1번의 Model은 클라이언트에서 서버로 보내온 정보들이고,
b의 Model은 Controller가 템플릿 엔진에게 보내는 Model(View에 적용할 정보들)
HTTP 메시지 이해
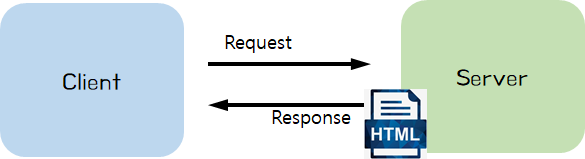
- Client 와 Server 간 Request, Response 는 HTTP 메시지 규약을 따름
(1) 메시지 구조
🌐 참고: HTTP 메시지 설명 (MDN Web Docs)
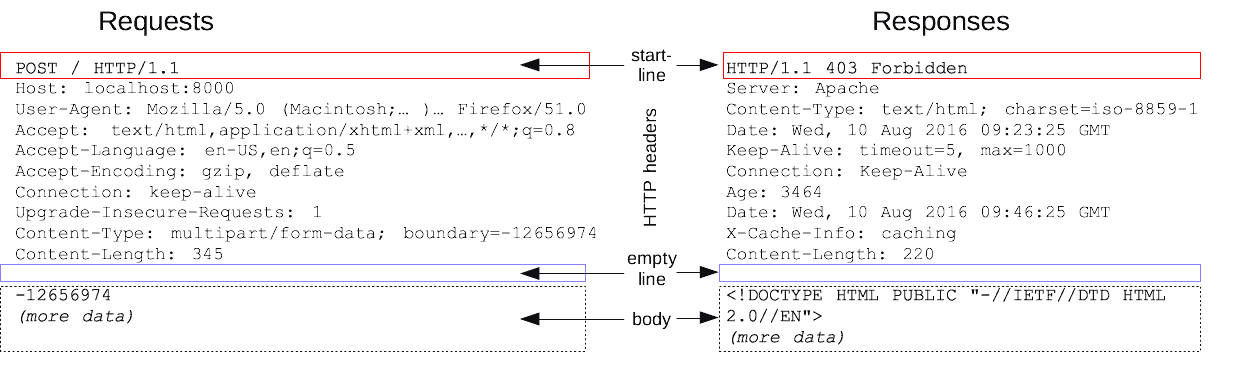
1. 시작줄 (start line)
1) Response 에선 '상태줄 (status line)' 이라고 부름
2. 헤더 (headers)
3. 본문 (body)(2) Request 메시지
- 시작줄: API 요청 내용
GET **naver.com** HTTP/1.1-
헤더
- Content type-
없음
-
HTML
태그로 요청 시Content type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded -
AJAX 요청
Content type: application/json
-
-
본문
a) GET 요청 시: (보통) 없음
b) POST 요청 시: (보통) 사용자가 입력한 폼 데이터name=홍길동&age=20
(3) Response 메시지
- 상태줄: API 요청 결과 (상태 코드, 상태 텍스트)
HTTP/1.1 **404** **Not Found**-
헤더
- Content type
1. 없음
2. Response - 본문 내용이 HTML 인 경우Content type: text/html -
Response - 본문 내용이 JSON 인 경우
Content type: application/json- Location : Redirect 할 페이지 URL
Location: http://localhost:8080/hello.html- 본문
- HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><title>By @ResponseBody</title></head>
<body>Hello, Spring 정적 웹 페이지!!</body>
</html>- JSON
{
"name":"홍길동",
"age": 20
}클라이언트가 요청을 보낼 때 그냥 보내는 것이 아니라, 내가 보내는 요청[정보]이 어떠한 형태의 컨텐츠[타입]임을 알려줌.
Controller 와 HTTP Response 메시지
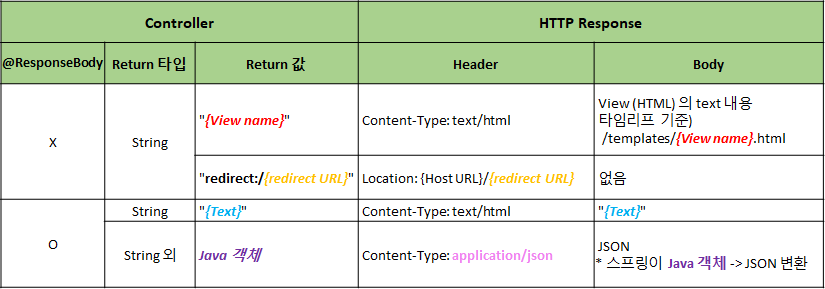
redicrect인 경우 Header에 Content-type은 없고 Location이 있다.
- @RequestMapping()
- 앞 부분에 공통적으로 붙는 url주소를 넣어준다.
- @ResponseBody
- View 를 사용하지 않고, HTTP Body 에 들어갈 String 을 직접 입력
🌐 http://localhost:8080**/hello/response/html/templates**<@GetMapping("/body/html")
@ResponseBody
public String helloStringHTML() {
return "<!DOCTYPE html>" +
"<html>" +
"<head><title>By @ResponseBody</title></head>" +
"<body> Hello, 정적 웹 페이지!!</body>" +
"</html>";
}Response 트랜드
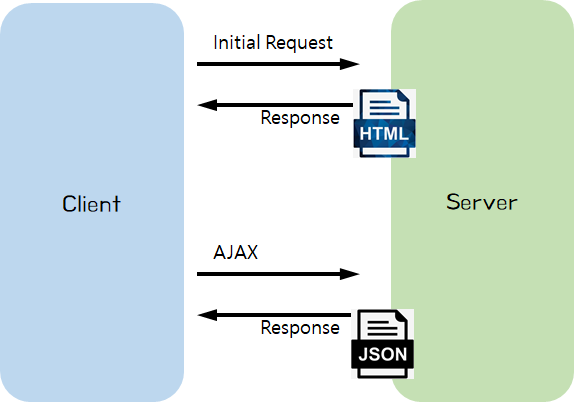
HTML은 딱 한번만 내려오고 그 이후로는 JSON 데이터만 왔다 갔다하는 모습
그래서 나온 것이 @RestController !!!
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponserBody
- 마치 @ResponserBody가 모든 메소드에 포함이 된 효과
🌐 참고: [싱글페이지 애플리케이션] (SPA, Single Page Application)
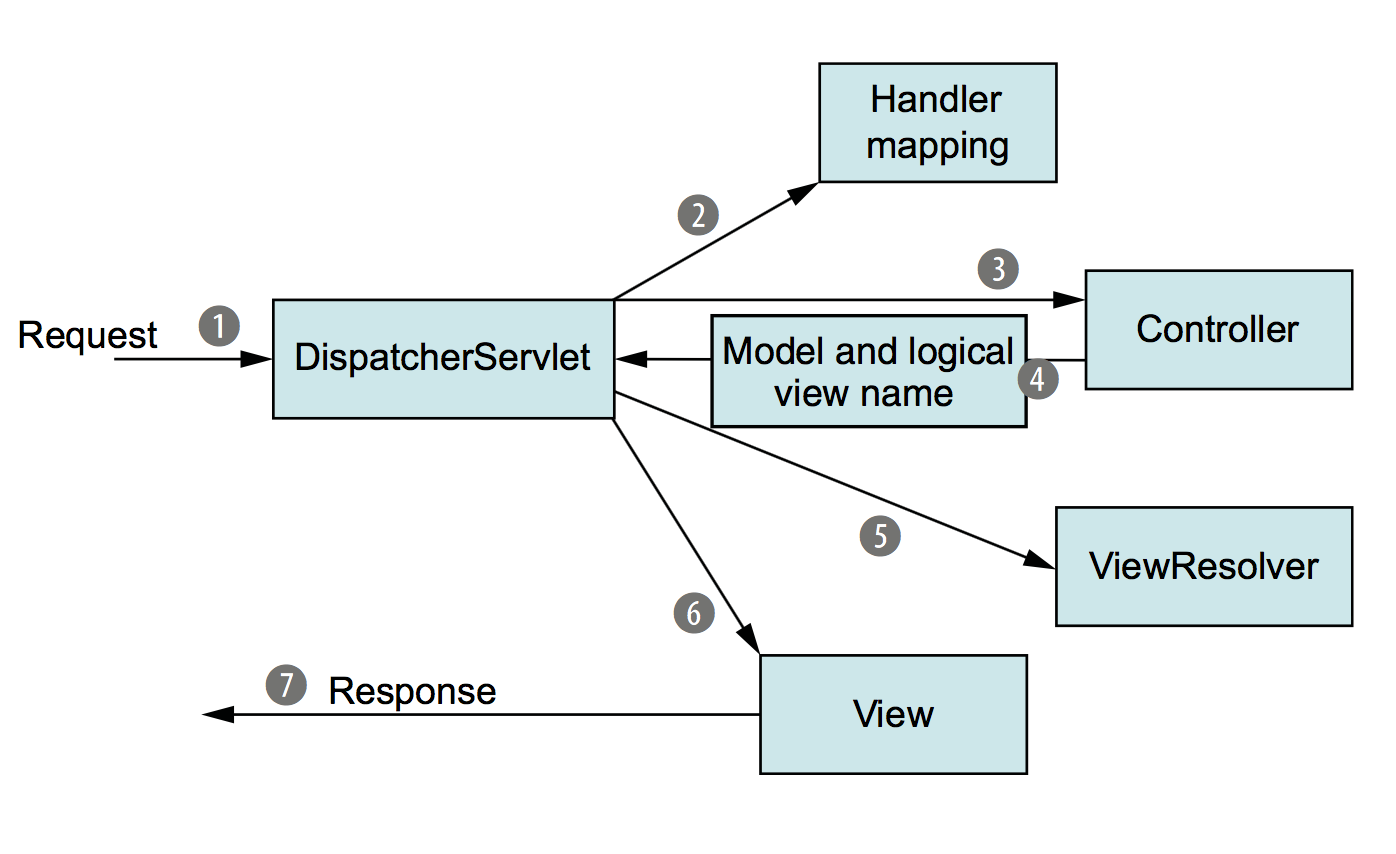
스프링 MVC 동작원리
@Controller 는 스프링 서버 개발자 입장에서는 시작점과 끝점으로 보이지만, 사실 스프링이 뒤에서 많은 부분을 보이지 않게 처리해 주고 있습니다.