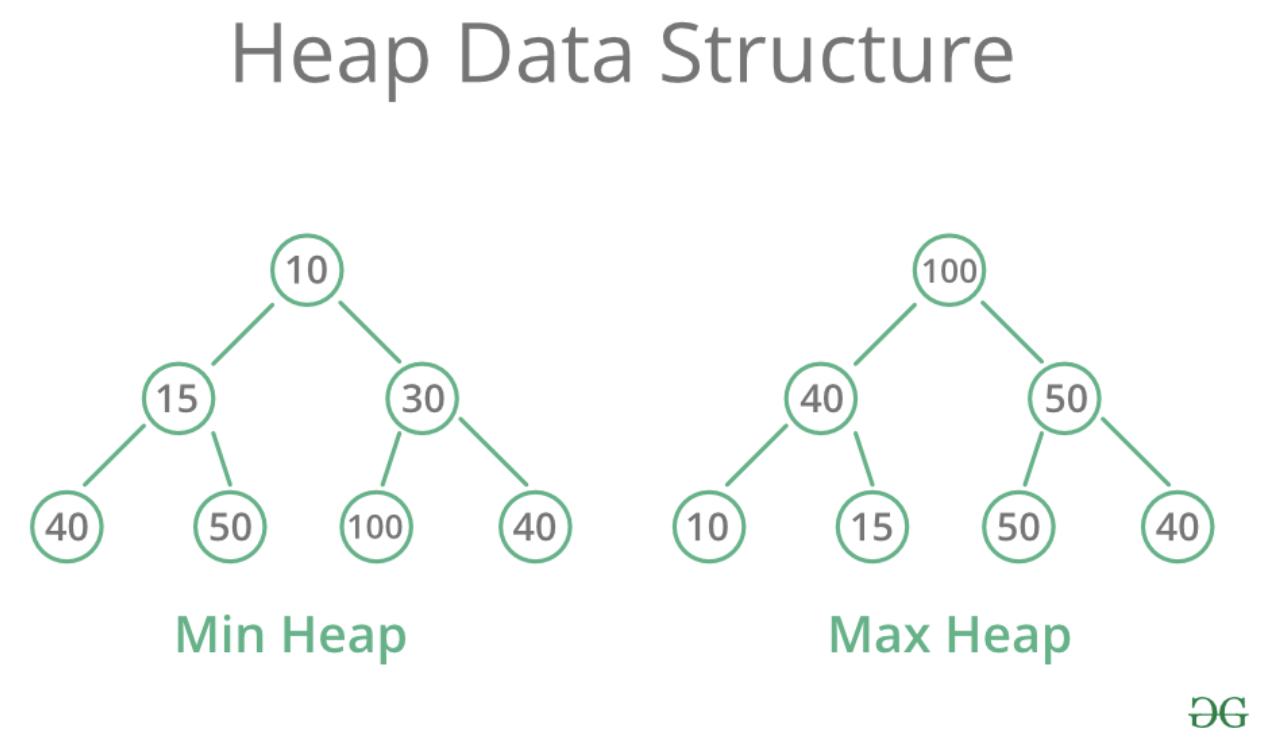
Heap

- 무엇인가를 쌓아놓은 더미와 같은 자료구조로 완전 이진 트리의 형태를 가진다.
- 항상 가장 위에 있는것을 우선하여 꺼낸다.
- 왼쪽, 오른쪽 노드 사이에 크기 제한은 없다
- 최소 힙이냐 최대 힙이냐에 따라 자식 노드와 부모 노드의 우선순위가 달라진다.
- 우선순위 큐를 구현하는데 사용된다.
PriorityQueue
우선순위 큐는 우선순위가 높은 데이터가 먼저 나가는 형태의 큐다. 기본 정렬은 오름차순을 따른다.
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 값 추가
priorityQueue.add();
priorityQueue.offer();
// 첫번째 값 반환 (없으면 NULL)
priorityQueue.poll();
// 첫번째 값 제거
priorityQueue.remove();
// 첫번째 값 출력
priorityQueue.peek();
// 초기화
priorityQueue.clear();
백준 1927 최소 힙
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1927
public class B_S2_1927 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int tc = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
PriorityQueue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int t = 0; t < tc; t++){
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if (n == 0) {
if (!q.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(q.poll());
} else {
System.out.println(0);
}
} else {
q.add(n);
}
}
}
}백준 11279 최대 힙
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11279
Collections.reverseOrder() 로 정렬을 역순으로 바꿔준다.
public class B_S2_11279 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int tc = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
PriorityQueue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
for (int t = 0; t < tc; t++){
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if (n == 0) {
if (!q.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(q.poll());
} else {
System.out.println(0);
}
} else {
q.add(n);
}
}
}
}
백준 11286 절댓값 힙
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11286
만약 임의의 클래스로 구성되어 있거나 우선순위 선정하는 방법을 변경하려는 경우에는 다음과 같은 방법으로 우선순위를 지정할 수 있다.
- 클래스에 Comparable 인터페이스 구현
- PriorityQueue 생성시에 Comparator를 매개 변수로 넣어주기
- 매개변수에 람다식 작성
public class B_S1_11286 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int tc = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
PriorityQueue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> {
if (Math.abs(o1) == Math.abs(o2)) {
return o1 > o2? 1 : -1;
} else {
return Math.abs(o1) - Math.abs(o2);
}
});
for (int t = 0; t < tc; t++){
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if (n == 0) {
if (!q.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(q.poll());
} else {
System.out.println(0);
}
} else {
q.add(n);
}
}
}
}백준 7662 이중 우선순위 큐
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7662
왠지 내가 모르는 알고리즘이나 자료구조가 존재할 것 같아 검색을 해보긴 했는데 또 구체적인 내용을 자세히 읽어버리면 답을 볼 것 같아 대충 눈을 가늘게 뜨고 클릭했다 껐다 했다.
결국 알게 된 것은 이중 우선순위 큐라는 자료구조는 없고 직접 만들어야 한다는 것이었는데, 언어별로 푸는 방법이 조금씩 달랐다.
공통적으로 보였던 풀이방법은 최소 힙과 최대 힙을 각각 생성해서 두 개의 큐를 만드는 것이었는데, 조금 비효율적인 것 같았다. 왜냐하면 하나의 큐에서 일어나는 연산을 다른 큐에서 하려면 결국 시간복잡도가 늘어날 것이라고 생각했다. (그리고 실제로 그렇게 해서 시간초과가 났다는 글도 봤다)
내가 선택한 방법은 어렴풋이 본 TreeMap이라는 자료구조를 쓰는 것이다. TreeMap은 간단히 설명하자면 키와 값 쌍으로 이루어진 객체를 레드 블랙 트리라는 self-balancing한 이진 탐색 트리 형태로 저장하는 Map 컬렉션이다.
TreeMap에 객체를 저장하면 오름차순으로 자동 정렬되며 검색, 조회 등에 log n의 시간이 소요된다. 이는 HashMap보다 열악한 조건이지만, 정렬된 데이터를 다뤄야하는 상황에서는 훨씬 효율적이다.
TreeMap<Integer, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
treeMap.put(1, "Hi");
treeMap.put(5, "java");
treeMap.put(2, "my");
treeMap.put(3, "name");
treeMap.put(4, "is");
System.out.println(treeMap.firstEntry());
// 1=Hi
System.out.println(treeMap.lastEntry());
// 5=java
해당 문제에서는 firstKey, lastKey 메소드를 이용하여 이중 우선순위 큐를 구현하였다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int tc = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int t = 0; t < tc; t++) {
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> q = new TreeMap<>();
for (int o = 0; o < n; o++) {
String[] temp = br.readLine().split(" ");
String op = temp[0];
int num = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]);
if (op.equals("I")) {
if (q.containsKey(num)) {
q.replace(num, q.get(num) + 1);
} else {
q.put(num, 0);
}
} else {
if (!q.isEmpty()) {
if (num == -1) {
if (q.get(q.firstKey()) > 0) {
q.replace(q.firstKey(), q.get(q.firstKey()) - 1);
} else {
q.remove(q.firstKey());
}
} else {
if (q.get(q.lastKey()) > 0) {
q.replace(q.lastKey(), q.get(q.lastKey()) - 1);
} else {
q.remove(q.lastKey());
}
}
}
}
}
if (q.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("EMPTY");
} else {
System.out.printf("%d %d \n", q.lastKey(), q.firstKey());
}
}
}
}참고
[JAVA/자료구조] 우선순위 큐(Priority Queue) (Heap)
java/ 백준 11286 절댓값 힙
TreeMap in Java