OS Internals
What is a Process?
: An instance of a program in execution
프로세스는 object의 개념이기때문에 한 개의 프로그램으로부터 여러개의 프로세스가 있을 수 있다. 즉 CPU가 여러 개일때, 커널 코드는 메모리에 한 개 있고 그거를 인스턴스로 만들어서 각각의 CPU에 올리게 되는 것 !
Process는 resource 할당의 단위가 된다. (PID 부여 받음)
Program to Process
Memory를 할당 받고, Code Data 등이 올라 간 상태
프로세스는 다른 프로세스에서 파생되는 형태 (fork() 이후 execv() )이기 때문에 OS가 부팅할 때 최초의 process를 실행하도 exeinit() 등을 통해 OS scheculer를 만든다.
Process Creation
fork()
: parent process와 동일한 child process를 만든다.
이때 address space를 복사하고, file descriptor는 공유
Called once, return twice
exec()
: 현재의 process를 새로운 program으로 대체
Called once, never return
error 발생시에만 -1 리턴
Zombie Process
: terminated, but not removed
보통은 parent가 wait()으로 child process 끝나는 거 기다려주거나 해야하는데 부모 process가 먼저 죽을 경우 init()이 child process를 kill
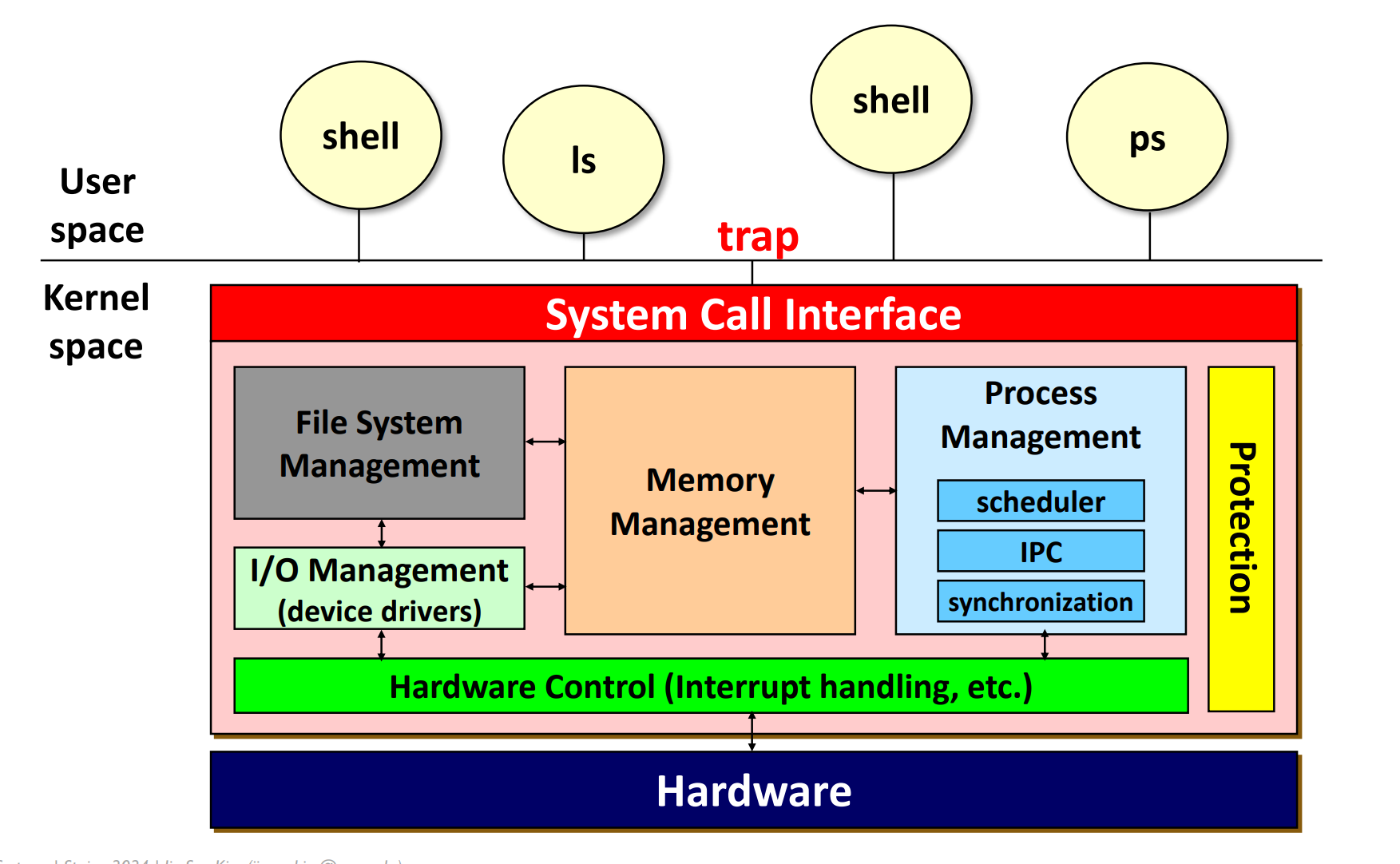
Implementing Processes
PCB(process Contrl Block) or Process Descriptor에 process 정보가 담겨 있음 (왜냐면 계속 왔다갔다할 때 얘 정보를 CPU에 넘겨줘야 하잖아 !!)
어떤 정보가 담겨져 있냐면
-CPU registers
-PID, PPID, proces group, prioity, process state, signals
-CPU scheudling information
-Memory management information
등등
Context Switch
CPU가 process를 바꾸는 동작
Administrative Overhead
- Saving and restoring registers and memory maps
- Flushing and reloading the memory cache
- Updating various tables and lists (ex. TLB)
Switches / sec는 사실 사람이 인식할 수 있는 수준까지만 늘리면 되고, 더 늘릴수록 overhead가 커지기 때문에 적정 수준까지만 올리면 된다.
Performing Context Switch in xv6
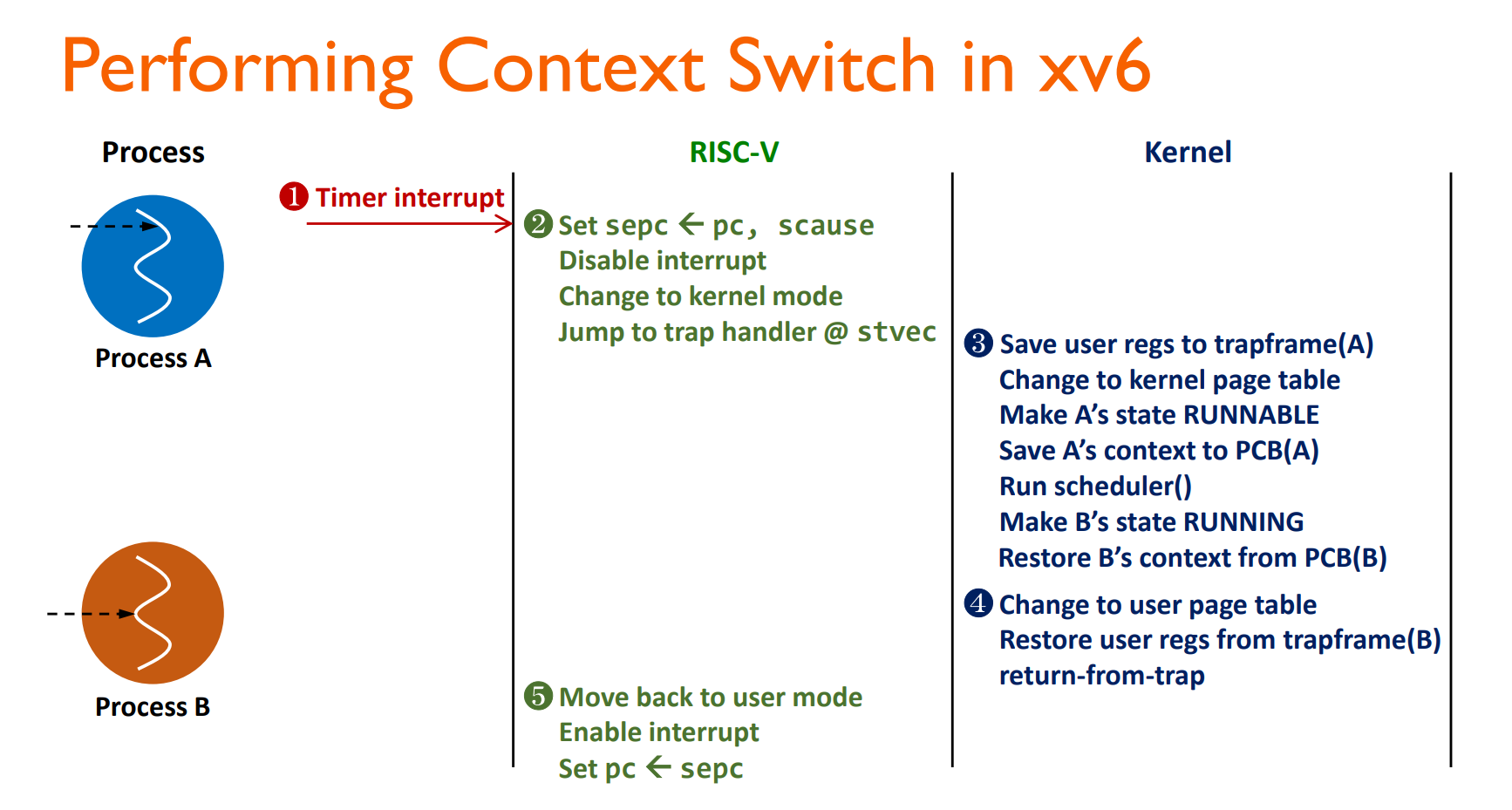
sepc도 사실은 PCB에 저장된 값임
한 번에 하나의 interrupt만 받도록 Disable하는 것
stvec은 kernel안의 trap handler 위치
Implementing fork()
- Creates and initializes a new PCB / address space
- parent의 address space 복사
- Initialize kernel resources to point to the resources used by the parent (ex. open files)
- PCB를 ready queue에 넣기
- Returns the child's PID to the parent, and zero to the child
이런 pid 값이 결국엔 trapframe에 있다고 이해하면 됨
Implementing exec()
- Stop the current process
- "prog"를 process의 address space에 넣음
(pid는 그대로인데 memory 영역이 아예 바뀌어 버린다고 생각) - PCB를 ready queue에 넣기