문제 설명
ROR 게임은 두 팀으로 나누어서 진행하며, 상대 팀 진영을 먼저 파괴하면 이기는 게임입니다. 따라서, 각 팀은 상대 팀 진영에 최대한 빨리 도착하는 것이 유리합니다.
지금부터 당신은 한 팀의 팀원이 되어 게임을 진행하려고 합니다. 다음은 5 x 5 크기의 맵에, 당신의 캐릭터가 (행: 1, 열: 1) 위치에 있고, 상대 팀 진영은 (행: 5, 열: 5) 위치에 있는 경우의 예시입니다.
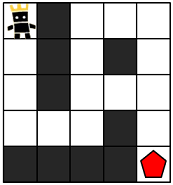
위 그림에서 검은색 부분은 벽으로 막혀있어 갈 수 없는 길이며, 흰색 부분은 갈 수 있는 길입니다. 캐릭터가 움직일 때는 동, 서, 남, 북 방향으로 한 칸씩 이동하며, 게임 맵을 벗어난 길은 갈 수 없습니다.
아래 예시는 캐릭터가 상대 팀 진영으로 가는 두 가지 방법을 나타내고 있습니다.
- 첫 번째 방법은 11개의 칸을 지나서 상대 팀 진영에 도착했습니다.

- 두 번째 방법은 15개의 칸을 지나서 상대팀 진영에 도착했습니다.

위 예시에서는 첫 번째 방법보다 더 빠르게 상대팀 진영에 도착하는 방법은 없으므로, 이 방법이 상대 팀 진영으로 가는 가장 빠른 방법입니다.
만약, 상대 팀이 자신의 팀 진영 주위에 벽을 세워두었다면 상대 팀 진영에 도착하지 못할 수도 있습니다. 예를 들어, 다음과 같은 경우에 당신의 캐릭터는 상대 팀 진영에 도착할 수 없습니다.
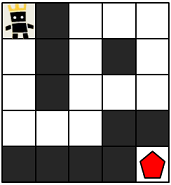
게임 맵의 상태 maps가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 캐릭터가 상대 팀 진영에 도착하기 위해서 지나가야 하는 칸의 개수의 최솟값을 return 하도록 solution 함수를 완성해주세요. 단, 상대 팀 진영에 도착할 수 없을 때는 -1을 return 해주세요.
제한 사항
- maps는 n x m 크기의 게임 맵의 상태가 들어있는 2차원 배열로, n과 m은 각각 1 이상 100 이하의 자연수입니다.
- n과 m은 서로 같을 수도, 다를 수도 있지만, n과 m이 모두 1인 경우는 입력으로 주어지지 않습니다.
- maps는 0과 1로만 이루어져 있으며, 0은 벽이 있는 자리, 1은 벽이 없는 자리를 나타냅니다.
- 처음에 캐릭터는 게임 맵의 좌측 상단인 (1, 1) 위치에 있으며, 상대방 진영은 게임 맵의 우측 하단인 (n, m) 위치에 있습니다.
입출력 예
| maps | answer |
|---|---|
[[1,0,1,1,1],[1,0,1,0,1],[1,0,1,1,1],[1,1,1,0,1],[0,0,0,0,1]] | 11 |
[[1,0,1,1,1],[1,0,1,0,1],[1,0,1,1,1],[1,1,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,1]] | -1 |
풀이 - 효율성 실패
from collections import deque
visited = [(0, 0)]
queue = deque()
path_costs = []
def solution(board):
destination_y = len(board) - 1
destination_x = len(board[0]) - 1
x = y = 0
def search_north(x, y):
if y - 1 < 0:
return
if (x, y - 1) not in visited:
if board[y - 1][x]:
queue.append((x, y - 1))
board[y - 1][x] = (board[y][x] + 1)
visited.append((x, y - 1))
def search_east(x, y):
if x + 1 > destination_x:
return
if (x + 1, y) not in visited:
if board[y][x + 1]:
if (x + 1) != destination_x or y != destination_y:
queue.append((x + 1, y))
board[y][x + 1] = (board[y][x] + 1)
else:
path_costs.append(board[y][x] + 1)
visited.append((x + 1, y))
def search_south(x, y):
if y + 1 > destination_y:
return
if (x, y + 1) not in visited:
if board[y + 1][x]:
if x != destination_x or (y + 1) != destination_y:
queue.append((x, y + 1))
board[y + 1][x] = (board[y][x] + 1)
else:
path_costs.append(board[y][x] + 1)
visited.append((x, y + 1))
def search_west(x, y):
if x - 1 < 0:
return
if (x - 1, y) not in visited:
if board[y][x - 1]:
queue.append((x - 1, y))
board[y][x - 1] = (board[y][x] + 1)
visited.append((x - 1, y))
while True:
search_north(x, y)
search_east(x, y)
search_south(x, y)
search_west(x, y)
if not len(queue):
break
coordinate = queue.popleft()
x = coordinate[0]
y = coordinate[1]
if not len(path_costs):
return -1
return min(path_costs)접근
기본적으로 인접해있는 길로 이동해야하는 알고리즘이기 때문에 DFS보다는 BFS로 접근하는 것이 더 적합하다 판단했다.
DFS는 현재 내 위치를 기준으로 먼저 만난 노드로 인접 노드를 계속 탐색하는 과정이라 한 번 막다른 길에 돌아가면 다시 되돌아와야 한다.
BFS는 자신을 기준으로 인접한 노드를 다 탐색한 후에 다음 노드로 넘어가 인접 노드를 파악하므로 갈림길이 나오더라도 모든 경로에 대해 판단이 가능하다.
그렇기에 python으로 BFS를 구현했다. 이때, count를 board의 요소 값을 변경하여 최종적으로 목적지에 도달했을 때 이동 횟수를 구할 수 있는 알고리즘으로 코드를 작성했다.
다만, 이 방법은 효율성에서 시간초과가 나는 문제가 발생했다.
다른 사람의 접근
다른 사람의 글을 보면서 x, y 좌표를 queue에 저장할 때, 이동 횟수인 count도 같이 저장하는 방식으로 시간 효율성을 더 좋게 할 수 있을 것 같다고 생각했다.
그리고, visited를 사용하지 않고 지나온 길을 0으로 변경하면 visited 효과와 동일하게 사용할 수 있을 것 같다 생각했다.
그렇게 푼 정답
from collections import deque
queue = deque()
path_costs = []
def solution(board):
destination_y = len(board) - 1
destination_x = len(board[0]) - 1
x = y = 0
count = 1
def search_north(x, y, count):
if y - 1 < 0:
return
if board[y - 1][x]:
queue.append((x, y - 1, count))
board[y - 1][x] = 0
def search_east(x, y, count):
if x + 1 > destination_x:
return
if (x + 1) != destination_x or y != destination_y:
if board[y][x + 1]:
queue.append((x + 1, y, count))
board[y][x + 1] = 0
else:
path_costs.append(count)
def search_south(x, y, count):
if y + 1 > destination_y:
return
if x != destination_x or (y + 1) != destination_y:
if board[y + 1][x]:
queue.append((x, y + 1, count))
board[y + 1][x] = 0
else:
path_costs.append(count)
def search_west(x, y, count):
if x - 1 < 0:
return
if board[y][x - 1]:
queue.append((x - 1, y, count))
board[y][x - 1] = 0
while True:
count += 1
search_north(x, y, count)
search_east(x, y, count)
search_south(x, y, count)
search_west(x, y, count)
if not len(queue):
break
coordinate = queue.popleft()
x = coordinate[0]
y = coordinate[1]
count = coordinate[2]
if len(path_costs):
return min(path_costs)
return -1visited의 초기화 과정을 쓰지 않고, count를 값으로 가지고 있음으로써 시간 효율성을 더 좋게 만들었다.