해시 테이블
키(key)와 값(value)으로 이루어진 자료구조 중 하나로 빠르게 데이터를 검색할 수 있다.
해시 테이블이 빠른 검색을 할 수 있는 이유는 내부적으로 배열을 사용하여 데이터를 저장하기 때문이다.
해시 테이블은 각각의 key 값에 해시함수를 적용해 배열의 고유한 index를 생성하고, 이 index를 활용해 값을 저장하거나 검색한다.
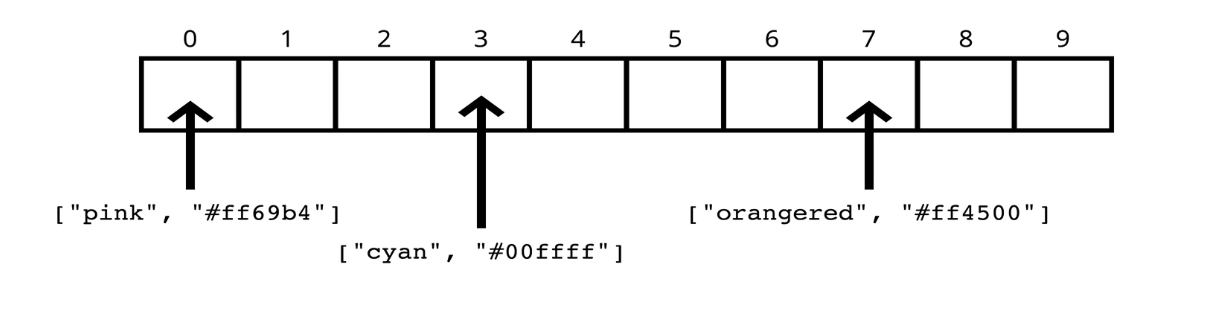
해시 함수
각각의 key에 특수한 알고리즘을 적용하여 고유한 index를 생성하는 함수이다.
해시 함수는 다음과 같은 조건을 만족해야 한다.
- 동일한 키는 동일한 인덱스를 반환해야 한다.
- 시간복잡도가 빨라야 한다.
- 데이터들이 균일하게 분배되어야 한다.
_hash(key) {
let total = 0;
let WEIRD_PRIME = 31;
for (let i = 0; i < Math.min(key.length, 100); i++) {
let char = key[i];
let value = char.charCodeAt(0) - 96;
total = (total * WEIRD_PRIME + value) % this.keyMap.length;
}
return total;
}해시 충돌
다른 key값 이어도 해시 함수를 통해 변환된 index가 같을 수 있다. 이러한 경우를 해시 충돌이라 한다.
해시 테이블에서는 해시 충돌에 대한 여러가지의 해결 방법이 있다.
그 중 개별 체이닝(Separate Chaining)에 대해 알아보자.
Seperate Chaining
출돌하는 데이터를 같은 인덱스에 중첩해서 저장하는 방법이다. 테이블의 길이보다 더 많은 데이터를 저장할 수 있다는 장점이 있다.
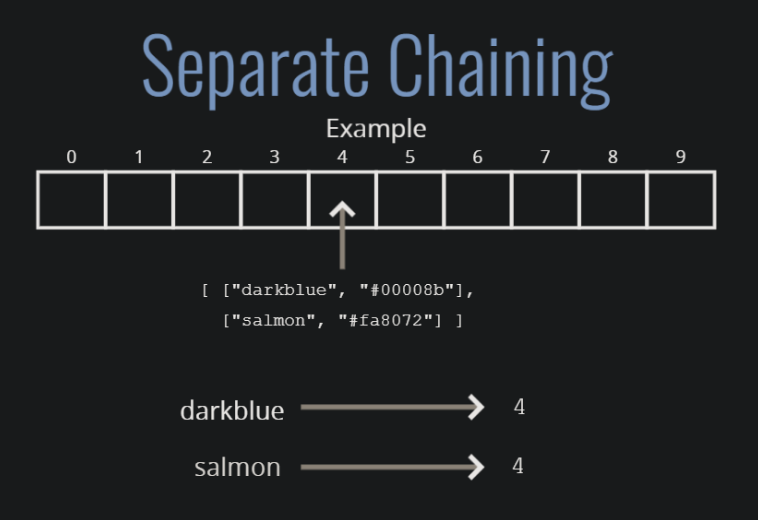
해시 테이블 구현
class HashTable {
constructor(size = 53) {
this.keyMap = new Array(size);
}
_hash(key) {
let total = 0;
let WEIRD_PRIME = 31;
for (let i = 0; i < Math.min(key.length, 100); i++) {
let char = key[i];
let value = char.charCodeAt(0) - 96;
total = (total * WEIRD_PRIME + value) % this.keyMap.length;
}
return total;
}
set(key, value) {
let index = this._hash(key);
if (!this.keyMap[index]) {
this.keyMap[index] = [];
}
this.keyMap[index].push([key, value]);
}
get(key) {
let index = this._hash(key);
if (this.keyMap[index]) {
for (let i = 0; i < this.keyMap[index].length; i++) {
if (this.keyMap[index][i][0] === key) {
return this.keyMap[index][i][1];
}
}
}
return undefined;
}
values() {
let valuesArr = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.keyMap.length; i++) {
if (this.keyMap[i]) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.keyMap[i].length; j++) {
if (!valuesArr.includes(this.keyMap[i][j][1])) {
valuesArr.push(this.keyMap[i][j][1]);
}
}
}
}
return valuesArr;
}
keys() {
let keysArr = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.keyMap.length; i++) {
if (this.keyMap[i]) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.keyMap[i].length; j++) {
if (!keysArr.includes(this.keyMap[i][j][0])) {
keysArr.push(this.keyMap[i][j][0]);
}
}
}
}
return keysArr;
}
}시간복잡도
Insert: O(1)
Deletion: O(1)
Access: O(1)