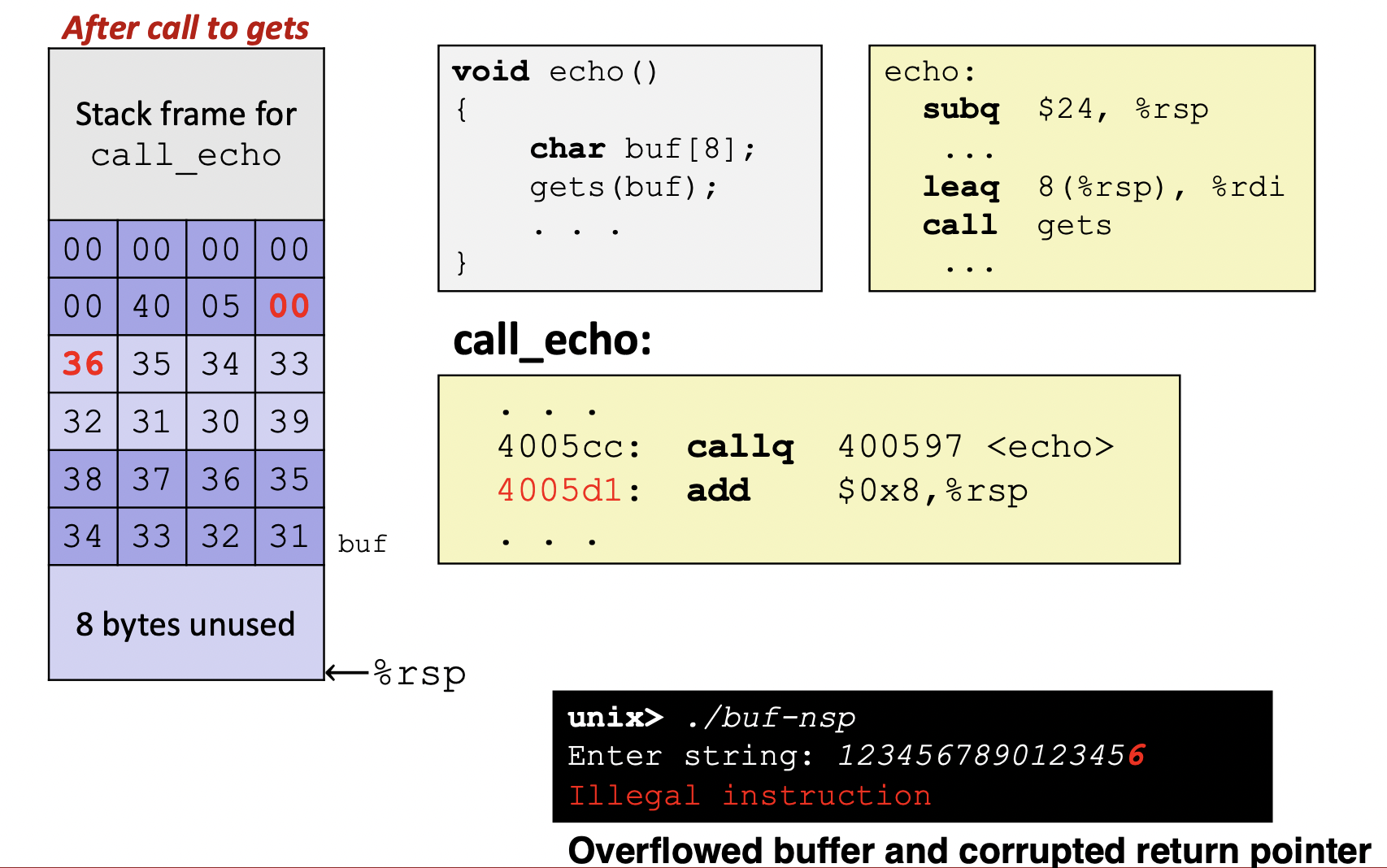
- Example 1
- Before call to gets
Malicious Use of Buffer Overflow
: Code Injection Attacks
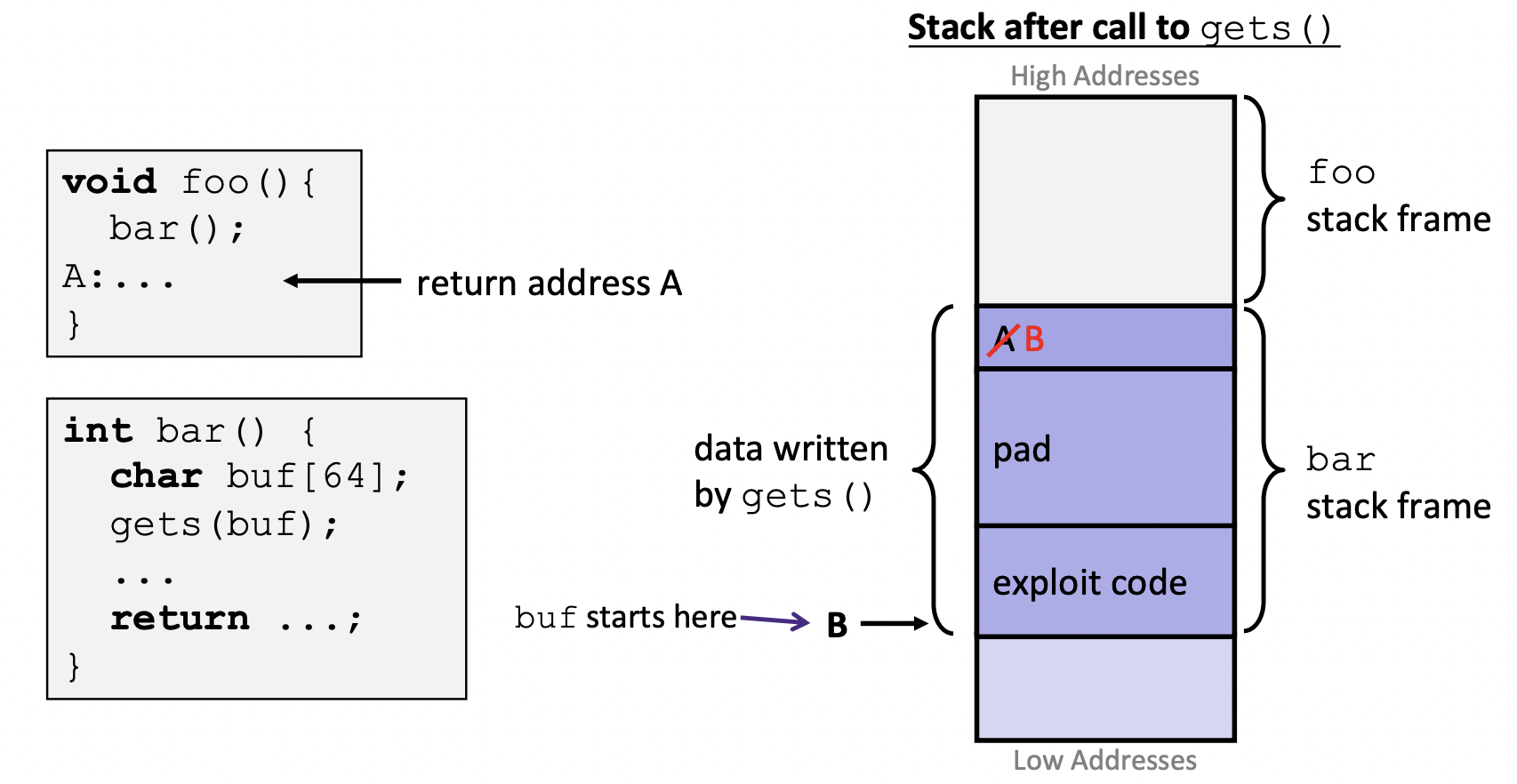
- Input string contains byte representation of executable code
- Overwrite return address A with address of buffer B
- When
bar()executes ret, will jump to exploit code
Defense against buffer overflows
System-Level Protections
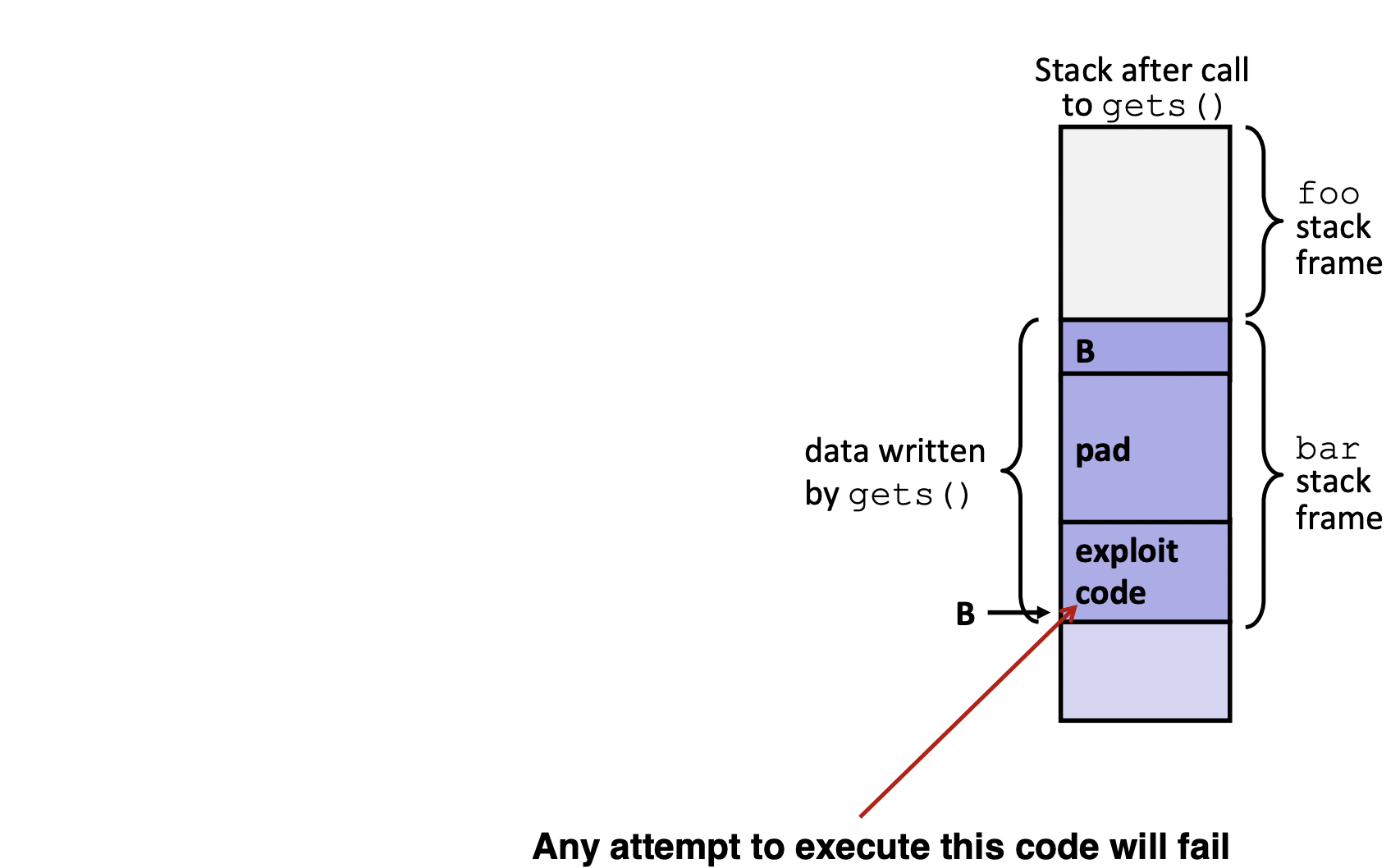
- non-executable code segments
- Works well, but can't always use it
- Many embedded devices do not have this protection
- Some exploits still work!
- return-oriented programming
- return to libc attack
- JIT-spray attack
Avoid Overflow Vulnerablities in Code

- Use library routines that limits string lengths
fgetsinsteadgets
(2nd argument tofgetssets limit)strncpyinsteadstrcpy- Don't use
scanfwith %s conversation specification- Use
fgetsto read the string - Use %ns where n is a suitable integer
- Use
- Don't use C.
Use a language that does array index bounds check- Buffer overflow is impossible in Java
- Rust language was designed with security in mind
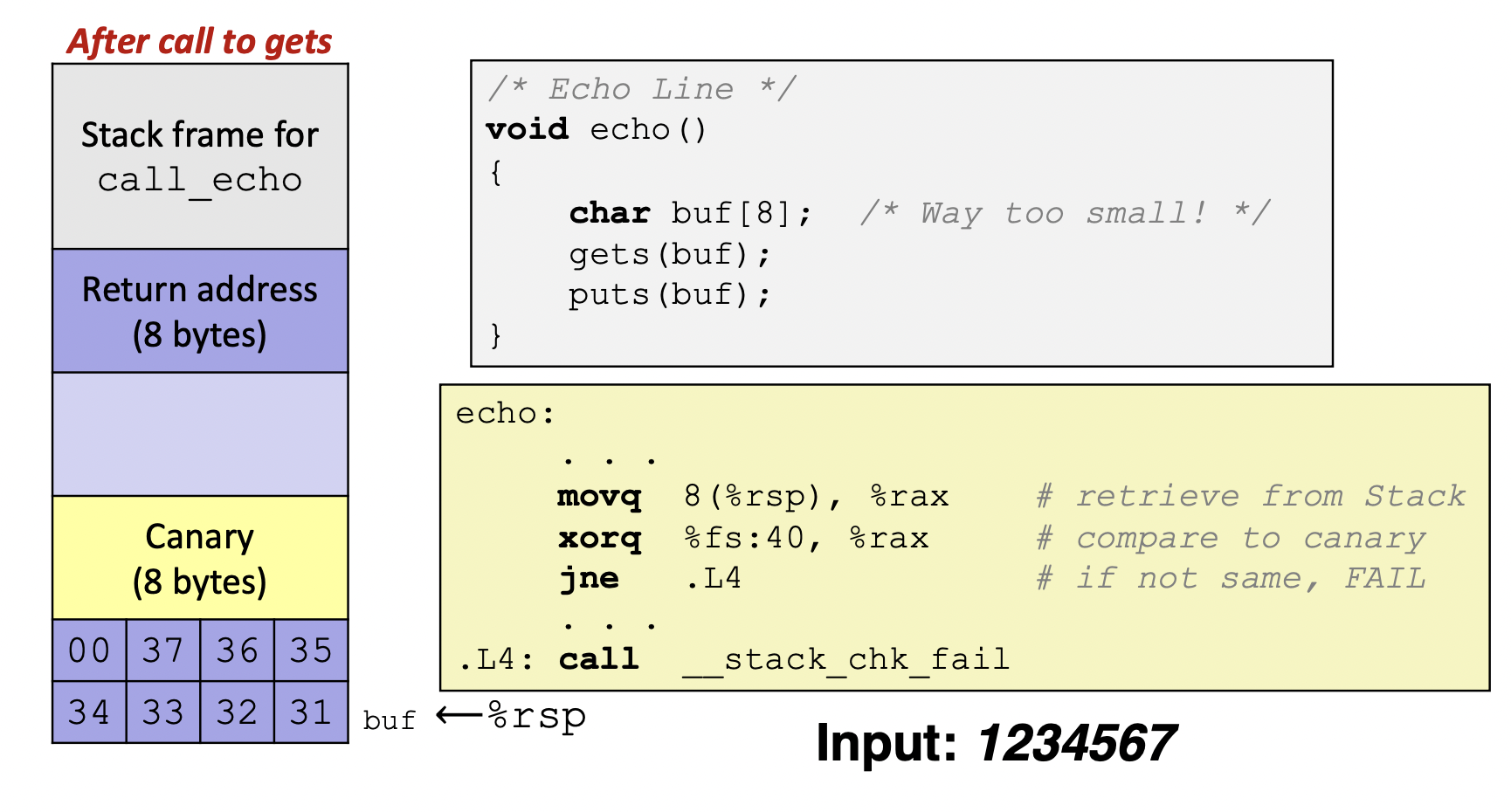
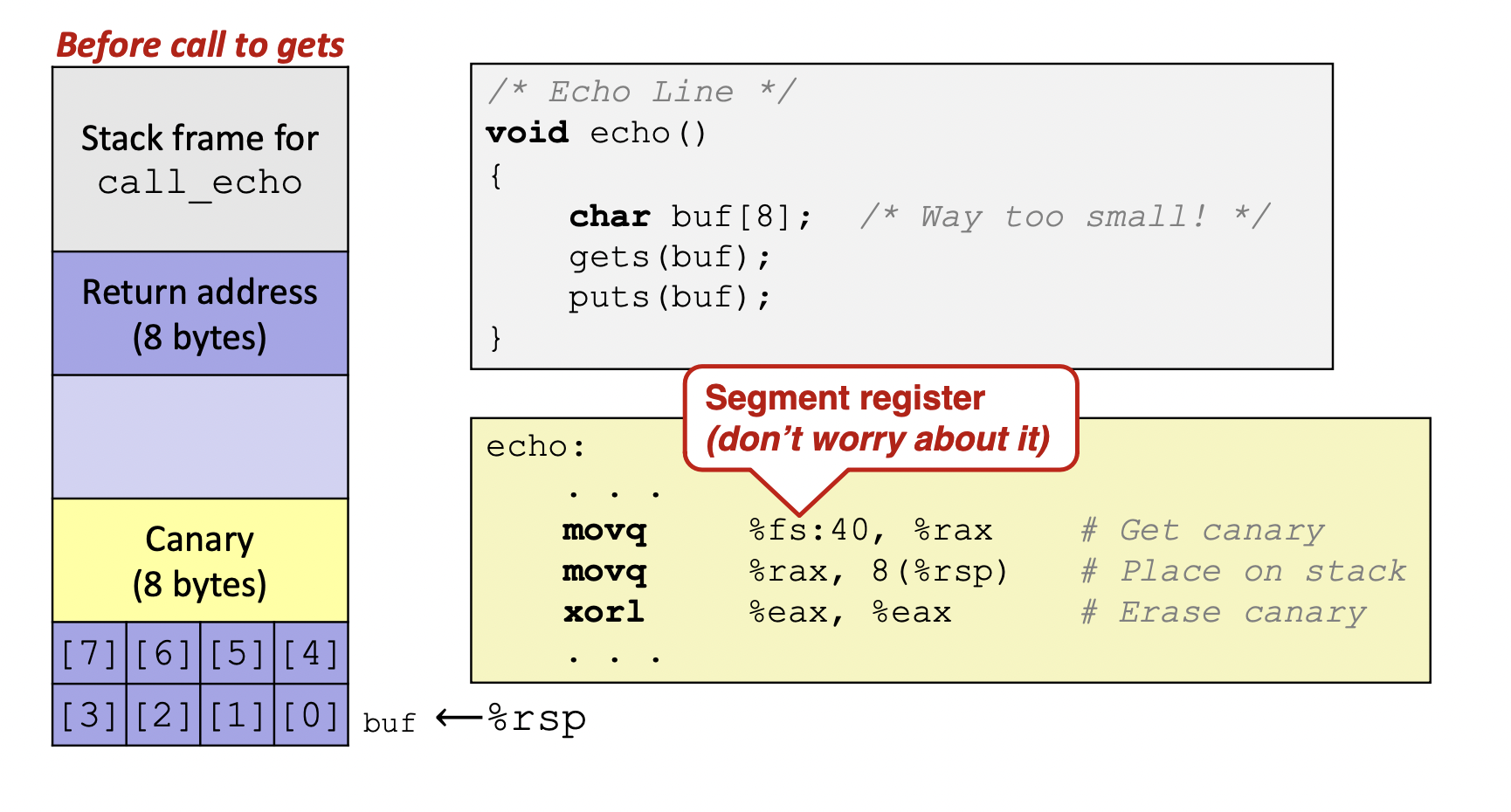
Stack Canaries
- Basic Idea : place special value('canary') on stack just beyond the buffer
- Secret value that is randomized before main()
- Placed between buffer and return address
- Check for corruption before exiting function
- GCC implementation
-fstack -protector

Disassembled
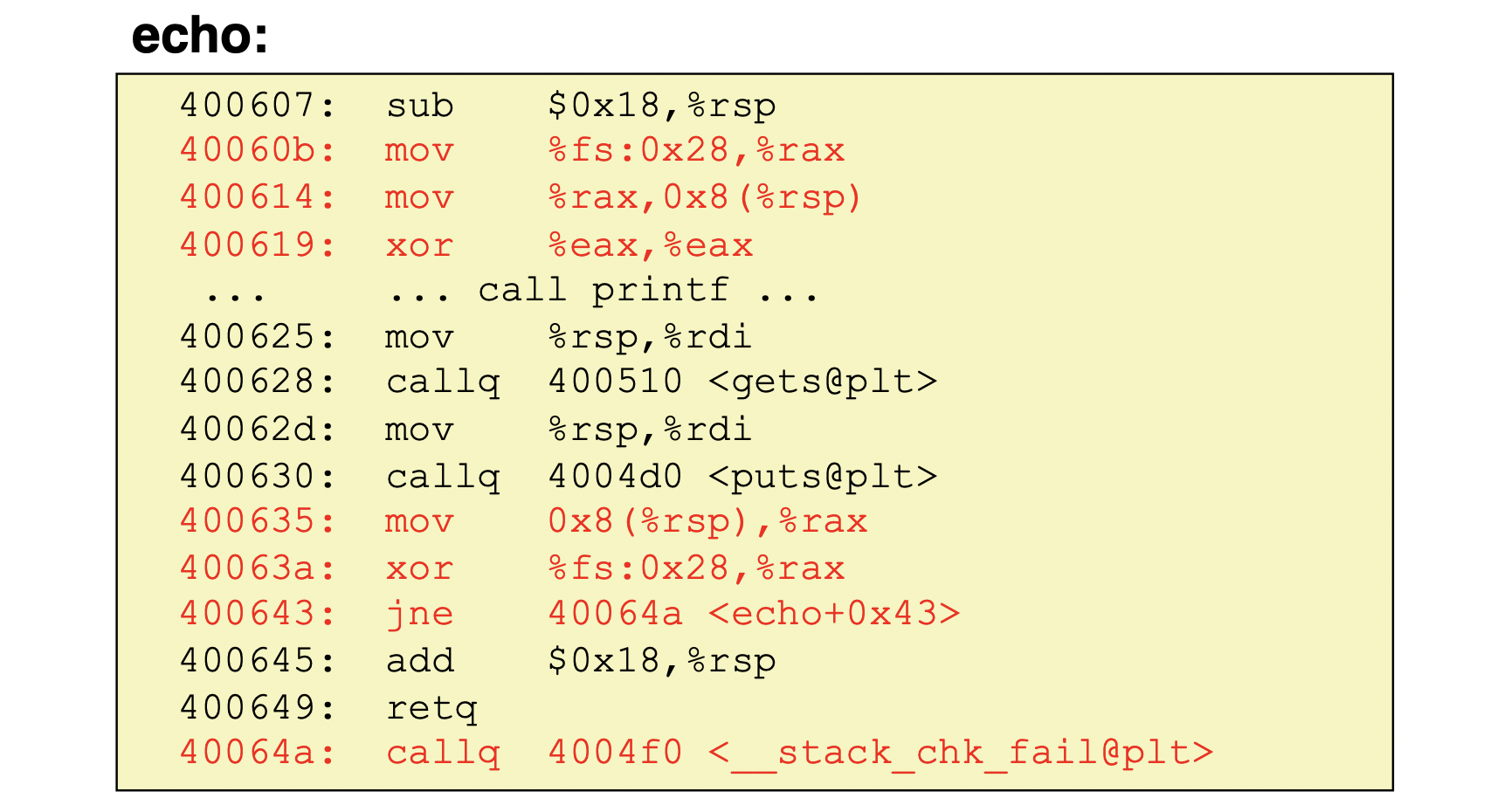
setting up canary
checking canary