ARP
Logical vs. Physical
- Logical address : IP address
- Network layer에서 이용되는 address
- host가 internet과 연결될 때 할당된다
- device의 고유번호가 아니기 때문에,
어디서 접속하느냐에 따라 달라진다.
- Physical address : Ethernet MAC address
- Data link layer에서 이용되는 address
- hardware마다 배정된다
- data forwarding at Data link layer
- physical address가 사용된다
- logical address should be mapped to a physical address
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
- 송신자가 destination IP는 알지만 MAC address를 모를 때, 사용한다.
- Broadcast ARP request
- 도메인 내의 모든 장치에 request를 보낸다
- 그에 상응하는 physical address를 갖고 있는 host가 ARP 답장을 보내준다
- 송신자는 ARP table에 받은 physical address를 기록한다.
- 이제 다시 물어볼 필요가 없다.
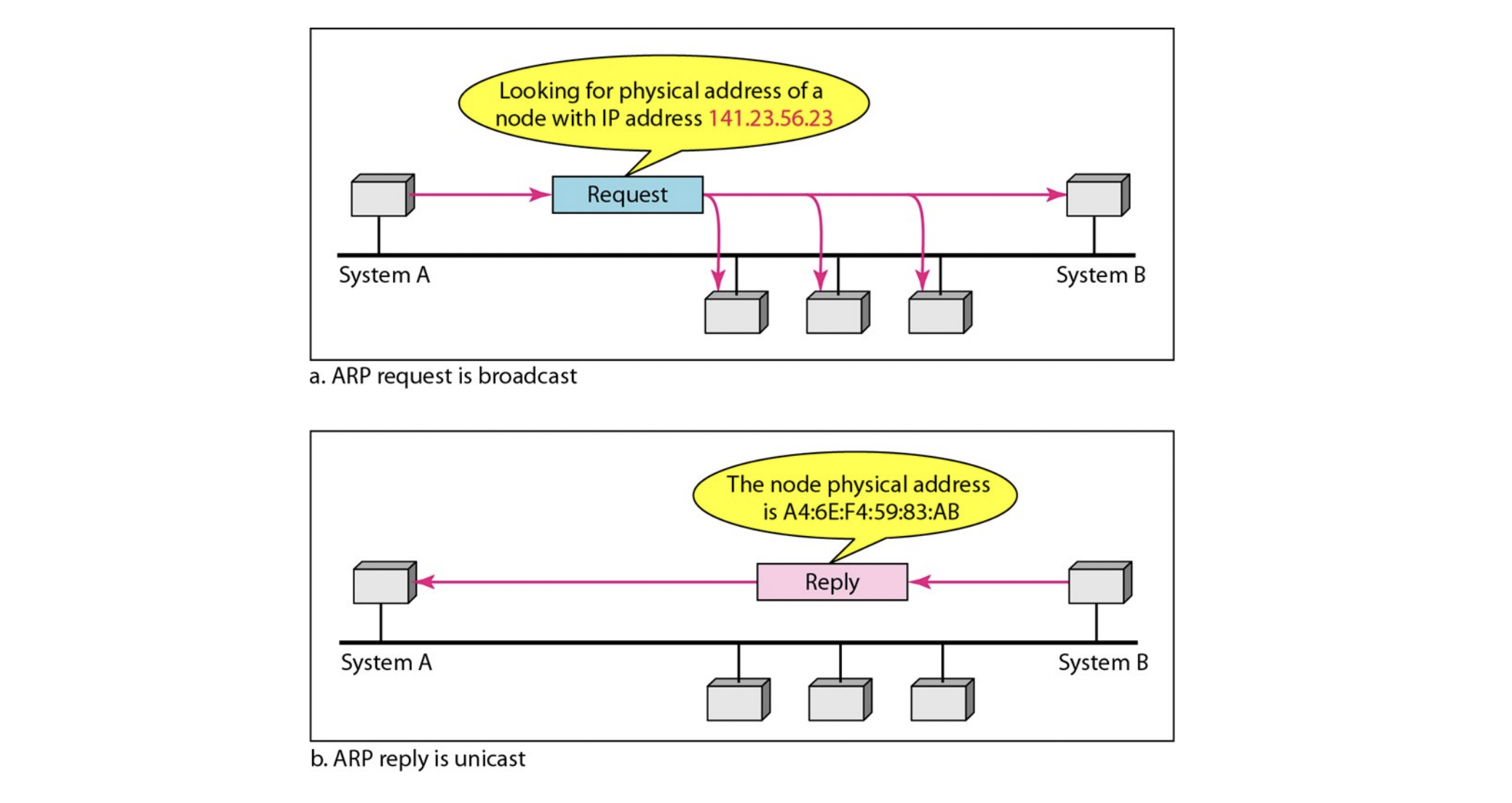
- ARP request is broadcast and
ARP reply is unicast
ARP packet format
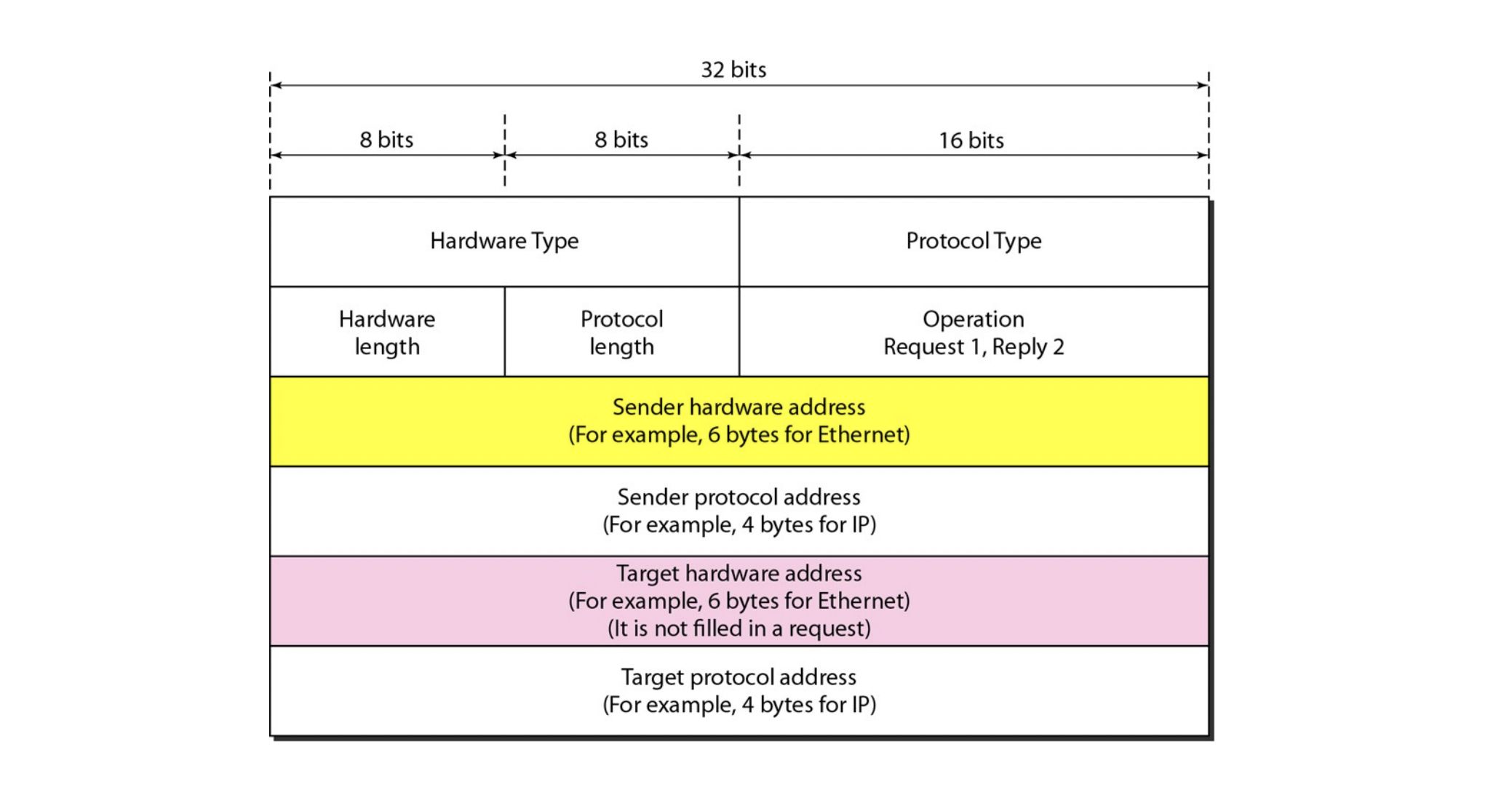
Hardware Type
- network type (e.g. Ethernet)
Protocol Type
- packet에서 사용되는 상위 protocol. (e.g. IP)
Hardware length
- MAC 주소(physical address)의 길이를 바이트 단위로 나타낸다
(e.g. Ethernet -> 6 bytes)
Protocol length
- IP 주소(logical address)의 길이를 바이트 단위로 나타낸다
(e.g. IP -> 4 bytes)
Operation
- ARP 요청 or ARP 응답을 나타낸다
- 1: 요청, 2: 응답
Encapsulation
- ARP packet은 data link frame에 encapsulate된다.
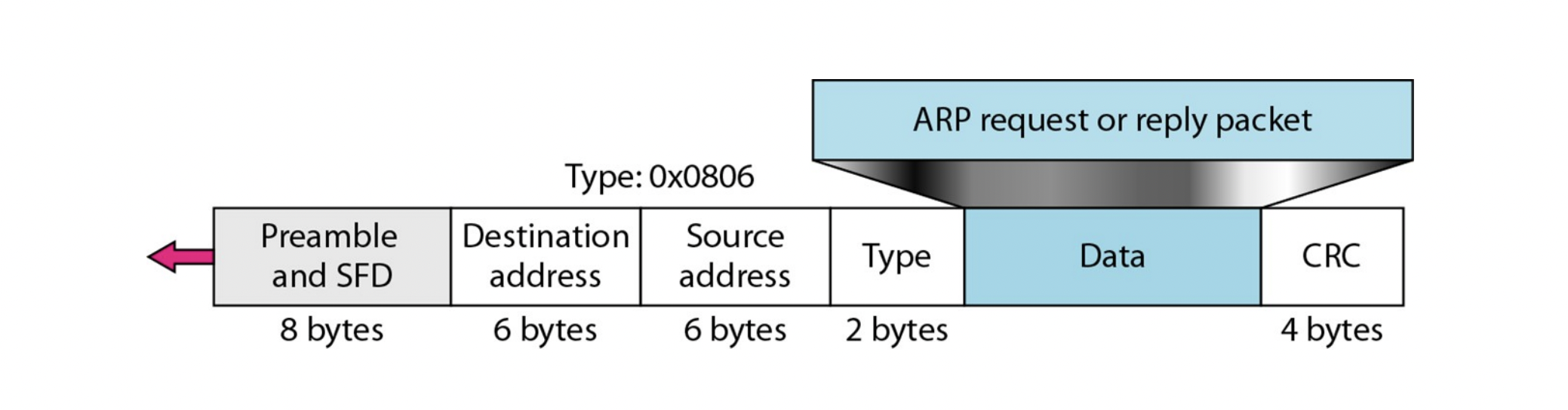
- 'Type' field는 ARP request/reply의 Data를 나타낸다
Operation
- Source는 Destination의 IP address는 알지만,
physical address를 모른다.
(따라서 packet을 보낼 수 없다)
- Source는 ARP request를 생성한다
- source IP address, physical address,
destination IP address를 포함한다.
- source IP address, physical address,
- ARP request is broadcast
- 같은 network에 있는 모든 host들이 request를 받는다
- destination IP address를 알고 있는 host가 packet에 답장을 보내고, 다른 host들은 packet을 버린다
- destination node가 source에게 ARP 답장을 보낸다
- packet은 source에게 unicast로 간다.
왜냐하면 destination은 source의 physical address를 알기 때문이다.
- packet은 source에게 unicast로 간다.
- Source는 ARP 답장을 받고 destination의 physical address를 알아낸다(??)
Example
-
host의
IP addrss = 130.23.43.20
physical address = B2:34:55:10:22:10 -
destination의
IP address = 130.23.43.25
physical address = A4:6E:F4:59:83:AB
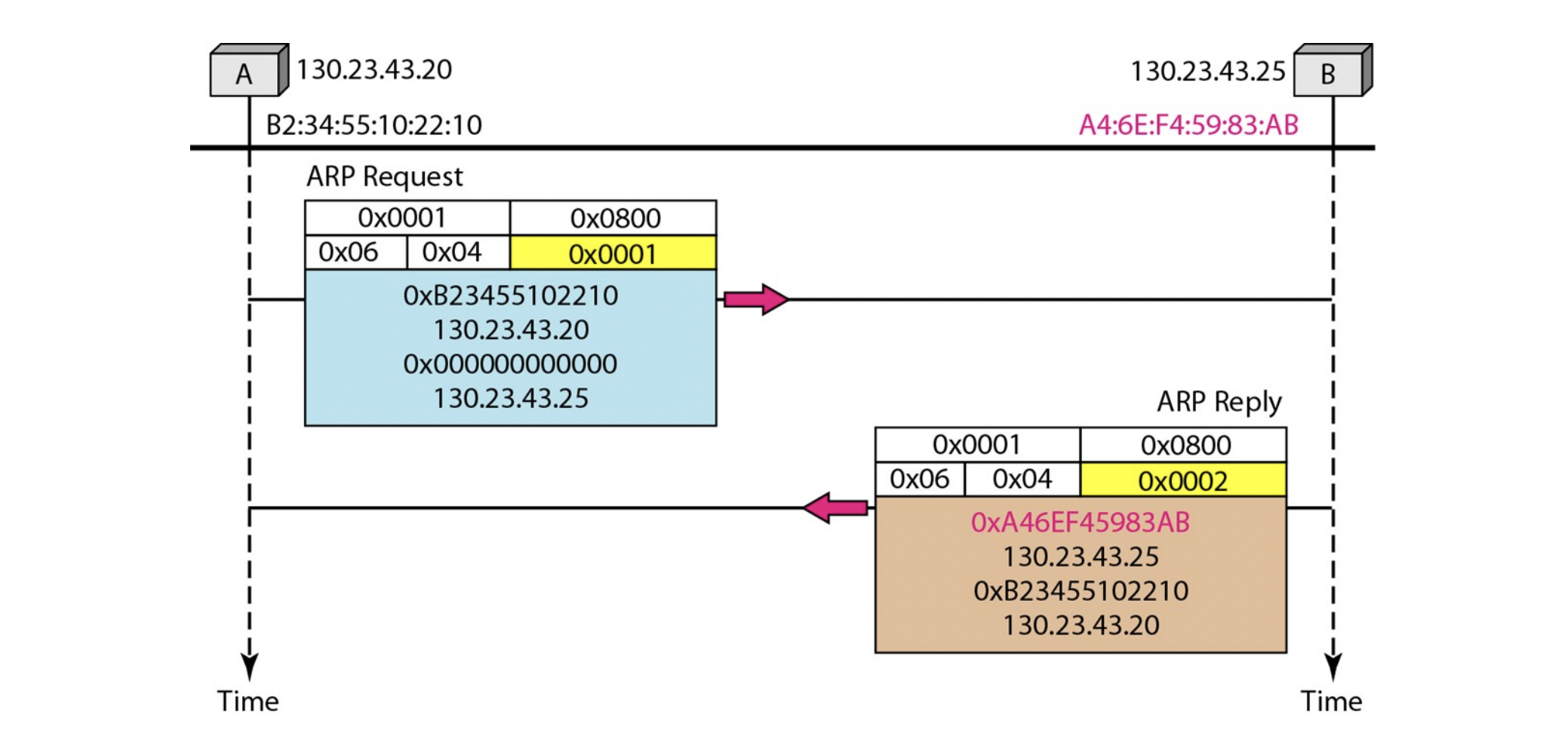
- reply 입장에서는 sender의 physical address field에 적어서 보내주고, sender는 이걸 이용해야 한다.
DHCP
Host Configuration
- Ethernet address (physical address)
- configured by manufacturer (제조사에 의해 구성)
- IP address (logical address)
- internetwork의 structure를 반영해야 한다.
- IP address는 현재 device가 어떤 네트워크에 연결되어있는지에 depend on
- device가 움직이면, IP address도 바뀐다
- 이를 수동으로 configuration하는 건 burdensome and error-prone
- internetwork의 structure를 반영해야 한다.
- Automatic configuration of IP address is needed
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
- network 내에 DHCP 서버가 존재한다
- administrative domain 내에 최소 하나의 DHCP 서버가 존재한다
- DHCP 서버는 가능한 address들의 pool을 유지한다
- DHCP 서버는 일정 기간동안 host에게 IP address를 임대해준다
- Host들은 address를 더 쓰고 싶으면 갱신해야 한다
- DHCP is an Application Layer Protocol
- 새로 네트워크에 부팅되거나 연결된 Host가
DHCP DISCOVER message를 broadcast한다 - DHCP relay가 DHCP server에게 unicast로 메세지를 보내고 응답을 기다린다
ICMP
- IP는 reporting error에 대한 mechanism이 없다.
- packet이 error 때문에 drop 되었을 때
- packet이 TTL 때문에 drop 되었을 때
- packet이 fragment의 loss 때문에 drop 되었을 때
- The purpose of ICMP is to report errors to the source
- ICMP is a Network Layer Protocol
ICMP Format
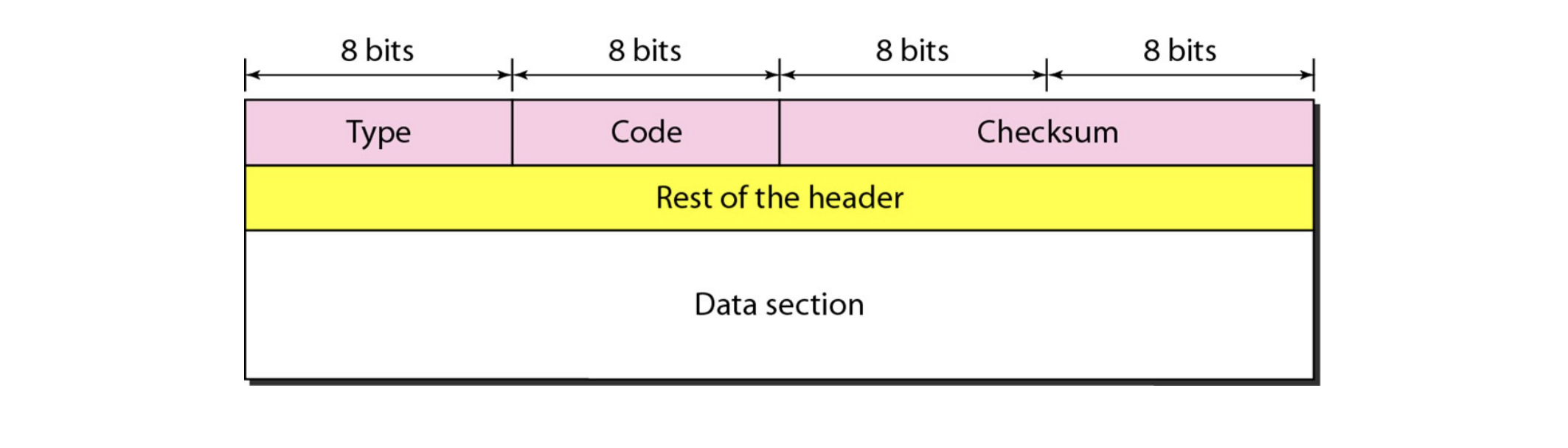
ICMP Functions
Error reporting
- ICMP는 다음과 같은 상황에서 source IP address에게 report를 보낸다
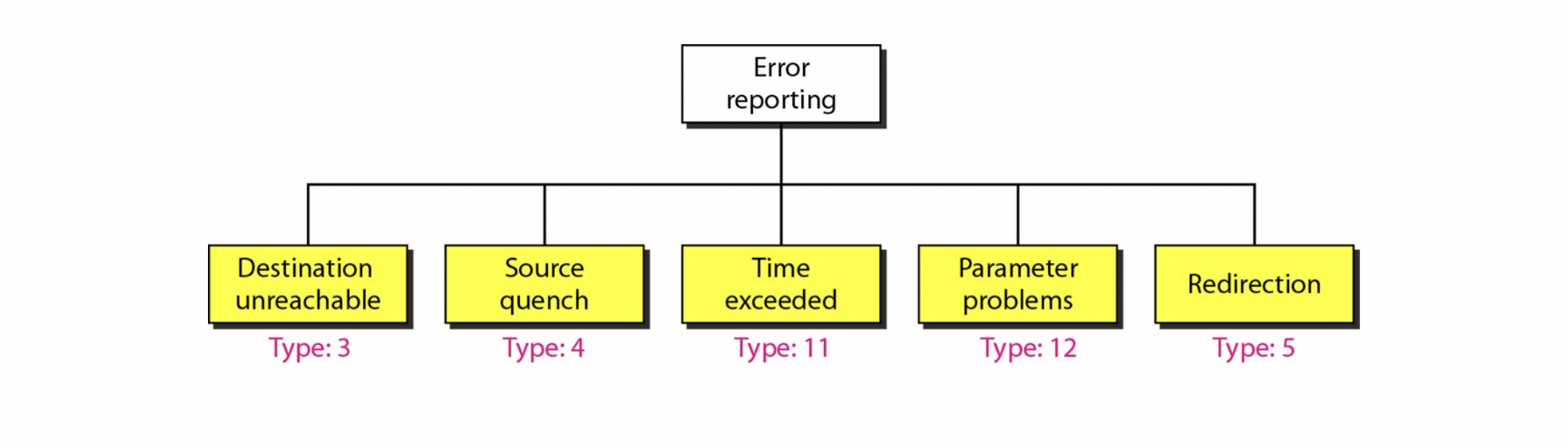
Destination Unreachable
- destination으로 가야 하는 next node를 찾지 못한다.
Source Quench
- 라우터나 호스트의 큐가 꽉 차서 더 이상 받지 못한다
Time Exceeded
- TTL이 0이 되었다
Parameter Problems
- 헤더에 문제가 생긴다. (ex. checksum이 맞지 않는다)
Redirection
- 위 case들과는 약간 결이 다르다 (packet drop x)
- host가 갈 수 있는 router가 여러 개일 때,
기본적으로 default gateway router를 선택한다. - 만약 더 좋은 route가 있다면,
router가 host에게 알려주고, routing table을 수정하도록 한다.
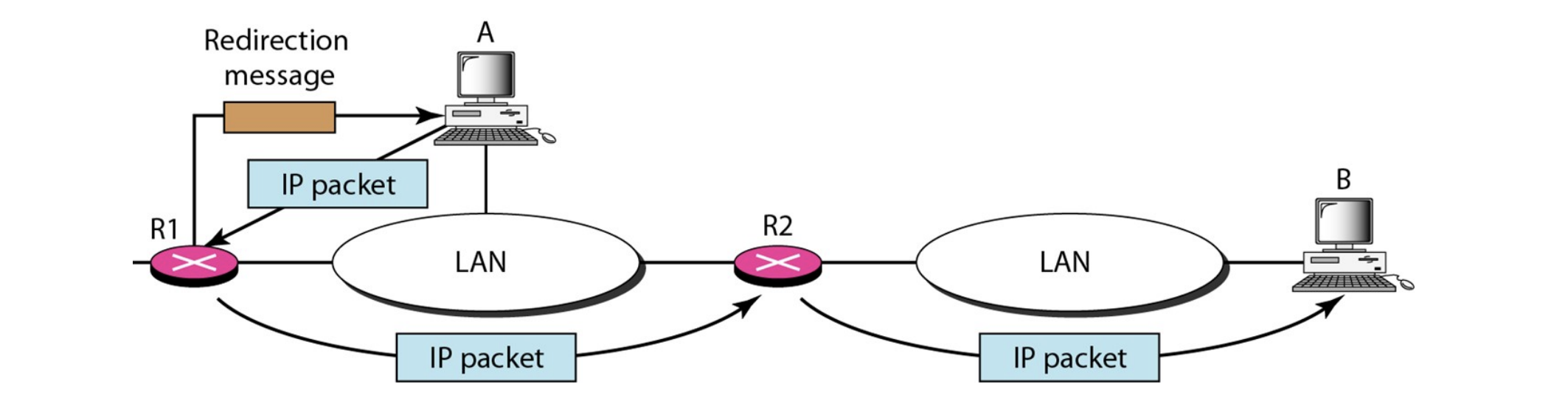
- R1과 R2는 A(host)와 같은 network에 있다.
- A의 default gateway는 R1이라서, data를 R1에게 보낸다.
- R1은 B로 가는 data는 R2로 보내는 게 더 좋다는 것을 find out.
- R1은 R2에게 packet 보내줄 건 보내주고,
A에게 redirection report를 보낸다.
Error reporting Rules
- ICMP packet은 ICMP packet 본인에 대해서는 생기지 않는다.
- 얘가 drop되면 그냥 운명인가보다... 해라
- fragment packet에 대해, 맨 처음 fragment에 대해서만 ICMP packet이 생긴다.
- ICMP는 multicast packet에 대해서는 생기지 않는다.
- 특수 목적으로 사용되는 주소(127.0.0.1, 0.0.0.0, ...)에 대해서는 ICMP가 생기지 않는다.
Query
- ICMP는 query information으로 사용될 수 있다.
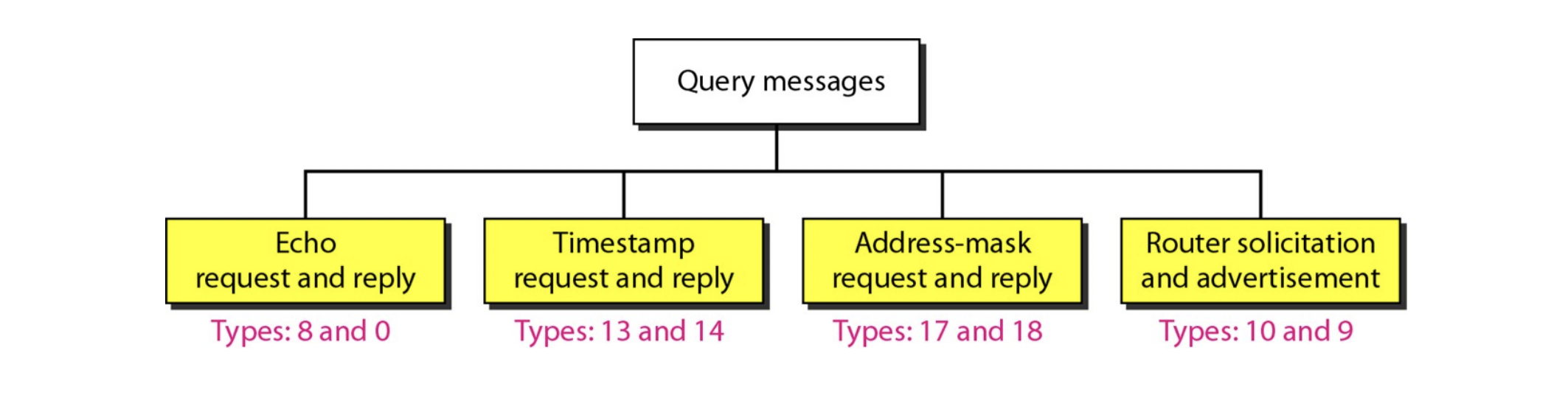
Echo request & reply
- ping
- destination이 available한지 체크하기 위해 사용한다
Time stamp request & reply
- destination까지의 round-trip time을 확인하기 위해 사용한다
Address-mask request and reply
- host가 IP address는 아는데, mask를 모른다
- broadcast로 address-mask request를 보내면
아무 node가 address-maks reply를 보내준다.
Router solicitation & advertisement
- host는 network에 무슨 router가 있는지 알고 싶어서 roter solicitation을 보낸다.
- router는 본인이 존재한다는 걸 host가 알도록 router advertisement를 보낸다.
IP-level debugging tool
- use ICMP for debugging purposes
ping
- An application to send ICMP messages to a destination host to find out if it is available
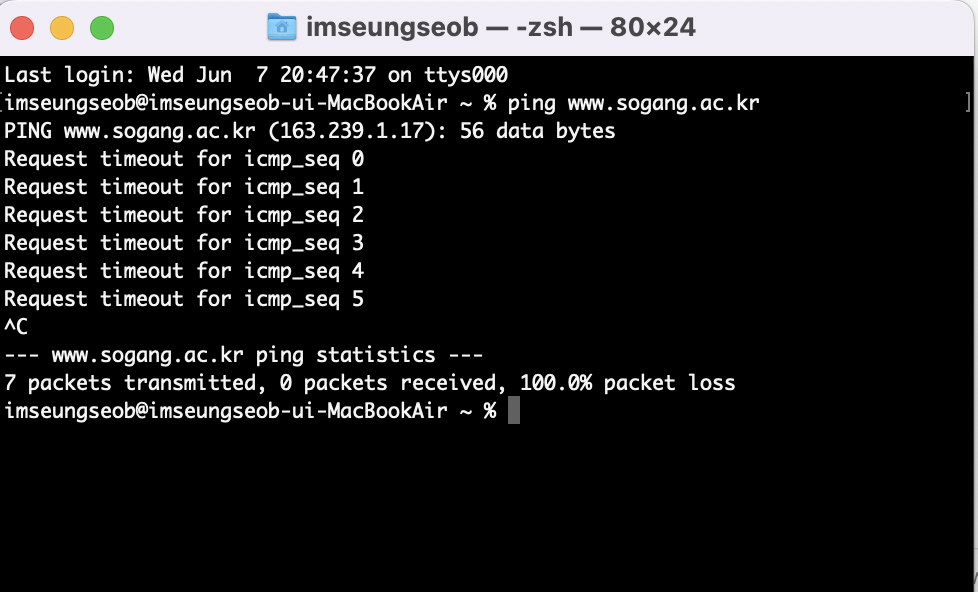
traceroute
- An application to trace routers between source and destination host
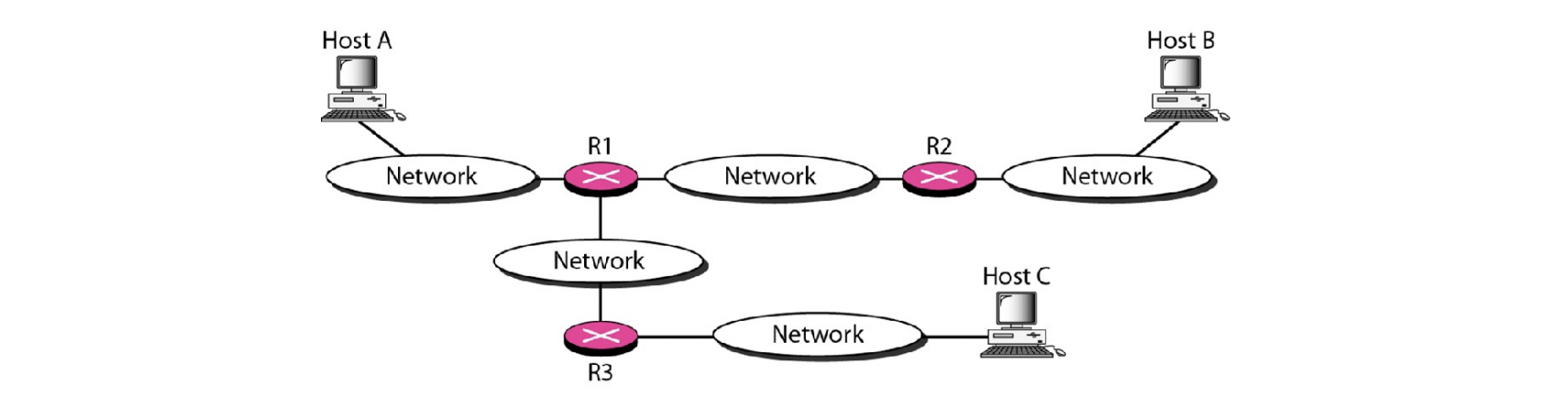
- A가 B에게 UDP packet(아무 의미 없는 packet)을 보낸다.
이 때, TTL은 1이다. (다음 router 가면 죽는다) - 그 packet은 R1에서 drop되고, ICMP가 A에게 보내진다.
- 이 ICMP를 이용해서, A는 R1의 IP address와 A부터 R1까지 round-trip time을 알 수 있다.
- 평균 round trip time을 알기 위해 여러 UDP packet을 보낸다.
- 이게 끝나면, TTL을 1 올린다
- Destination host에서는 ICMP가 A로 보내지지 않는다.
- 하지만, destination host에는 traceroute packet을 받는 UDP port가 없다. 즉, 받을 수가 없다.
- 따라서 ICMP (destination unreachable)이 생성되어 A로 보내진다.
- A가 B에게 UDP packet(아무 의미 없는 packet)을 보낸다.
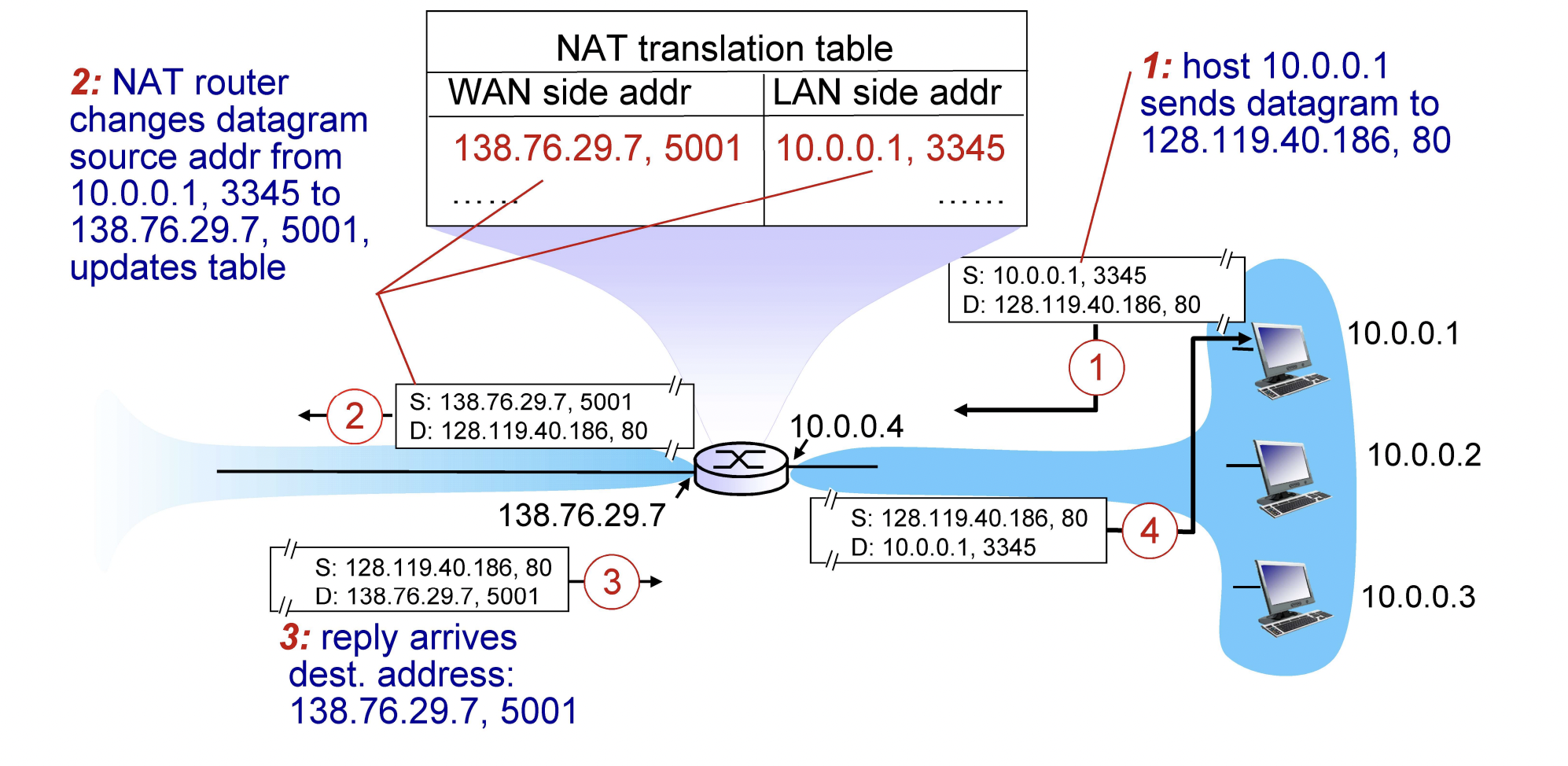
NAT
Network Address Translation
-
하나의 routersms NAT를 이용해서 local network를 생성할 수 있다.
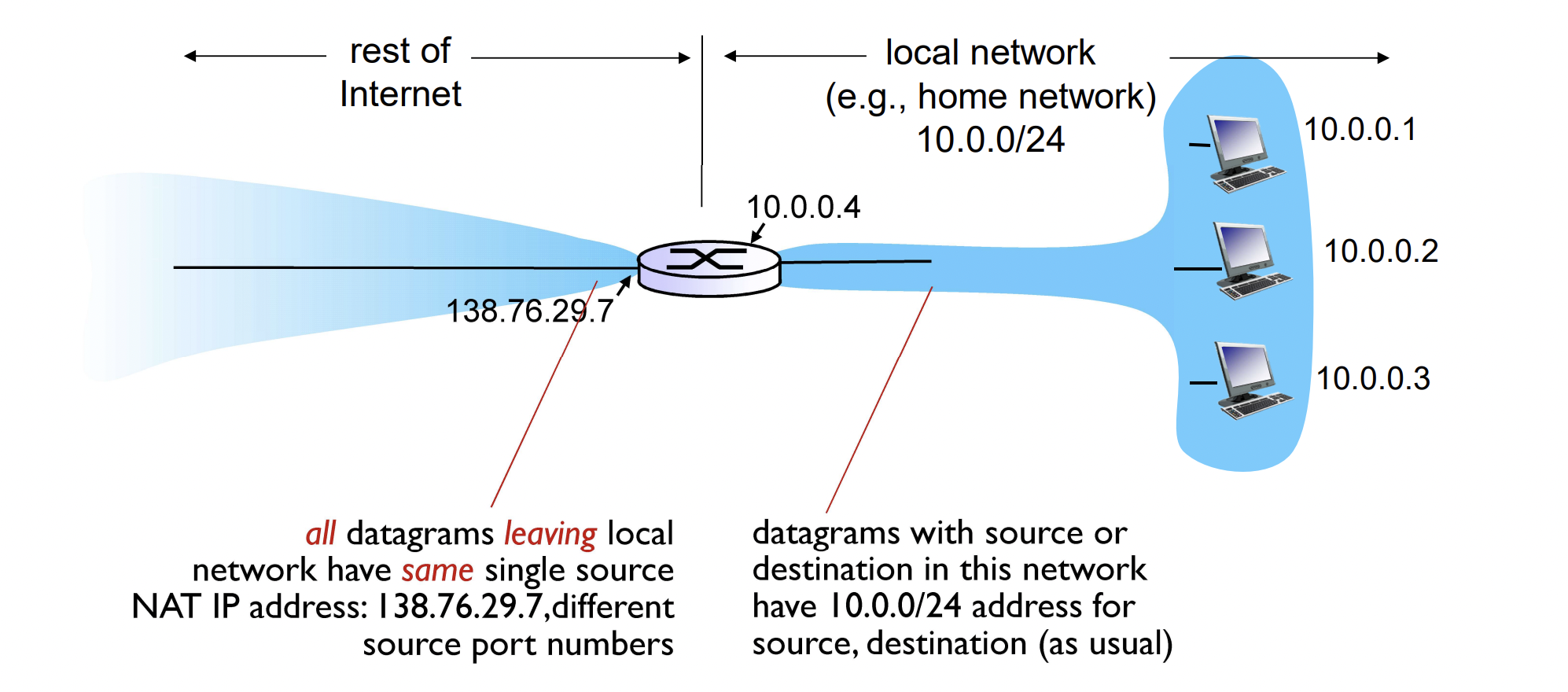
- 본인이 DHCP 서버 역할을 해서,
본인에게 접속하는 device들에게 address를 할당한다 - 바깥에서 보면 모두 138.76.29.7이지만,
안에서 보면 각자 private address가 있다.
- 본인이 DHCP 서버 역할을 해서,
-
Motivation : 바깥 세상에서 보았을 때는 local network가 just one IP address만 사용하는 것으로 보인다
- ISP로부터 address의 범위가 필요하지 않다.
- just one IP address for all devices
- 바깥 세상에 알리지 않고 local network 내의 device들의 주소를 바꿀 수 있다.
- local network 내의 device들의 주소를 바꾸지 않고 ISP를 바꿀 수 있다.
- Devices inside local network NOT explicitly addressable, visible by outside world (a security benefit)
- ISP로부터 address의 범위가 필요하지 않다.
NAT router function
- outgoing datagrams
- replace (source IP address, port #) of every outgoing datagram
to (NAT IP address, new port #)- remote clients/servers will respond
using (NAT IP address, new port #) as destination address
- remote clients/servers will respond
- replace (source IP address, port #) of every outgoing datagram
- Remember (in NAT translation table)
every (source IP address, port #) to (NAT IP address, new port #)
translation port
- incoming datagrams
- replace (NAT IP address, new port #) in dest fields of every incoming datagram with corressponding
(source IP address, port #) stored in NAT table
- replace (NAT IP address, new port #) in dest fields of every incoming datagram with corressponding