자 !
이제 나머지 함수들을 작성하여 게임을 끝내보자 !
그래픽 체력 미터 그리기
def drawHealthMeter(currentHealth):
for i in range(currentHealth): # draw red health bars
pygame.draw.rect(DISPLAYSURF,RED,(15,5+(10*MAXHEALTH)-i*10,20,10))
for i in range(MAXHEALTH): # drwa the white outlines
pygame.draw.rect(DISPLAYSURF,WHITE,(15,5+(10*MAXHEALTH)-i*10,20,10),1)
현재 체력은 빨강색으로 전체 체력은 흰색 테두리로 그린다.
terminate() 함수
def terminate():
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()ㅇㅇ
sine 함수의 수학
def getBounceAmount(currentBounce,bounceRate,bounceHeight):
#bounce에 관련된 변수에 따라 몇 픽셀이나 점프할 것인지 값을 결정해서 반환한다.
#bounceRate 숫자가 크면 느린 점프가 된다.
#bounceHeight 숫자가 크면 높은 점프가 된다.
#CurrentBounce 는 항상 BounceRate 보다 작다.
return int(math.sin((math.pi/float(bounceRate))*currentBounce)*bounceHeight)python은 math모듈에 수학 함수를 가지고 있다.
math.sin()에 정수나 실수를 넘겨주면 sine값인 실수를 반환해 준다
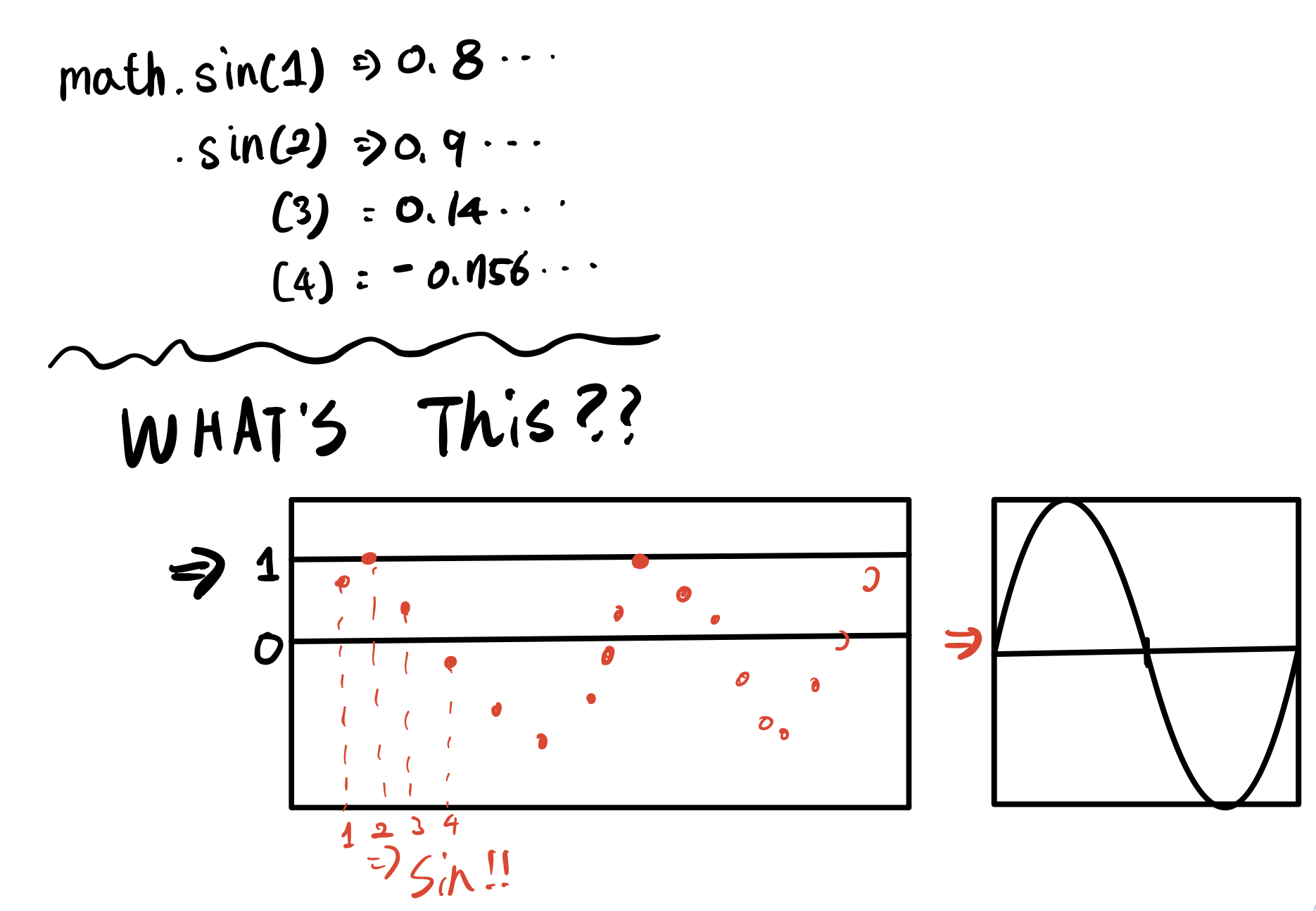
이런식으로 사인의 값을 반환해주는것이다 !
그렇기에 3.14/6 = 0.5234로 0~3.14까지 Bouncerate 만큼 구간을 쪼개주었다.
이런식으로 하여 점프를 사인함수와 동일한 물결 모양의 패턴을 반환한다
python2 와 하위 호환성
float(bouncerate)라고 작성한 이유는 pyrhon ver2 에서도 동작하도록 하기 위해서이다.
그 이유는 버전2에서는 나누는 값에 실수가 없다면 실수로 절대로~ 반환하지 않기 때문이다!
getRandomVelocity()
def getRandomVelocity():
speed = random.randint(SQUIRRELMINSPEED,SQUIRRELMAXSPEED)
if random.randint(0,1) == 0 :
return speed
else:
return -speed그냥 랜덤 속도 준당 방향두 ~
다람쥐와 잔디를 추가할 장소 찾기
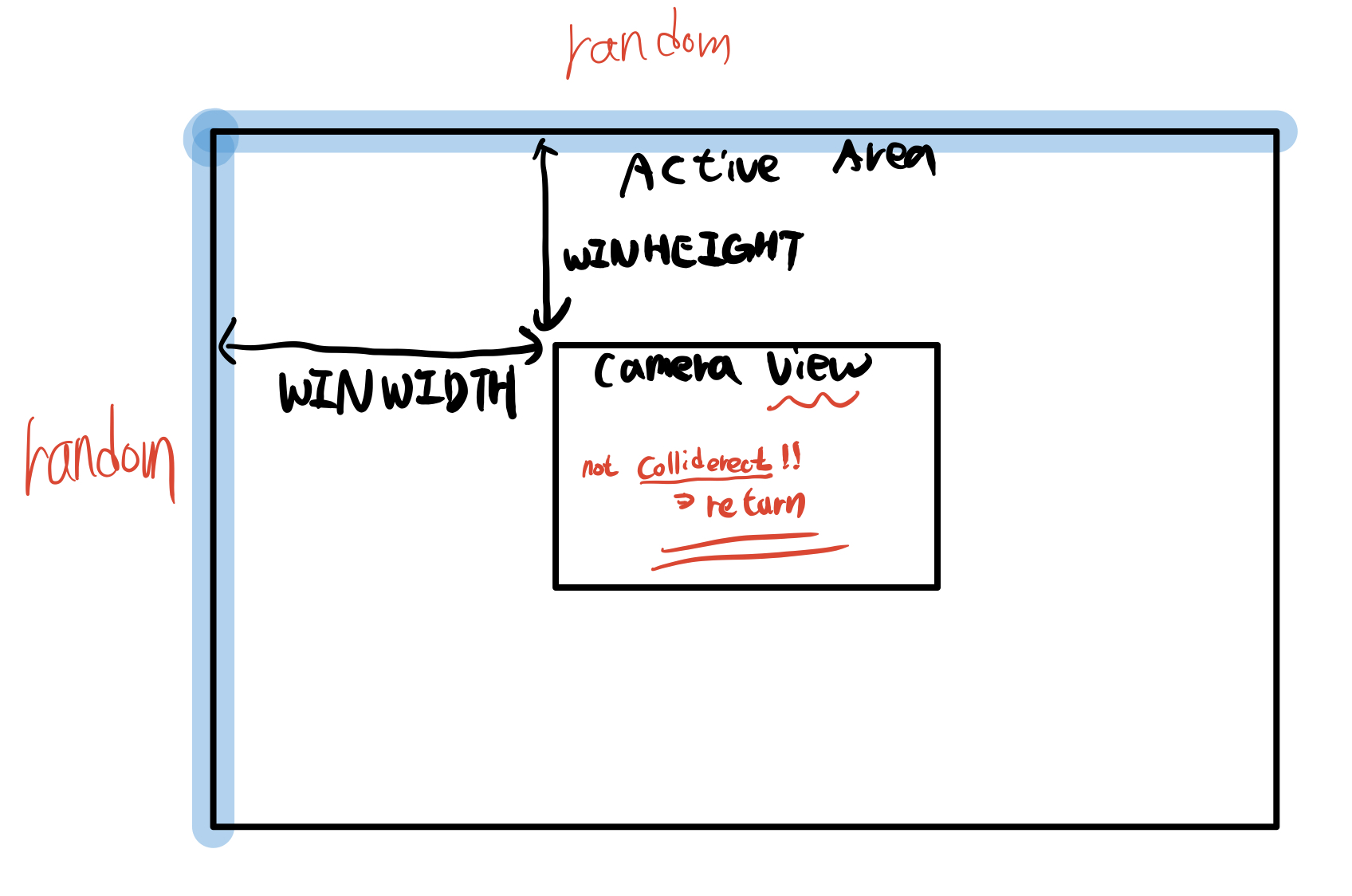
def getRandomOffCameraPos(camerax,cameray,objWidth,objHeight):
#setting camera view Rect object
cameraRect = pygame.Rect(camerax,cameray,WINWIDTH,WINHEIGHT)
while True:
x = random.randint(camerax - WINWIDTH, camerax + (2 * WINWIDTH))
y = random.randint(cameray - WINHEIGHT, cameray + (2 * WINHEIGHT))
# create a Rect object with the random coordinates and use colliderect()
# to make sure the right edge isn't in the camera view.
objRect = pygame.Rect(x, y, objWidth, objHeight)
if not objRect.colliderect(cameraRect):
return x, y게임 세계 안에 새 다람쥐와 잔디 객체를 만들고 나면 이 객체들은 활성 영역 안에 있어야 하지만 카메라 뷰 안에 있으면 안된다.
우선 카메라 영역을 표시하는 Rect객체를 만든다 !
다음
이 활성영역에 랜덤으로 받고 카메라 영역의 Rect와 충돌하지 않는다면 return x,y 를 한다 !
적 다람쥐 데이터 구조 만들기
def makeNewSquirrel(camerax, cameray):
sq = {}
generalSize = random.randint(5, 25)
multiplier = random.randint(1, 3)
sq['width'] = (generalSize + random.randint(0, 10)) * multiplier
sq['height'] = (generalSize + random.randint(0, 10)) * multiplier
sq['x'], sq['y'] = getRandomOffCameraPos(camerax, cameray, sq['width'], sq['height'])
sq['movex'] = getRandomVelocity()
sq['movey'] = getRandomVelocity()
if sq['movex'] < 0: # squirrel is facing left
sq['surface'] = pygame.transform.scale(L_SQUIR_IMG, (sq['width'], sq['height']))
else: # squirrel is facing right
sq['surface'] = pygame.transform.scale(R_SQUIR_IMG, (sq['width'], sq['height']))
sq['bounce'] = 0
sq['bouncerate'] = random.randint(10, 18)
sq['bounceheight'] = random.randint(10, 50)적 다람쥐 만드는 과정은 잔디와 비슷하다.
우선 모든 적 다람쥐는 딕셔너리에 저장되고, 크기는 랜덤~ 이고 멀티플라이어를 곱해서 일정한 크기로 맞춘다 !
적 다람쥐는 카메라뷰 밖에서 생성된다
속도/방향은 랜덤 ~
그리고 방향,점프 등을 설정해준다.
잔디 데이터 구조 만들기
def makeNewGrass(camerax, cameray):
gr = {}
gr['grassImage'] = random.randint(0, len(GRASSIMAGES) - 1)
gr['width'] = GRASSIMAGES[0].get_width()
gr['height'] = GRASSIMAGES[0].get_height()
gr['x'], gr['y'] = getRandomOffCameraPos(camerax, cameray, gr['width'], gr['height'])
gr['rect'] = pygame.Rect( (gr['x'], gr['y'], gr['width'], gr['height']) )
return gr잔디를 만들고 설치한댱~
활성 영역 바깥인지 검사하기
def isOutsideActiveArea(camerax, cameray, obj):
# Return False if camerax and cameray are more than
# a half-window length beyond the edge of the window.
boundsLeftEdge = camerax - WINWIDTH
boundsTopEdge = cameray - WINHEIGHT
boundsRect = pygame.Rect(boundsLeftEdge, boundsTopEdge, WINWIDTH * 3, WINHEIGHT * 3)
objRect = pygame.Rect(obj['x'], obj['y'], obj['width'], obj['height'])
return not boundsRect.colliderect(objRect)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()이를 통해 활성 영역과 겹치는지 확인할수 있다.
요약
다람쥐 먹기 게임은 여러명의 적이 한꺼번에 나오는 게임이다.
적을 여러 개 만드는 방법은 각 적 다람쥐를 동일한 값을 가진 딕셔너리로 만드는 것이다.
이렇게 해서 게임 루프에서 여러 다람쥐들을 다루기 위해 같은 코드를 사용할 수 있다.
카메라에 대한 개념도 새로배웠다.
사인함수도 다뤘다 !
이제 다음 포스트에서 전체코드를 보고 실행해보자 !