배경지식
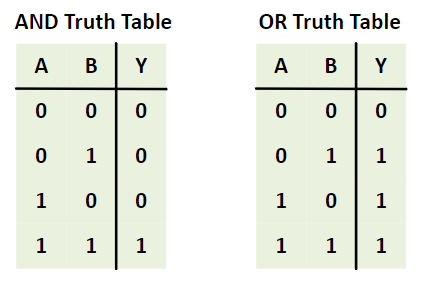
위의 표는 AND 게이트와 OR 게이트의 진리표이다.
AND는 모두 참이면 참, OR는 하나라도 참이면 참을 반환한다.
이 정도 지식만 있으면 Short Circuit Evaluation을 이해할 수 있다.
본론
- AND
#include <stdio.h>
int ReturnTrue() {
printf("Return True.\n");
return 1;
}
int ReturnFalse() {
printf("Return False.\n");
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
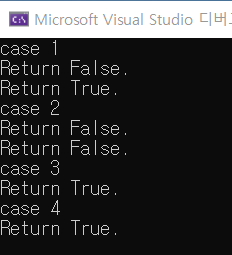
printf("case 1\n");
if (ReturnFalse() && ReturnTrue()) {}
printf("case 2\n");
if (ReturnFalse() && ReturnFalse()) {}
printf("case 3\n");
if (ReturnTrue() && ReturnTrue()) {}
printf("case 4\n");
if (ReturnTrue() && ReturnFalse()) {}
return 0;
}위의 코드를 실행하게 된다면 결과는 아래와 같다.

- case 1, 2의 경우
AND연산에서는 모두 참을 반환해야 참이다.
printf("case 1\n");
if (ReturnFalse() && ReturnTrue()) {}
printf("case 2\n");
if (ReturnFalse() && ReturnFalse()) {}ReturnFalse() 함수의 경우엔 0을 반환하며 False이다.
따라서 뒤의 식에서 True가 나오던, False가 나오던 결국 False이다.
이때 뒤의 ReturnTrue()나 ReturnFalse()는 진행되지 않는다.
- case 3, 4의 경우
printf("case 3\n");
if (ReturnTrue() && ReturnTrue()) {}
printf("case 4\n");
if (ReturnTrue() && ReturnFalse()) {}반대로 ReturnTrue() 함수의 경우 참이다.
그러므로 뒤의 식까지 진행을 해봐야 결과를 알 수 있다.
따라서 이 경우 ReturnTrue()와 ReturnFalse()모두 실행이 되는 것이다.
- OR
#include <stdio.h>
int ReturnTrue() {
printf("Return True.\n");
return 1;
}
int ReturnFalse() {
printf("Return False.\n");
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
printf("case 1\n");
if (ReturnFalse() || ReturnTrue()) {}
printf("case 2\n");
if (ReturnFalse() || ReturnFalse()) {}
printf("case 3\n");
if (ReturnTrue() || ReturnTrue()) {}
printf("case 4\n");
if (ReturnTrue() || ReturnFalse()) {}
return 0;
}위의 코드를 실행하게 되면 다음과 같다.
OR연산은 하나만 True여도 True를 반환한다.
- case1, 2 경우
printf("case 1\n");
if (ReturnFalse() || ReturnTrue()) {}
printf("case 2\n");
if (ReturnFalse() || ReturnFalse()) {}ReturnFalse()에서 False를 반환하므로 뒤의 식까지 검사해야 전체 결과가
True인지 False인지 알 수 있다.
하지만
- case3, 4경우
printf("case 3\n");
if (ReturnTrue() || ReturnTrue()) {}
printf("case 4\n");
if (ReturnTrue() || ReturnFalse()) {}ReturnTrue()에서 True를 반환하므로 뒤의 식의 결과에 관계 없이 True를 반환하게 된다.
따라서 뒤는 볼 필요가 없이 실행하지 않는다.
다른 예제
1번
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 1;
if (x || ++x) {
printf("%d", x);
}
return 0;
}
Output
1
2번
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
float nr = 5, dr = 0;
dr && printf("a/b = %.2f", nr / dr);
}
Output
// No Output
