- 추상 메서드의 집합
- 구현된 것이 전혀 없는 설계도.껍데기(모든 멤버가 public)
interface 인터페이스 이름 { public static final 타입 상수이름 = 값; // 상수만 된다. 변수x public abstract 메서드이름(매개변수목록); // 추상 메서드 }
interface PlayingCard {
public static final int SPADE = 4;
final int DIAMOND = 3; // public static final int DIAMOND = 3;
static int HEART = 2; // public static final int HEART = 2;
int CLOVER = 1; // public static final int CLOVER = 1;
public abstract String getCardNumber();
String getCardKind(); // abstract 생략가능. 구현부가 없기때문에 알아서 붙는다.
}인터페이스의 상속
- 인터페이스의 조상은 인터페이스만 가능(Object가 최고 조상 아님)
- 다중 상속이 가능.(추상메서드는 충돌해도 문제 없음)
interface Fightable extends, Movable, Attackable {} interface Movable { void move(int x, int y); } interface Attackable { void attack(Unit u); }
인터페이스의 구현
- 인터페이스에 정의된 추상 메서드를 완성하는 것
class 클래스이름 implements 인터페이스이름 { // 인터페이스에 정의된 추상메서드를 완성시켜야 한다. }
interface Fightable {
void move(int x, int y);
void attack(Unit u);
}
class Fighter implements Fightable {
public void move(int x, int y) {}
public void attack(Unit u) {}
}이 때, Fighter 클래스는 Fightable 인터페이스를 구현했다. 라고 한다.
- 일부만 구현하는 경우, 클래스 앞에 abstract를 붙여야 함.
abstract class Fighter implements Fightable { public void move(int x, int y) {} }
인터페이스란?
추상 메서드의 집합
추상 클래스와 인터페이스의 공통점은?
추상 메서드를 가지고 있다.(미완성 설계도)
추상 클래스와 인터페이스의 차이점은?
인터페이스는 추상메서드만 된다.(상수, static메서드, 디폴트메서드 등등도 되지만 메인은 저것)
인터페이스를 이용한 다형성
- 인터페이스도 구현 클래스의 부모
- 인터페이스 타입 매개변수는 인터페이스 구현한 클래스의 객체만 가능
interface Fightable { void move(int x, int y); void attack(Fightable f); // Fightable 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스의 인스턴스만 가능 } class Fighter extends Unit implements Fightable { public void move(int x, int y) {} public void attack(Fightable f) {} } Unit u = new Fighter(); Fightable f = new Fighter(); f.move(100, 200); f.attack(new Fighter());
- 인터페이스를 메서드의 리턴타입으로 지정할 수 있다.
Fightable method() { // Fightable 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스의 인스턴스를 반환 ... Fighter f = new Fighter(); return f; // return new Fighter(); } class Fighter extends Unit implements Fightable { public void move(int x, int y) {} public void attack(Fightable f) {} } ------------ main ------------- Fightable f = method(); --- 위의 내용은 아래의 문장과 같다 --- Fightable f = new Fighter();
인터페이스의 장점
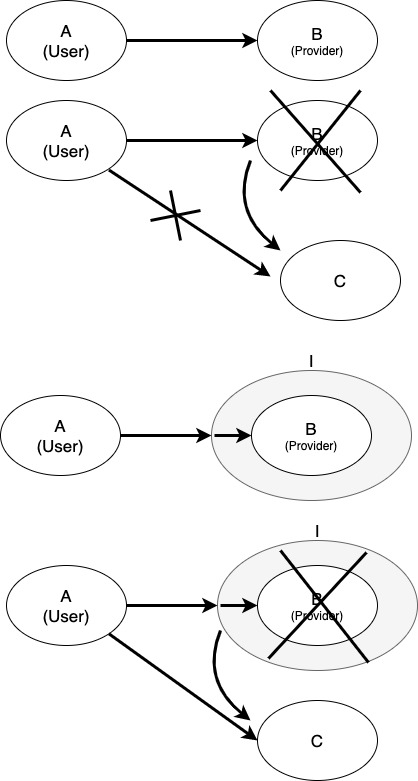
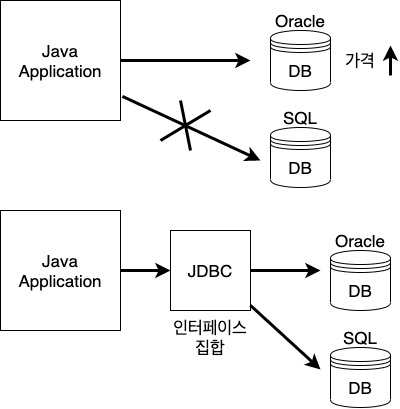
두 대상(객체) 간의 '연결, 대화, 소통'을 돕는 '중간 역할'을 한다.
선언(설계)와 구현을 분리시킬 수 있게 한다.
interface I { public void method(); // 선언부만 떼어내기(껍데기) } class B implements I { public void method() { System.out.println("methodInb"); } }인터페이스 덕분에 B가 변경되어도 A는 안바꿀 수 있게 된다.(느슨한 결합)
-> 코드예시
----- 직접적인 관계의 A, B 클래스 ----- class A { public void method(B b) { b.methodB(); } } class B { public void methodB () { System.out.println("methodB()"); } } class InterfaceTest { public static void main(String args[]) { A a = new A(); a.methodA(new B()); } } ----- 간접적인 관계의 A, B 클래스 ----- class A { public void method(I i) { i.methodB(); } } interface I { void methodB(); } class B implements I { public void methodB() { System.out.println("methodB()"); } } class C implements I { public void methodB() { System.out.println("moethodB() in C"); } }직접적인 관계의 경우 A 클래스에서 C 클래스를 받으려면 B를 C로 바꿔야한다. 하지만 간접적인 경우 C 클래스가 추가되어도 A 클래스를 바꾸지 않아도 된다.
개발 시간을 단축할 수 있다.
변경에 유리한 유연한 설계가 가능하다.
표준화가 가능하다.
서로 관계없는 클래스들의 관계를 맺어줄 수 있다.
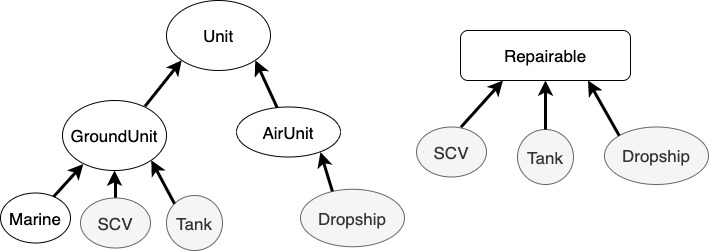
---- 아래의 경우에 GroundUnit 클래스에 포함된 ---- --- Marine은 병사이기 때문에 수리를 할 수 없다. --- void repair(Tank t) { // Tank를 수리한다. } void repair(Dropship d) { // Dropship을 수리한다. } void repair(GroundUnit gu) { // 매개변수로 넘겨진 지상유닛(GroundUnit)을 수리한다. } --- 그래서 인터페이스를 이용해서 기계만 따로 묶는다 --- interface Repairable {} class SCV extends GroundUnit implements Repairable { // ... } class Tank extends GroundUnit implements Repairable { // ... } class Dropship extends AirUnit implements Repairable { // ... } void repair(Repairable r) { if (r instanceof Unit) { Unit u = (Unit)r; while(u.hitPoint!=u.MAX_HP) { u.hitPoint++; } } }
디폴트 메서드와 static 메서드
- 인터페이스에 디폴트 메서드, static 메서드 추가 가능.(JDK1.8부터)
- 인터페이스에 새로운 메서드(추상 메서드)를 추가하기 어려움.
해결책 => 디폴트 메서드(default method)- 디폴트 메서드는 인스턴스 메서드(인터페이스 원칙 위반)
interface Myinterface { void method(); void newMethod(); // 추상 메서드 } -------------------------- interface Myinterface { void method(); default void newMethod() {}; // 디폴트 메서드 }
- 디폴트 메서드가 기존의 메서드와 충돌할 때의 해결책
- 여러 인터페이스의 디폴트 메서드 간의 충돌
-인터페이스를 구현한 클래스에서 디폴트 메서드를 오버라이딩해야 한다.- 디폴트 메서드와 조상 클래스의 메서드 간의 충돌
-조상 클래스의 메서드가 상속되고, 디폴트 메서드는 무시된다.
-> 그냥 직접 오버라이딩하면 해결.