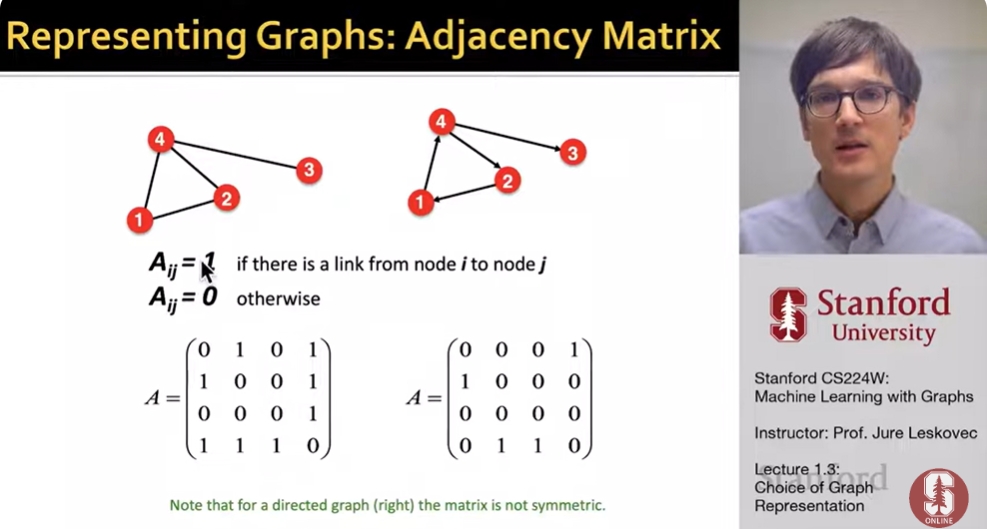
Directed vs Undirected Graphs
Undirected
Links: undirected (symmetrical, reciprocal)
ex) collaborations, friendship on Facebook
Directed
Links: directed
ex) Phone calls, Following on Twitter


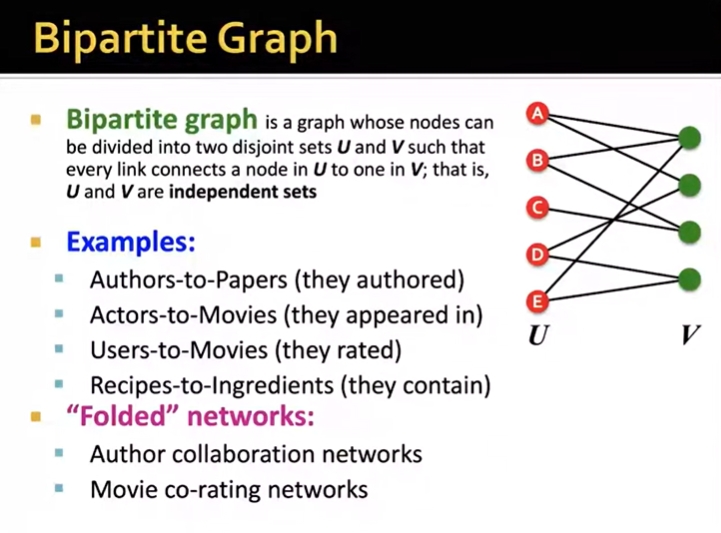
Node & Edge Attributes
possible options:
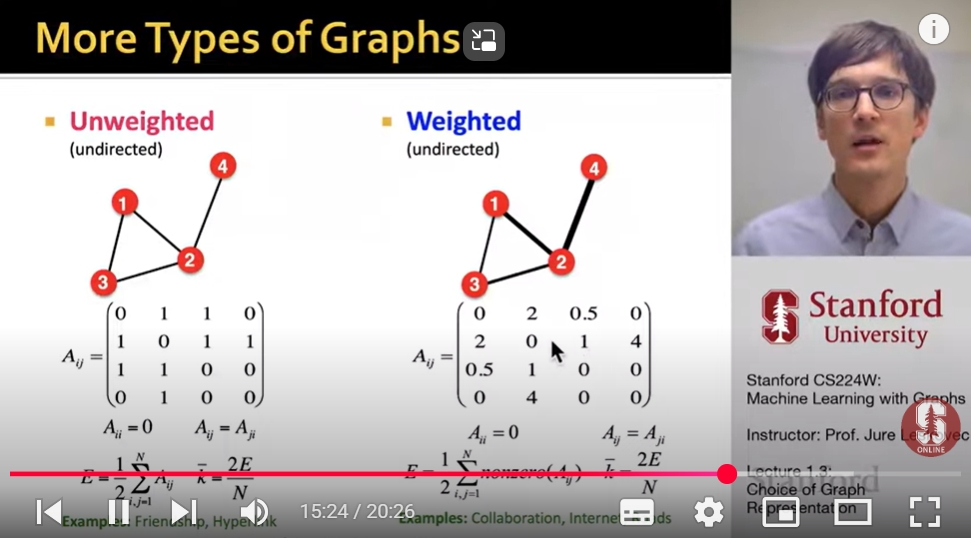
Weight (e.g frequency of communication)
Ranking (best friend, second best friend)
Type (friend, relative, co-worker)
sign: Friend vs Foe, Trust vs Distrust
Properties depending on the structure of the rest of the graph: number of common friends
strength of the connection

Machine learning tasks: Review
- Node-level prediction
- Link-level prediction
- Graph-level prediction
Traditional ML Pipeline
- Design features for nodes/links/graphs
- Obtain features for all traing data
Train ML model (random forest, SVM, Neural network)
Apply the model ( given a new node/link/graph, obtain its features and desing a prediction
Node-level features
characterize the structure and position of a node in the network
-node degree
-node centrality
clustering coefficient
-graphlets
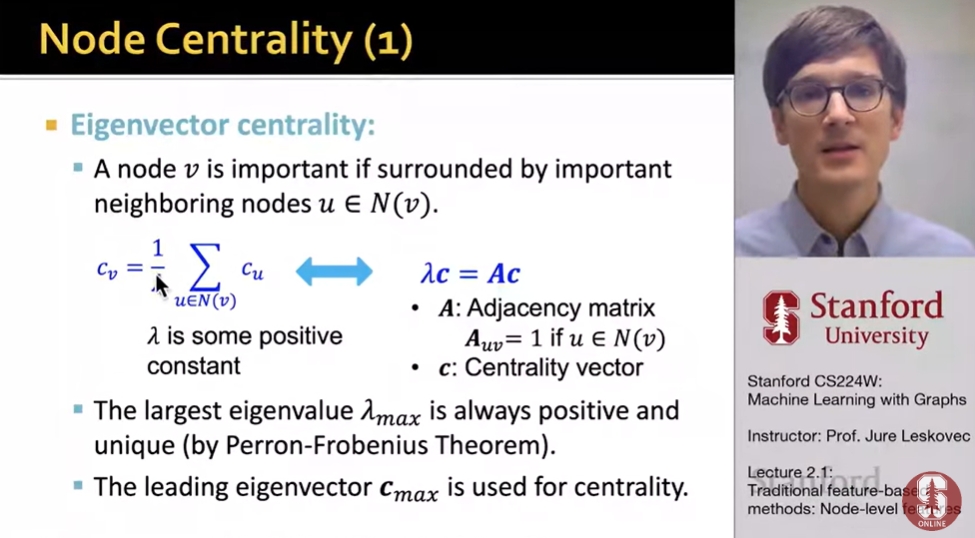
Node Centrality
-Node degree counts the neighboring nodes without capturing their importance
-node centrality cv takes the node importance in a graph into accont
Different ways to model importance:
-Eigenvector centralit
-Betweenness centrality
-Closeness centrality
and many others...


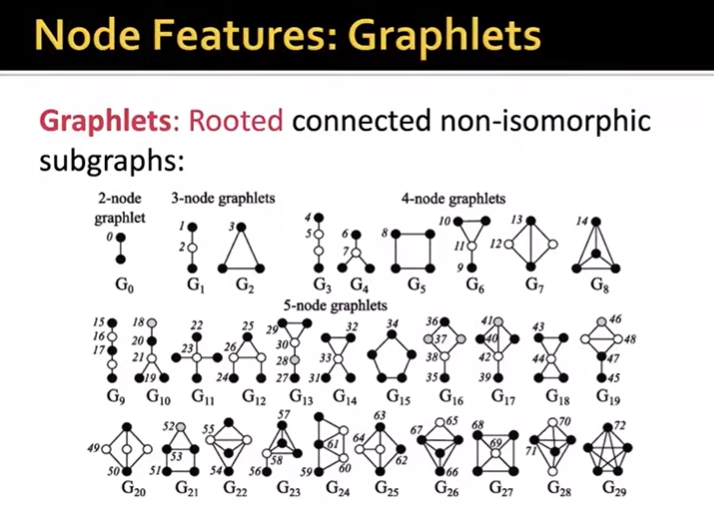
Graphlets
-
Graphlet Degree vector(GDV): Graphlet-based features for nodes
-Degree counts (edges) that a node touches
-Clustering coefficient counts (trangles) that a node touches GDV counts (graphlets) that a node toouches
-Considering graphlets on 2 to 5 nodes we get: -
vector of 73 coordinates is a signature of a node
that describes the topology of node's neighborhood
-captures its interconnectivities out to a distance of 4 hops -
Graphlet degree vector provides a measure of a node's local network topology:
-Comparing vectors of two nodes provides a more detailed measure of local topological similarity than node degrees or clustering coefficient
Node-level feature
can be categorized as:
-
Importance-based features:
-Node degree
-Different node centrality measures -
Structure-based features:
-Node degree
-Clustering coefficient
-Graphlet count vector
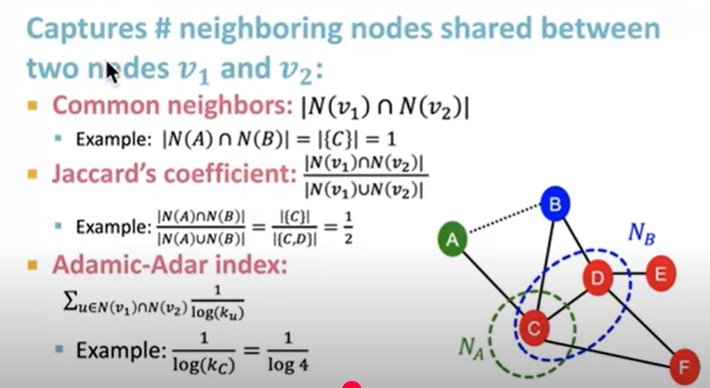
Global neighborhood
- Katz index: count the number of paths of all lengths between a given pair of nodes
How to compute paths between two nodes?
-use powers of the graph adjacency matrix

Link-level features summary
Distance-based features
- uses the shortest path length between two nodes but does not capture how neighborhood overlaps
Local neighborhood overlaps
- Captures how many neighboring nodes are shared by two nodes
- becomes zero when no neighbor nodes are shared
Global neighborhood overlap
- Uses global graph structure to score two nodes
katz index counts paths of all legths between tow nodes
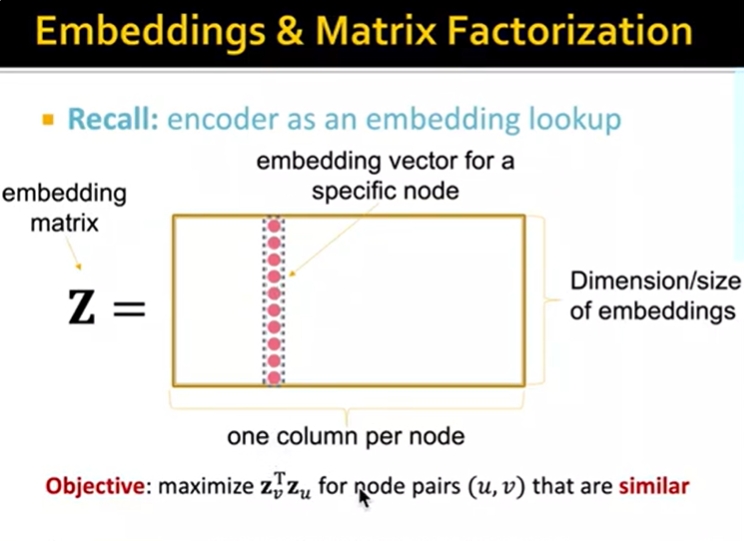
Embeddings & Matrix Factorization



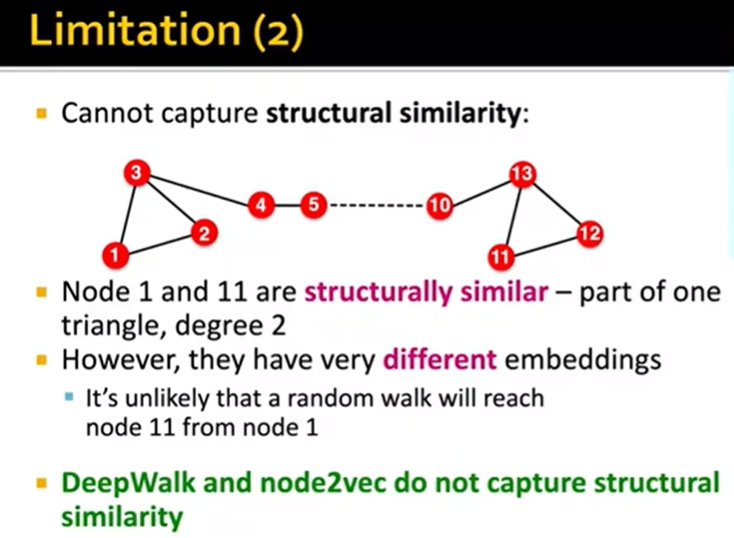
Limitations
-
limitations of node embeddings via matrix factorization and random walks
-cannot obtain embeddings for nodes not in the training set -
cannot capture structural similarity

Summary
-
Pagerank
-measures importance of nodes in graph
-can be efficiently computed by power iteration of adjacency matrix -
Personalized pagerank (PPR)
-measures importance of nodes with respect to a particular node or set of nodes
-can be efficiently computed by random walk -
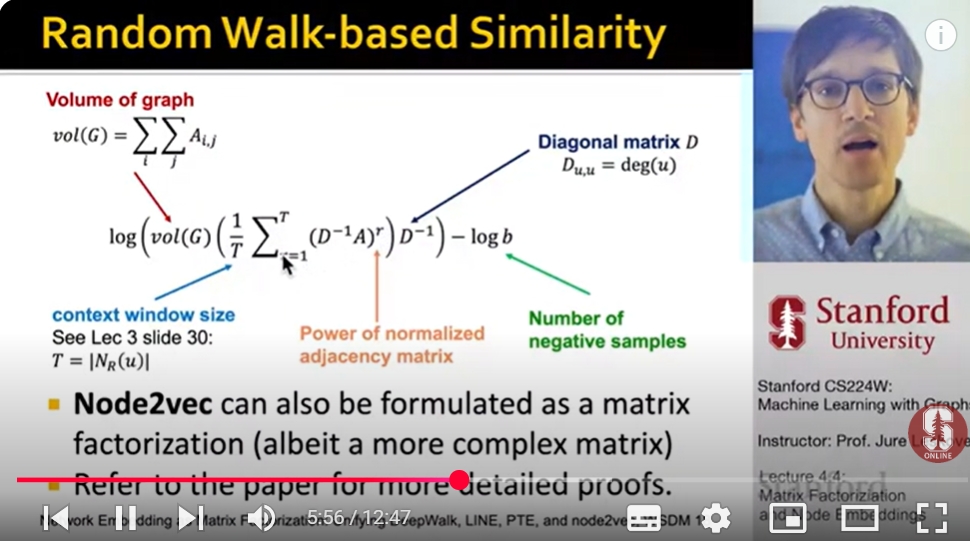
Node embeddings based on random walks can be expressed as matrix factorization
-
viewing graphs as metrics plays a key role in all ahvove algorithms
