
데코레이터?
함수 내부의 코드를 직접 수정하는 대신 데코레이터를 사용해서 추가적인 처리를 하도록 해주는 디자인 패턴.
어디에 쓰나?
- 서버에 요청이 왔을 때 전처리, 후처리가 필요한 경우. 요청에 대한 로직을 처리하기 전 token 검증
- 특정 함수의 로직이 완료될 때까지의 시간 측정
- 반복되는 로직을 코드에 복사 붙여넣기하는 대신 함수 위에 데코레이션
first class citizen
파이썬에서의 함수는 일급 객체다. 비행기를 타면 퍼스트 클래스에 탈 수 있다.
def function1():
print("function1")
def function2(f):
f()
function2(function1)function2를 호출할 때 function1을 인수로 넘기고 실행시킬 수 있다.
일급 객체의 특징은 객체를 변수에 할당하거나, 함수의 인수로 넘기거나, 반환(return)할 수 있다는 것이다.
함수 전, 후에 동작 추가
def function1(function):
def wrapper():
print("1")
function()
print("2")
return wrapper
def hello():
print("hello")
wrapper = function1(hello)
wrapper()function1에 hello 객체를 인수로 넘겨주고 wrapper 변수는 wrapper 함수를 할당받는다. 이후 wrapper를 호출하면 "hello" 전 후로 "1", "2"가 찍힌다
기존 함수명 대신 변수에 할당함으로써 function aliasing을 할 수 있다.
def function1(function):
def wrapper():
print("1")
function()
print("2")
return wrapper
@function1
def hello():
print("hello")
hello()호출할 함수인 hello에 데코레이터를 작성해줘도 똑같이 동작한다.
함수에 인수 전달하기
def function1(function):
def wrapper(*args):
print("1")
function(*args)
print("2")
return wrapper
@function1
def hello(n):
print(n)
hello(1.5)데코레이터가 적용된 함수가 인자를 받아서 사용해야 한다면 래퍼함수에 *args를 전달해서 사용한다.
def function1(function):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print("1")
function(*args, **kwargs)
print("2")
return wrapper
@function1
def hello(n, name="hello"):
print(n, name)
hello(1.5)keyword argument도 전달할 필요가 있다면 **kwargs를 사용한다.
함수 값 반환하기
def function1(function):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print("1")
v = function(*args, **kwargs)
print("2")
return v
return wrapper
@function1
def hello(x, y):
return x + y
result = hello(1, 9)
print(result)래퍼함수 내에서 전처리를 하고 후처리하기 전에 값을 v에 할당하고 마지막에 반환해준다. hello 함수의 데코레이터의 래퍼함수가 반환한 값은 v가 된다.
함수 실행 시간 재기
import time
def timer(function):
def wrapper():
start = time.time()
function()
end = time.time()
return end - start
return wrapper
@timer
def sleep():
time.sleep(0.1)
slept_time = sleep()
print(slept_time)https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r7Dtus7N4pI
@wraps 데코레이터를 사용하면 데코레이터에 의해 감싸진 원본 함수의 docstring과 함수명을 유지할 수 있다.
from functools import wraps
def greeting_decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(data1, data2):
"""
decorator docs
"""
print(data1)
result = func(data1, data2)
print(data2)
print(result)
return "DONE"
return wrapper
@greeting_decorator
def hi(data1, data2):
"""original docs"""
print('help me decorator')
return "return value"
result = hi(1, 2)
print(result)
print(f"this is func name : {hi.__name__}")
print(f"this is func doc : {hi.__doc__}")결과
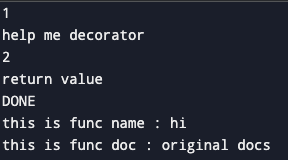
@wraps를 제거하면 데코레이터의 docstring과 메서드이름이 출력된다.
from functools import wraps
def greeting_decorator(func):
def wrapper(data1, data2):
"""
decorator docs
"""
print(data1)
result = func(data1, data2)
print(data2)
print(result)
return "DONE"
return wrapper
@greeting_decorator
def hi(data1, data2):
"""original docs"""
print('help me decorator')
return "return value"
result = hi(1, 2)
print(result)
print(f"this is func name : {hi.__name__}")
print(f"this is func doc : {hi.__doc__}")결과
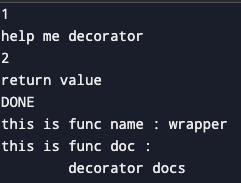
django에서 데코레이터를 활용해서 view 함수 앞뒤에 로깅하기
logger.py
class LogDecorator(LoggerMixin):
@staticmethod
def post_method_log_decorator(func):
@wraps(func)
def wrapper(self, request: Request, *args, **kwargs):
self.header_logger()
self.request_logger(payload=request.data)
response = func(self, request, *args, **kwargs)
self.response_logger(payload=response.data)
return response
return wrapperclass BlahViewSet(MappingViewSetMixin, CreateModelMixin):
serializer_action_map = {"give_point": BlahRequestSerializer}
@view_post_schema
@LogDecorator.post_method_log_decorator
def give_point(
self,
request: Request,
*args,
**kwargs,
) -> Response:
...
return Response()