Wi-Fi
-
A name for local area wireless computer networking technology
-
Based on IEEE 802.11 standards
on Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) -
Used as a synonym for WLAN (Wireless LANs)
- physical layer와 data link layer에서 정의된다
802.11 standards: The main stream
Legacy 802.11 (1997)
- 주파수 대역 : 900MHz, 전송속도 : 2Mbps
- Frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS)
802.11b (1999)
- 2.4GHz band, 11Mbps
- Direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS)
802.11a (1999)
- 5GHz band, 54Mbps
- Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM)
802.11g (2003)
- 2.4GHz band, but OFDM and 54Mbps
- compatible with 802.11b
802.11n (2009)
- 2.4GHz and 5GHz band
- OFDM
- up to 600Mbps with 40MHz channel, 4x4 MIMO
802.11ac (2014)
- Gigabit throughput
- Wider RF bandwidth, more MIMO streams, high-density modulation
and many others...
Wireless Channel
- signal은 transmit (TX) antenna로부터 wireless channel로 전송된다
- signal은 공기 중을 날아서 receive (RX) antenna에게 도착한다
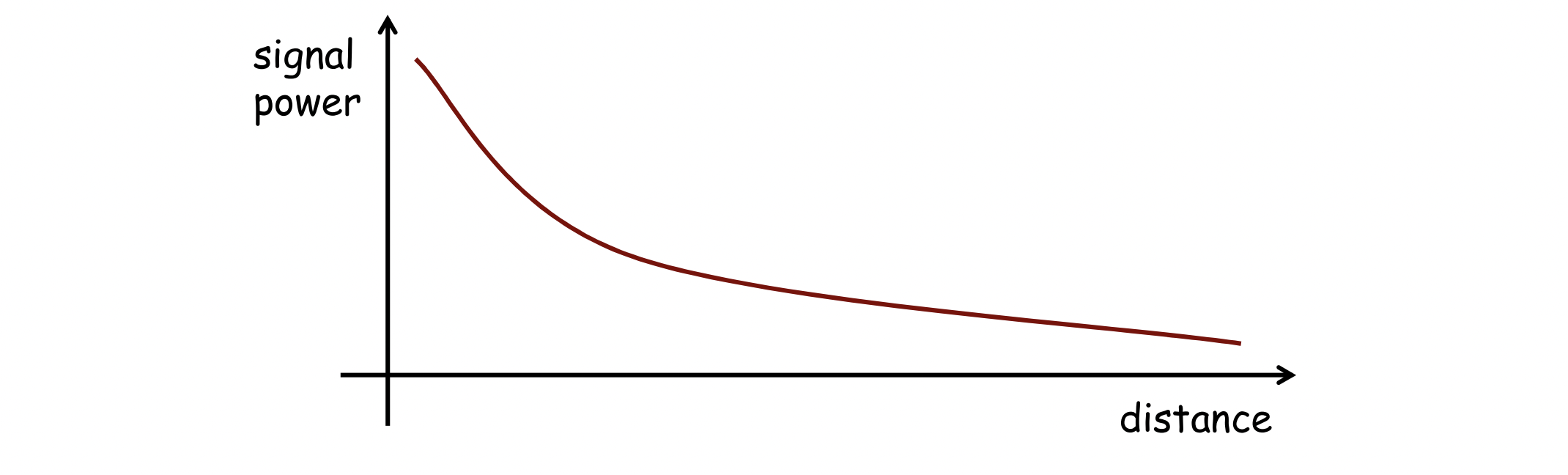
Signal Attenuation
- signal이 공기 중을 날아갈수록, power는 감쇄한다
Pathloss
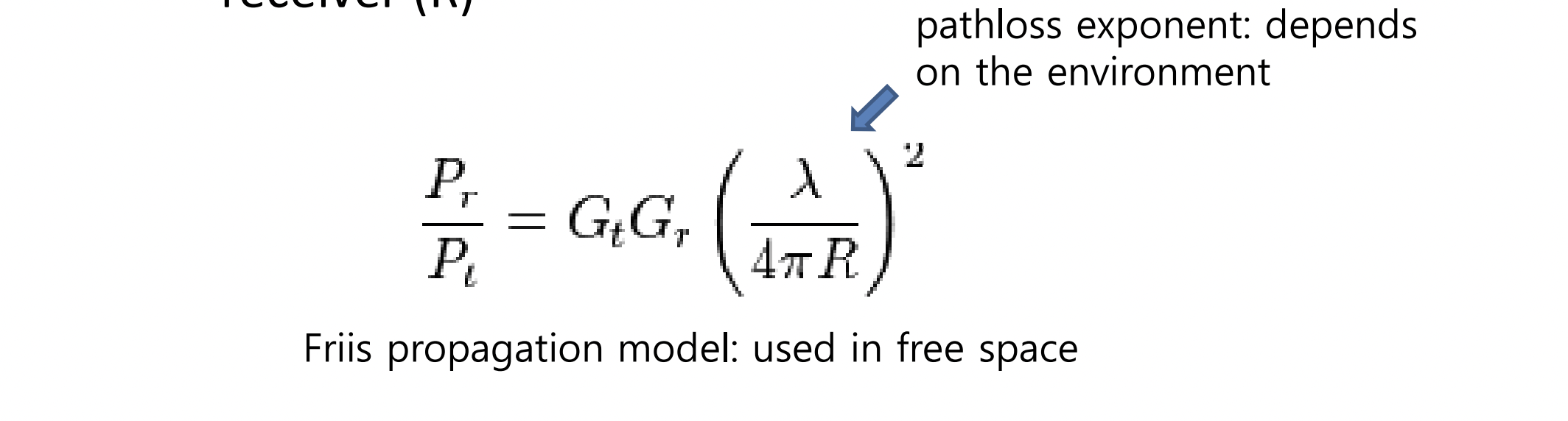
- The receiver (Pr) is basically a function of transmit power (Pt) and the distance between transmitter and receiver
- Signal attenuation based on distance is called pathloss
Receiver Sensitivity
- Receive antenna는 signal power가 receiver sensitivity보다 강할 때만 signal을 받을 수 있다
- Receiver sensetivity depends on the hardware
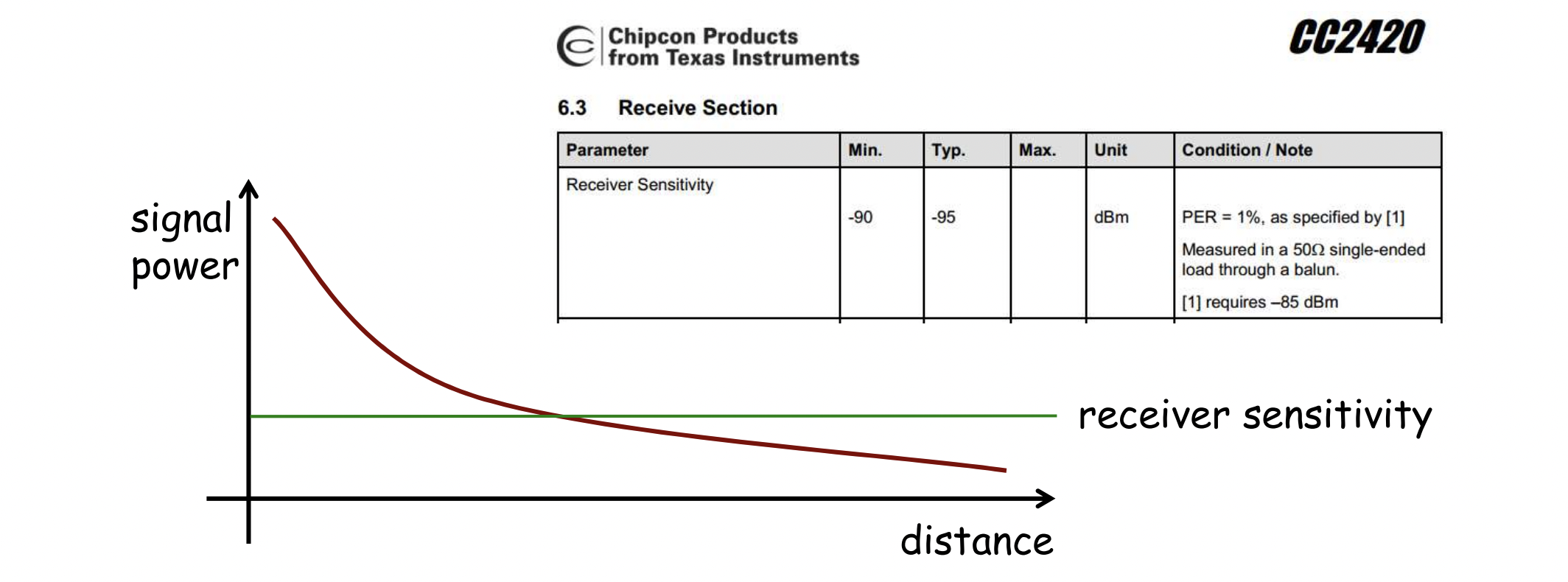
- Receiver sensetivity depends on the hardware
SNR
-
signal이 RX sensitivity보다 강하게 받아졌다고 하더라도,
receiver가 signal을 decode할 수 있을지는 SNR(Signal-to-Noise Ratio)에 달려있다
-
때때로, SINR(Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio)이 이용되기도 한다
-
decoding하기 위한 minimum SNR은 mudulation과 coding에 의존한다
-
Higher modulation and coding level requires higher SNR
Fading
-
received signal power에 영향을 주는 요소는 Pathloss와 Fading이 있다
-
Fading : Deviation of attenuation affecting a signal
-
Slow fading (large-scale fading, shadowing)
- 단순히 장애물 때문에 발생하는 감쇄의 차이
-
Fast fading (small-scale fading)
- 파장의 강화 or 상쇄로 인한 감쇄의 차이
Slow (large-scale) fading
- Large obstruction such as hill or large building obscures the main signal path between the transmitter and the receiver
- Modeled using log-normal distribution
Fast (small-scale) fading
- Caused by multipath propagation
- Amplitude and phase change imposed by the channel varies considerably over the period of use
- 파장의 강화 or 상쇄로 인한 감쇄의 차이
-
Wi-Fi : Physical Layer Aspects
Physical Layer에서,,,
- Signal generation from bits
- Recovery of bits from the received signal
- Tightly coupled with physical medium
- Modulation and coding scheme (MCS)
Modulation
-
정보를 담고 있는 modulating signal을 이용해서
carrier signal의 하나 이상의 properties를 구분하는 과정 -
carrier signal : a high frequency signal for carrying data
- E.g. WLAN channels
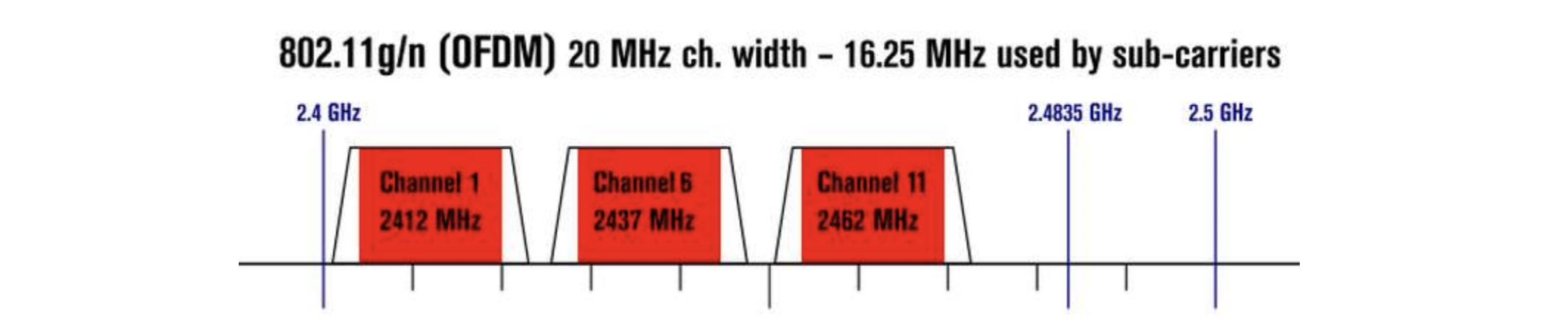
- E.g. WLAN channels
Modulation
- ASK, FSK, PSK
- QAM (PSK + ASK)
Modulation used in Wi-Fi
- BPSK (Binary PSK) : encode 1 bit on a symbol
- 2 different signals
- QPSK (Quadrature PSK) : encode 2 bits on a symbol
- 4 different signals
- 16-QAM : encode 4 bits on a symbol
- 16 different signals
- 64-QAM : encode 6 bits on a symbol
- 64 different signals
Coding (Channel Coding)
- message가 에러에 tolerable할 수 있도록
error-correcting codes (ECC)를 삽입한다- E.g. Hamming (7, 4) code
: corrects 1-bit error in a 7-bit message
- E.g. Hamming (7, 4) code
- Coding rate
- message에서 data bit의 비율
- E.g. 3/4 coding rage : 75% data, 25% ECC
높아질수록 데이터 효율은 증가하지만,
에러 발생했을 때 correction이 줄어든다
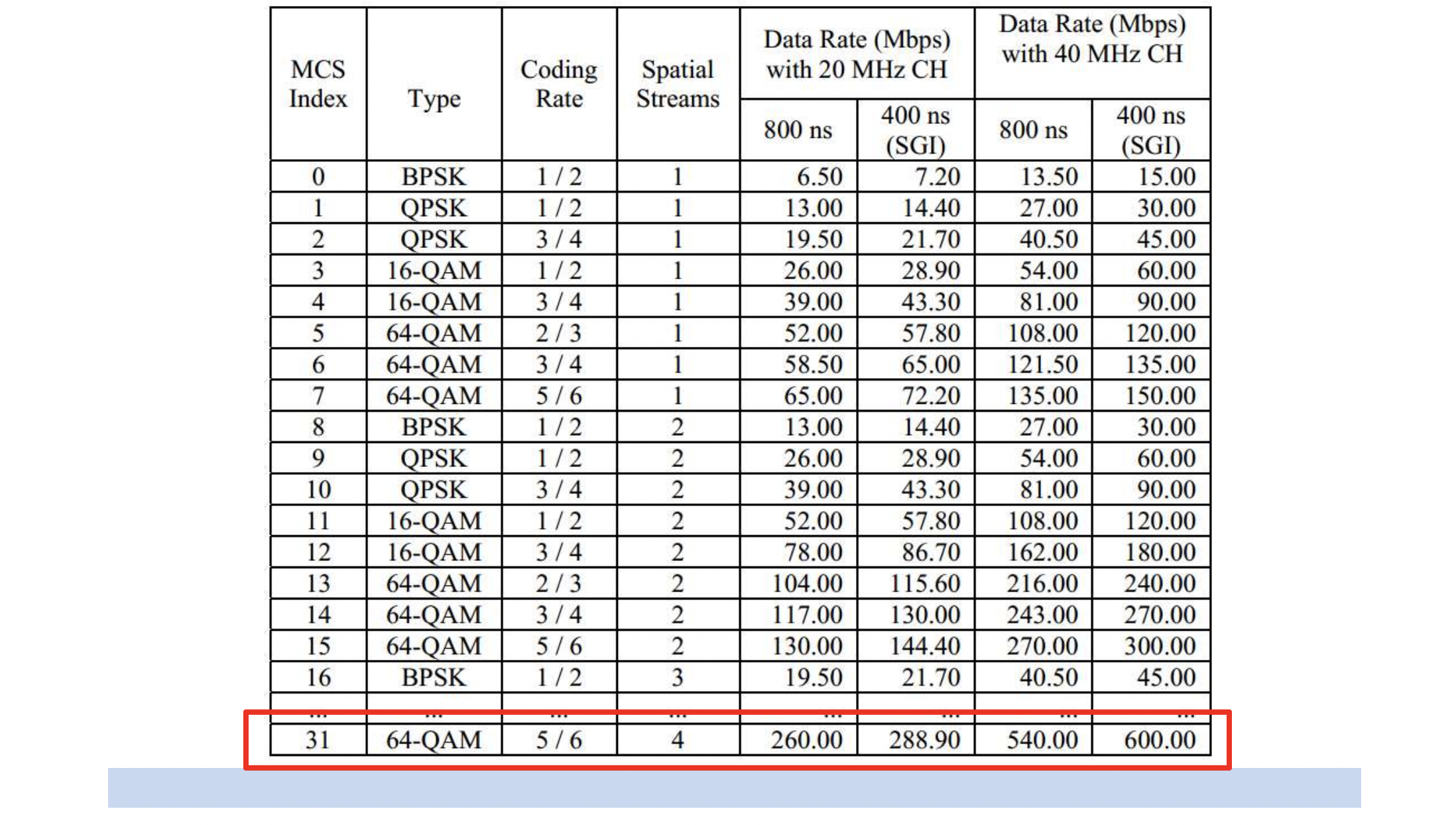
MCS (Modulation and Coding Scheme)
- modulation scheme과 coding rate를 정의한다
- transmitter는 receiver에게 어떤 MCS level을 사용할 지 알려줘야 한다
- MCS table
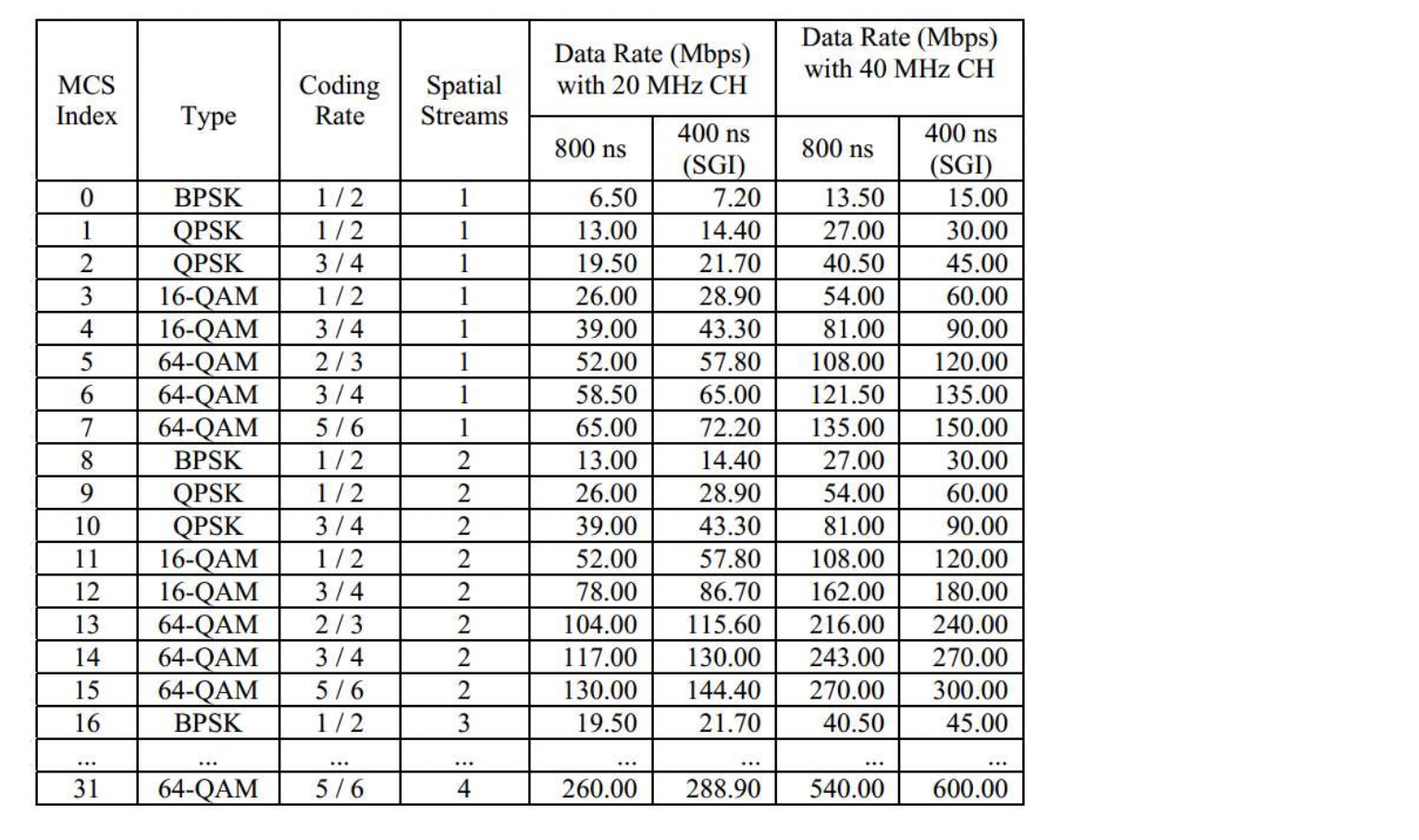
- MCS level의 선택은 link quality에 의존한다
- Higher MCS level requires higher SNR
- SNR이 동적으로 변할 수 있기 때문에,
그에 맞춰서 MCS level도 변한다
MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output)
- communication performance를 향상시키기 위해
transmitter와 receiver 둘 다 여러 개의 안테나를 사용한다
advantage
- array gain : improves spectral effiency
- transmit different data on multiple antennas
- 안테나 간의 공간 분리를 이용해서
동일한 전력 수준으로 더 멀리 있는 수신기까지 신호 전송이 가능해진다 - M transmit antenna, N receive antenna가 있을 때,
array gain = min(M, N)
- diversity gain : improves link reliablity
- transmit the same data on multiple antennas using space-time coding
- 여러 개의 안테나별로 fading이 다르기 때문에
그 중 가장 좋은 걸 고르거나 합쳐서 SNR을 향상시킬 수 있다
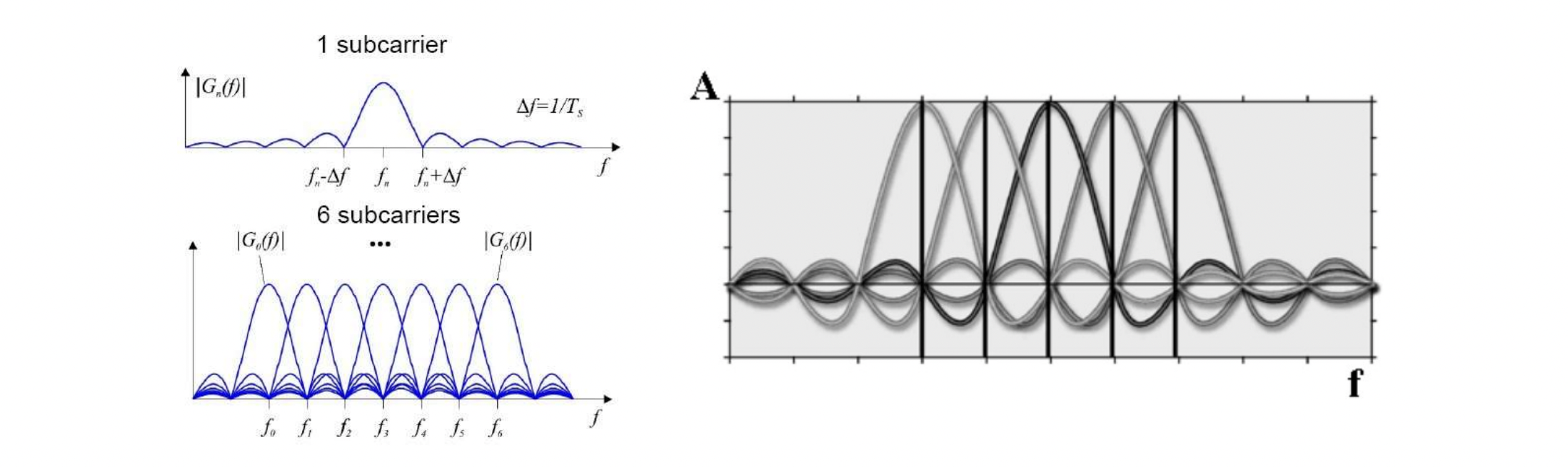
Physical layer: OFDM
- A specialized FDM (frequency division multiplexing)
- 서로서로 orthogonal인 sub-carrier들이 선택된다
- 서로서로 interfere하지 않는다.
- can easily adapt to channel conditions
- robust against narrow-band co-channel interference
- robust against inter-symbol interference (ISI)
and fading casued by multipath propagation - High spectrum efficiency compared to spread spectrum techniques
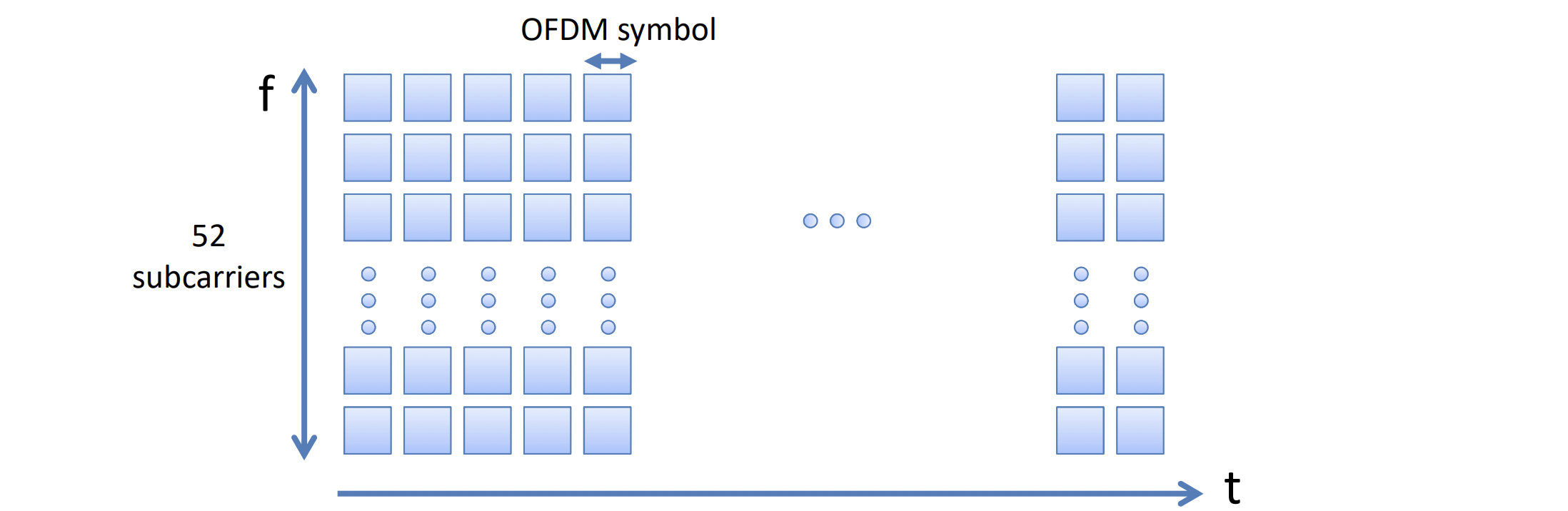
802.11n OFDM - 20MHz channel
- 20MHz channel, divided into 56 subcarriers
- 실제로는 52 subcarriers가 data에 사용되고,
4 subcarriers는 pilot이다 - 각 subcarrier : 312.5kHz,
signal bandwidth : 17.5MHz - symbol duration : 3.6us (guard interval : 0.4us 포함)
802.11n OFDM - 40MHz channel
- 40MHz channel, divided into 114 subcarriers
- 108 subcarriers used for data,
6 subcarriers for pilot - Each subcarriers : 312.5kHz
signal bandwidth : 35.625MHz - symbol duration : 3.2us + guard interval
802.11n OFDM - Modulation & Coding
600Mbps를 만들기 위해,
- Modulation : 64QAM
- subcarrier 하나에 6 bit가 code된다
- Coding : 5/6
- 16.6% redundant bits for error correction
- Data bits per OFMD symbol (40MHz)
- 6 (5/6) 108 subcarriers = 540 bits
- Number of OFDM symbols per second
- 1s / 3.6us = 277,777
- Data rate
- 540 * 277,777 = 150Mbps
- MIMO
- Linear capacity growth with minimum number of antennas
- Use 4x4 MIMO : 150Mbps -> 600Mbps