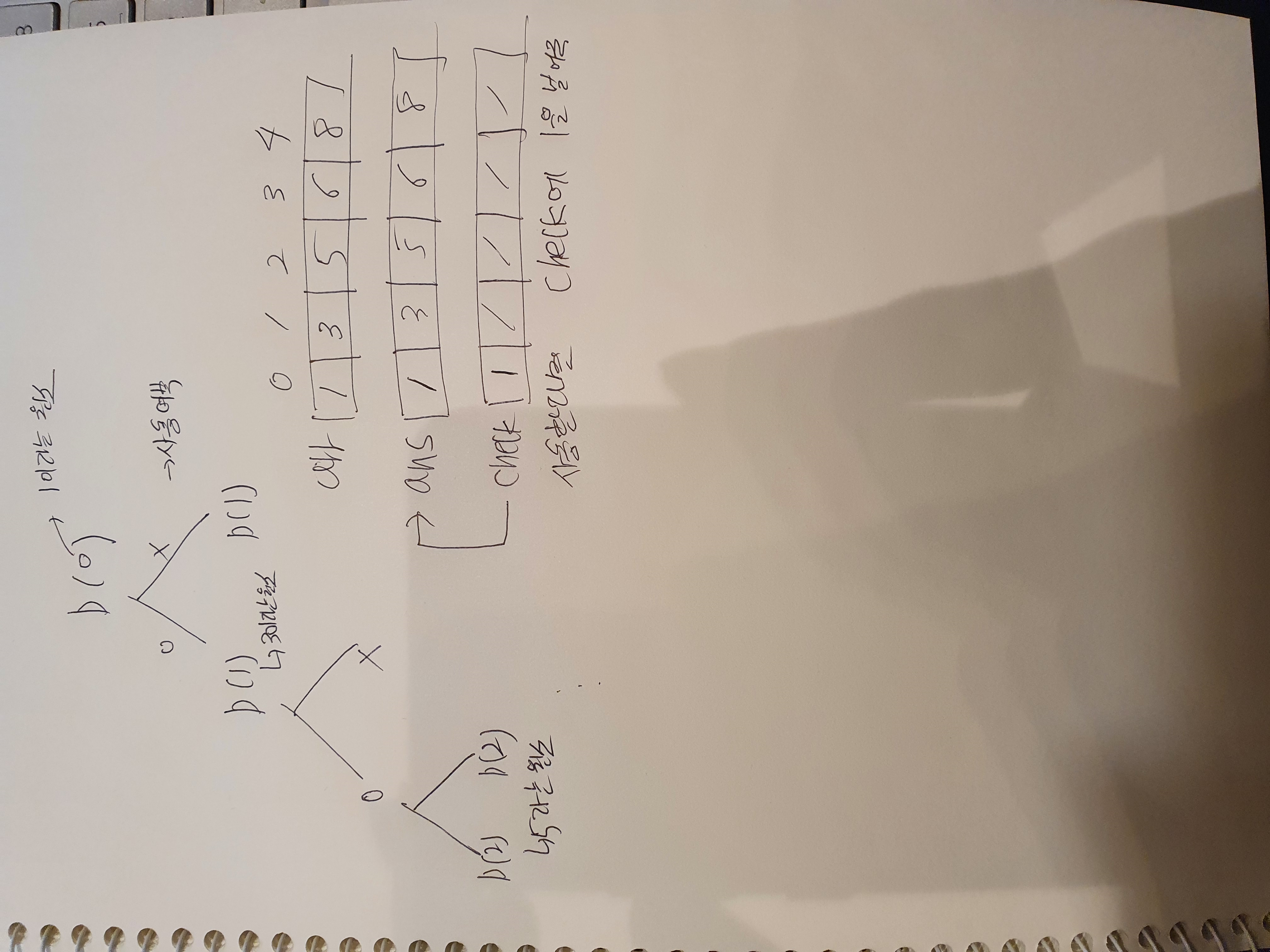1. DFS로 부분집합 구하기
- 주어진 값
- n개의 원소
ex) 5, 1,3,5,6,8 //첫번째 5는 원소의 개수, 1,3,5,6,8은 원소를 의미
- DFS - 해당 원소를 사용하냐 안하냐로 구하기
- static 변수
- static int n;
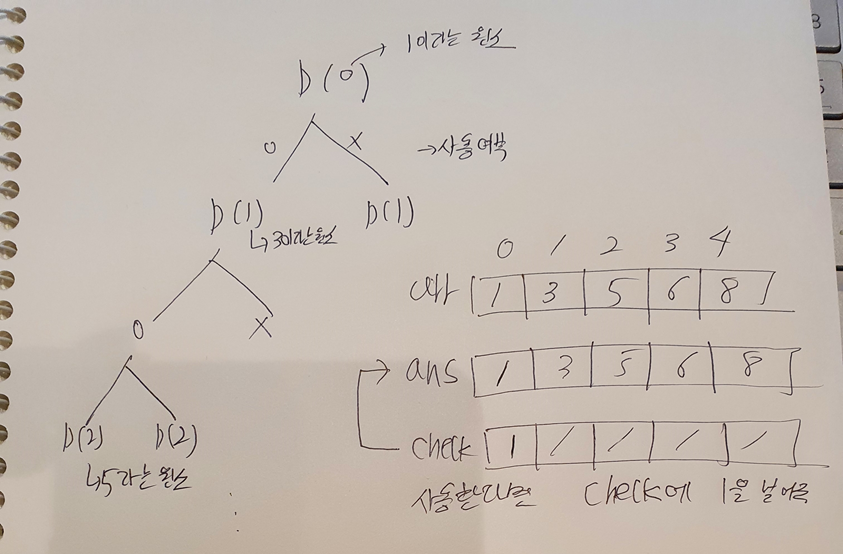
- static int check[]; // 해당 원소 사용여부
- static int ans[]; // 원소를 사용할때 담을 정답 배열
- static int arr[]; // 원소가 들어있는 문제 배열
package inflearn.section7_dfs;
import java.util.*;
public class 부분집합 {
static int check[];
static int n;
static int ans[];
static int arr[];
static int count;
public static void dfs(int l) {
if (l==n) {
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
if (check[i]==1) {
System.out.print(ans[i]+" ");
}
}
count++;
System.out.println();
}
else {
check[l]=1;
ans[l]=arr[l];
dfs(l+1);
check[l]=0;
ans[l]=0;
dfs(l+1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
n=scan.nextInt();
check=new int[n];
ans=new int[n];
arr=new int[n];
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
arr[i]=scan.nextInt();
}
dfs(0);
System.out.println("총 몇개:"+count);
}
}
BFS로 넓이 우선 탐색
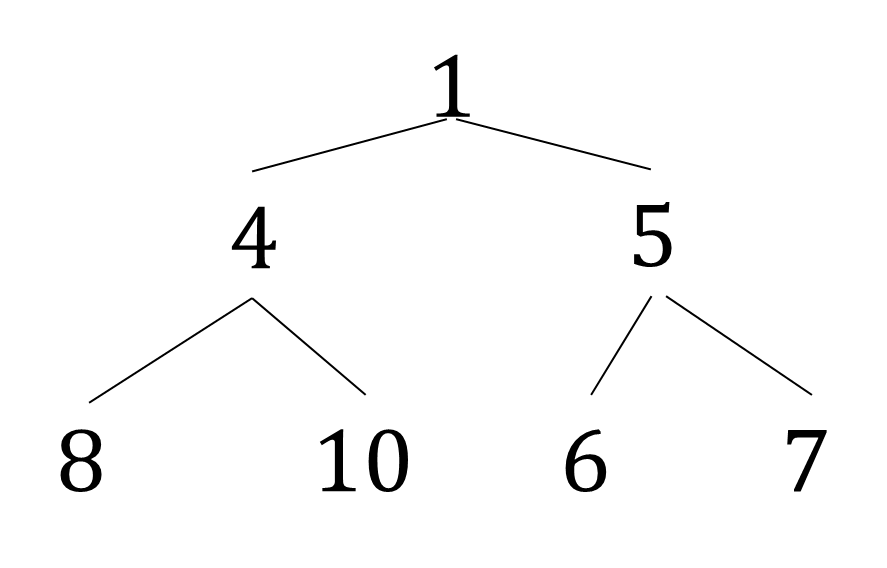
- 1 4 5 8 10 6 7 로 출력하기
- 풀이
1. node랑 연결된 hashmap 만들기
2. bfs로 노드 추가 후 queue for 문 돌기
3. queue에서 노드 뽑고, 왼쪽 오른쪽 추가하기
package inflearn.section7_dfs;
import java.util.*;
public class 이진트리순회bfs {
static class Point{
int left;
int right;
Point (int left, int right) {
this.left=left;
this.right=right;
}
}
static HashMap<Integer, Point>hashmap=new HashMap<>();
public static void bfs(int node) {
Queue<Integer>queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(node);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size=queue.size();
for (int i=0;i<size;i++) {
int k=queue.poll();
System.out.print(k+" ");
if (hashmap.containsKey(k)) {
Point point=hashmap.get(k);
queue.add(point.left);
queue.add(point.right);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
hashmap.put(1,new Point(4,5));
hashmap.put(4,new Point(8,10));
hashmap.put(5,new Point(6,7));
bfs(1);
}
}
송아지 찾기 BFS
문제 풀이
- 큐 사이즈를 구하고
- 큐 사이즈 만큼 for문을 돌고
- 큐에서 poll를 하고
- 주어진 방향대로(3방향) 대로 큐에 추가한다.
4-1. 이때 방향에서 벗어나거나 check 배열에서 벗어나는 경우는 추가 안하기 (또 안가게 하기 위해서) 또 가면 시간 초과 발생
- 큐를 돌았으면 answer를 증가하고
- target이 큐에 있으면 answer를 출력
주의점
- check 배열을 반드시 사용할것 - 사용지점은 다시 안가게 해야됨 (또 가면 시간 초과 발생)
- 방향에서 벗어나는 경우는 queue에 추가 안하기
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int[]dx={-1,1,5};
static int target;
static int answer;
static int check[];
public static void bfs(int start) {
Queue<Integer>queue=new LinkedList<>();
check[start]=1;
queue.add(start);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size=queue.size();
for (int i=0;i<size;i++) {
int k=queue.poll();
for (int j=0;j<3;j++) {
int nx=k+dx[j];
if (nx>=1 && nx<=10000 && check[nx]==0) {
queue.add(nx);
check[nx]=1;
}
}
}
answer++;
if (queue.contains(target)) {
System.out.println(answer);
return;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int input1 = in.nextInt();
target = in.nextInt();
check=new int[10001];
bfs(input1);
return ;
}
}