행맨 게임 플레이하는 곳 : hangmanwordgame.com
🗂️ Day7 프로젝트 : 행맨
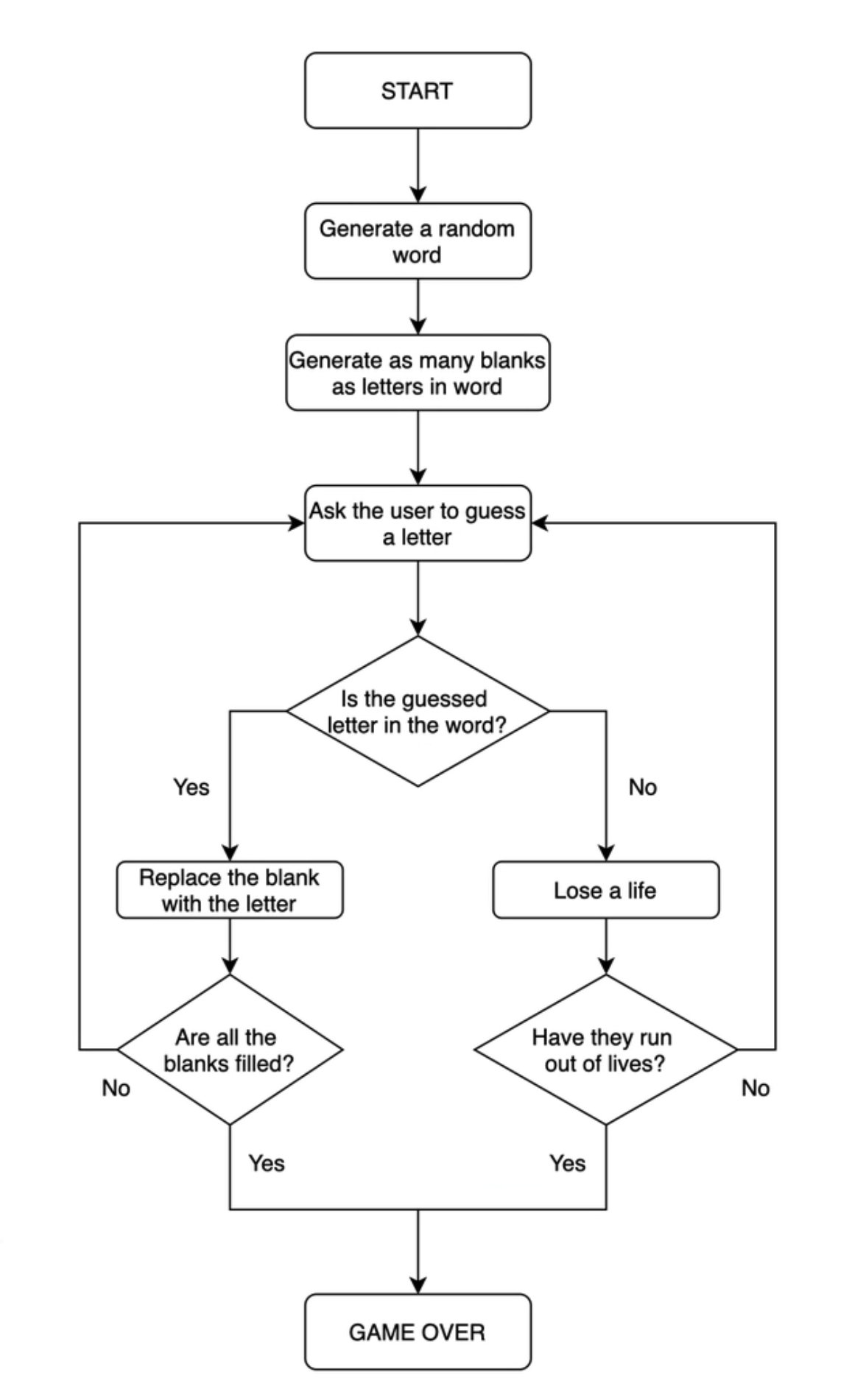
◇ Flow chart Programming
순서도를 통해 복잡한 문제를 단순하게 만들기
◇ 랜덤으로 단어를 고르고 플레이어의 정답 확인하기
🔍 유의 사항
- 리스트에 관한 정보 : Google for Education > Python Lists
- 랜덤으로 골라진 단어는 변수 chosen_word에 저장
- 사용자가 추측한 글자 letter는 변수 guess에 저장
- guess가 chosen_word의 각 글자와 일치하는지 하나씩 확인
- 출력한 결과물의 경우 리스트에서 랜덤으로 골라진 단어는 "baboon" 임을 알 수 있음
⌨️ 작성한 코드
#Step 1
word_list = ["aardvark", "baboon", "camel"]
#TODO-1 - Randomly choose a word from the word_list and assign it to a variable called chosen_word.
import random
chosen_word = random.choice(word_list)
#TODO-2 - Ask the user to guess a letter and assign their answer to a variable called guess. Make guess lowercase.
guess = input("Guess a letter : ").lower()
#TODO-3 - Check if the letter the user guessed (guess) is one of the letters in the chosen_word.
for letter in chosen_word:
if letter == guess:
print("right")
else:
print("wrong")Guess a letter : ❚a
Wrong
Right
Wrong
Wrong
Wrong
Wrong
◇ 빈칸을 플레이어가 맞춘 글자로 바꾸기
🔍 유의 사항
- chosen_word의 글자 수만큼의 빈칸("_")을 리스트 display로 생성
- guess가 chosen_word의 각 글자와 일치하는지 하나씩 확인해서
- 일치한다면, 빈칸을 guess로 변경
- 불일치한다면, 빈칸을 그대로 둠
- 테스팅 코드는 chosen_word가 무엇인지 출력 → 편하게 디버그하기 위한 용도
⌨️ 작성한 코드
#Step 2
import random
word_list = ["aardvark", "baboon", "camel"]
chosen_word = random.choice(word_list)
#Testing code
print(f'Pssst, the solution is {chosen_word}.')
#TODO-1: - Create an empty List called display.
#For each letter in the chosen_word, add a "_" to 'display'.
#So if the chosen_word was "apple", display should be ["_", "_", "_", "_", "_"] with 5 "_" representing each letter to guess.
display = []
for letter in chosen_word:
display.append("_")
print(display)
guess = input("Guess a letter: ").lower()
#TODO-2: - Loop through each position in the chosen_word;
#If the letter at that position matches 'guess' then reveal that letter in the display at that position.
#e.g. If the user guessed "p" and the chosen word was "apple", then display should be ["_", "p", "p", "_", "_"].
i = 0
for letter in chosen_word:
if letter == guess:
display[i] = letter
i += 1
else:
i += 1
#TODO-3: - Print 'display' and you should see the guessed letter in the correct position and every other letter replace with "_".
#Hint - Don't worry about getting the user to guess the next letter. We'll tackle that in step 3.
print(display)Pssst, the solution is baboon.
['_', '_', '_', '_', '_', '_']
Guess a letter: ❚b
['b', '_', 'b', '_', '_', '_']
🖍️ 답안
#TODO-1
display = []
word_length = len(chosen_word)
for _ in range(len(chosen_word)):
display += "_"
print(display)
guess = input("Guess a letter: ").lower()
#TODO-2
for position in range(word_length):
letter = chosen_word[position]
#print(f"Current position: {position}\n Current letter: {letter}\n Guessed letter: {guess}")
if letter == guess:
display[position] = letter- TODO-1
- len(chosen_word)를 자주 쓰게 되기 때문에 word_length에 값을 저장
- 두 리스트를 + 연산자로 이어 붙일 수 있으므로, append() 대신 사용 가능
- TODO-2
- range() 함수를 사용
- 특정 위치에 있는 요소만 변경할 때 더 적절한 방법이다(더 간결한 코드 가능)
- range(word_length)의 범위는 0, 1,..., word_length-1
- position은 각각의 글자에 대한 위치를 숫자로 나타냄
- 맨 첫 글자일 경우 position은 0 반환
- display[position]으로 글자를 letter에 넣어줘야 if문을 에러없이 실행 가능
- range() 함수를 사용
◇ 플레이어가 이겼는지 확인하기
🔍 유의 사항
- 유저가 모든 단어를 맞출 때까지(display 리스트에 빈칸이 없어질 때까지) while문으로 글자 맞추기 반복
- 오답에 대한 조치는 다음 단계에서
- not 연산자 활용
- in 연산자 활용
valueincollection- 특정 요소가 리스트 안에 있는지 확인할 때 사용 가능
- True/False 값 반환
⌨️ 작성한 코드
#Step 3
import random
word_list = ["aardvark", "baboon", "camel"]
chosen_word = random.choice(word_list)
word_length = len(chosen_word)
#Testing code
print(f'Pssst, the solution is {chosen_word}.')
#Create blanks
display = []
for _ in range(word_length):
display += "_"
#TODO-1: - Use a while loop to let the user guess again. The loop should only stop once the user has guessed all the letters in the chosen_word and 'display' has no more blanks ("_"). Then you can tell the user they've won.
while "_" in display:
guess = input("Guess a letter: ").lower()
#Check guessed letter
for position in range(word_length):
letter = chosen_word[position]
print(f" Current position: {position}\n Current letter: {letter}\n Guessed letter: {guess}")
if letter == guess:
display[position] = letter
print(display)
print("You win!")Pssst, the solution is camel.
Guess a letter: ❚c
Current position: 0
Current letter: c
Guessed letter: c
Current position: 1
Current letter: a
Guessed letter: c
Current position: 2
Current letter: m
Guessed letter: c
Current position: 3
Current letter: e
Guessed letter: c
Current position: 4
Current letter: l
Guessed letter: c
['c', '_', '_', '_', '_']
Guess a letter: ❚a
Current position: 0
Current letter: c
Guessed letter: a
Current position: 1
Current letter: a
Guessed letter: a
Current position: 2
Current letter: m
Guessed letter: a
Current position: 3
Current letter: e
Guessed letter: a
Current position: 4
Current letter: l
Guessed letter: a
['c', 'a', '_', '_', '_']
Guess a letter: ❚l
Current position: 0
Current letter: c
Guessed letter: l
Current position: 1
Current letter: a
Guessed letter: l
Current position: 2
Current letter: m
Guessed letter: l
Current position: 3
Current letter: e
Guessed letter: l
Current position: 4
Current letter: l
Guessed letter: l
['c', 'a', '_', '_', 'l']
Guess a letter: ❚m
Current position: 0
Current letter: c
Guessed letter: m
Current position: 1
Current letter: a
Guessed letter: m
Current position: 2
Current letter: m
Guessed letter: m
Current position: 3
Current letter: e
Guessed letter: m
Current position: 4
Current letter: l
Guessed letter: m
['c', 'a', 'm', '_', 'l']
Guess a letter: ❚e
Current position: 0
Current letter: c
Guessed letter: e
Current position: 1
Current letter: a
Guessed letter: e
Current position: 2
Current letter: m
Guessed letter: e
Current position: 3
Current letter: e
Guessed letter: e
Current position: 4
Current letter: l
Guessed letter: e
['c', 'a', 'm', 'e', 'l']
You win!
🖍️ 답안
#TODO-1
end_of_game = False
while not end_of_game:
guess = input("Guess a letter: ").lower()
#Check guessed letter
for position in range(word_length):
letter = chosen_word[position]
#print(f"Current position: {position}\n Current letter: {letter}\n Guessed letter: {guess}")
if letter == guess:
display[position] = letter
print(display)
#Check if there are no more "_" left in 'display'. Then all letters have been guessed.
if "_" not in display:
end_of_game = True
print("You win.")- 변수 end_of_game 생성
(작성한 코드에서는 while문 조건에 "_" in display 를 넣어서 해당 과정 생략)- 초기값은 False
- end_of_game == False 일 동안 while문 반복
- while문 마지막에는 display 리스트에 빈칸이 더 이상 없는지 확인
- 빈칸이 있다면 그대로 while문 처음으로 돌아가 다시 실행
- 빈칸이 더는 없다면 조건 end_of_game을 True로 변경하고 while문 빠져나오기
◇ 플레이어의 남은 목숨 세기
🔍 유의 사항
- 행맨의 목숨은 변수 lives에 저장되며, 초기값은 6
- 리스트 stages에 남은 목숨에 따른 아스키 아트가 문자열로 저장됨
- 틀린 글자를 입력할 때마다 알맞은 아스키 아트를 출력해야 함
- 이기는 경우 뿐만 아니라 지는 경우(lives = 0) 또한 종료 조건으로 넣어야 함
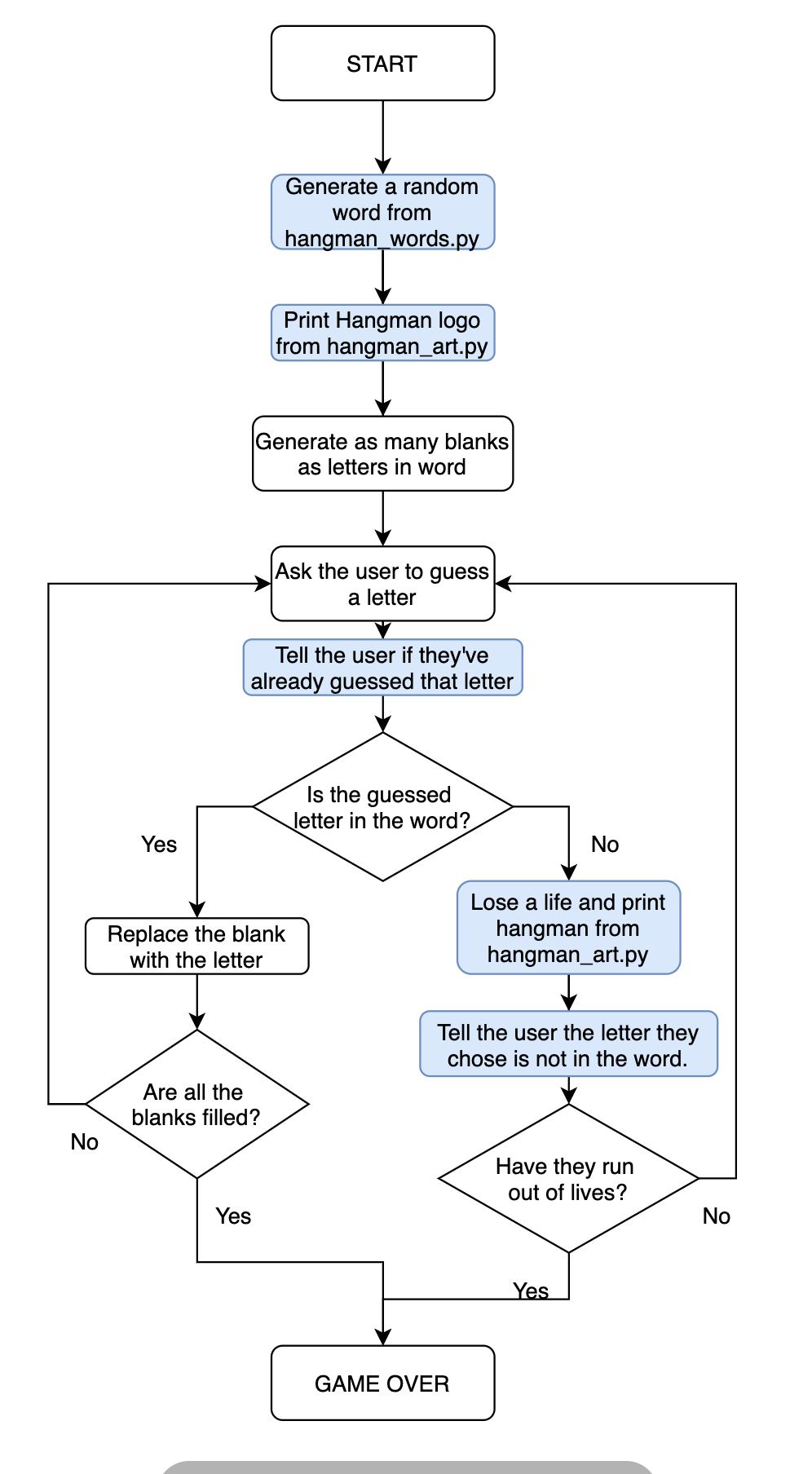
- 플로우 차트
⌨️ 작성한 코드
#Step 4
import random
stages = ['''
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
/ \ |
|
=========
''', '''
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
/ |
|
=========
''', '''
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
|
|
=========
''', '''
+---+
| |
O |
/| |
|
|
=========''', '''
+---+
| |
O |
| |
|
|
=========
''', '''
+---+
| |
O |
|
|
|
=========
''', '''
+---+
| |
|
|
|
|
=========
''']
end_of_game = False
word_list = ["ardvark", "baboon", "camel"]
chosen_word = random.choice(word_list)
word_length = len(chosen_word)
#TODO-1: - Create a variable called 'lives' to keep track of the number of lives left.
#Set 'lives' to equal 6.
lives = 6
#Testing code
print(f'Pssst, the solution is {chosen_word}.')
#Create blanks
display = []
for _ in range(word_length):
display += "_"
while not end_of_game:
guess = input("Guess a letter: ").lower()
#Check guessed letter
for position in range(word_length):
letter = chosen_word[position]
# print(f"Current position: {position}\n Current letter: {letter}\n Guessed letter: {guess}")
if letter == guess:
display[position] = letter
#TODO-2: - If guess is not a letter in the chosen_word,
#Then reduce 'lives' by 1.
#If lives goes down to 0 then the game should stop and it should print "You lose."
if guess not in chosen_word:
lives -= 1
if lives == 0:
end_of_game = True
print("You lose.")
#Join all the elements in the list and turn it into a String.
print(f"{' '.join(display)}")
#Check if user has got all letters.
if "_" not in display:
end_of_game = True
print("You win.")
#TODO-3: - print the ASCII art from 'stages' that corresponds to the current number of 'lives' the user has remaining.
print(stages[lives])[ 출력 결과 ]
Pssst, the solution is baboon.
Guess a letter: q
_ _ _ _ _ _
+---+
| |
O |
|
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: w
_ _ _ _ _ _
+---+
| |
O |
| |
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: e
_ _ _ _ _ _
+---+
| |
O |
/| |
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: r
_ _ _ _ _ _
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: t
_ _ _ _ _ _
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
/ |
|
=========
Guess a letter: y
You lose.
_ _ _ _ _ _
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
/ \ |
|
=========◇ 플레이어 경험 개선시키기
🔍 유의 사항
- 복잡하거나 긴 코드를 따로 다른 파일에 저장
- 📄 hangman_words.py 의 word_list 에 많은 양의 단어 저장
- 방법1 (파일 전체를 import)
가져오기 :importhangman_words
사용하기 :hangman_words.word_list- 방법2 (파일에서 필요한 것만 import)
가져오기 :fromhangman_wordsimportword_list
사용하기 :word_list- 📄 hangman_art.py 에 stages와 게임 로고의 아스키 아트 저장
fromhangman_artimportlogo, stages- 유저 편의성 개선
- 이미 입력한 글자를 또 입력했을 경우, 이미 시도했던 글자라고 알려주기
- chosen_word에 없는 글자를 입력했을 경우, 단어에 들어있지 않은 글자라고 알려주기
- from replit import clear : replit 모듈의 clear()
- 입력할 때마다 계속 밑으로 스크롤하면서 찾지 않아도 되도록 개선하기
- 글자를 입력할 때마다 콘솔창에 있던 이전 내용이 초기화됨
📄 hangman_words.py
word_list = [
'abruptly', 'absurd', 'abyss', 'affix', 'askew', 'avenue', 'awkward', 'axiom', 'azure',
'bagpipes', 'bandwagon', 'banjo', 'bayou', 'beekeeper', 'bikini', 'blitz', 'blizzard', 'boggle', 'bookworm', 'boxcar', 'boxful', 'buckaroo', 'buffalo', 'buffoon', 'buxom', 'buzzard', 'buzzing', 'buzzwords',
'caliph', 'cobweb', 'cockiness', 'croquet', 'crypt', 'curacao', 'cycle',
'daiquiri', 'dirndl', 'disavow', 'dizzying', 'duplex', 'dwarves',
'embezzle', 'equip', 'espionage', 'euouae', 'exodus',
'faking', 'fishhook', 'fixable', 'fjord', 'flapjack', 'flopping', 'fluffiness', 'flyby', 'foxglove', 'frazzled', 'frizzled', 'fuchsia', 'funny',
'gabby', 'galaxy', 'galvanize', 'gazebo', 'giaour', 'gizmo', 'glowworm', 'glyph', 'gnarly', 'gnostic', 'gossip', 'grogginess',
'haiku', 'haphazard', 'hyphen',
'iatrogenic', 'icebox', 'injury', 'ivory', 'ivy', 'jackpot', 'jaundice',
'jawbreaker', 'jaywalk', 'jazziest', 'jazzy', 'jelly', 'jigsaw', 'jinx', 'jiujitsu', 'jockey', 'jogging', 'joking', 'jovial', 'joyful', 'juicy', 'jukebox', 'jumbo',
'kayak', 'kazoo', 'keyhole', 'khaki', 'kilobyte', 'kiosk', 'kitsch', 'kiwifruit', 'klutz', 'knapsack',
'larynx', 'lengths', 'lucky', 'luxury', 'lymph',
'marquis', 'matrix', 'megahertz', 'microwave', 'mnemonic', 'mystify',
'naphtha', 'nightclub', 'nowadays', 'numbskull', 'nymph',
'onyx', 'ovary', 'oxidize', 'oxygen',
'pajama', 'peekaboo', 'phlegm', 'pixel', 'pizazz', 'pneumonia', 'polka', 'pshaw', 'psyche', 'puppy', 'puzzling',
'quartz', 'queue', 'quips', 'quixotic', 'quiz', 'quizzes', 'quorum',
'razzmatazz', 'rhubarb', 'rhythm', 'rickshaw',
'schnapps', 'scratch', 'shiv', 'snazzy', 'sphinx', 'spritz', 'squawk', 'staff', 'strength', 'strengths', 'stretch', 'stronghold', 'stymied', 'subway', 'swivel', 'syndrome',
'thriftless', 'thumbscrew', 'topaz', 'transcript', 'transgress', 'transplant', 'triphthong', 'twelfth', 'twelfths',
'unknown', 'unworthy', 'unzip', 'uptown',
'vaporize', 'vixen', 'vodka', 'voodoo', 'vortex', 'voyeurism',
'walkway', 'waltz', 'wave', 'wavy', 'waxy', 'wellspring', 'wheezy', 'whiskey', 'whizzing', 'whomever', 'wimpy', 'witchcraft', 'wizard', 'woozy', 'wristwatch', 'wyvern',
'xylophone',
'yachtsman', 'yippee', 'yoked', 'youthful', 'yummy',
'zephyr', 'zigzag', 'zigzagging', 'zilch', 'zipper', 'zodiac', 'zombie',
]📄 hangman_art.py
아스키 아트 로고 저장⌨️ 작성한 코드
#Step 5
import random
from hangman_words import word_list
from hangman_art import logo, stages
#TODO-1: - Update the word list to use the 'word_list' from hangman_words.py
chosen_word = random.choice(word_list)
word_length = len(chosen_word)
end_of_game = False
lives = 6
#TODO-3: - Import the logo from hangman_art.py and print it at the start of the game.
print(logo)
#Testing code
#print(f'Pssst, the solution is {chosen_word}.')
#Create blanks
display = []
for _ in range(word_length):
display += "_"
while not end_of_game:
guess = input("Guess a letter: ").lower()
#TODO-4: - If the user has entered a letter they've already guessed, print the letter and let them know.
if guess in display:
print(f"The letter {guess} is already tried.")
#Check guessed letter
for position in range(word_length):
letter = chosen_word[position]
#print(f"Current position: {position}\n Current letter: {letter}\n Guessed letter:{guess}")
if letter == guess:
display[position] = letter
#Check if user is wrong.
if guess not in chosen_word:
#TODO-5: - If the letter is not in the chosen_word, print out the letter and let them know it's not in the word.
print(f"The letter {guess} is not in the word. You lose one life.")
lives -= 1
if lives == 0:
end_of_game = True
print(f"You lose. The answer was {chosen_word}")
#Join all the elements in the list and turn it into a String.
print(f"{' '.join(display)}")
#Check if user has got all letters.
if "_" not in display:
end_of_game = True
print("You win.")
#TODO-2: - Import the stages from hangman_art.py and make this error go away.
print(stages[lives])
[ 출력결과 ]
_
| |
| |__ __ _ _ __ __ _ _ __ ___ __ _ _ __
| '_ \ / _` | '_ \ / _` | '_ ` _ \ / _` | '_ \
| | | | (_| | | | | (_| | | | | | | (_| | | | |
|_| |_|\__,_|_| |_|\__, |_| |_| |_|\__,_|_| |_|
__/ |
|___/
Guess a letter: ❚e
The letter e is not in the word. You lose one life.
_ _ _ _ _ _
+---+
| |
O |
|
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: ❚a
The letter a is not in the word. You lose one life.
_ _ _ _ _ _
+---+
| |
O |
| |
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: ❚o
The letter o is not in the word. You lose one life.
_ _ _ _ _ _
+---+
| |
O |
/| |
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: ❚u
The letter u is not in the word. You lose one life.
_ _ _ _ _ _
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: ❚i
_ _ _ i _ _
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: ❚i
The letter i is already tried.
_ _ _ i _ _
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: ❚s
s _ _ i _ _
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: ❚t
s _ _ i t _
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
|
|
=========
Guess a letter: ❚y
The letter y is not in the word. You lose one life.
s _ _ i t _
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
/ |
|
=========
Guess a letter: ❚l
The letter l is not in the word. You lose one life.
You lose. The answer was spritz
s _ _ i t _
+---+
| |
O |
/|\ |
/ \ |
|
=========