이 글은 다음을 참고하여 작성하였음
PyTorch의 Deep Q Learning 예제를 분석하면서 설명을 추가하려고 한다.
먼저 PyTorch에서 제공하는 Gymnasium의 CartPole 데이터를 다운로드한다.
준비
Gymnasium 설치
%%bash
pip install gymnasium[classic_control]CartPole 예제는 Gymnasium 패키지에 포함되어 있는 것으로 Cart 안에 세워 놓은 Pole이 쓰러지지 않도록 균형을 맞추는 사고 실험을 기반으로 만들어진 데이터이다.
필요 패키지 import 및 기본 설정
패키지 import
import gymnasium as gym
import math
import random
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from collections import namedtuple, deque
from itertools import count
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.nn.functional as FEnvironment를 CartPole로 설정 (CartPole 예제에 대한 데이터와 상태가 모두 정의되어 환경을 구성함)
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1")matplotlib 설정(이후에 실행 결과를 그래프로 나타낼 수 있도록 함)
# set up matplotlib
is_ipython = 'inline' in matplotlib.get_backend()
if is_ipython:
from IPython import display
plt.ion()<contextlib.ExitStack at 0xfd28b3e4f320>
torch 사용 환경 설정
(실습 환경은 그래픽 카드를 사용할 수 없는 가상 머신 환경이므로 cpu를 사용하여 학습을 진행하게 되었음)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")Overview
Q-function
- state의 수가 Q-Learning에 비해 너무 많기 때문에 function을 사용
DQN Architecture
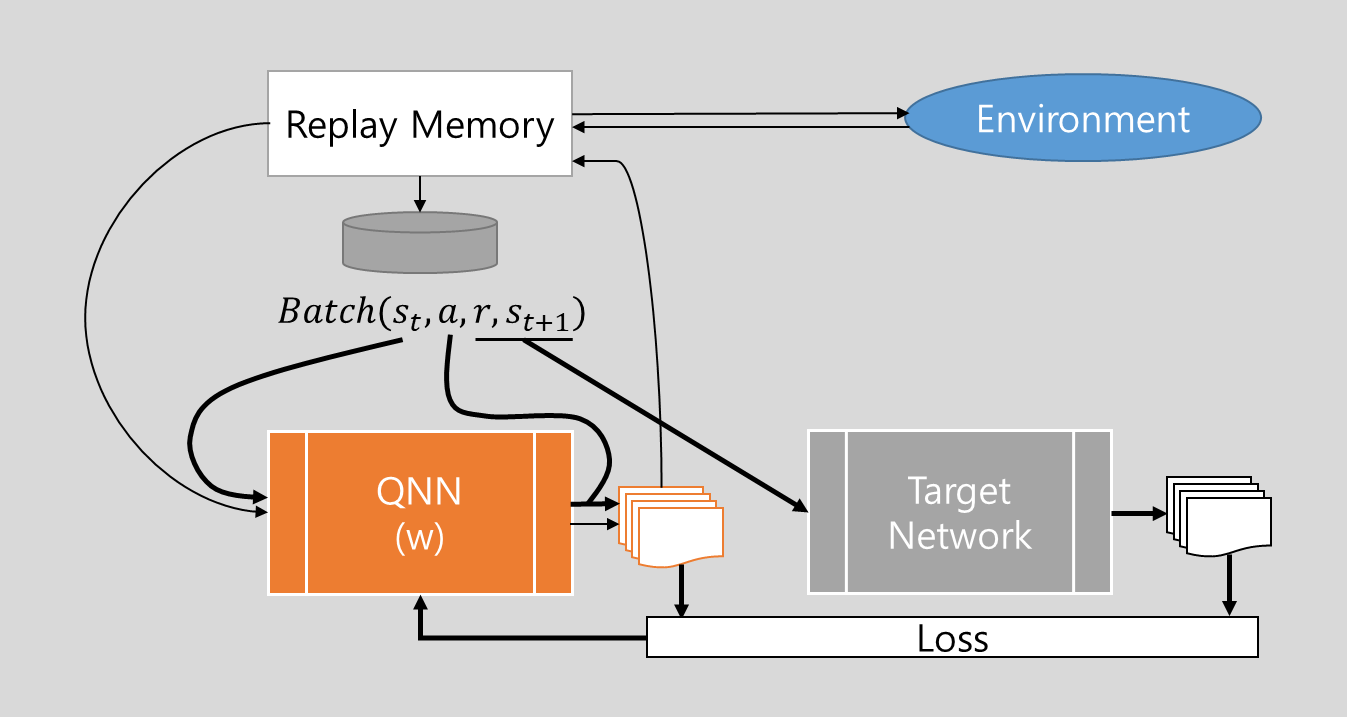
- QNN - optimal Q-Value를 생성, 표준적인 신경망 아키텍처
- Target Network - 복제된 QNN
Replay Memory
-
Experience Replay를 이용해
- Environment와 상호작용하여 -greedy에 따라 action을 선택하여 실행
- reward와 next state를 받음
Transition : (state, action) pair -> (next-state, reward) pair
-
Transition (state, action, next-state, reward)를 받아 Replay Memory에 Training Data로 저장
-
Q-Network의 예측 Q-Value 및 Target Network의 Target Q-Value를 산출, Deep Q Learning을 위한 sample data 추출
# Transition 설정
Transition = namedtuple('Transition', ('state', 'action', 'next_state', 'reward'))# Replay Memory 정의
class ReplayMemory(object):
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.memory = deque([], maxlen=capacity)
def push(self, *args):
# Save a Transition
self.memory.append(Transition(*args))
# sampling transition for training agent randomly
def sameple(self, batch_size):
return random.sample(self.memory, batch_size)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.memory)Q-Network
- Agent로써 작동하며, input으로 current state를 받는다.
- state에 대한 가능한 모든 Q-Value를 output으로 내놓는다.
여기서는 간단한 구조의 신경망 네트워크를 사용한다.
class DQN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_observations, n_sactions):
super(DQN, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Linear(n_observations, 128)
self.layer2 = nn.Linear(128,128)
self.layer3 = nn.Linear(128, n_actions)
# input layer - relu(get value that more than 0) - hidden layer (1) - relu - output layer
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.layer1(x))
x = F.relu(self.layer2(x))
return self.layer3(x)Training
hyperparameters 및 기본 설정
이곳에서 policy net, target net 및 replay memory를 위한 메모리 사이즈 등을 설정한다.
BATCH_SIZE = 128 # replay buffer에서 샘플링하는 transition 수
GAMMA = 0.99 # discount factor
EPS_START = 0.9 # epsilon(exploration speed)의 초기값 (고점)
EPS_END = 0.05 # epsilon의 나중 값 (저점)
EPS_DECAY = 1000 # epsilon의 감쇠율 (클수록 감쇠율이 낮음)
TAU = 0.005 # target net의 갱신 주기
LR = 1e-4 # AdamW optimizer의 학습 주기# gym data로부터 받아오는 action 수
n_actions = env.action_space.n
# 관찰할 state의 수
state, info = env.reset()
n_observations = len(state)
# QNN (policy net) 및 Target Net 설정
policy_net = DQN(n_observations, n_actions).to(device)
target_net = DQN(n_observations, n_actions).to(device)
# copy policy net to target net
target_net.load_state_dict(policy_net.state_dict())<All keys matched successfully>
optimizer = optim.AdamW(policy_net.parameters(), lr=LR, amsgrad=True)
memory = ReplayMemory(10000)steps_done = 0def select_action(state):
global steps_done
# action selected randomly
sample = random.random()
# epsilon-greedy strategy curve
eps_threshold = EPS_END + (EPS_START - EPS_END) * math.exp(-1. * steps_done / EPS_DECAY)
steps_done += 1
# action select with max result for pick action with the largest reward
if sample > eps_threshold:
with torch.no_grad():
return policy_net(state).max(1).indices.view(1,1)
else:
return torch.tensor([[env.action_space.sample()]], device=device, dtype=torch.long)episode_durations = []- 이 코드는 시각화를 위한 설정이다. 이 코드를 통해 실시간으로 Training 결과를 출력하고 갱신한다.
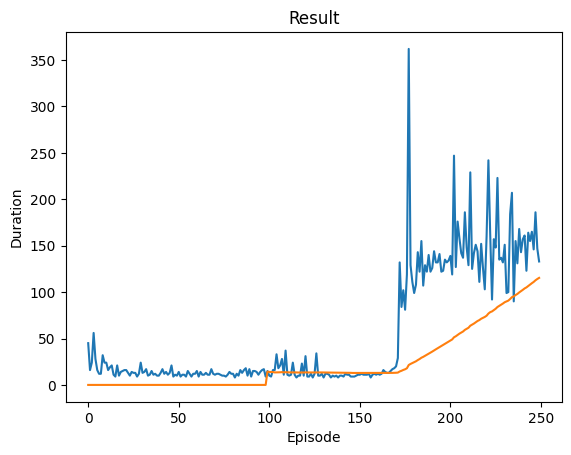
# get results and plot it
def plot_durations(show_result=False):
plt.figure(1)
durations_t = torch.tensor(episode_durations, dtype=torch.float)
if show_result:
plt.title('Result')
else:
plt.clf()
plt.title('Training...')
plt.xlabel('Episode')
plt.ylabel('Duration')
plt.plot(durations_t.numpy())
if len(durations_t) >= 100:
means = durations_t.unfold(0,100,1).mean(1).view(-1)
means = torch.cat((torch.zeros(99), means))
plt.plot(means.numpy())
plt.pause(0.001)
if is_ipython:
if not show_result:
display.display(plt.gcf())
display.clear_output(wait=True)
else:
display.display(plt.gcf())Training Loop
optimizer
- main training loop를 설정하는 코드이다.
- Replay Memory에서 Random으로 Transition을 가져온다.
- Transition의 state를 policy net에 input하여 Q를 얻고 Transition의 action에 따른 추정 Q-Value를 취한다.
- Transition의 reward 및 next state를 input으로 하여 Target net을 통해 나온 Q 값 중 max Q를 취해 Target Q-Value를 얻는다.
- Target Q-Value 및 추정 Q 값을 이용하여 Loss를 계산한다.
- loss를 이용해 policy net의 weight를 업데이트하고 이를 Target net에 반영한다.
def optimize_model():
if len(memory) < BATCH_SIZE:
return
transitions = memory.sameple(BATCH_SIZE)
# batch-array of Transition to transition of batch-array
batch = Transition(*zip(*transitions))
# compute a mask of non-final state and concatenate(like chain) the batch elements
non_final_mask = torch.tensor(tuple(map(lambda s: s is not None, batch.next_state)), device=device, dtype=torch.bool)
non_final_next_states = torch.cat([s for s in batch.next_state if s is not None])
state_batch = torch.cat(batch.state)
action_batch = torch.cat(batch.action)
reward_batch = torch.cat(batch.reward)
# compute Q(s_t, a) - get Q and select action, according to policy_net
state_action_values = policy_net(state_batch).gather(1, action_batch)
# compute V(s_{t+1}) for all next states, expected values of actions for non-final_next_state are computed
# selecting their best reward with max(1).values
next_state_values = torch.zeros(BATCH_SIZE, device=device)
with torch.no_grad():
next_state_values[non_final_mask] = target_net(non_final_next_states).max(1).values
# compute expected Q
expected_state_action_values = (next_state_values * GAMMA) + reward_batch
# compute huber loss (in this example)
criterion = nn.SmoothL1Loss()
loss = criterion(state_action_values, expected_state_action_values.unsqueeze(1))
# optimize the model
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
# in-place gradient clipping
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_value_(policy_net.parameters(), 100)
optimizer.step()RL set episode
이제 initialization -> optimization(main training loop) 순서로 학습을 진행한다.
- 600 episode for GPU, otherwise 200 episodes
- 이 테스트에서는 cuda 지원이 되지 않는 M2 Mac Mini의 Ubuntu 가상 머신 환경에서 테스트했기 때문에 200회만 학습을 진행시켜 보았다. (학습시키는 데 약 30초 정도가 소요되었다)
- initialization
- Environment reset
- replay memory에 저장한 Transition sample을 policy net을 이용해서 생성한다.
- policy net에서 나온 Q-value를 이용해 -greedy에 따라 action을 선택하여 Transition에 저장한다.
- Transition을 Memory에 저장한다.
- optimization
if torch.cuda.is_available():
num_episodes = 600
else:
num_episodes = 200
for i_episode in range(num_episodes):
# initialization
state, info = env.reset()
state = torch.tensor(state, dtype=torch.float32, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
for t in count():
action = select_action(state)
observation, reward, terminated, truncated, _ = env.step(action.item())
reward = torch.tensor([reward], device=device)
done = terminated or truncated
if terminated:
next_state = None
else:
next_state = torch.tensor(observation, dtype=torch.float32, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
# store the transition in memory
memory.push(state, action, next_state, reward)
# move to the next state
state = next_state
# perform one step of the optimization (policynet)
optimize_model()
# target net update: θ' <- τθ + (1-τ)θ'
target_net_state_dict = target_net.state_dict()
policy_net_state_dict = policy_net.state_dict()
for key in policy_net_state_dict:
target_net_state_dict[key] = policy_net_state_dict[key]*TAU + target_net_state_dict[key]*(1-TAU)
target_net.load_state_dict(target_net_state_dict)
if done:
episode_durations.append(t+1)
plot_durations()
break
print('Complete.')
plot_durations(show_result=True)
plt.ioff()
plt.show()Complete.
<Figure size 640x480 with 0 Axes> <Figure size 640x480 with 0 Axes>