Transaction Concept
- A transaction is a unit of program execution
that accesses and possibly updates various data items
- ex). Transfer $50 from account A to account B
1. read(A) // tuple이 disk에서 buffer로 올라오고, 그 buffer로부터 "read"
2. A = A - 50 // register에서 값 변경 (buffer 값 변경 x)
3. write(A) // buffer 값 업데이트
4. read(B)
5. B = B + 50
6. write(B)- 2가지 main issue
- hardware failure, system crash와 같은 다양한 실패
- 여러 transaction들의 동시 실행
ACID Properties
4가지 requirement
Atomicity Requirement
- 만약 step 3와 step 6 사이에서 transaction이 fail했으면,
money will be "lost" - ALL OR NOTHING. 100% 반영하거나, 그게 아니라면 아예 database에 반영하지 않는다.
Durability requirement
- user가 transaction이 완료되었다고 notify하면,
transcaction에 의한 db update는 반드시 진행되어야 한다.
(even if there are software or hardware failures)
Consistency requirement
- 위 예시에서). transaction 실행에 의한 A + B 값은 변함이 없어야 한다.
- 일반적으로 consistency requirement는 다음을 포함한다 :
- explicitly specified integrity constraints such as primary keys and foreign keys
- implicit integrity constraints such as sum of balances of all accounts
- During transaction execution, db may be temporarily inconsistent
- When transaction completes successfully, db must be consistent
Isolation requirement
- 위 예시에서). 3번과 6번 step 사이에 다른 transaction T2가 A, B값에 접근하려고 하면, inconsistent database가 된다.
- transaction들을 순차적으로(serially) 실행시킴으로서 보장받을 수 있다.
- 하지만, multiple transaction을 동시에 실행시키는 건 분명히 이점이 있다.
Summary
-
A transaction is a unit of program execution
that accesses and possibly updates various data items.
To preserve integrity of data, db system must ensure 4 things -
Atomicity : Either all operations of the transaction are properly reflected in the db or none are.
-
Consistency : Execution of a transaction in isolation preserves the consistency of the db.
-
Isolation : Although multiple transaction may execute concurrently,
each transaction must be unaware of other concurrently executing transactions.
Immediate transaction results must be hidden from other concurrently executed transactions. -
Durability : After a transaction completes successfully,
the change it has made to the db persist,
even there are system failures.
Transaction State
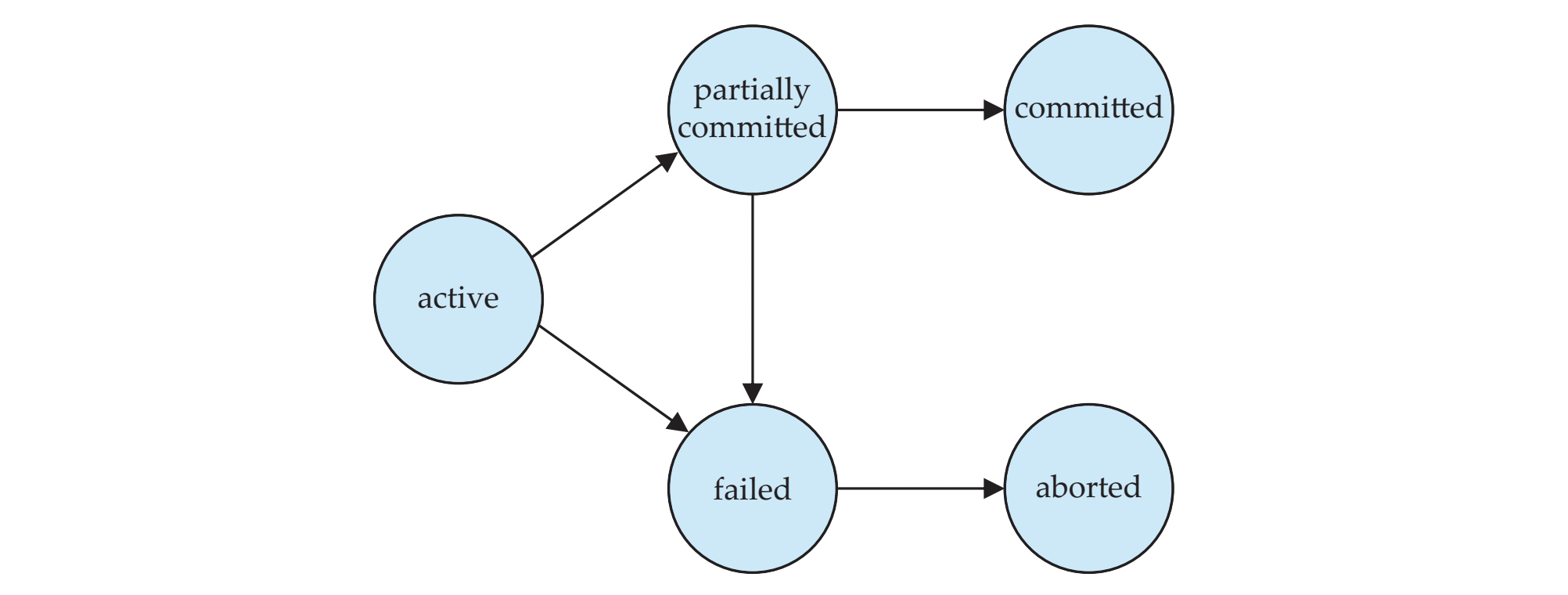
- Active : 현재 진행중.
- the initial state;
- transaction이 실행중일 때 이 state에 있는다
- Partially committed : buffer에 update 완료 (disk에 쓰기 전)
- after the final statement has been executed
- Failed
- after the discovery that normal execution can no longer proceed
- Aborted : 실행 중단 -> 실행하기 전 상태
- after the transaction has been rolled back and the db restored to its prior to the start of the transaction.
- Two options
- Restart the transaction
- internal logical error가 없을 때 가능
- Kill the transaction
- Restart the transaction
- Committed : disk에 write 완료
- after successful completion
Concurrent Executions
- multiple transaction은 동시에 실행될 수 있다
- Advantages :
- 향상된 processor와 disk의 utilization,
leading to better transaction throughput - transaction에 대한 average response time 감소 :
short transactions need NOT wait behind long ones
- 향상된 processor와 disk의 utilization,
- Concurrency control schemes
: Mechanisms to achieve isolation- concurrent transactions 사이의 interaction을 control한다
Schedule
- A sequence of instructions that specify the chronological order in which instructions of concurrent transactions are executed
- transaction 집합의 schedule은 그 transaction들의 모든 instruction을 포함하고 있어야 한다
- 각 transaction의 instruction 순서를 유지해야 한다
- 성공적으로 실행을 마친 transaction은 마지막 statement에서
commit instruction을 갖는다 - 성공적으로 실행을 실패한 transaction은 마지막 statement에서
abort instruction을 갖는다
Schedule 1
A serial schedule in which T1 is followed by T2 :
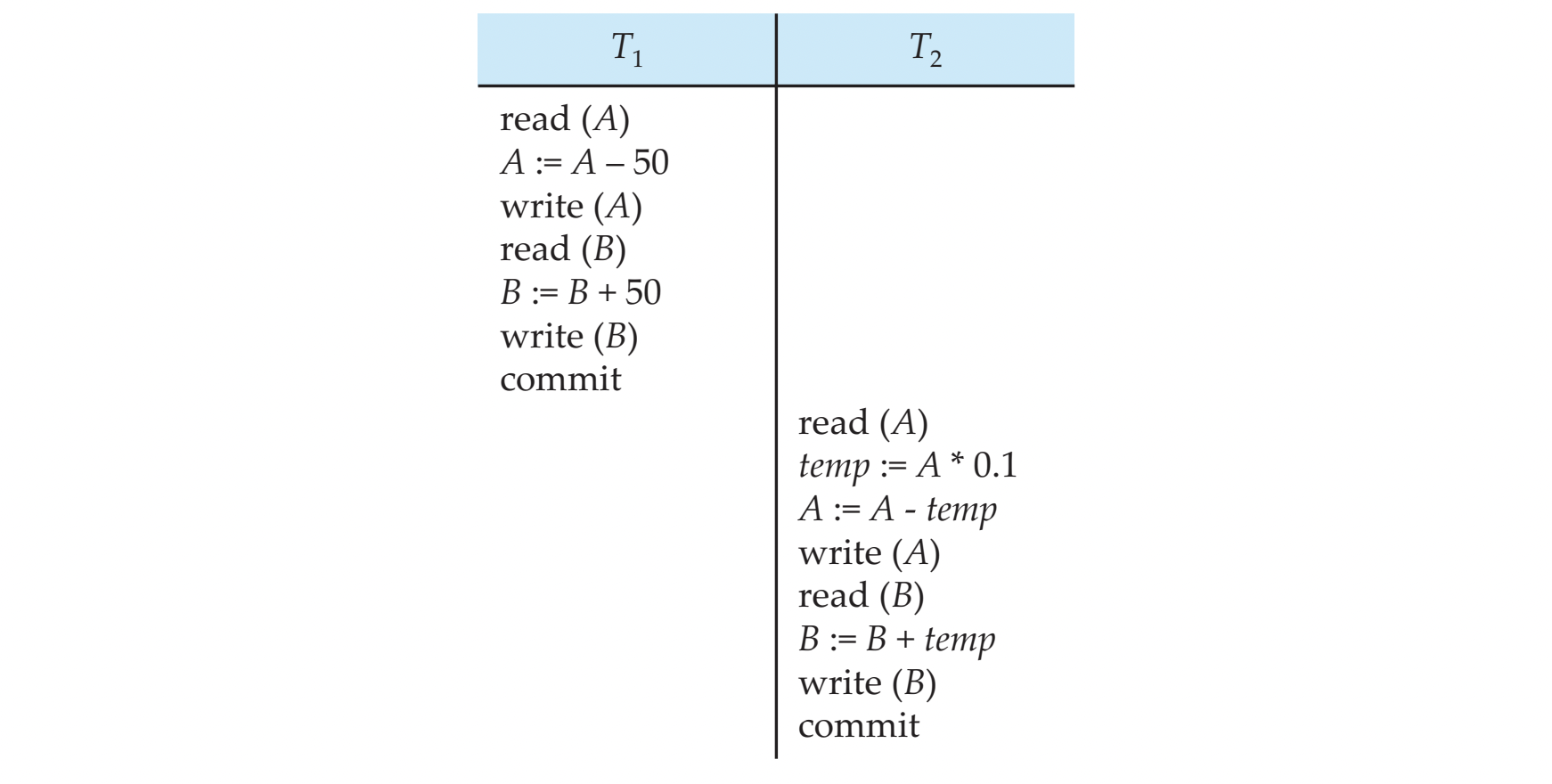
- A + B 계속 200 유지
- (100, 100) (50, 150) (45, 155)
Schedule 2
A serial schedule where T2 is followed by T1 :
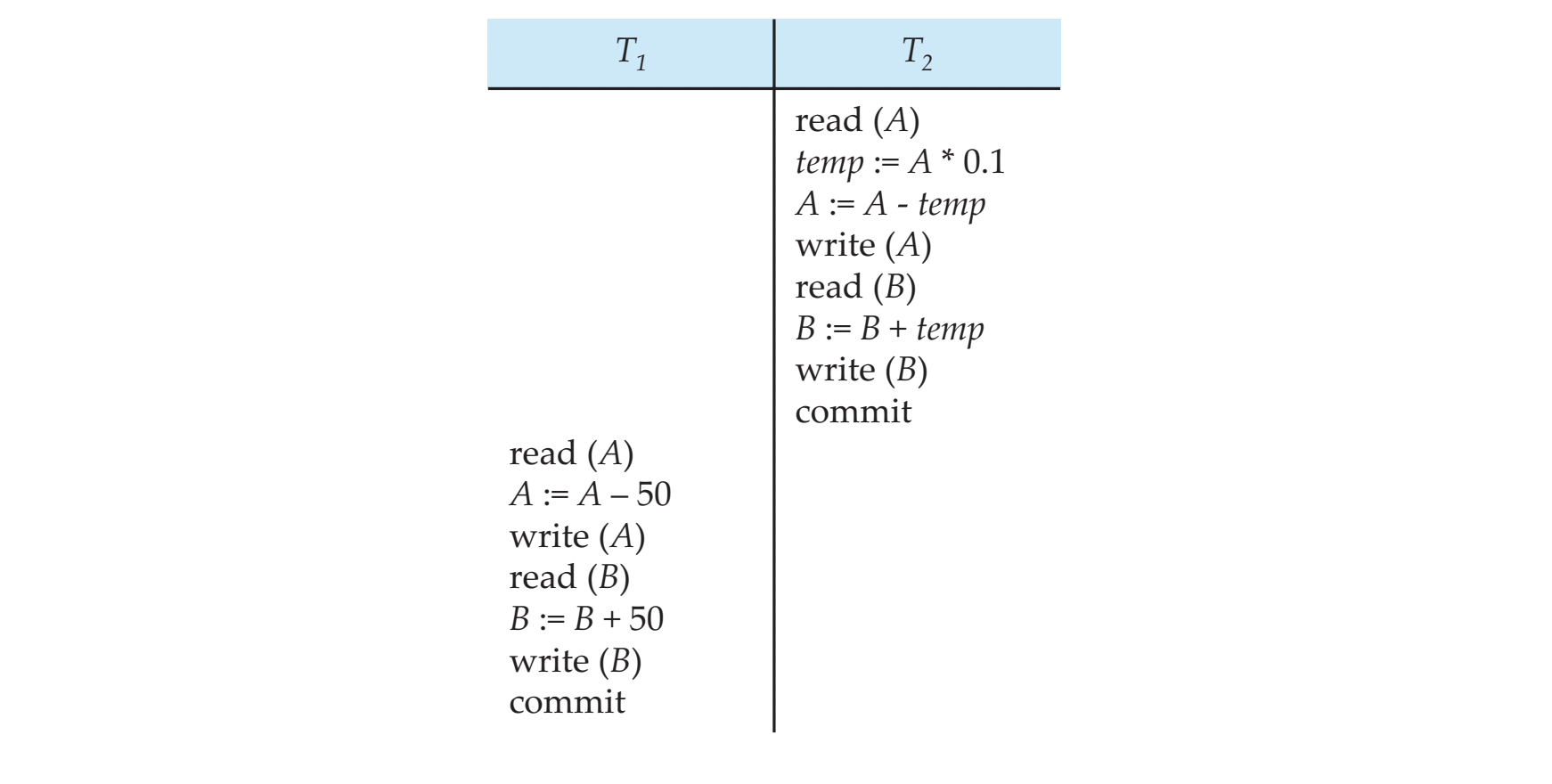
- A + B 계속 200 유지
- (100, 100) (90, 100) (40, 160)
Schedule 3
NOT a serial schedule, equivalent to Schedule 1
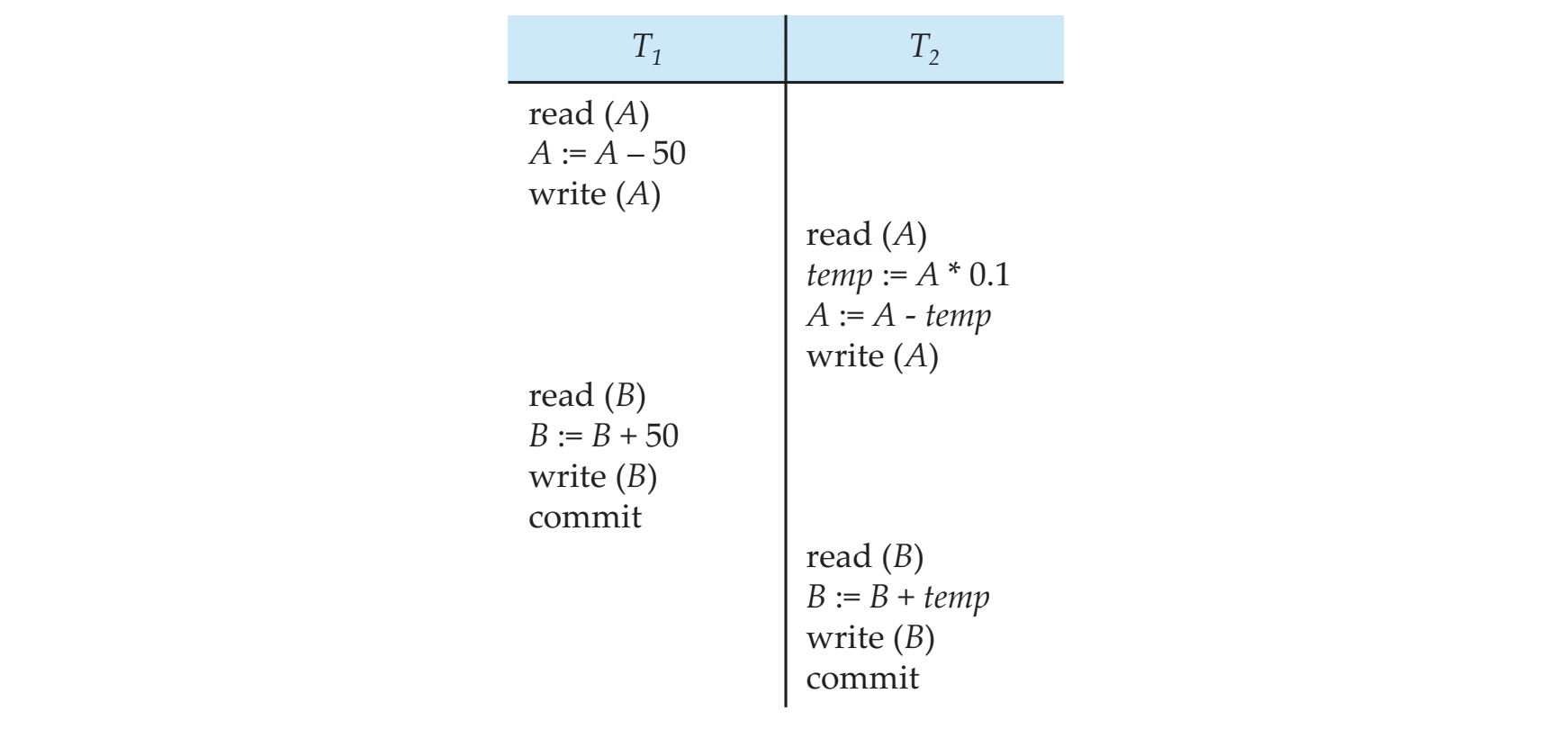
- A + B 계속 200 유지
- (100, 100) (50, 100) (45, 100) (45, 150) (45, 155)
Schedule 4
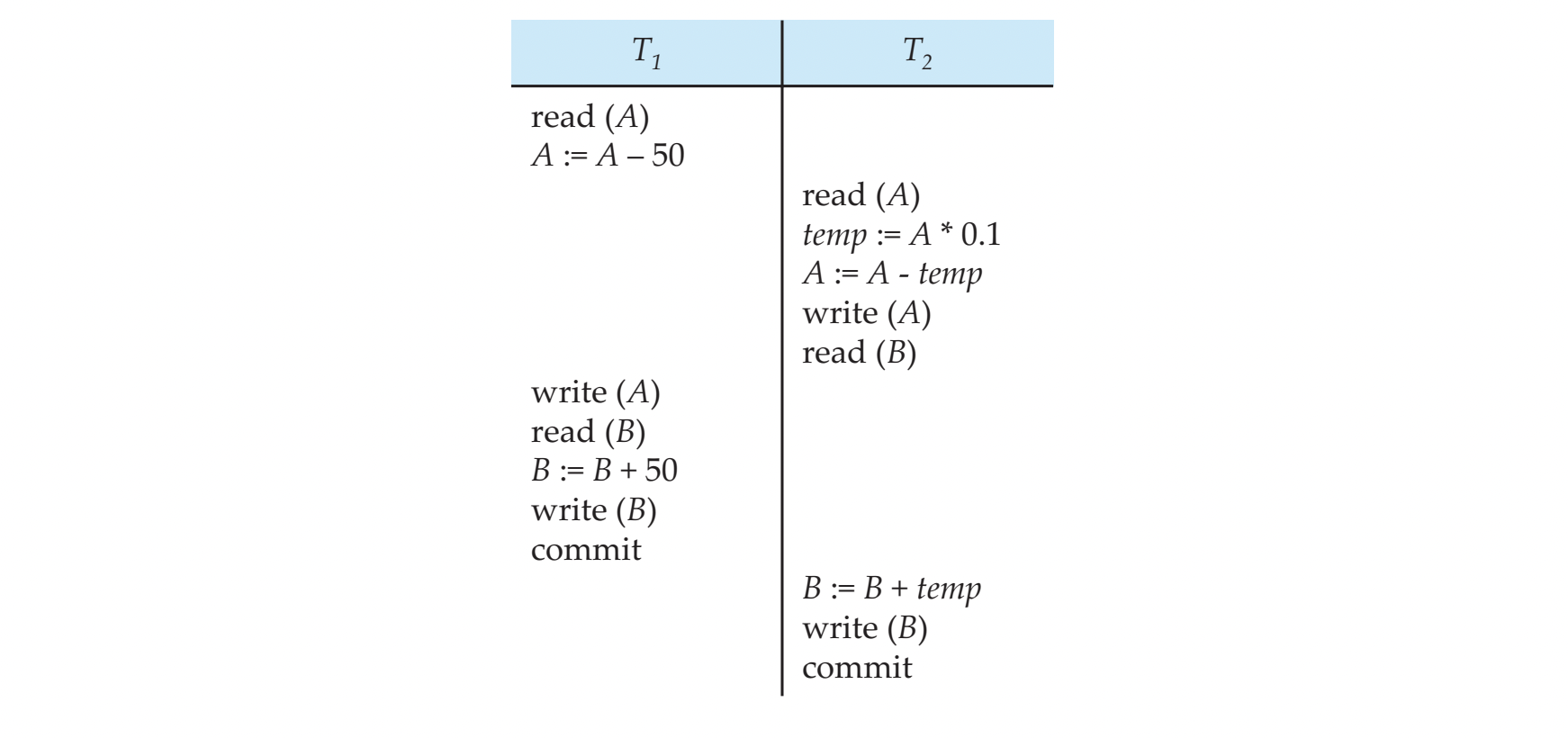
- Does NOT preserve the value of A + B
- (100, 100) (90, 100) (50, 100) (50, 150) (50, 110)
Serializability
- 기본 가정 : Each transaction preserves db consistency
- 따라서, transaction 집합의 serial execution은 preserves db consistncy
- 어떤 schedule이 serial schedule과 동일한 결과를 내면,
it is serializble
- Conflict serializability와 View serializability가 있는데, 주로 conflict serializability에 대해 배운다.
- Simplified View of transaction
- read와 write 이외의 operation은 모두 무시한다
Conflict Instruction
- transaction Ti, Tj와
각각의 instruction Ii, Ij,
얘네가 둘 다 접근하는 item Q에 대해,
다음과 같은 상황에서 conflict 발생 (전자가 Ii, 후자가 Ij)- read(Q), read(Q) : Don't conflict
- read(Q), write(Q) : conflict
- write(Q), read(Q) : conflict
- write(Q), write(Q) : conflict
- 둘 사이의 conflict는 강제적으로 순서를 갖게 한다
-
schedule에서 둘이 연속적이고, conflict가 발생하지 않으면,
둘이 순서가 바뀌어도 결과는 동일하다 -
만약 non-conflicting instruction의 swap에 의해
schedule S가 S'으로 바뀌었다면,
S와 S'은 conflict equivalent하다
- schedule S가 serial schedule과 conflict equivalent하면,
S는 conflict serializable하다
conflict serializable example
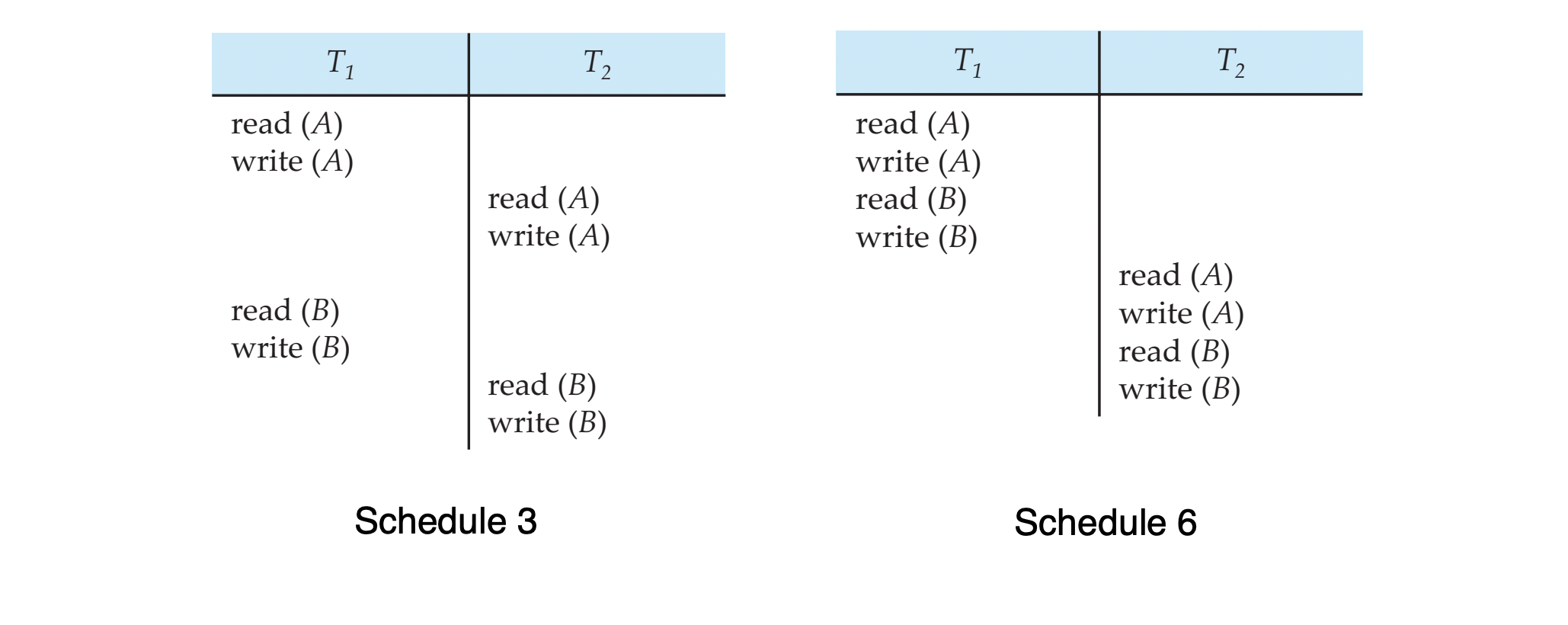
- schedule 3는 schedule 6로 바뀔 수 있다.
- T2의 read(A)/write(A)와 T1의 read(B)/write(B)는 서로 conflict하지 않기 때문에 위치가 바뀔 수 있다.
- schedule 6는 serial schedule이기 때문에,
schedule 3는 conflict serializable하다
NOT conflict serializable example
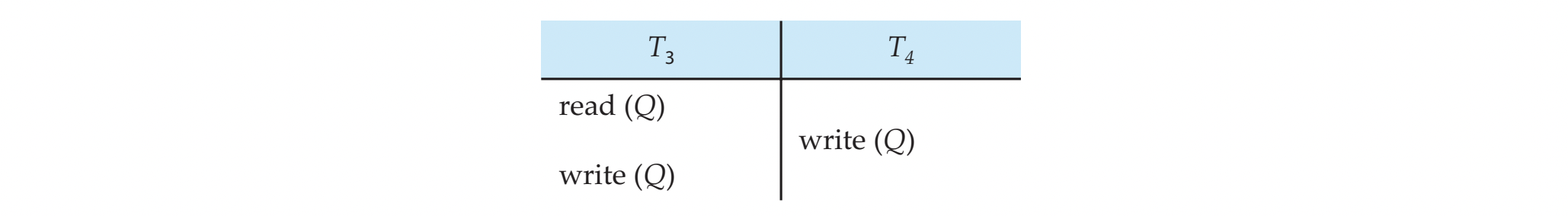
- 위 schedule을 <T3, T4> 또는 <T4, T3>처럼 serial schedule로 바꿀 수 없다.
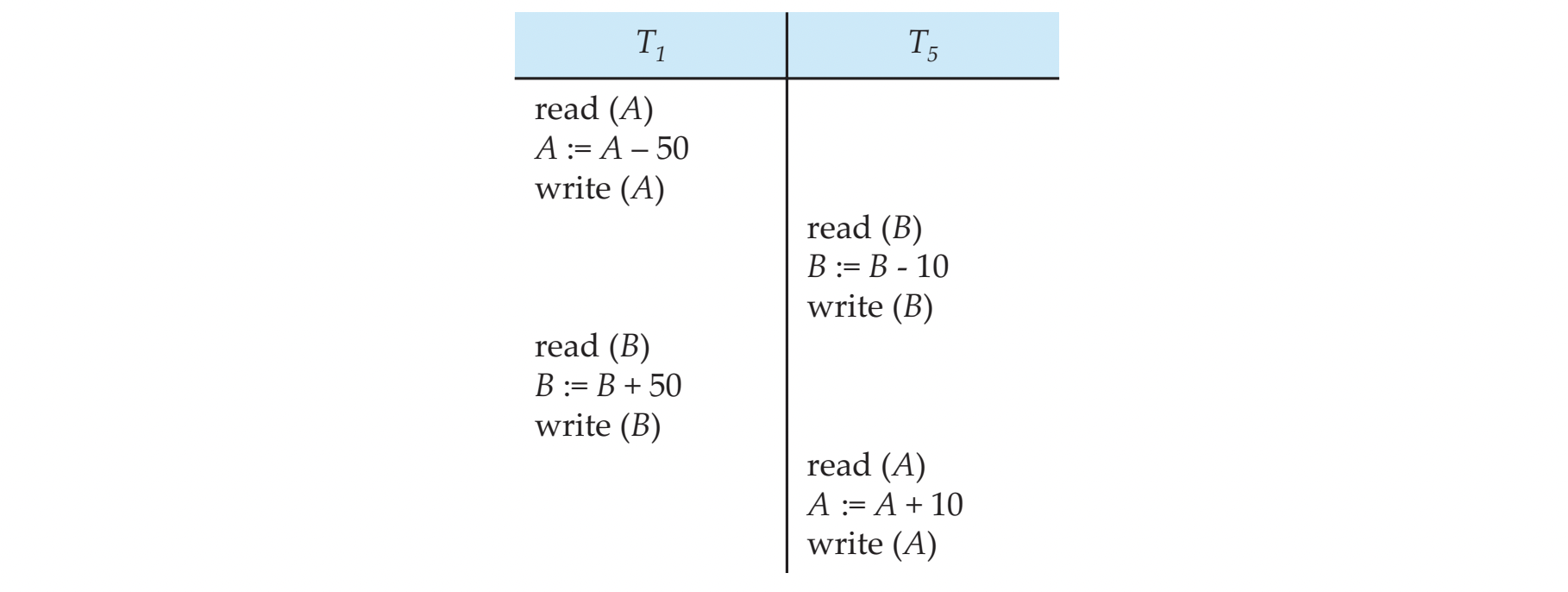
NOT conflict serial but same outcome
Testing for Serializability
- Consider some schedule of a set of transactions T1, ..., Tn
- Precedence graph : vertices가 transaction name인, direct graph
- 만약 graph가 acyclic하면, schedule is conflict serializable
- acyclic한지는 DFS를 이용해서 찾는다. (n^2 or n+e)
- graph가 acylic할 때, serializability order는 topological sorting에 의해 계산될 수 있다.
- 노드의 indegree가 0인 노드 먼저 하고, 이거 삭제하고
다음 indegree가 0인 노드 하고, 삭제하고,
계속 반복한다
- 노드의 indegree가 0인 노드 먼저 하고, 이거 삭제하고
Recoverability
Recoverable schedule
- Tj가 이전에 Ti에 의해 write된 data를 읽을 때,
Ti의 commit operation이 Tj의 commit 보다 이전에 나타나야 한다.
- NOT recoverable
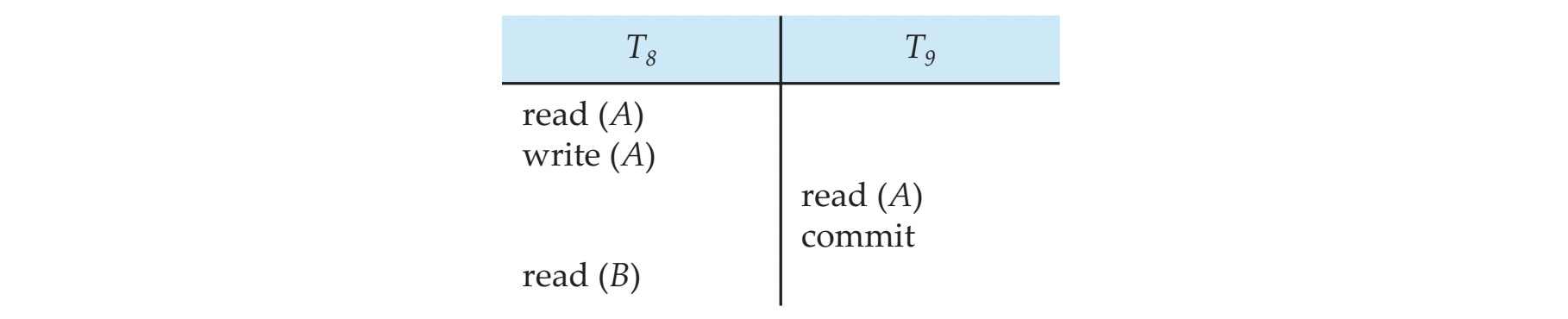
- 뭐가 문제나면,
만약 T8이 abort되면, T8에 의한 작업은 모두 취소가 되어야 한다.
T9은 이미 commit이 되었기 때문에 취소가 안되는 상태인데,
그럼 얘가 읽은 A값은 inconsistent한 값이 된다!!
- 뭐가 문제나면,
Cascading Rollback
- single transaction failure가 series of transaction rollbacks을 발새시킨다
- 아래 그림은 아무 transaction도 commit이 되지 않은 schedule이다.
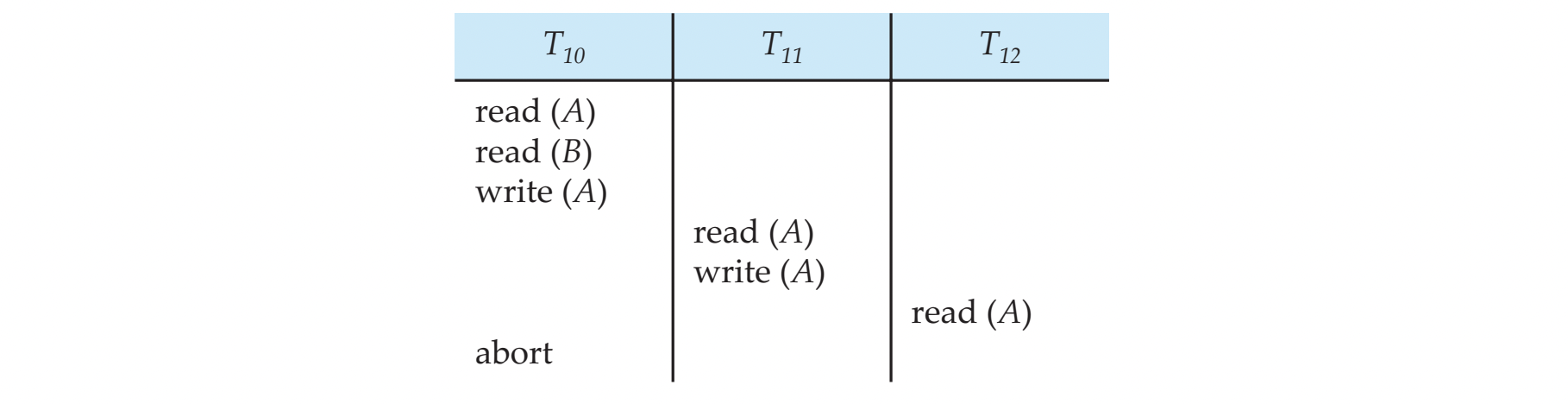
- T10이 abort나면, T11, T12도 모두 취소된다.
- recoverable
Cascadeless Schedule
- cascading rollback이 일어날 수 없다.
- Tj가 Ti에 의해 write된 data를 read할 때,
Ti의 commit operation이 Tj의 read보다 먼저 나타난다. - Every cascadeless schedule is also recoverable
- 아주 바람직한 방법이다.
Concurrency Control
- db는 반드시 모든 schedule이 다음 조건을 만족하게 해야 한다
- conflict serializable 하거나,
- recoverable하고 가능하다면 cascadeless.
- 단순히 serializable하게 하면 좋긴 하지만 concurrency 측면에서 낮은 결과가 나온다.
- Goal : to develop concurrency control protocols that will ensure serializability
- Schedule은 반드시 conflict serializable하고, recoverable하고, 가능하다면 cascadeless해야 한다. db의 consistency를 위해.
- concurrency-control은 amount of concurrency they allow와 amount of overhead that they incur 사이의 tradeoff가 있다.