요약
- Express 장점:
- 조건문(if-elif)으로 라우팅을 처리했던 것이 보다 간편해짐.
- 각각의 요청을 처리하는 함수의 분리로 인해 직관적으로 코드를 설계할 수 있다.
0. 들어가며
노드 개발자는 npm 에 등록 되어있는 노드 패키지(라이브러리 or 프레임워크)에 대한 주기적인 관심을 늘 가져야 함
Node.js와 호환 될 수 있는 Server-side Framework 들이 무수히 많기 때문
동향 파악: React conference, GraphQL conference, JavaScript conference
1. Express.js 없이 HTTP API 서버 구축하기
1-1. 간단한 API server
1. directory를 생성 및 프로젝트 시작 ($ : 명령프롬프트, 터미널)
$ mkdir westagram-backend
$ cd westagram-backend
$ npm init -y
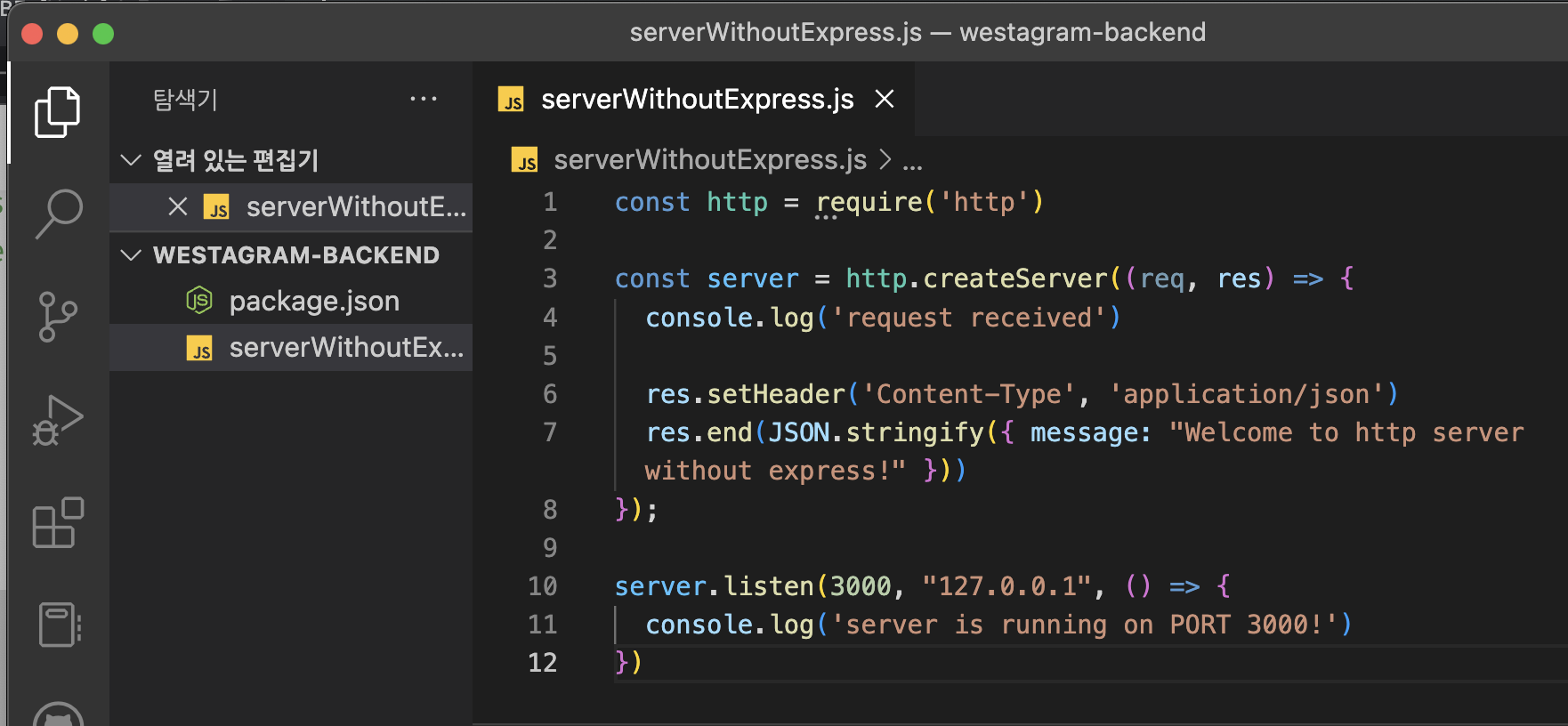
2. serverWithoutExpress.js 파일 생성
// serverWithoutExpress.js
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
console.log('request received')
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json')
res.end(JSON.stringify({ message: "Welcome to http server without express!" }))
});
server.listen(3000, "127.0.0.1", () => {
console.log('server is running on PORT 3000!')
}) 
1) Node.js 내장 http모듈을 가져와 변수에 담는다.
const http = require('http') 2) 서버에 요청이 들어오면 http.createServer 메소드는 인자로 또 다른 함수(콜백함수)를 받아 실행한다.
- req: http request 의 정보가 담겨있는 객체
- res: http response 객체
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
//이하 내용 3) 참조
} );3) 요청에 대한 응답의 header 를 application/json 형태로 세팅.
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json')res.end 함수의 인자로 클라이언트가 받는 응답을 넘겨주어 마무리한다
res.end(JSON.stringify({ message: "Welcome to http server without express!" })4) server의 객체의 listen 함수는 인자로 서버를 열 포트 번호와 서버 실행될 떄의 로직인 콜백함수(서버가 켜져있다는 로그 메시지)를 받는다.
server.listen(3000, "127.0.0.1", () => {
console.log('server is running on PORT 3000!')
}) Port 번호 3000
Express 프레임워크에서 공식적으로 지정한 default Port 번호.
늘 고정된 값은 아니며 3000 이외의 번호로도 언제든지 서버를 열 수 있다!
3. 서버를 실행한다(노드 서버 개설!)
$ node serverWithoutExpress.js
4. 응답 확인하기
-
웹브라우저
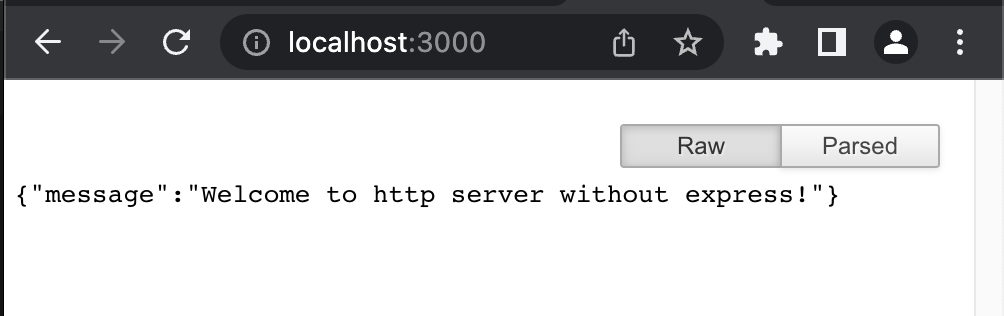
-
httpie(터미널 전용 http client 프로그램)
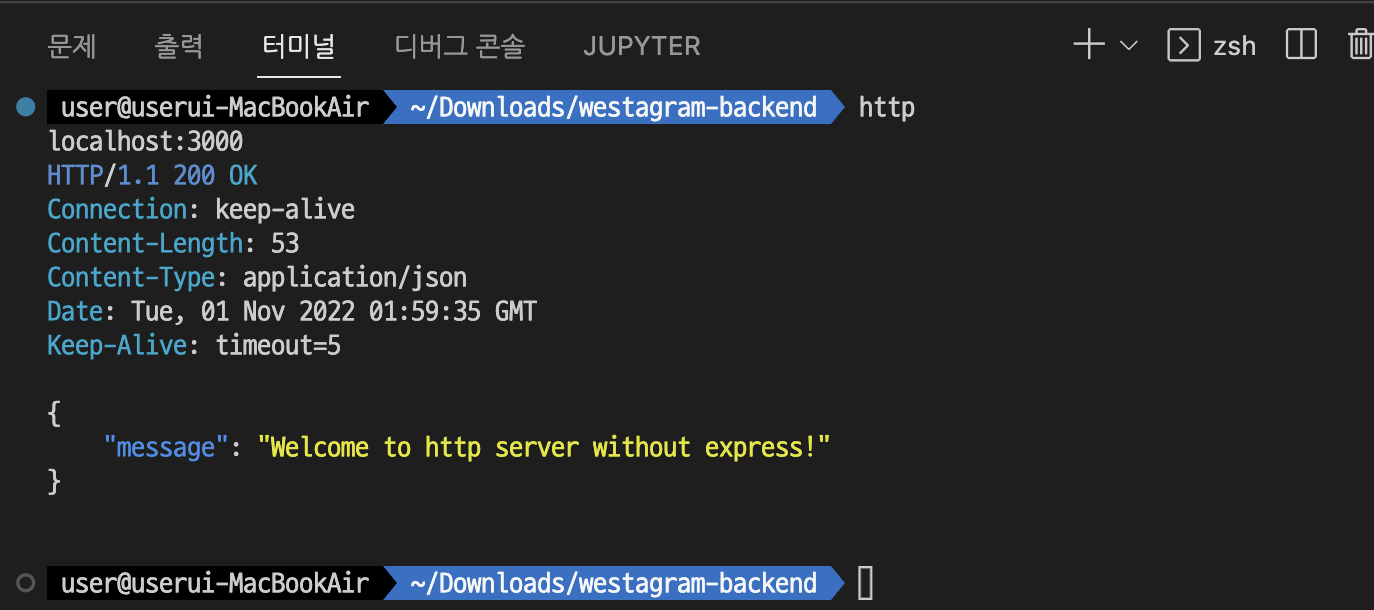
-
postman(http client 프로그램)
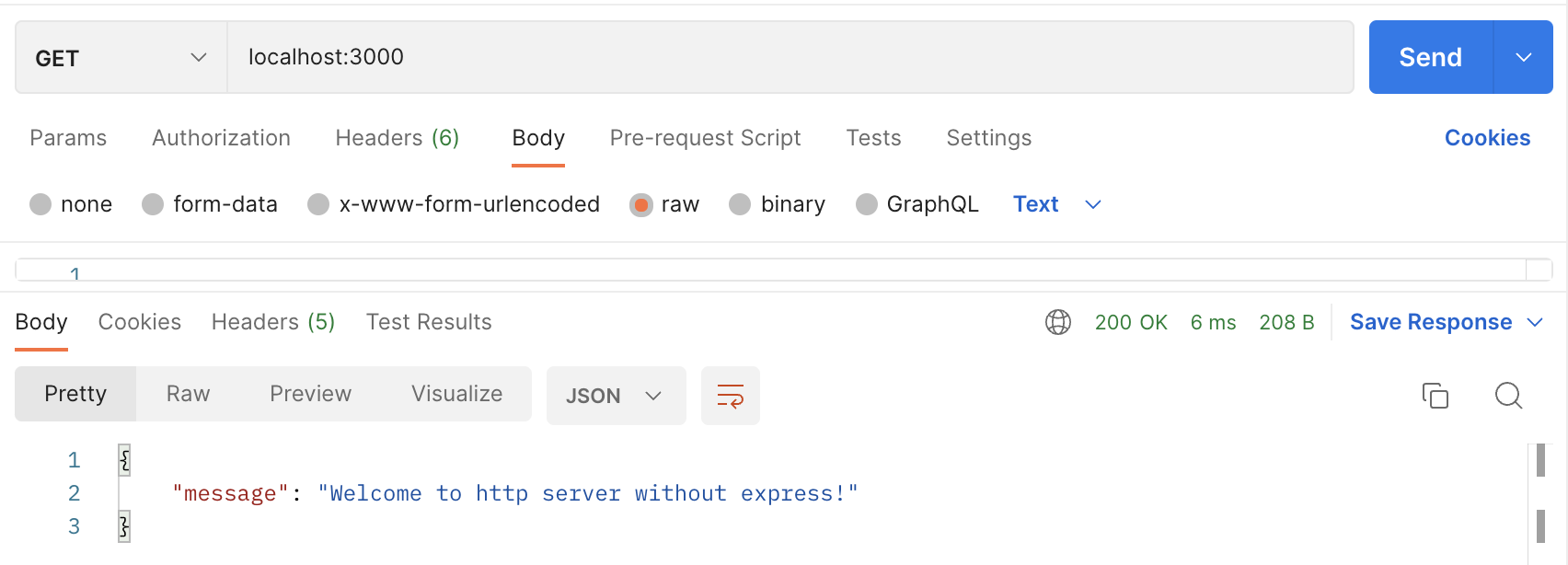
1-2. 복잡한 API server
웹 프레임워크를 적용하지 않으면 코드가 복잡해진다
1. 회원, 게시물 변수 생성 & 데이터 담기
const users = [
{
id: 1,
name: "Rebekah Johnson",
email: "Glover12345@gmail.com",
password: "123qwe",
},
{
id: 2,
name: "Fabian Predovic",
email: "Connell29@gmail.com",
password: "password",
},
];
const posts = [
{
id: 1,
title: "간단한 HTTP API 개발 시작!",
content: "Node.js에 내장되어 있는 http 모듈을 사용해서 HTTP server를 구현.",
userId: 1,
},
{
id: 2,
title: "HTTP의 특성",
content: "Request/Response와 Stateless!!",
userId: 1,
},
];2. 조건문 분기로 라우팅 진행하기
request 객체에서 url과 method에 따라 조건문으로 분기하여 라우팅.
회원가입, 게시물 확인 등 다양한 로직을 처리.
라우팅은 http method 별로 GET, POST, PUT, DELETE 등의 내용을 적절한 로직으로 안내하여 이루어진다.
const http = require("http");
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
const { url, method } = request;
if (method === "GET") {
if (url === "/ping") {
response.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "application/json" });
response.end(JSON.stringify({ message: "pong" }));
} else if (url === "/users") {
response.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "application/json" });
response.end(JSON.stringify({ users: users }));
} else if (url.startsWith("/users")) {
const userId = parseInt(url.split("/")[2]);
const user = users.find((user) => user.id === userId);
response.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "application/json" });
response.end(JSON.stringify({ user: user }));
} else if (url === "/posts") {
response.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "application/json" });
response.end(JSON.stringify({ posts: posts }));
}
} else if (method === "POST") {
if (url === "/users") {
let body = "";
request.on("data", (data) => {
body += data;
});
request.on("end", () => {
const user = JSON.parse(body);
users.push({
id: user.id,
name: user.name,
email: user.email,
password: user.password,
});
response.end("ok");
});
} else if (url === "/posts") {
let body = "";
request.on("data", (data) => {
body += data;
});
request.on("end", () => {
const post = JSON.parse(body);
posts.push({
id: post.id,
name: post.title,
content: post.content,
});
response.end("ok");
});
}
} else if (method === "PATCH") {
if (url.startsWith("/posts")) {
let body = "";
request.on("data", (data) => {
body += data;
});
request.on("end", () => {
const inputPost = JSON.parse(body);
const postId = parseInt(url.split("/")[2]);
const post = posts.find((post) => post.id === postId)
post.title = inputPost.title;
post.content = inputPost.content;
response.writeHead(200, { "Content-Type": "application/json" });
response.end(
JSON.stringify({
id: post.id,
title: post.title,
content: post.content,
})
);
});
}
} else if (method === "DELETE") {
if (url.startsWith("/posts")) {
const postId = parseInt(url.split("/")[2]);
const post = posts.find((post) => post.id === postId);
delete post;
response.writeHead(204, { "Content-Type": "application/json" });
response.end(
JSON.stringify({
message: "NO_CONTENT",
})
);
}
}
});
server.listen(3000, "127.0.0.1", () => {
console.log("Listening to requests on port 3000");
});순수한 node.js로만 코드를 짜면?
- 그 규모가 커지면 다양한 로직들에 대해
if-else if의 연쇄 중첩을 적용하여 분기처리와 소스코드의 양이 배 이상으로 증가.- 서버 실행 함수 내에 수많은 조건문과 로직을 모듈화 하는 불필요한 수고로움 발생.
- 가독성이 떨어짐
👉 Express.js로 불편함 해결!
Routing(라우팅)
해당 자원에 대해 다른 함수(로직)을 실행하도록 하는 것.
👉 유저의 회원가입, 로그인 처리, 프론트엔드 측에서 요구하는 다양한 정보에 응답 등
2. Express.js로 HTTP API 서버 구축하기
” Express is fast, unopinionated, minimalist web framework for node.js.”
” Express는 빠르고 자유롭고 가벼운 웹 프레임 워크이다.”
라우팅과 로직의 모듈화
개발자가 더욱더 읽기 쉽고 유연하며 지속가능한 백엔드 앱을 개발할 수 있게 돕는 도구
- 필요한 요청에 필요한 비즈니스 로직이 적재적소에 쓰일 수 있게 구성됨
- 기능별로 소스코드를 별도의 파일로 관리 가능.
왜 Express.js여야 하는가?
- 빠르고 자유롭고 가벼운 프레임워크이다
- 최소한의 기능부터 가볍게 웹서버를 구현할 수 있다
- 개발입문자가 동작원리를 초석부터 다지기 좋다
2-1. 실행
- serverWithExpress.js
const modularizedFunctions = require('./modularizedFunctions.js')
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
app.use(express.json())
//get 요청 처리 라우팅
app.get('/ping', (req, res) => {res.json({ message: '/pong'})})
app.get('/users', modularizedFunctions.getUsers)
app.get('/users/:userId', modularizedFunctions.getUserByUserId)
app.get('/posts', modularizedFunctions.getPosts)
//post 요청 처리 라우팅
app.post('/users', modularizedFunctions.createUser)
app.post('/posts', modularizedFunctions.createPost)
//patch 요청 처리 라우팅
app.patch('/posts/:postId', modularizedFunctions.updatePost)
//delete 요청 처리 라우팅
app.delete('/posts/:postId', modularizedFunctions.deletePost)
app.listen(3000, "127.0.0.1", function() {
console.log('listening on port 3000')
})- modularizedFunctions.js
// 먼저 서버통신시 가공할 데이터를 정의합니다.
const users = [
{
id: 1,
name: "Rebekah Johnson",
email: "Glover12345@gmail.com",
password: "123qwe",
},
{
id: 2,
name: "Fabian Predovic",
email: "Connell29@gmail.com",
password: "password",
},
];
const posts = [
{
id: 1,
title: "간단한 HTTP API 개발 시작!",
content: "Node.js에 내장되어 있는 http 모듈을 사용해서 HTTP server를 구현.",
userId: 1,
},
{
id: 2,
title: "HTTP의 특성",
content: "Request/Response와 Stateless!!",
userId: 1,
},
];
// 앞서 express 없이 작성한 sendPosts 함수와 비교했을 때,
// express 덕분에 JSON.stringify 함수를 별도로 사용할 필요없이
// response 객체의 json 메소드를 활용합니다.
const getUsers = (req, res) => {
res.json({ users })
}
const getUserByUserId = (req, res) => {
const userId = req.params.userId
const user = users.find((user) => user.id == userId)
res.json({ user })
}
const getPosts = (req, res) => {
res.json({ posts })
}
const createUser = (req, res) => {
const user = req.body
const newUser = users.push({
id: user.id,
name: user.name,
email: user.email,
password: user.password,
});
res.json({ message: 'created!', 'user_id' : newUser })
}
const createPost = (req, res) => {
const post = req.body
const newPost = posts.push({
id: post.id,
title: post.title,
content: post.content,
});
res.json({ message: 'created!', 'post_id' : newPost })
}
const updatePost = (req, res) => {
const inputPost = req.body
const postId = req.params.postId
const post = posts.find((post) => post.id == postId)
post.title = inputPost.title;
post.content = inputPost.content;
res.json({ message: 'updated!', 'updatedPost' : post })
}
const deletePost = (req, res) => {
const postId = req.params.postId
const indexOfPostId = posts.findIndex((post) => post.id == postId)
delete posts[indexOfPostId]
res.json({ message: 'deleted!'})
}
// serverWithExpress.js 에서 사용하기 위해 모듈로 내보냅니다.
module.exports = {
getUsers,
getUserByUserId,
getPosts,
createUser,
createPost,
updatePost,
deletePost
};웹 프레임워크
이미 존재하는 코드들을 제공받아 재사용할 수 있게 하는 간편한 서비스
ex) Express.js
프레임워크 장단점
장점 단점 효율성 상승 학습기간 길다(복잡한 구조 이해) Quality 향상(버그 발생 빈도 감소) 제작자의 의도된 제약사항(구조) 유지보수 유리(체계적 구조)


