DFS(Depth First Search)란?
- DFS는 BFS와 함께 대표적인 그래프 탐색 알고리즘으로, node의 자식들을 먼저 탐색을 해나가는 방법이다.
- 즉, 특정 분기(branch)를 탐색하게 된다면 다른 branch로 가기 전에 해당 branch의 탐색을 마치고 넘어간다.
- 사용하는 경우 - 모든 node를 탐색하고자 하는 경우 DFS를 사용한다.
DFS의 특징
- 재귀적으로 동작한다.
- BFS에 비해서 탐색 속도가 느리다.
- visited list와 같이 방문을 한 node의 list를 만들어 체크를 하지 않으면 무한루프에 빠질 위험이 있다.
- 방문한 node들의 연결 node들을 접근 할때 깊이 우선으로 하기 위해 Queue대신 Stack을 사용한다.
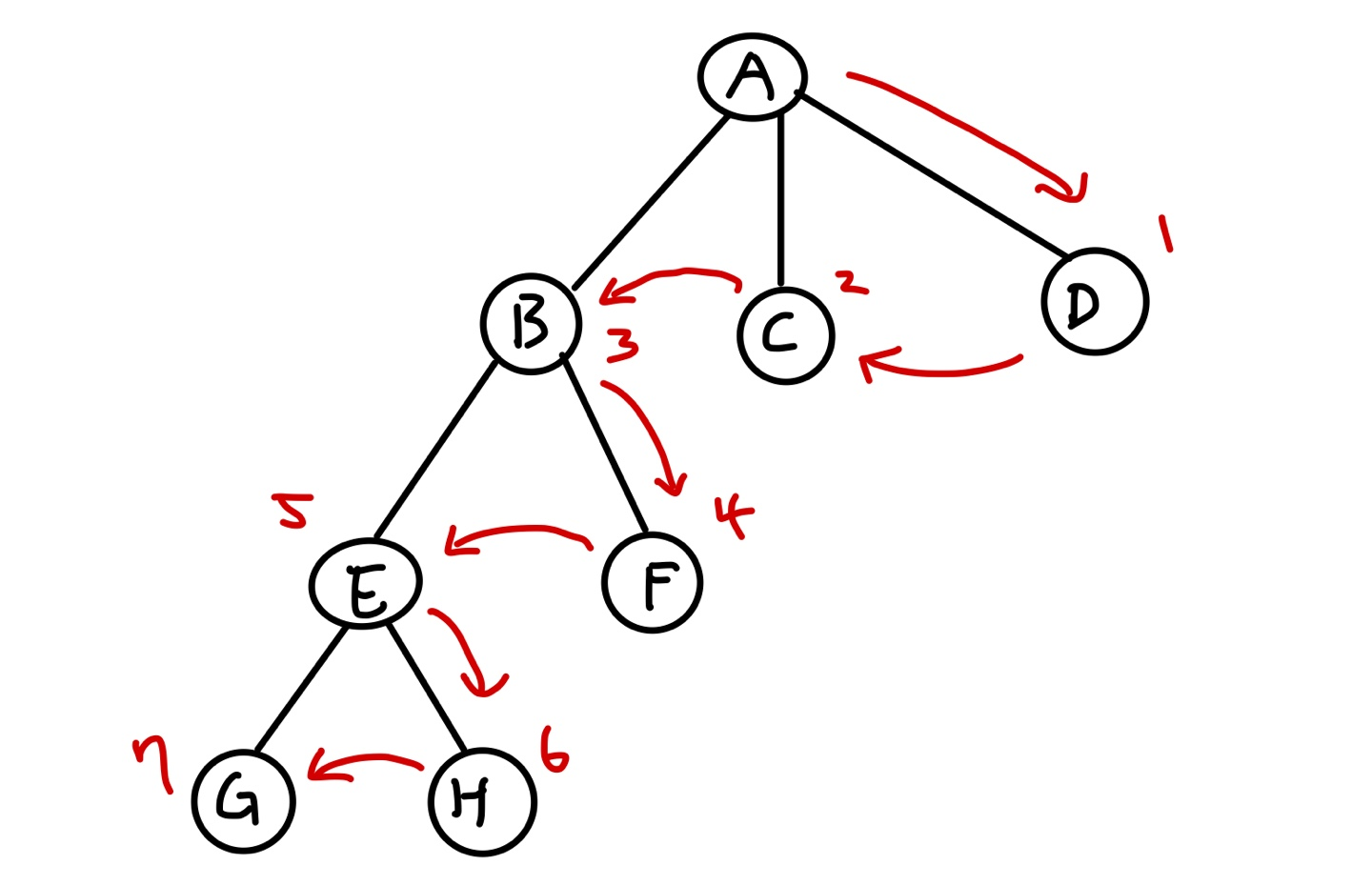
DFS 예제
Java코드로 구현
package algorithm;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
public class DFS {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String[]> grapgh = new HashMap<>();
String[][] nodeInfo = {{"B","C","D"},
{"A", "E", "F"},
{"A"},
{"A"},
{"B","G","H"},
{"B"},
{"E"},
{"E"}};
// nodeInfo에는 A~H순서대로 각 Node당 연결된 node들을 저장해둔다.
// HashMap에는 put을 통해 바로 array를 넣을 수 없기에 이렇게 지정해야한다.
grapgh.put("A", nodeInfo[0]);
grapgh.put("B", nodeInfo[1]);
grapgh.put("C", nodeInfo[2]);
grapgh.put("D", nodeInfo[3]);
grapgh.put("E", nodeInfo[4]);
grapgh.put("F", nodeInfo[5]);
grapgh.put("G", nodeInfo[6]);
grapgh.put("H", nodeInfo[7]);
System.out.println(dfs(grapgh, "A"));
}
public static List<String> dfs(HashMap<String, String[]> grapgh, String search){
List<String> visited = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> needVisit = new ArrayList<>();
String node;
needVisit.add(search);
while (!needVisit.isEmpty()) {
node = needVisit.remove(needVisit.size()-1); //bfs와 다르게 Stack을 사용하여 맨 뒤 수를 다음 node로 사용
// node가 visited에 없으면 visited에 추가 및 node의 연결된 node를 need_visited에 추가!
if (!visited.contains(node)) {
visited.add(node);
needVisit.addAll(Arrays.asList(grapgh.get(node)));
// addAll은 list데이터를 넣어야하기에 array로 되어있는
// grapgh.get(node)의 값을 List로 변경 후 넣어준다.
}
}
return visited;
}
}
Backtracking을 활용해 recursive하게 짠 코드
N Queens알고리즘에서 발췌한 DFS알고리즘입니다.
public static void dfs(int n, int currentRow, List<Integer> currentCandidate, List<List<Integer>> finalResult) {
if (currentRow == n) {
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i : currentCandidate)
temp.add(i);
finalResult.add(temp);
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (isAvailable(currentCandidate, i)) {
currentCandidate.add(i);
dfs(n, currentRow + 1, currentCandidate, finalResult);
currentCandidate.remove(currentCandidate.size()-1);
}
}
}
}