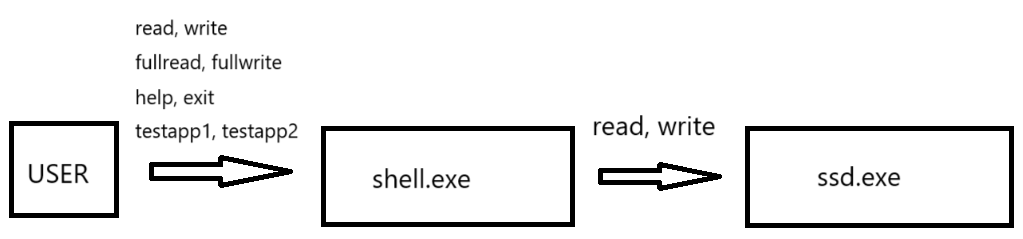
전체적인 구상도
user가 shell.exe를 이용해 ssd.exe를 제어한다.
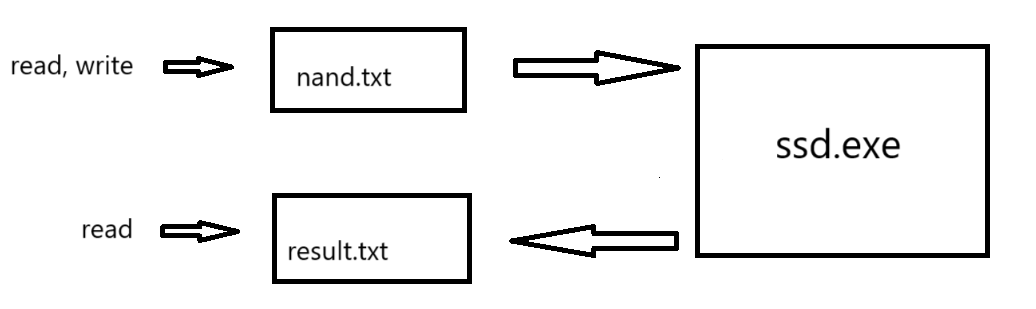
ssd.exe
write하면 nand.txt에 값 저장 read하면 result.txt에 읽은 값 저장
shell.exe
write: ssd에 명령어 전달
read: ssd에 명령어 전달 + result 출력
fullwrite: LBA 0번부터 99번까지 write 수행
fullread: LBA 0번부터 99번까지 read 수행
유효성검사
LBA의 범위는 0 ~ 99
값은 16진수로 A ~ F, 0 ~ 9까지 숫자범위 허용
없는 명령어 수행 시 "INVALID COMMAND" 출력
ssd.cpp
#include "storage.h"
#include <fstream>
#include <string.h>
class SSD: public Storage{
private:
std::string buf[100]; // LBA는 4Byte 크기
std::string line;
public:
void write(uint32_t address, std::string value){
std::ofstream fout("nand.txt", std::ios::app);
fout << address << '-' << value << '\n';
fout.close();
}
void read(uint32_t address, bool flag){
std::ifstream fin("nand.txt");
while (std::getline(fin, line)) {
if(line[1] == '-'){
buf[stoi(line.substr(0, 1))] = line.substr(2);
}
else if(line[2] == '-'){
buf[stoi(line.substr(0, 2))] = line.substr(3);
}
}
fin.close();
if(flag){
std::ofstream fout("result.txt", std::ios::app);
fout << buf[address] << '\n';
fout.close();
}
else{
std::ofstream fout("result.txt");
fout << buf[address] << '\n';
fout.close();
}
}
SSD(){
std::fill_n(buf, 100, "00000000");
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){ // argv[0]은 파일명
SSD ssd;
if(strcmp(argv[1], "W") == 0){
ssd.write(atoi(argv[2]), argv[3]);
}
else if(strcmp(argv[1], "R") == 0){
if(strcmp(argv[3], "FULL") == 0) {
ssd.read(atoi(argv[2]), 1);
}
if(strcmp(argv[3], "ONE") == 0) {
ssd.read(atoi(argv[2]), 0);
}
}
}address + '-'로 몇번 LBA에 저장되어있는지 파악
SSD클래스 생성자를 이용해 buf를 "00000000"로 초기화, 부분집합을 이용해 숫자값만 buf에 저장 후 result에 저장
"R"을 입력 받을 시 "FULL"인 경우 모두 읽기 "ONE"인 경우 한개만 읽기
std::ios::app 이용 시 기존 파일내용부터 시작
main함수 인자로 argv이용
storage.h
#ifndef __STORAGE_H__
#define __STORAGE_H__
#include <iostream>
#include <stdint.h>
class Storage{
public:
virtual void write(uint32_t address, std::string value) = 0;
virtual void read(uint32_t address, bool flag) = 0;
};
#endif추상클래스를 이용해 확장성 보장
shell.cpp
#include "val.h"
#include "exefc.h"
#include "fcssd.h"
int main() {
std::ofstream fout1("nand.txt");
fout1.close();
std::ofstream fout2("result.txt");
fout2.close();
std::string s, LBA_s, h;
int LBA;
while (1) {
std::cout << "명령어를 입력하세요: ";
std::cin >> s;
if (s == "write") {
std::cin >> LBA_s;
std::cin >> h;
if(write(LBA_s, h) == false){
continue;
}
}
else if (s == "fullwrite") {
std::cin >> h;
if(fullwrite(h) == false){
continue;
}
}
else if (s == "read") {
std::cin >> LBA_s;
if(read(LBA_s) == false){
continue;
}
}
else if (s == "fullread") {
if(fullread() == false){
continue;
}
}
else if (s == "help") {
help();
}
else if (s == "exit") break;
else if(s == "testapp1"){
std::cin >> h;
if(fullwrite(h) == false){
continue;
}
if(fullread() == false){
continue;
}
}
else if(s == "testapp2"){
for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++){
if(write(std::to_string(j), "0xAAAABBBB") == false){
continue;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
if(write(std::to_string(i), "0x12345678") == false){
continue;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
if(read(std::to_string(i)) == false){
continue;
}
}
}
else {
getline(std::cin, s); // 쓰레기값 치우기
std::cout << "INVALID COMMAND" << std::endl;
}
}
return 0;
}초기에 파일 초기화
else에서 getline으로 뒤에 입력받은 값 처리
각 기능들 함수로 만들어 testapp구현 시 용이
fcssd.h
#ifndef __FCSSD_H_
#define __FCSSD_H_
#include "exefc.h"
#include "val.h"
bool write(std::string LBA_s, std::string h);
bool fullwrite(std::string h);
bool read(std::string LBA_s);
bool fullread();
void help();
#endiffcssd.cpp
#include "fcssd.h"
bool write(std::string LBA_s, std::string h){
int LBA;
try{
LBA = std::stoi(LBA_s);
}
catch(std::invalid_argument&){
std::cout << "LBA로 올바른 타입을 입력하세요" << std::endl;
return false;
}
if (isLBA(LBA) == 0) {
std::cout << "LBA범위 오류" << std::endl;
return false;
}
if (isHexadecimal(h) == 0 || h.size() != 10) {
std::cout << "16진수 입력 값 오류" << std::endl;
return false;
}
else h = h.substr(2);
//std::cout << LBA_s << h;
if(exefc("a.exe", "W", LBA_s, h) == false){
std::cerr << "\nSSD 실행에 실패했습니다!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool fullwrite(std::string h){
std::ofstream fout1("nand.txt");
fout1.close(); // 속도저하
if (isHexadecimal(h) == 0 || h.size() != 10) {
std::cout << "16진수 입력 값 오류" << std::endl;
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if(exefc("a.exe", "W", std::to_string(i), h) == false){
std::cerr << "\nSSD 실행에 실패했습니다!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool read(std::string LBA_s){
int LBA;
std::string line;
try{
LBA = std::stoi(LBA_s);
}
catch(std::invalid_argument&){
std::cout << "LBA로 올바른 타입을 입력하세요" << std::endl;
return false;
}
if (isLBA(LBA) == 0) {
std::cout << "LBA범위 오류" << std::endl;
return false;
}
if(exefc("a.exe", "R", LBA_s, "ONE") == false){
std::cerr << "\nSSD 실행에 실패했습니다!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
std::ifstream fin("result.txt");
while (std::getline(fin, line)) {
std::cout << line << std::endl;
}
fin.close();
return true;
}
bool fullread(){
std::string line;
std::ofstream fout("result.txt");
fout.close(); // 초기화
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
if(exefc("a.exe", "R", std::to_string(i), "FULL") == false){
std::cerr << "\nSSD 실행에 실패했습니다!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
}
std::ifstream fin("result.txt");
while (std::getline(fin, line)) {
std::cout << line << std::endl;
}
fin.close();
return true;
}
void help(){
std::cout << "====명령어 사용 방법======" << std::endl;
std::cout << "write: LBA에 입력\n ex) write LBA번호 입력값" << std::endl;
std::cout << "read: 화면출력\n ex) write LBA번호" << std::endl;
std::cout << "exit: Shell 종료\n ex) exit" << std::endl;
std::cout << "help: 명령어 사용방법 출력\n ex) help" << std::endl;
std::cout << "fullwrite: LBA 0번부터 99번까지 입력\n ex) fullwrite 입력값" << std::endl;
std::cout << "fullread: LBA 0번부터 99번까지 출력\n ex) fullwrite" << std::endl;
}유효성검사 + execfc를 이용해 a.exe에 인자 전달
val.h
#ifndef __VAL_H_
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
bool isHexadecimal(const std::string& input);
bool isLBA(const int& input);
#endifval.cpp
#include "val.h"
bool isHexadecimal(const std::string& input) {
// 입력 문자열이 빈 문자열인지 검사
if (input.empty()) return false;
// 0x 또는 0X로 시작하면 이를 무시 (16진수 표기법)
size_t startIndex = 0;
if (input.length() > 2 && (input[0] == '0') && (input[1] == 'x' || input[1] == 'X')) {
startIndex = 2;
}
else{
return false;
}
// 남은 문자가 모두 16진수 값인지 검사
for (size_t i = startIndex; i < input.length(); ++i) {
if (!std::isxdigit(input[i])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool isLBA(const int& input) {
if (input >= 0 && input < 100) return true;
else return false;
}유효성검사
exefc.h
#ifndef __EXEFC_H_
#include <process.h>
#include "val.h"
bool exefc(std::string p_name, std::string ist, std::string LBA, std::string h);
#endifexefc.cpp
#include "exefc.h"
#include "val.h"
bool exefc(std::string p_name, std::string ist, std::string LBA, std::string h){
const char* program = p_name.c_str();
const char* args[] = { program, ist.c_str(), LBA.c_str(), h.c_str(), NULL };
int result = _spawnvp(_P_WAIT, program, args); // _P_WAIT _P_NOWAIT
if (result == -1) return false;
else return true;
}인자를 모두 string으로 받은 후 c_str()로 const char*형으로 변환
_P_WAIT를 이용해 a.exe가 끝날 때 까지 기다린 후 종료
추상클래스 사용으로 SSD클래스 외 다른 클래스도 read, write하게 만들고 shell의 기능들을 함수로 만들어 testapp만들 때 편리했다.
main함수로 인자를 받는 argv와 새로운 프로세스를 생성하는 _spawnvp 이용해 2개의 실행파일이 연결되게 했다