Basic Concept
- Indexing mechanism은 원하는 data에 접근하는 시간을 단축시키기 위해 사용된다. ex. 도서관에 저자 catalog
- Search Key : a set of attributes used to look up records in a file
- Index file은 records(index entries)를 포함하고,
각 record는 다음과 같은 형태를 가진다.

- pointer : search key에 대한 주소
- Index file은 보통 original file보다 size가 매우 작다
- Two basic kinds
- Ordered Indices : search keys are stored in sorted order
- Hash Indices : search keys are distributed uniformly across "buckets" using a hash function
- Index evaluation metrics
- access time, insertion time, deletion time, space overhead
Ordered Indices
- index entries가 search key에 대해 정렬되어 있다.
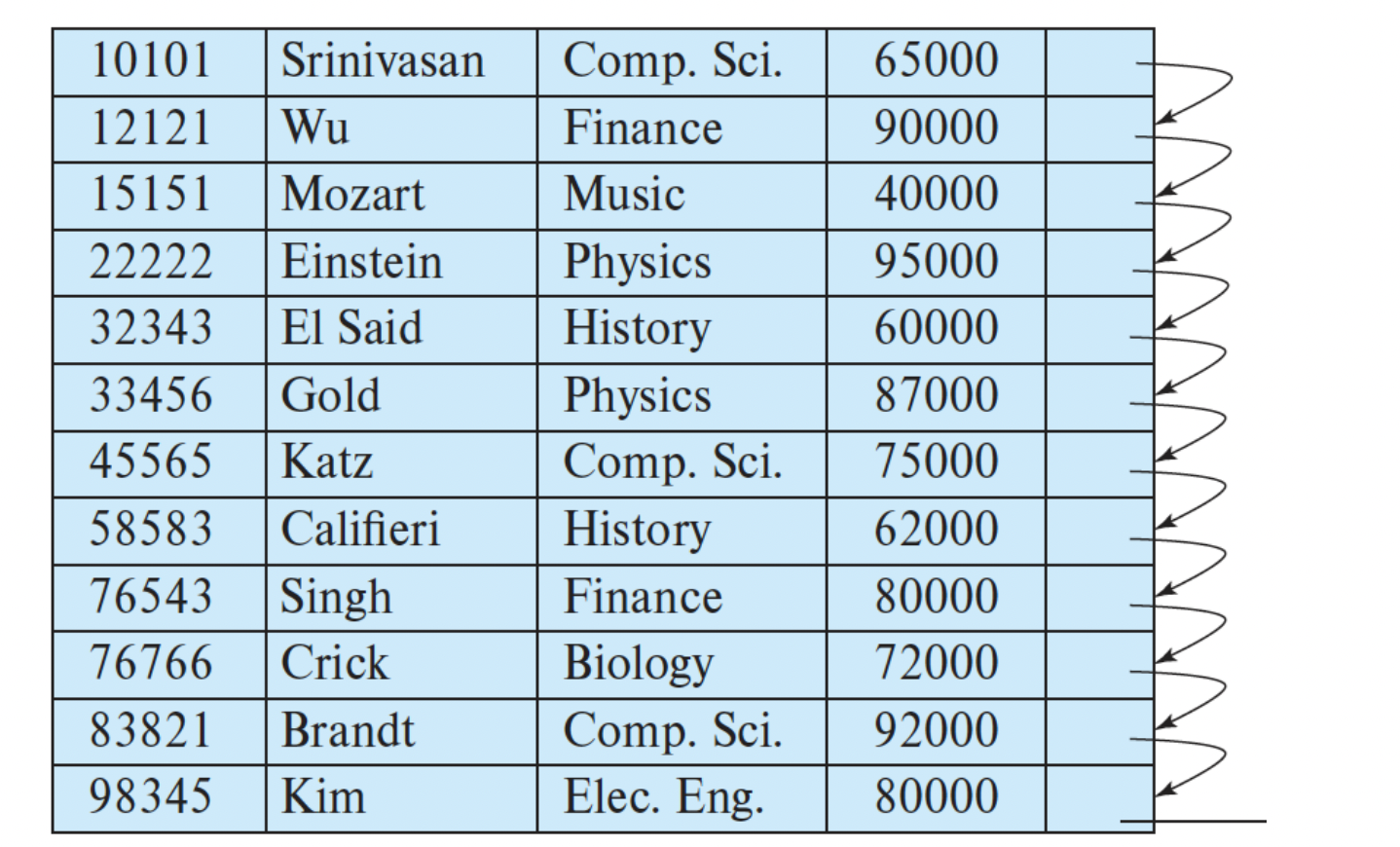
- Clustering index : the index whose search key specifies the sequential order of the file
- also called primary index
- 주로 primary key를 사용하지만, 꼭 primary key일 필요는 없다.
- 위 예시에서는 ID가 clustering index가 된다.
- Secondary index : an index whose search key specifies an order different from the sequential order of the file(??)
- also called nonclustering index
- 얘의 search key는 저장 순서를 따르지 않는다.
- Index-sequential file : sequential file ordered on a search key, with a clustering index on the search key
Dense Index file
- Dense index : index record appears for every search-key value in the file
- 모든 search key에 대해 entry가 존재한다
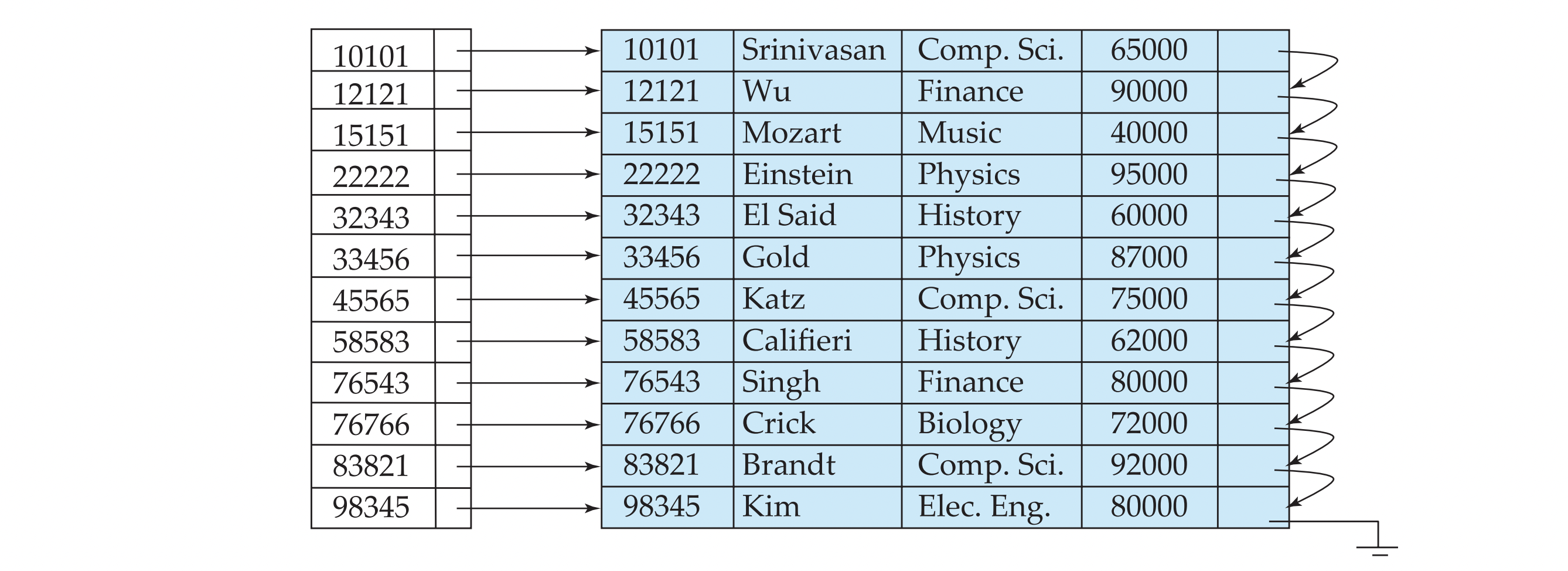
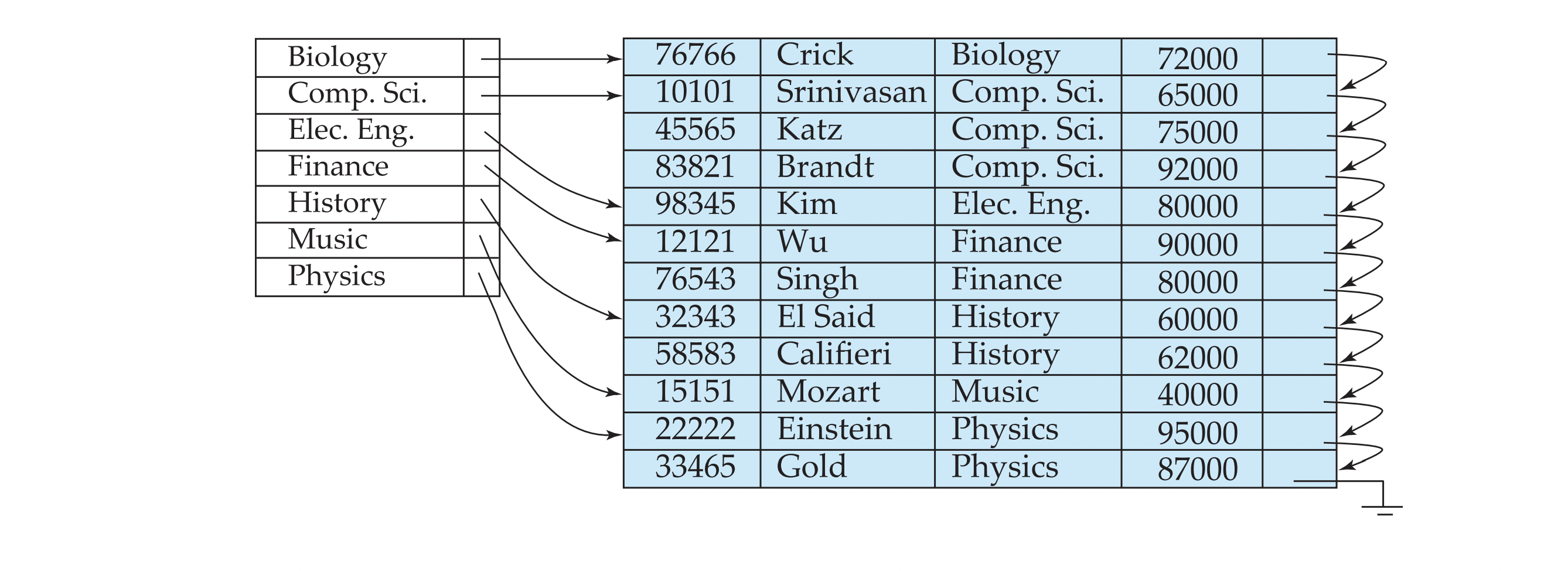
Clustering vs Nonclustering Indices
clustering index를 쓰면,
- 특정 tuple을 검색하거나 sequential scan을 할 때에는 efficient하다
- 하지만 record 삽입/삭제될 때마다 모든 index가 update되어야 한다.
nonclustering index를 쓰면 반대로
- scan하는 데 불필요한 I/O가 많이 발생하기 때문에 매우 expensive
- 하지만 수정될 때는 수정된 속성에 대한 index만 update하면 된다.
Sparse Index file
- Sparse index : 몇몇 search key value에 대한 index record를 가진다.
- search key로 sequentially 정렬된 record에 적합하다.
즉, clustering index에 대해서만 가능하다
- search key로 sequentially 정렬된 record에 적합하다.
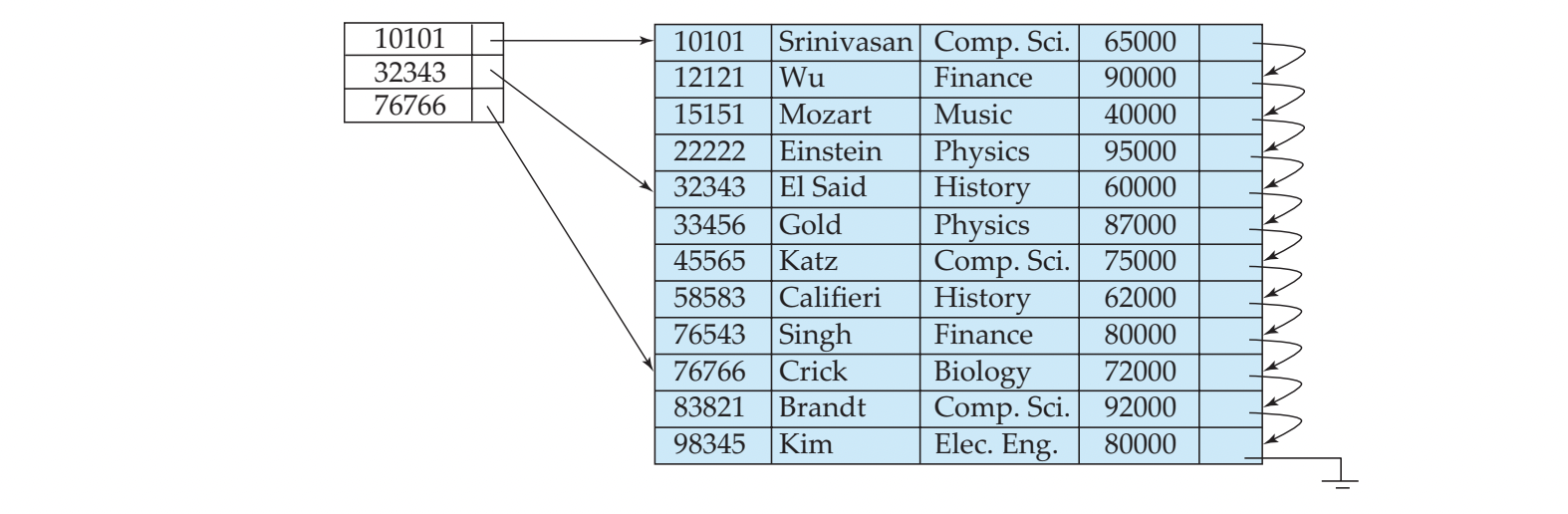
- Search key value가 K인 record를 위치시키기 위해서는
- K보다 작은 것중에 가장 큰 search key value를 갖는 index record를 찾는다
- Search file sequentially starting at the record to which the index record points.
즉, 다음꺼 하나씩 비교해가면서 위치를 파악한다
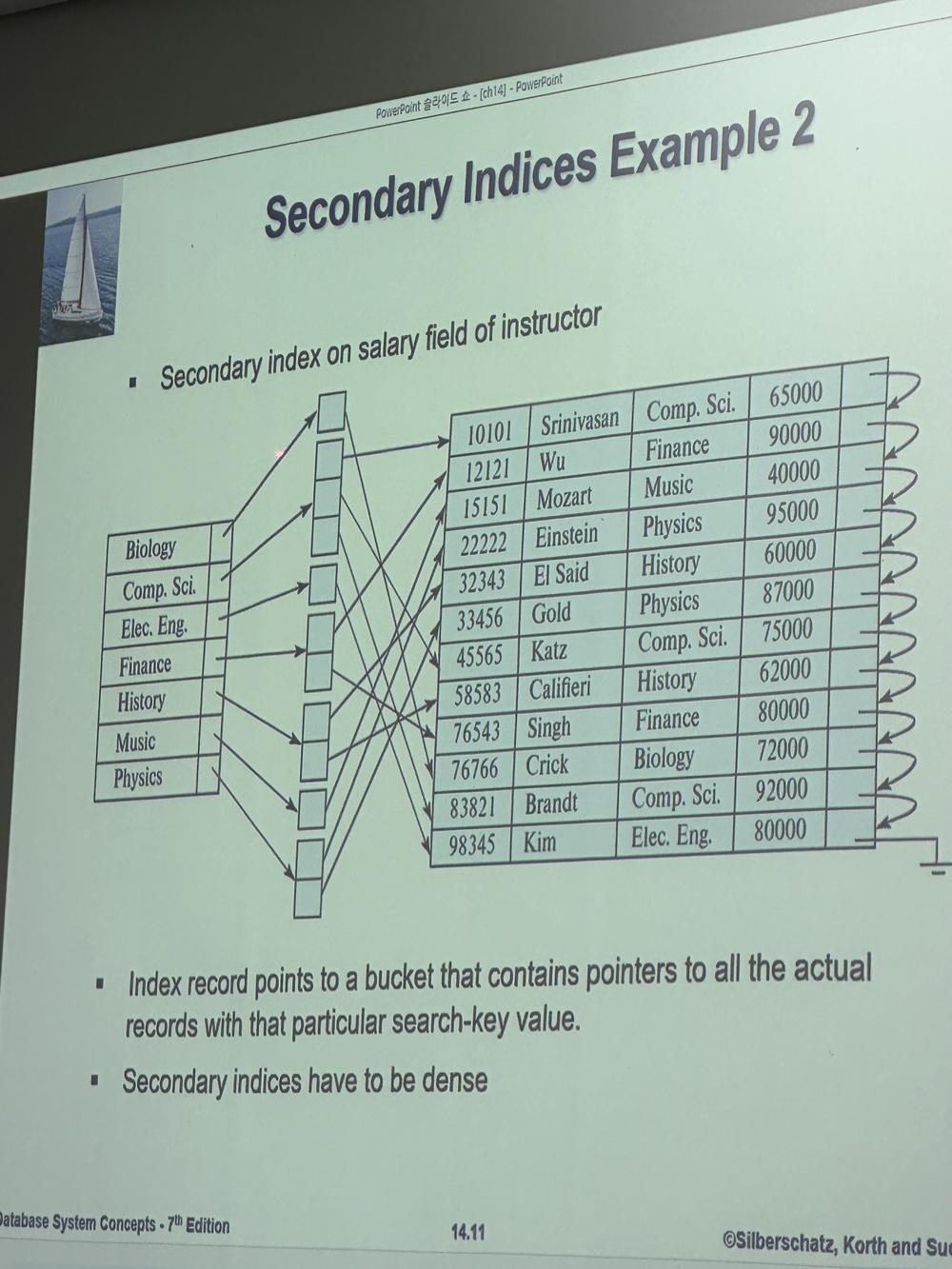
Secondary Indices
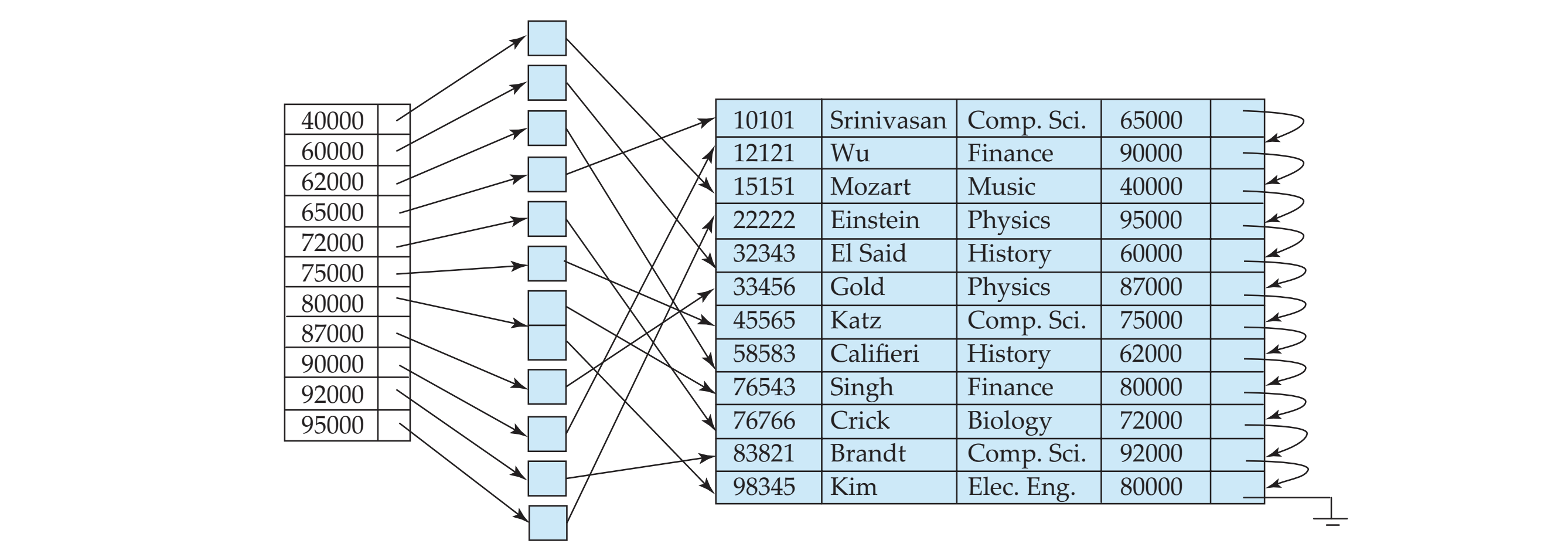
- 추가적인 bucket(일종의 disk block)을 만들어서 여기에 주소를 저장하도록 한다.
- disk I/O가 2번 발생한다
- (설명) Index record points to a bucket that contains pointers to all the actual records with that particular search-key value
- 반드시 dense해야 한다
- sparse면 찾을 수가 업숴
- 그런데 위의 그림처럼 block 하나에다가 data 하나씩만 저장하고 있으면
block에 대한 활용도가 낮다
하나의 block에는 여러 data를 저장할 수 있다.
Dense vs. Sparse
sparse 기준
장점
- index size가 작아서 storage overhead(space overhead)가 적다.
- index에 없는 걸 삭제하거나 삽입해도 할 게 없어서, update에 대한 overhead가 적다
단점 - record 위치를 찾기 위해서 검색할 때 속도나 느리다 (검색 시간이 오래걸린다)
Good trade-off
- for clustered index,
sparse index with an index entry for every block in file, corresponding to least search-key value in the block- 일종의 sparse index라고 할 수 있다. block의 맨 처음 tuple을 가리키게 한다
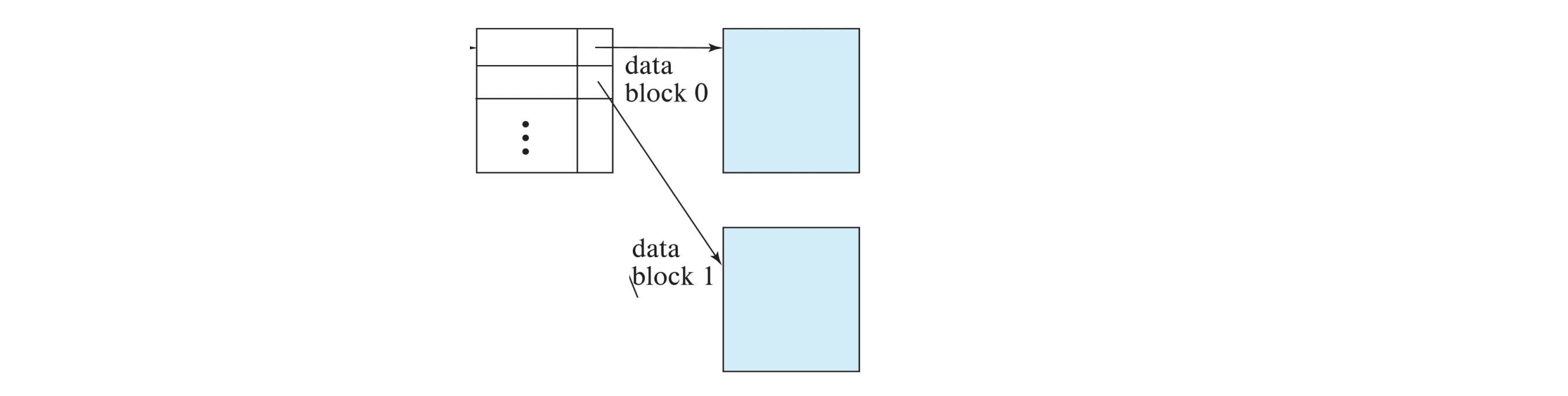
- 일종의 sparse index라고 할 수 있다. block의 맨 처음 tuple을 가리키게 한다
- for unclustered index,
sparse index on top of dense index (multilevel index)- dense한 index 위에 이거에 대한 index를 하나 더 빌드한다.
- dense한 index 위에 이거에 대한 index를 하나 더 빌드한다.
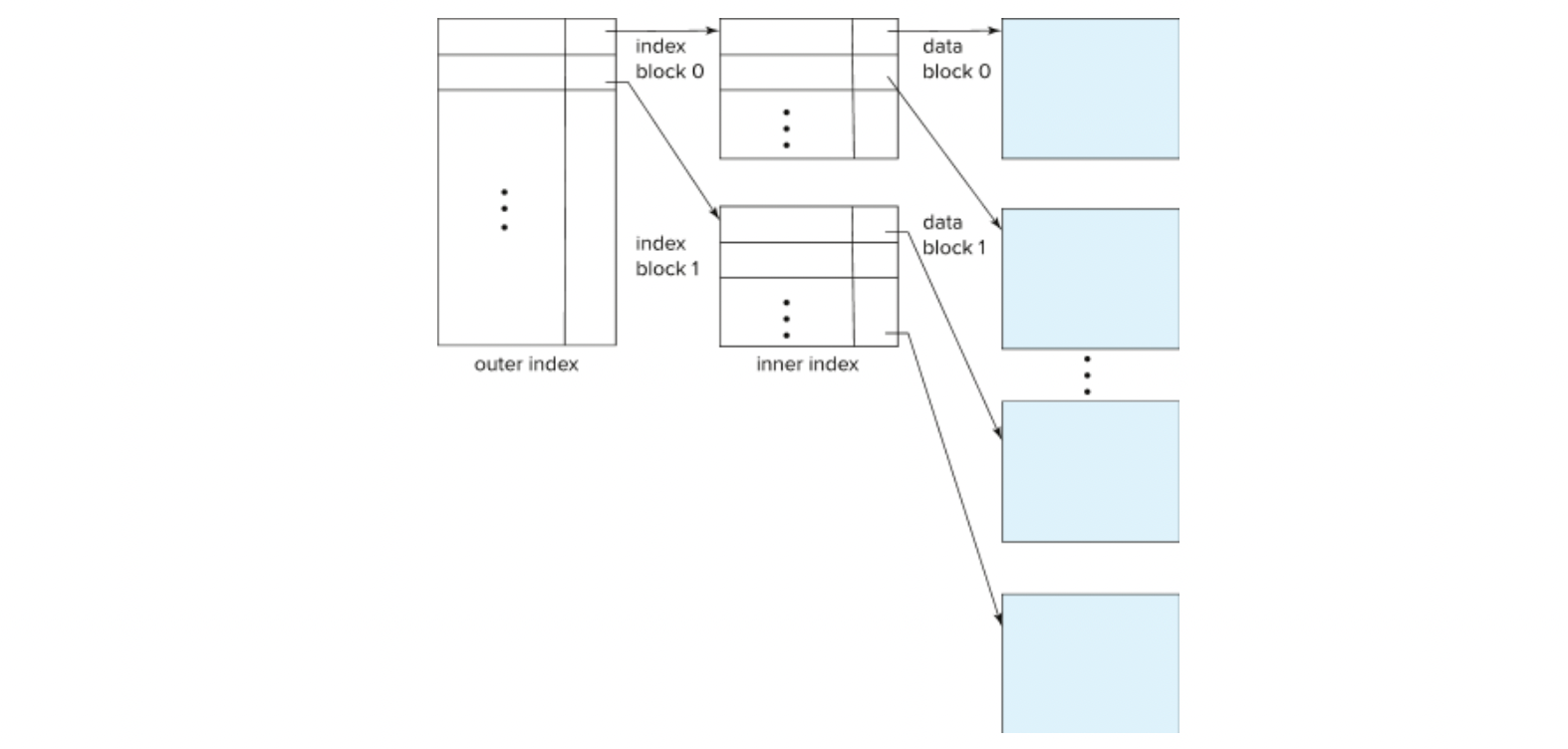
Multilevel Index
- 만약 index가 너무 커서 memory에 다 안 올라가게 되면, access도 become expensive
- 해결 방법 : treat index kept on disk as a sequential file
and construct a sparse index on it
(index 자체를 sequential로 간주하고, sparse index를 build한다)- outer index : sparse index of the basic index
- 왼쪽에 있는거
- inner index : the basic index file
- 오른쪽에 있는거
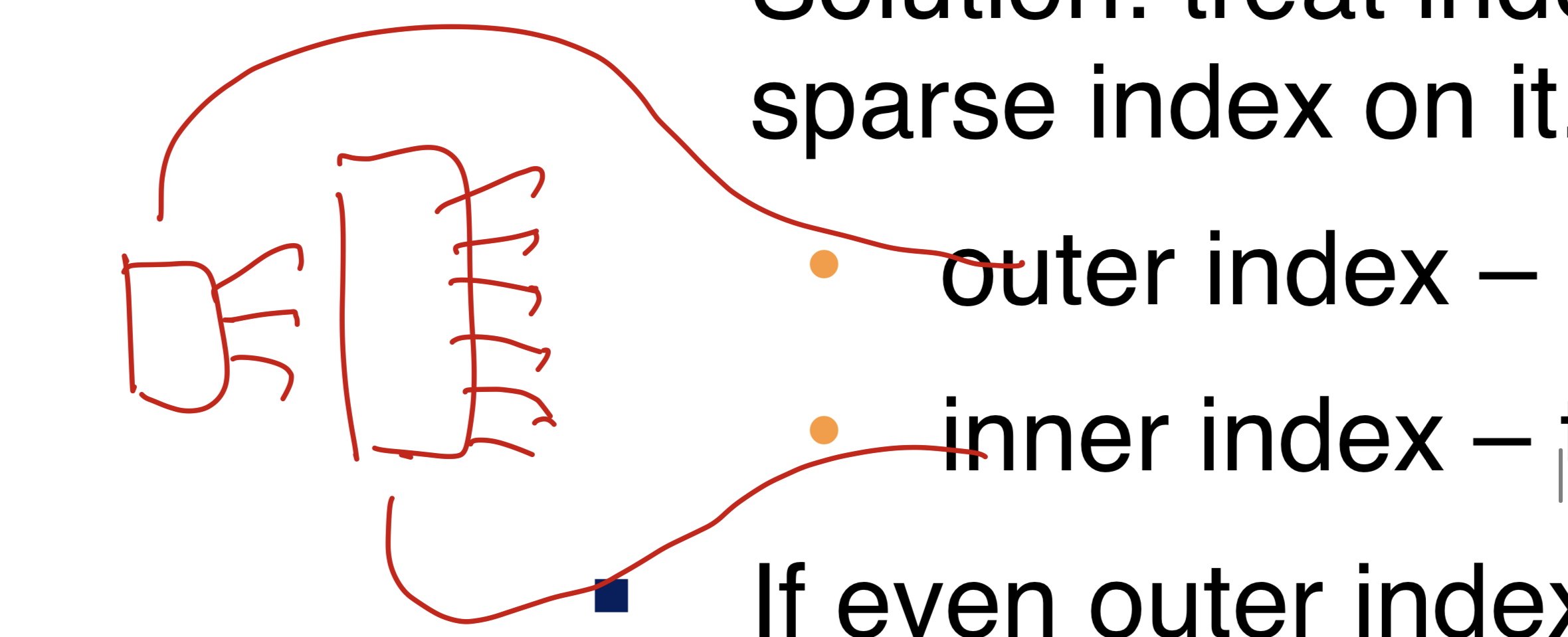
- 오른쪽에 있는거
- outer index : sparse index of the basic index
- 만약에 outer index가 아직도 너무 크면, 또 새로운 level을 만들면 된다
- Indices at all levels must be updated on insertion or deletion from the file
- 맨 outer에 있는 index만 memory에 있다고 본다.
(충분히 작게 만들고 memory에 올려) - 애초에 outer를 만든 이유가 memory에 들어가지 못할 만큼 커서.
- 메모리에서 scan하는 건 I/O로 취급하지 않는다.
- 위 그림에서 I/O = 1
Index Update
Deletion
(ppt 같이 보면서 공부하기)
- 삭제해야 하는 record가 걔의 search-key value의 유일한 record였으면,
그 search key도 index에서 삭제되어야 한다.
-
Dense : deletion of search-key is similar to file record
-
Sparse : 일단 index에 걔가 있으면 지워주고, 지운 그 자리는
걔의 다음 애의 다음으로 대체시킨다. 만약에 그 다음의 다음이 이미 있으면 따로 대체시키지 않고 그냥 없앤다.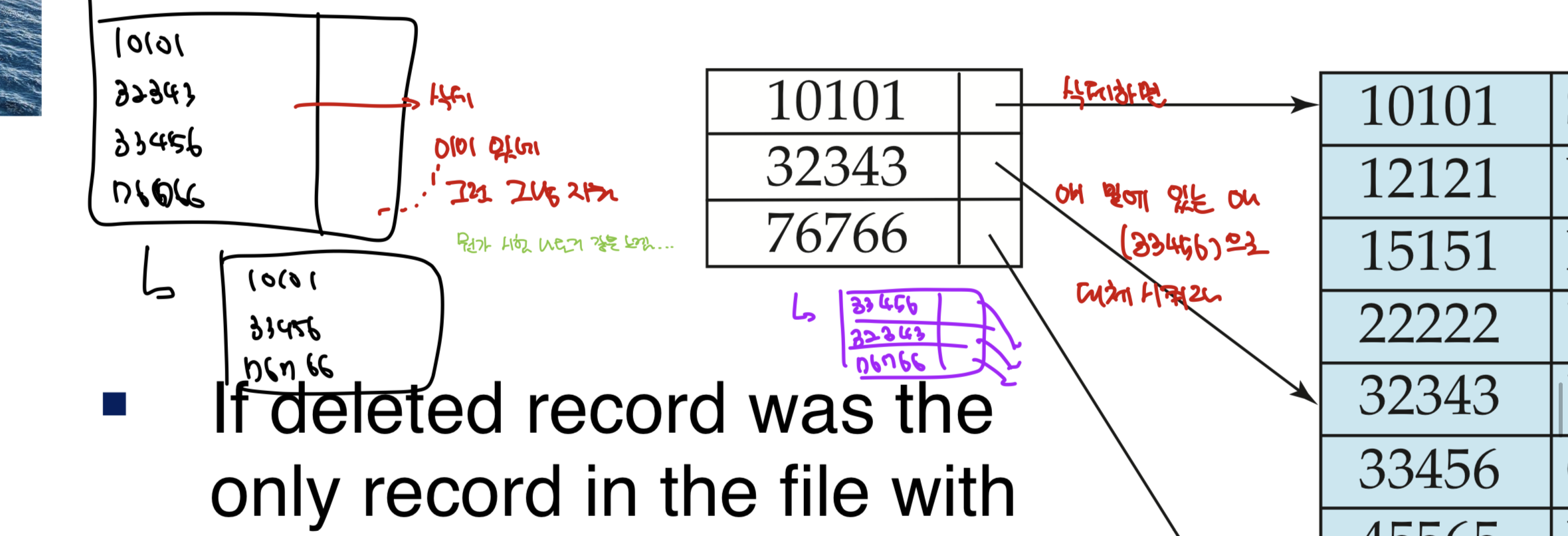
Insertion
- 삽입해야 할 record의 search key value를 이용해서 위치를 잡는다
- Dense : 그 search key가 없으면, 삽입해라
- sequential하게 유지시켜줘야 함
- overflow block이 아마 필요할거야
- Sparse : 각 block의 첫 번째 tuple 가리키고 있다고 치자.
- 그럼 기존에 있는 block에다가 record 삽입하는 건 Index 입장에서 할 게 없다.
- 다만, 새로운 block을 생성할 거면 그 block의 first search key를 Index에 넣어줘야 한다.
Multilevel일 때 algorithms are simple extensions
Indices on Multiple Keys
Composite search key
-
사전 순서대로 정렬해라
(John, 12121) < (Johm, 13514)
(John, 13514) < (Peter, 11223) -
name으로 검색하나 (name, ID)로 검색하나 동일하다.
-
ID로 검색하는 건 불가능
- 뒤에 있는 걸로는 검색이 불가능하다