5. 양과 늑대
문제 해결 방법
- 갈 수 있는 모든 경우의 수를 다 탐색 해야됨 -> DFS
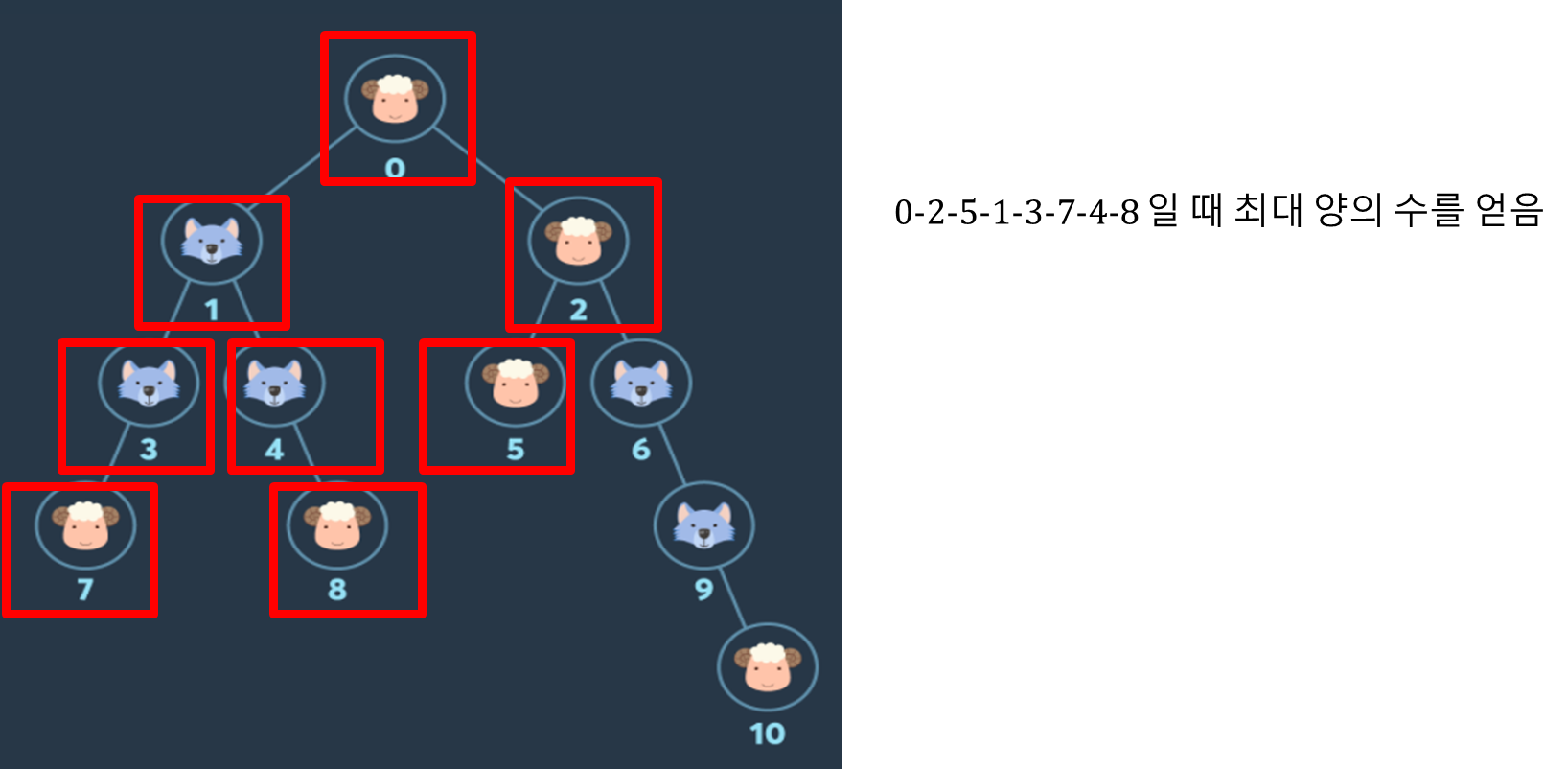
- 그래프 만들기 -> Map을 이용
key는 Node, Value는 연결된 Node 정보들
HashMap<Integer, ArrayList>graph=new HashMap<>();
- DFS 이용 (int 현재노드, int 양의 수, int 늑대 수, List 다음 갈곳)
- 2-1. 만약 갈 노드가 0(양)이라면 양 증가, 아니라면 늑대 증가
- 2-2. 늑대가 더 많다면 탐색 종료 -> return
- 아니라면 양의 수를 최대값 갱신, max값과 비교
- 2-3. 다음 갈곳 list에 새로 갈 list를 만들어서 복사
- 만약 그대로 사용한다면 가야할 node를 또 못감. (또 가기 위해서 list 복사)
- 2-4. 연결된 node값을 add
- 2.5. 현재 방문한 곳은 remove
- 2.6 for문을 돌면서 다음 갈곳 dfs
용법
- Integer.parseInt & Integer.valueOf 차이
- Integer.parseInt : primitive tpye인 int형을 반환
- Integer.valueOf : Wrapper Object인 Integer를 반환
Integer.valueOf(node)로 사용
코드
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static HashMap<Integer,ArrayList>graph;
static int max;
static int infos[];
public void dfs(int node, int sheep, int wolf, ArrayList<Integer>list) {
if (infos[node]==0) sheep+=1;
else wolf+=1;
if (sheep<=wolf) return;
max=Math.max(max,sheep);
ArrayList<Integer> nextlist=new ArrayList<>();
nextlist.addAll(list);
if (graph.containsKey(node)) {
nextlist.addAll(graph.get(node));
}
nextlist.remove(Integer.valueOf(node));
for (int next:nextlist) {
dfs(next,sheep,wolf,nextlist);
}
return;
}
public int solution(int[] info, int[][] edges) {
int answer = 0;
max=0;
graph=new HashMap<>();
infos=info.clone();
for (int edge[]:edges) {
int key=edge[0];
int value=edge[1];
ArrayList<Integer>arraylist=new ArrayList<>();
if (graph.containsKey(key)) {
arraylist=graph.get(key);
arraylist.add(value);
}
else {
arraylist.add(value);
}
graph.put(key,arraylist);
}
ArrayList<Integer>nodelist=new ArrayList<>();
nodelist.add(0);
dfs(0,0,0,nodelist);
return max;
}
}
6. 파괴되지 않는 건물
효율성 테스트에서 실패 -> 누적합으로 구해야 한다고 함.

코드
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
static int[][]map;
static int n;
static int m;
static int answer;
public void attack(int r1,int c1, int r2, int c2, int degree) {
for (int i=r1;i<=r2;i++) {
for (int j=c1;j<=c2;j++) {
map[i][j]+=degree;
}
}
}
public void check_map() {
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
for (int j=0;j<m;j++) {
if (map[i][j]>0) {
answer++;
}
}
}
}
public void print_map() {
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) {
for (int j=0;j<m;j++) {
System.out.print(map[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public int solution(int[][] board, int[][] skill) {
map=board;
n=board.length;
m=board[0].length;
answer=0;
for (int i=0;i<skill.length;i++) {
int type=skill[i][0];
int r1=skill[i][1];
int c1=skill[i][2];
int r2=skill[i][3];
int c2=skill[i][4];
int degree=skill[i][5];
if (type==1) {
degree*=-1;
}
attack(r1,c1,r2,c2,degree);
}
check_map();
return answer;
}
}


