
Information extract가 무엇인가?
Information extraction은 어떤 종류의 문서라도 핵심 정보를 추출할 수 있는 기술을 의미한다.
기존의 사전 구축형 정보 추출(prebuilt IE)은 특정 문서 유형에 맞춰 fine-tuning을 해야 하지만,
Universal IE는 추가적인 학습이나 customizing process없이 아무 문서나 바로 처리하고 필요한 정보를 추출할 수 있다.
Schema
정보추출을 위한 스키마를 얻는 방법에는 2가지가 있다.
- Automatic schema generation
- Manual schema design
Automatic schema generation
스키마를 수동으로 직접 설계하는 일은 번거롭다.
반면, Schema Generation API를 사용하면 최대 3개의 샘플 파일만으로 초기 스키마를 손쉽게 생성할 수 있다.
추출된 스키마는 문자열 형태의 JSON 객체로 메시지 내용에 반환된다.
이 스키마는 Information Extract API의 JSON Schema 문법 및 입력 스키마 규칙을 따른다.
또한 사용자는 system message를 통해 스키마 생성에 대한 의도를 API에 전달할 수 있다.
Manual schema design
Schema는 JSON schema syntax에 따라 작성되어야 하고 사용가능한 type은 아래와 같다.
type에는 총 6개의 종류가 존재하며, string, number, integer, boolean, array, object가 있다.

여기서 주의해야할 점은 root object는 반드시 object type 이어야 한다는 것이다.
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"transactions": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"transaction_date": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Date on which each transaction occurred."
},
"transaction_description": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Description of each transaction."
}
}
}
}
}
}Arrays
같은 key에 대해 여러 값을 추출해야 한다면, array type을 사용할 수 있다.
{"type": "array"} 형태로 작성할 때에는, 배열 내부값의 구조를 정의하기 위해 "items" keyword를 반드시 포함해야한다.
Objects
하나의 key 아래에 여러 properties를 정의하려면 object type을 사용한다.
{"type": "object"}로 선언한 후, 구조를 정의하기 위해서 "properties" keyword가 이어져야 한다.
더불어, object type은 array의 items로도 사용될 수 있어, table처럼 여러 row를 표현할 때 활용된다.
Schema design restrictions
직접 스키마를 설계할 때는 다음과 같은 제약사항들이 존재한다.
스키마 내 모든 property 이름과 definition 이름의 총 문자열 길이는 10,000자를 초과할 수 없다.
-
동기(synchronous) API: 최대 100개의 object property / 최대 15,000자까지 허용
-
비동기(asynchronous) API: 최대 5,000개의 object property / 최대 120,000자까지 허용
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"bank_name": {
"type": "object", # ❌ Object type properties are not allowed in the first-level
"properties": {
...
}
}
}
}first-level property는 반드시 다음 타입 중 하나여야 한다. string, integer, number, array (object 타입은 최상위 레벨에 허용되지 않는다.)
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"bank": {
"type": "array",
"items": { "type": "array", "items": {...}} # ❌ Nested arrays are not allowed
}
}
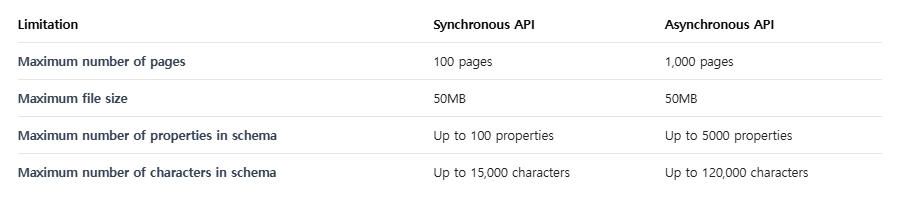
}좀 더 쉬운 이해를 위해 아래 표를 참고하여 동기 API와 비동기 API의 차이점을 설명하도록 하겠다.
Synchronous API
요청이 발생하면, 처리가 완료될때까지 기다리고 즉시 결과를 반환한다.
동기 API는 작은 문서 처리, 간단한 스키마, 빠른 응답이 필요한 경우에 적합하다.
제한사항으로는 동기 API가 문자수와 property 수 제한에 더 엄격하다는 것이다.
동기 API는 결과를 받을때까지 연결을 유지해야한다.
Asynchronous API
요청이 발생하면, 즉시 task ID를 반환하고 나중에 별도 요청으로 결과를 조회한다.
비동기 API는 대용량의 문서, 복잡한 스키마, 여러문서를 한번에 처리하는 batch 작업에 적합하며 긴 처리시간이 예상되는 경우에 적절하다.
비동기 API는 더 넓은 범위(최대 5,000 properties, 120,000 chars)를 지원한다.
비동기 API는 연결을 유지할 필요없기 때문에 네트워크 risk 감소효과가 있다.
Advantages of using Asynchronous API?
비동기 API는 다음과 같은 장점이 있다.
- 대용량 문서와 복잡한 스키마를 장시간 연결을 유지하지 않고도 처리가 가능하다.
- 하나의 요청에 여러 문서를 batching하여 대량으로 처리 가능하다.
- 대규모 문서처리 workflow에서 resources 사용 최적화가 가능하다.
간단하게 정리하자면, 비동기 API를 사용함으로써 오래 걸리는 작업이나 대규모 문서처리가 효율적이게 된다. 반대로, 단일 문서를 빠르게 처리해야하고 즉시 결과물이 필요한 경우에는 비동기 API 대신 동기 API를 사용하는 것이 좋다.
Additional parameters
비동기 API는 동기 API와 동일하게 데이터 추출 능력을 강화하기 위해 다양한 추가 파라미터를 지원한다.
- Mode: standard와 Enhanced 중 선택 가능
- doc_split: 하나의 파일안에 여러 문서가 포함되어 있을 경우, 이를 자동으로 분할해 각각의 문서에서 정보를 추출하는 기능
- location: 추출된 각 field에 대해 page number, bounding box 좌표(x,y) 등의 위치 정보를 함께 제공하도록 설정
- Confidence: 각 추출 field에 대해 high / low 형태의 confidence score를 포함하여 결과의 신뢰성을 평가할 수 있게 하는 option
data = {
"model": "information-extract",
"schema": json.dumps(schema),
"mode": "enhanced", # Use enhanced mode
"location": True, # Get location coordinates
"confidence": True # Get confidence scores
}
response = requests.post(
f"{BASE_URL}/async",
headers=headers,
files=files,
data=data
)Basic Async job workflow
import requests
import time
import json
API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY"
BASE_URL = "https://api.upstage.ai/v1/information-extraction"
#Step 1: Create async job
headers = {"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}"}
files = {
"documents": [
("documents", open("document1.pdf", "rb")),
("documents", open("document2.pdf", "rb"))
]
}
data = {
"model": "information-extract",
"schema": json.dumps({
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"bank_name": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The name of bank in bank statement"
}
}
})
}
response = requests.post(f"{BASE_URL}/async", headers=headers, files=files, data=data)
job_data = response.json()
job_id = job_data["job_id"]
print(f"Job created: {job_id}")
#Step 2: Poll job status
while True:
response = requests.get(f"{BASE_URL}/jobs/{job_id}", headers=headers)
job_info = response.json()
status = job_info["status"]
print(f"Job status: {status}")
if status in ["COMPLETED", "FAILED", "CANCELED"]:
break
time.sleep(5) # Wait 5 seconds before checking again
#Step 3: Retrieve results
if status == "COMPLETED":
response = requests.get(
f"{BASE_URL}/jobs/{job_id}?with_result=true",
headers=headers
)
results = response.json()
print(json.dumps(results, indent=2))Upstage Information extract?
- 어떤 문서 타입도 처리 가능
복잡한 PDF, 스캔 이미지, Microsoft Office 문서 등 다양한 형식의 문서를 안정적으로 처리하여 데이터를 추출할 수 있다. - 스키마에 구애받지 않는 처리(schema-agnostic)
주어진 schema에 따라 동적으로 구조화된 출력을 생성할 수 있어, 다양한 사용 사례에 맞춰 즉석에서 customizing이 가능하다. - 숨겨진 정보까지 추출
문서에 명시적으로 적혀 있지 않은 정보도 추론하여 추출할 수 있다.
예를 들어, 여러 라인 아이템을 기반으로 total amount을 계산하거나, 문서에 직접적으로 라벨링되지 않은 핵심 정보를 찾아낼 수 있다. - 추가 학습 불필요
사전에 만들어진 템플릿이나 모델 재학습 없이도 문서에서 필요한 정보를 바로 추출할 수 있다.
Reference
https://www.upstage.ai
https://console.upstage.ai/docs/capabilities/extract/writing-a-schema
https://console.upstage.ai/docs/capabilities/extract/universal-extraction-async
