Android System
안드로이드는 운영체제가 아니다. 프레임 워크다.
- 모바일 또는 착용 장치용 오픈 소스 소프트웨어
- 전체 스택: 운영 체제, 미들웨어, 응용 프로그램
- Linux 운영체제 기반
- 대부분의 경우 Java(SDK)로 개발이 이루어짐
[개발 (development)]
• Android SDK
• Android NDK (C)
• Platform Tools : adb(Android Debug Bridge)
• IDE- Eclipse (Not supported)
- Android Studio
(램이 적어도 16GB 이상이 있어야 원활하게 안드로이드 환경 개발 가능)
Android SDK vs. Java
• Syntax is the same : Android SDK == Java
• Android API는 대부분 Java API를 포함하고 있지만 일부 라이브러리는 포함되어 있지 않음
=> 자바 어플리케이션을 만드는 SDK - 모바일에 필요없는 기능 + 모바일 어플리케이션에 필요한 API (GPS, 전화 관련 기능 등)
• Android SDK = Java SE – AWT/Swing + Android API
[참고 사이트]
• https://developer.android.com/about/dashboards/index.html
• https://android.googlesource.com
Android Platform Architecture
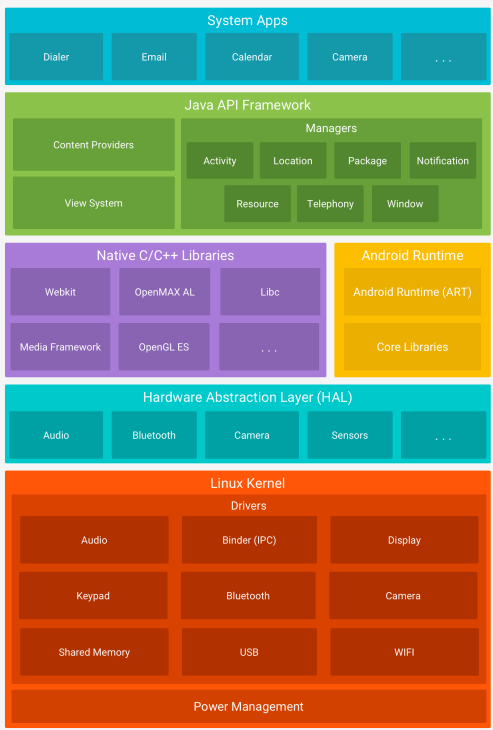
• Linux Kernel
• Native Library : 핸드폰의 기능들이 여기에 들어가있음
• Android Runtime
• Java API Framework
Android Runtime
Zygote (맨처음 실행) → Dalvik VM → ...
Dalvik VM 에서 실행할 수 있는 코드 : Dalvik byte code (low level)
↳ 이 부분에 문제가 생기면 기본적인 동작에서부터 막힘 (ex. 앱이 안열림)

[(왼) 일반적인 java 실행 / 모바일 실행 장면 (오)]
• Android based on Android API which almost like JAVA
• 자바 응용 프로그램은 자바 가상 머신 상에서 실행 -> 안드로이드 응용 프로그램은 달빅(Dalvik) 상에서 실행
DEX (Dalvik Excutable)
: java를 기반으로 만들어진 파일 : Dalvik bytecode 모아놓은 것
Dalvik vs. ART
• Dalvik : Android 5.0 이전.
• ART : Android 5.0 이후
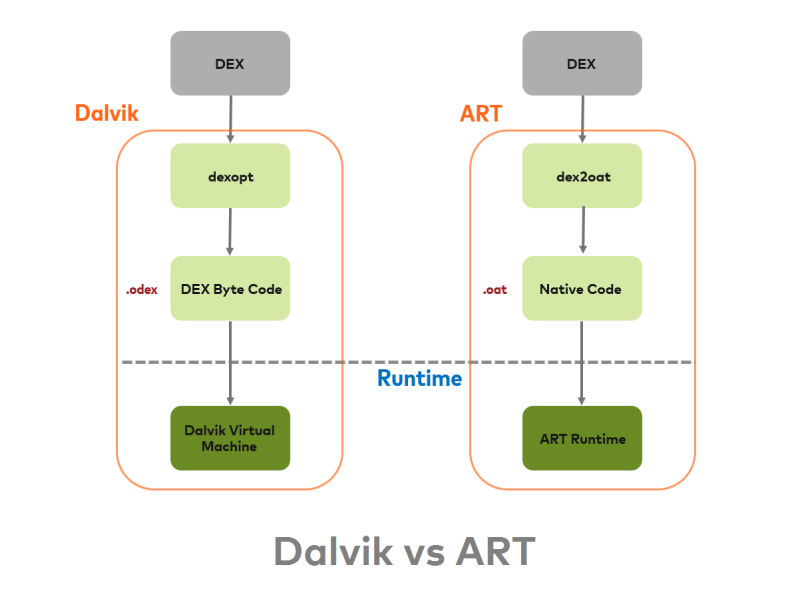
Dalvik
vm위에서 코드를 돌린다는 건
중간에 거쳐가는 놈이 하나 있다는 것
메모리와 자원을 먹음(vm)
vm안에서 코드를 돌려서 밑으로(native 형태로) 내려주는 방식
=> 느릴 수 밖에 없음 => 과거에 아이폰 대비 안드로이드가 시간이 지날 수록 느려졌던 이유
현재는 cpu 성능이 뛰어나게 좋아짐
Dalvik VM은 구글이 개발한 새로운 JVM(Java Virtual Machine)
• 기존의 스택 기반 JVM과 다른, 더 효율적인 실행 방식인 레지스터 기반 시스템을 사용
(모바일 기기 성능 최적화에 기여)
• JDK와는 다른 일련의 Java 라이브러리
Dalvik VM은 모바일 기기에 최적화되어 있음
• 그리 강력하지 않은 CPU
• 메모리 부족
• Dalvik Executable인 .dex 형식은 compact (공간을 적게 차지하게 압축해서 저장)
• 효율적으로 여러 VM을 실행
ART
부팅하는 과정에서 native 형태로 바꿔 cpu로 처리하도록 바꿈 (최적화)
부팅 속도↓ but, 실행하는 속도↑
• ART와 Dalvik은 Dalvik bytecode를 실행하는 호환되는 런타임 환경
• ART는 Dalvik 가상 머신이 처리하는 Dalvik 바이트코드를 실행 가능
하지만, Dalvik에서 동작하는 일부 기술은 ART에서 작동하지 않을 수 있음
ART → Dalvik, !Dalvik → ART
Comparison
Dalvik
• Lower stoarge, Space cossumption from JIT
• Take a time for cache, Fater booting time
• Lower internal storage(Old model)
• Stable...
↕
ART
• Fast load time, lower processor usage
• Long booting time
• More internal storage -> Compiled app + APK
• Unstable???
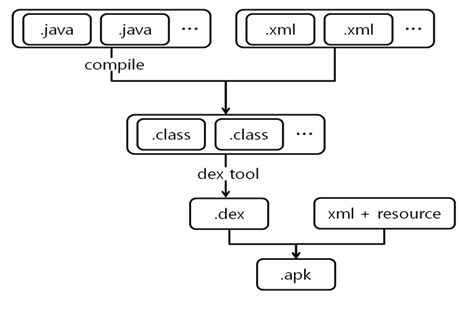
APK 파일이란? (.apk)
: Android 기기에 앱을 설치하는 데 사용되는 Google Android 앱 파일
컴파일 된 클래스는 DEX파일의 형태로 포함시키고 AndroidManifest.xml과 리소스등의 파일도 포함됨
Android Rooting
Rooting이란?
모바일 기기에서 구동되는 안드로이드 운영체제 상에서 최상위 권한(루트 권한)을 얻는 것
(selinux 기반 => 루팅을 해도 최고 권한은 아니긴함)
• By rooting an android device a user can bypass all the restrictions implemented by hardware manufactures and carriers
• The term “root” comes from the Unix/Linux world and is used to describe a user who has “super user” rights or permissions to all the files and programs in the OS
Rooting의 이점
• 배터리 수명을 늘리는 것
• Using Custom Recoveries
• 사용자 정의 ROM 사용
• 장치의 속도를 높이는 것
Rooting의 단점
• 장치를 수리할 수 없을 정도로 고장나거나 손상시키는 것
• Security (Malware, Virus)
• 보증을 무효화 (일부 경우에)
• 데이터 손실
매지스크 하이드 -> 매지스크로 루팅된건 못잡음
Rooting 하는 법
• The Process of Rooting an android device varies based on the model of your device
• By either googling or searching XDA forums
https://www.xda-developers.com/root/
Rooting 탐지
• Almost rooting detection
Focus on the final result(Executable file) on some specified path
• Disadvantage
• Detection based on signature(Fiexed file name and path)
-> Easy to bypass
• Because of false positive, use limited signature
루트 권한을 얻기 위한 행동으로 인한 부산물들의 흔적을 탐지하는 방식
Have to detect and protect the rooting on some App?
